PR Exam 1 Chapter 1-3
4.8(5)Studied by 58 people
Card Sorting
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Public Relations UARK
Last updated 5:08 PM on 2/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
1
New cards
The Challenge of PR
PR is multi-faceted
Several Elements of PR Process
Several Elements of PR Process
2
New cards
The Challenge of PR: PR is multi-faceted
Public relations professionals have many roles and skills in
\-written
\- interpersonal communications media
\- social media
\- research
\-negotiation
\-creativity
\- logistics facilitations
\- problem solving
\- strategic thinking
\-written
\- interpersonal communications media
\- social media
\- research
\-negotiation
\-creativity
\- logistics facilitations
\- problem solving
\- strategic thinking
3
New cards
The Challenge of PR
Elements of PR Process:
Elements of PR Process:
Deliberate
planned
performance
public interest
two-way communication
strategic management function
planned
performance
public interest
two-way communication
strategic management function
4
New cards
The PR Processes
RACE
Research
Action
Communication
Evaluation
Research
Action
Communication
Evaluation
5
New cards
Definition of PR
PR is the management function that identifies, e establishes and maintains mutually beneficial relationships between an organization and the various public on whom its success or failure depends
\
The management of communication between an organizations and its publics
\
The management of communication between an organizations and its publics
6
New cards
Key Words frame most definitions?
Deliberate: PR activity is intentional
Planned: PR activity is organized
Performance: actual polices and performance
Public Interest: PR activity should be mutually benififcal to the or. and public
Two-way communication: listening and engaging in a conversation with various publics
Management function: PR is most effective when it’s strategic and inegreal part of decision making by top management
Planned: PR activity is organized
Performance: actual polices and performance
Public Interest: PR activity should be mutually benififcal to the or. and public
Two-way communication: listening and engaging in a conversation with various publics
Management function: PR is most effective when it’s strategic and inegreal part of decision making by top management
7
New cards
The Diversity of PR Work
Research
Media Relations
Publicity
Employee relations
Community Relations
Public affairs
Government affairs
Issue management
Financial relations
Special events
Marketing communications
Media Relations
Publicity
Employee relations
Community Relations
Public affairs
Government affairs
Issue management
Financial relations
Special events
Marketing communications
8
New cards
PR V Journalism: Scope
PR: Many components
Journalism: Two components: writing and media relations
Journalism: Two components: writing and media relations
9
New cards
PR V Journalism: Objective
PR: Advocates to inform public and change attitudes
Objective observers: news and information
Objective observers: news and information
10
New cards
PR V Journalism: Audience
PR: defined publics
Journalism: Mass Audience
Journalism: Mass Audience
11
New cards
PR V Journalism: channel
PR: a variety of channels
J: one channel
J: one channel
12
New cards
PR v Advertising: Scope
PR: Broader scope
AD: MArketing communication funtion
AD: MArketing communication funtion
13
New cards
PR v Advertising: Objective
PR: Corporate comm/.mkt comm./AD
AD: tools to support marketing/corporate comm. (PR)
AD: tools to support marketing/corporate comm. (PR)
14
New cards
PR v Advertising: Audience
PR: Messages to specialized external audiences and other internal publics
AD: directed to potential buyers of goods and services
AD: directed to potential buyers of goods and services
15
New cards
PR v Advertising: Channel
PR: various channels
AD: Mass media
AD: Mass media
16
New cards
PR v Marketing: Problem-solving strategy
PR: cooperation
mkt: competition
mkt: competition
17
New cards
PR v Marketing: Role in mgt
PR: all departments
mkt: product positioning and sales
mkt: product positioning and sales
18
New cards
PR v Marketing: Objective
PR: relationship building
mkt: customers and consumers
mkt: customers and consumers
19
New cards
How Public Relations supports marketing?
Public Relations is the fifth “P” in marketing strategies
20
New cards
Five “P” in marketing strategies
Product, Price, Place, Promotion, PR
21
New cards
Fueling Integrated Perspective?
Downsizing of org.
Tighter budget
Adverting is increasing clutter (fragmented audience and lack credibility)
Public and social policy issue
Tighter budget
Adverting is increasing clutter (fragmented audience and lack credibility)
Public and social policy issue
22
New cards
Integrated Perspective: IMC or MPR
Integrated Marketing Communications
Marketing PR
Marketing PR
23
New cards
Marketing objectives
Coordinated communication strategies-→
\-Targeting -Big Idea -Media Timing: -→
Adverting, PR, Sales Promotion, Direct Response, Packaging -→
Program Evaluation
\-Targeting -Big Idea -Media Timing: -→
Adverting, PR, Sales Promotion, Direct Response, Packaging -→
Program Evaluation
24
New cards
A Career in PR: 5 main courses for PR majors
Into PR
PR research
PR writing and production
internship
PR ethics/mgt./case studies
PR research
PR writing and production
internship
PR ethics/mgt./case studies
25
New cards
Essential PR Career Skills
Writing
Research ability
Planned expertise
Problem-solving
Business/economics competence
Expertise in social media
Research ability
Planned expertise
Problem-solving
Business/economics competence
Expertise in social media
26
New cards
Value of PR: The world doesn’t need more information but does need…
…sensitive communicators and facilitators who can explain the goals and aspirations of individuals, organizations, and governments to others in a socially responsive manner
27
New cards
Value of PR: Public relation practitioners…
Public relation practitioners… explain the goals and objectives of clients and employees to the public and provide them with guidance
28
New cards
Four Classic Models of Public Relations
Press Agentry/Publicity
Public Information
2-Way Asymmetric
2-Way Symmetric
Public Information
2-Way Asymmetric
2-Way Symmetric
29
New cards
Public Agentry/ Publicity
ONE WAY communication; initiated by an organization with little concern for accuracy or completeness
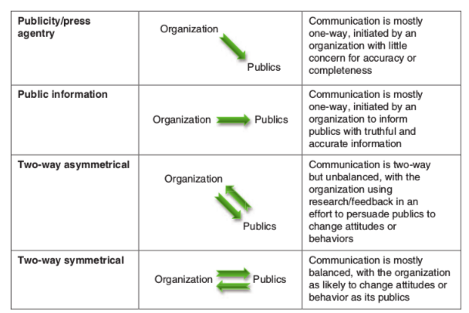
30
New cards
Public Information
ONE WAY communication, initiated by an organization to inform publics with truthful and accurate information
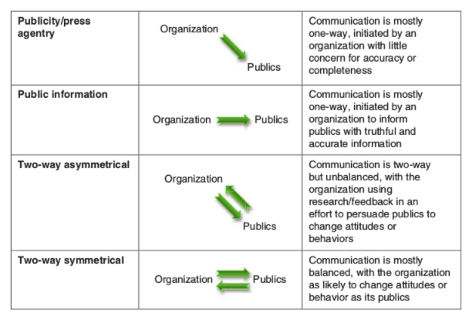
31
New cards
Two-Way asymmetrical
TWO WAY comm. BUT unbalanced, with the organization using research/feedback in an effort to persuade publics to change attitudes or behaviors
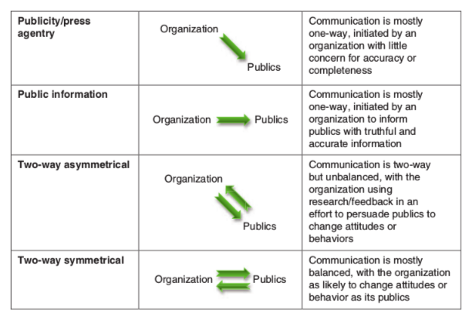
32
New cards
Two-Way Symmetrical
BALANCED comm. with the organization as likely to change attitudes or behavior as its publics
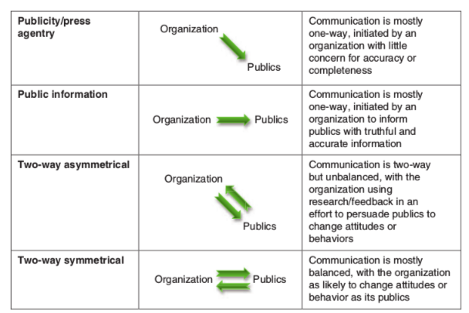
33
New cards
Early Beginnings: Persuasion
used to accept the authority of government and religion through PR
34
New cards
Early Beginnings: The Rosetta Stone
publicity release touting an Egyptian pharaoh accomplishments
35
New cards
Early Beginnings: Olympic games
Promoted to enhance the aura of athletes as heroes
36
New cards
Early Beginnings: Julius Caesar
First politician to publish book :commentaries” to further his ambitions to become emperor of Roman Empire
37
New cards
The Middle Ages: Church?
The Roman Catholic Church a major practitioner of public relations
38
New cards
The Middle Ages: Pope Gregory of the College of Propaganda
Used propaganda to propagate the faith
39
New cards
The Middle Ages: Bankers in Venice
Practiced art of investor relations, adopted the concept of corporate philanthropy
40
New cards
Cononial America: Land Companies
Promotion of colonization to generate revenues from what the colonist were able to manufacture or grow; was a commercial propisition
41
New cards
Colonial America: American Independence- Sam Adams
He refined a sense of how symbolism could sway public opinion
“the Father of press agentry”
Did the Boston Tea Party, Boston Massacre
“the Father of press agentry”
Did the Boston Tea Party, Boston Massacre
42
New cards
The 1800s: The Golden Age of Press Agentry
Promoting?
Promoting?
Promoting the westward movement: Publicity and promotion to help populate the west
Expiation of railroads dependent on this
Expiation of railroads dependent on this
43
New cards
The 1800s: The Golden Age of Press Agentry
P.T. Barnum:
P.T. Barnum:
Hype and press agentry
The great American showman
Exaggeration to promote public entertainment
The great American showman
Exaggeration to promote public entertainment
44
New cards
The 1800s: The Golden Age of Press Agentry
Corporate…?
Corporate…?
Early corporate initiatives: wave of industrialization and urbanization created many new businesses that competed in the market place
45
New cards
1900-1950: The Age of Pioneers
Ivy Lee
Ivy Lee
\-The first Public Relations Counsel
\-Open Parker and Lee in 1905
\-One first clients: Pennsylvania Railroad
\-1913-1914 railroad freight hike campaign “landmark in history of PR”
\-Best known for work with Rockefeller family
\-Open Parker and Lee in 1905
\-One first clients: Pennsylvania Railroad
\-1913-1914 railroad freight hike campaign “landmark in history of PR”
\-Best known for work with Rockefeller family
46
New cards
Ivy Lee: Declarations of principles
New model of public relations practice of public information
Emphasis on dissemination of truthful accurate information
Emphasis on dissemination of truthful accurate information
47
New cards
Lee contributions to PR
1: Advancing the concept that business and industry should align themselves with the public interest
2: Dealing with top executives and carrying out no program without the active support of management
3: Maintain open communications with news media
4: Emphasizing the necessity of humanizing business and making PR community
2: Dealing with top executives and carrying out no program without the active support of management
3: Maintain open communications with news media
4: Emphasizing the necessity of humanizing business and making PR community
48
New cards
1900-1950: The Age of Pioneers
Edward L. Bernays
Edward L. Bernays
“Father of Modern PR”
Emphasized the concept of “Scientific persuasion”
Believed in public relations should emphasize science to change peoples perceptions and encourage certain behaviors
Emphasized the concept of “Scientific persuasion”
Believed in public relations should emphasize science to change peoples perceptions and encourage certain behaviors
49
New cards
Edward L. Bernays: Father of Modern Public Relations
Crystallizing Public Opinion
Classic Campaigns
Crystallizing Public Opinion
Classic Campaigns
Crystallizing Public Opinion: Outline the scope, function, methods, techniques and social responsibilities of a public relations council
Classic campaigns: Ivory Soap, Torches of Liberty, Light’s golden Jubilee
Classic campaigns: Ivory Soap, Torches of Liberty, Light’s golden Jubilee
50
New cards
George Creel
Former newspaper reporter: asked by president Woodrow organize massive PR effort for WWI
Committee on Creel persuaded news to help
American Red Cross development
Committee on Creel persuaded news to help
American Red Cross development
51
New cards
Author Page
Vice President of American Telephone and Telegraph (AT&T)
Credited with making public relations a part of higher management
Credited with making public relations a part of higher management
52
New cards
1950-2000: Public Relations Come of Age
Reasons
Reasons
Economy
The growth of big business
Big Labor
Big Government
Scientific and Technological advances
The communications revolution
Financial considerations
The growth of big business
Big Labor
Big Government
Scientific and Technological advances
The communications revolution
Financial considerations
53
New cards
1950-2000: Public Relations Come of Age
Biz turned to PR
Mass media: media relations
Issue management
Management function
Mass media: media relations
Issue management
Management function
54
New cards
Today’s practice and trends in PR
Multicultural world
Recruitment of Minorities
Public demand for transparency
Expanded role for PR
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Increased emphasis on Measurement (ROI)
Managing the 24/7 new cycle
Continued growth of Digital Media
Outsourcing to PR firms
The need for lifelong professional development
Recruitment of Minorities
Public demand for transparency
Expanded role for PR
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Increased emphasis on Measurement (ROI)
Managing the 24/7 new cycle
Continued growth of Digital Media
Outsourcing to PR firms
The need for lifelong professional development
55
New cards
Ethics
standards of conduct; which indicates how __one should__ behave based upon moral deputies and virtues rising from principles of right from wrong
\-right v wrong; fair v unfair ect…
\
\-right v wrong; fair v unfair ect…
\
56
New cards
Values
Central beliefs that determine how __we will behave__ in certain situations
57
New cards
Ethical PR professionals
Should have values as…
honesty
openness
loyalty
fair-mindedness
respect
integrity
forthright communication
ie: code of ethics
honesty
openness
loyalty
fair-mindedness
respect
integrity
forthright communication
ie: code of ethics
58
New cards
Burden of making ethical decision to be considered in PR
1) Public interest
2) Employers self interest
3) Standards of the public relations profession
4) Personal values
2) Employers self interest
3) Standards of the public relations profession
4) Personal values
59
New cards
Personal values: Ethical orientation
Absolutist
Absolutist
Something is either completely right or wrong
The end cannot justify the means
Refuse to do anything that crosses an ethical boundary
The end cannot justify the means
Refuse to do anything that crosses an ethical boundary
60
New cards
Personal values: Ethical orientation
Existentialist
Existentialist
Choice is base on undertaking an assignment (may not be ethical) but executing in a way that doesn’t cross any ethical boundaries
Seeking balance or midpoint
Balance between two extremes
Seeking balance or midpoint
Balance between two extremes
61
New cards
Personal values: Ethical orientation
Utilitarian
Utilitarian
Each decision is based on the result that causes the least harm and the most good
“the greatest good for the greatest number of people”
The ends can justify the means
“the greatest good for the greatest number of people”
The ends can justify the means
62
New cards
6 Core values of the PRSA code of ethics
Deliberate
Planned, Performance
Public Interest
Two-way communication
management function
Planned, Performance
Public Interest
Two-way communication
management function
63
New cards
Professional Codes of Conduct
Act with honest and integrity
Tell the Truth
Tell the Truth
64
New cards
Professionalism in PR
Education
Training
Literature
Research
Code of Ethics
Training
Literature
Research
Code of Ethics
65
New cards
Professional Practitioners should have
\-A sense of independence
\-A sense of responsibility to society and the public interest
\-Manifest concern for the competence and honor of the profession as a whole
\-Higher loyalty to the standards of profession and fellow professionals than to the employer of the moment
\-A sense of responsibility to society and the public interest
\-Manifest concern for the competence and honor of the profession as a whole
\-Higher loyalty to the standards of profession and fellow professionals than to the employer of the moment
66
New cards
Other Steps Toward Professionalism
1) Changing mindset of practitioners without formal education in PR
2) A standardized curriculum/ establishing PR as an academic discipline
3) Expanding body of knowledge
4) Professional accreditation
2) A standardized curriculum/ establishing PR as an academic discipline
3) Expanding body of knowledge
4) Professional accreditation
67
New cards
Professional Accreditation
International Association of Business Communicators Model (IABC)
The Public Relations Society of America Model
The Public Relations Society of America Model
68
New cards
The Public Relations Society of America Model
* Preview course: readiness questionnaire; portfolio
* 2.5 hour exam 4-step (30%), ethics/law (15%) theory (15%), business literacy (10%), management (10%), crisis (10%), media relations (5%), IT (2%), history/current issues (2%), advanced communication skills (1%)
* 4,000 APR to date, 20% of membership
* 2.5 hour exam 4-step (30%), ethics/law (15%) theory (15%), business literacy (10%), management (10%), crisis (10%), media relations (5%), IT (2%), history/current issues (2%), advanced communication skills (1%)
* 4,000 APR to date, 20% of membership
69
New cards
APR designation as being accredited by PRSA
Certifies your drive, professionalism and principles, setting you apart from your peers and positioning you as a leader and mentor in the competitive public relations field.
The APR (Accreditation in Public Relations) asserts professional competence
The APR (Accreditation in Public Relations) asserts professional competence
70
New cards
Definitions of bottom line PRO and CON
PRO: t*he profitability of a business after all expenses are deducted from revenues*
CON:the profitability of a business after all expenses are deducted from revenues.Bottom-line profits are net profits after all the costs of the business have been accounted for
CON:the profitability of a business after all expenses are deducted from revenues.Bottom-line profits are net profits after all the costs of the business have been accounted for
71
New cards
PRO: How does PR shape the image?
Image, crisis, shape brand, attract
72
New cards
PRO: How Tylenols scandal made PR important
Tylenol bottles laced with cyanide killing users at random. They recalled all current products on shelves across America and rebranded their product. They created a seal on their bottles, so consumers knew if the product had been tampered with or not. Tylenol rebranded themselves from this crisis and became the pain and fever company that cares about your health.
73
New cards
PRO: 5 Ways a Corporate Crisis Can Affect the Bottom Line
a. Destruction of Shareholder Value
b. Loss Of Revenue
c. Loss of (Or Inability to Attract) Talented Employees
d. Increased Costs
e. Loss of Stakeholder Trust
74
New cards
CON Key points
Marketing contributes to bottom line and PR indirectly does business goals
75
New cards
CON types of PR
Crisis management
Event Management
Reputation Management
Event Management
Reputation Management