Pancrease
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Describe the different types of hormones the cells of the islets of Langerhans secrete
Cells of the islets of Langerhans:
Insulin: B(β) cells – 65 ‐ 70% of the cells
Glucagon: A (α) cells ‐ ~20% of the cells
Somatostatin: D(δ) cells – is an inhibitory peptide (inhibits islets’ cells secretion)
Gastrin (G-cells) - stimulates gastric acid secretion
Describe what hormones are secreted after a meal and their functions
After a meal:
Amylin:
reduces food intake,
slows gastric emptying,
suppresses postprandial glucagon release.
Insulin:
anabolic hormone
promotes nutrient storage
Glucagon:
catabolic hormone
mobilizes glycogen, fat, and protein during fasting
Somatostatin:
inhibits pancreatic hormone secretion
When insulin is released, what other hormone is being released in equimolar amounts?
What is the function of this hormone?
Clinical importance of C-peptide?
C-Peptide:
Active insulin and C peptide are secreted by exocytosis in equimolar amounts
Function:
Plasma levels provide information about β‐ cell function
Improves renal and neuronal functions in patients with diabetes
Repairs the muscular layer of arteries
Protects functional β-cell mass from oxidative stress
Clinical Importance:
potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of diabetes-associated complication
Describe what stimulates insulin secretion
Plasma levels?
Hormones?
Nervous System Stimulation?
Describe what Inhibits insulin secretion
Plasma levels?
Hormones?
Nervous System Stimulation?
Stimulators of insulin secretion:
Plasma levels: Increase in Glucose, AA, FA, Ketones
Hormones:
Gastrointestinal hormones:
Glucagon-like peptide-1(GLP-1)
cholecystokinin (CCK)
Glucagon,
epinephrine (β2‐AR)
Nervous System:
Sympathetic stimulation (β2‐AR)
Parasympathetic stimulation (Ach)
Inhibitors of insulin secretion:
Plasma levels: Decrease in Glucose, AA, FA
Hormones:
Somatostatin
Epi/Norepi (α2-AR)
Nervous System:
Sympathetic stimulation (α2-AR)
Describe the mechanism which leads to insulin secretion by the pancreatic B cells:
Glucose (major), amino acids (leucine) pathway?
Adenylyl cyclase/cAMP pathway:
Phospholipase C, DAG/IP3 pathway:
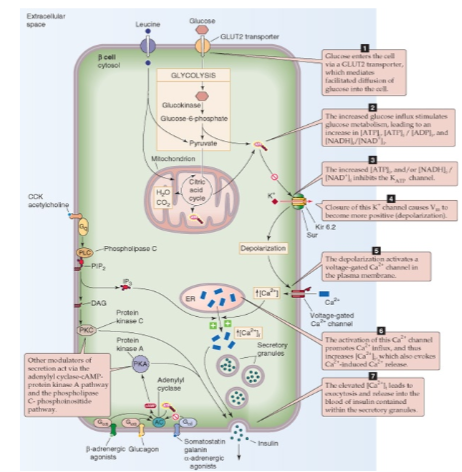
Glucose (major), amino acids (leucine) (steps):
Glucose enters (via Glut-2) as well as Leucine → ↑ATP & ↑NADH/NAD+ ratio →inhibits K+ channels→ ↓K+ efflux → cell depolarization → Opens the voltage-gates Ca2+ channels → ↑ Ca2+ influx → ↑ Ca2+ release from ER → insulin exocytosis
Adenylyl cyclase/cAMP pathway:
Activation (Gs)
glucagon
β2-adrenergic receptors (epi,NE)
GLP-1
Inhibition (Gi)
α2-adrenergic receptors (Epi, NE)
somatostatin
Phospholipase C pathway:
Gq signal cascade (DAG/IP3)
Ach, CCK
What is the Incretin Effect and why does this occur
Incretin Effect:
Oral glucose > Intravenous administered glucose in regards to insulin response
This is because oral glucose secrete gastrointestinal hormones which stimulates Insulin. Intravenous does not activate these gastrointestinal hormones
Describe the structure of insulin receptors IR ?
Effects?
Compare and contrast IR vs IGF1R
transmembrane receptor with an extracellular ligand-binding domain and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain
Effects:
Cellular metabolism
Membrane transport
Cellular growth, development, survival
IR vs IGF1R:
strucually similar
IGF primarily supports growth and development
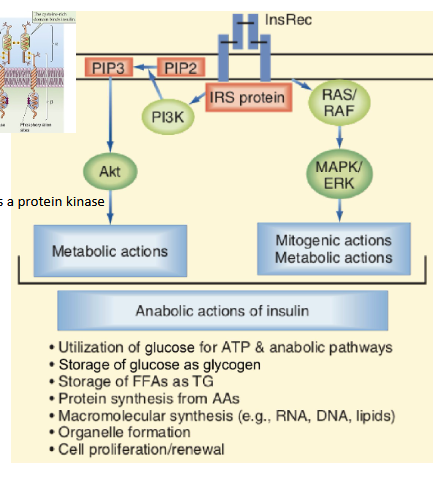
Describe the mechanism and function of Insulin’s PI3K–Akt pathway vs RAS–MAPK pathway
PI3K–Akt pathway (Anabolic effects):
Initiated by PI3K-mediated phosphorylation
Promotes metabolic and anabolic processes
Essential for glucose uptake via GLUT4
RAS–MAPK pathway (Growth-promoting Effects):
Regulates transcription factors
Controls cell growth, differentiation, and survival
Supports anti-apoptotic signals and membrane transport of ions and amino acids
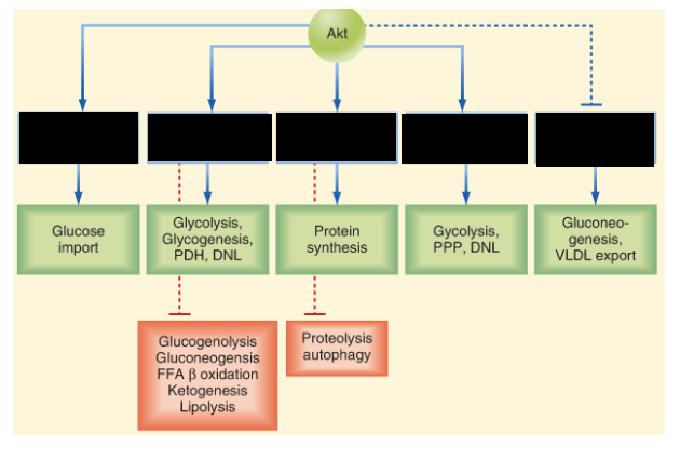
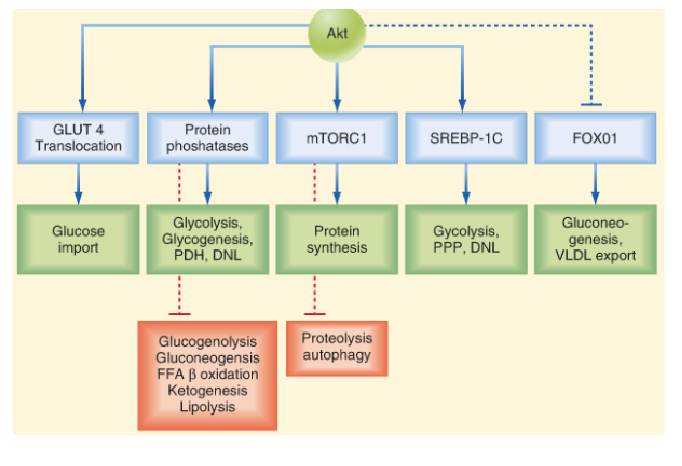
Describe how Insulin helps w/ Glucose Uptake?
Describe the relationship between Insulin and K+
What other substances does Insulin help cellular uptake of?
Glucose uptake:
Insulin induces vesicle translocation and fusion of GLUT-4 in insulin sensitive tissues (skeletal muscles/adipose tissues)
K+ and other substance’ relationship to Insulin
K+
Lowers plasma level by increasing Na⁺/K⁺‐ATPase pump
Aid in hyperkalemia management
Insulin also enhances cellular uptake of:
AA, Mg²⁺, and PO₄³⁻
Via specific channels/transporters
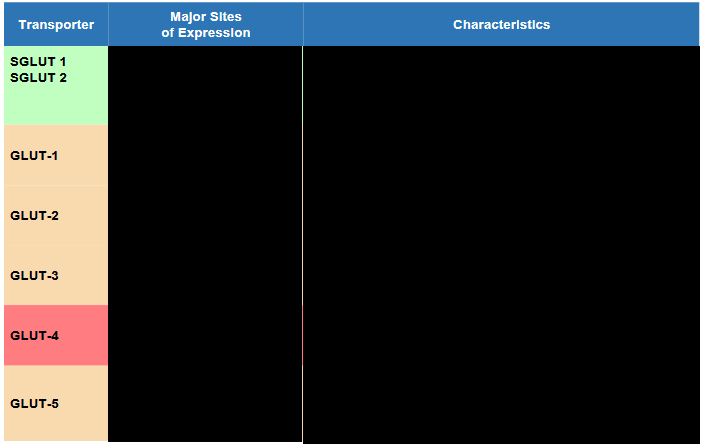


Describe Insulin’s Effect in:
Brain
Kidney
Cardiovascular
Bone
Brain:
CNS growth, development, and metabolism (neurotrophic)
improve cognitive function and reduce depressive symptoms
(prefrontal cortex and hippocampus)
suppress appetite and reduce body weight
(hypothalamic nuclei)
***GLUCAGON ALSO DOES THIS***
Does not directly regulate glucose uptake
Instead, affecting the expression and translocation of GLUT1 and GLUT3 transporters
Supports reproductive competence via the hypothalamic pituitary‐gonadal axis
Kidney (glomerular, mesangial cells, epithelial and endothelial cells):
Regulates glomerular and tubular functions
Increase Na Reabsorption
Increases Plasma Volume
GNG
Cardiovascular System:
Increases in
contractility
HR
Glucose Uptake
blood flow (via NO-dependent vasodilation)
***Glucagon also Increases HR and CONTRACTILITY***
Decrease Apoptosis
Bone (osteoblasts):
Controls osteoblasts’ development and metabolism
Diabetes I is linked to osteoporosis and bone fragility
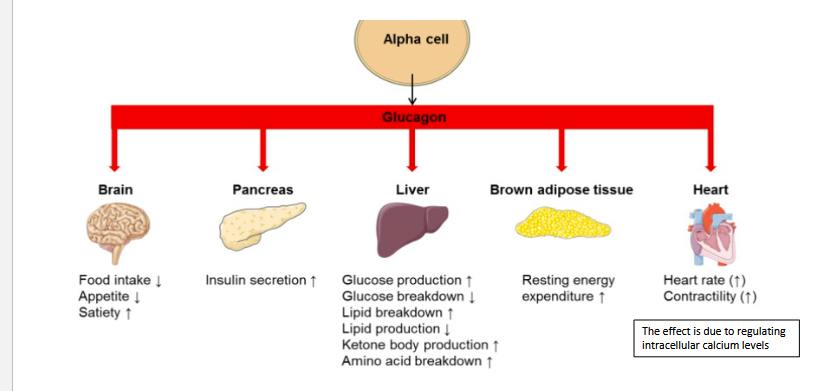
What G-proteins does Glucagon use?
Metabolic Effects of Glucagon?
Major Target Organs?
What Hormone does Glucagon Stimulate?
Glucagon Receptors (GCGRs):
Gs: cAMP is the second messenger
Gq: PLC/IP3/Ca+
Metabolic effects- Increases:
glucose
FA
keto acids,
AA
urea production
Major Target Organ:
liver and adipose tissue
Stimulation:
also stimulates Insulin Production
Explain the potential Potential Therapeutic Effects of GLP-1 agonists
Obesity?
Diabetes?
Cardiovascular health?
Fatty Liver Disease?
Neurodegenerative Disorders?
Potential Side Effects?
Potential therapeutic Effects and side effects of GLP-1 agonists :
Obesity:
Appetite suppression,
weight loss
Type 2 Diabetes:
Enhances insulin release,
lowers blood glucose
Cardiovascular Health:
BP control,
risk reduction
Fatty Liver Disease:
Improves liver metabolism
Neurodegenerative Disorders:
May benefit Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
anti‐inflammatory and neuroprotective effects
Neuropathic Pain
Addiction & Psychiatric Disorders
Potential Side Effects:
Common: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, headache, dizziness
Rare but serious: Pancreatitis, worsening diabetic retinopathy
Describe what Stimulate/Inhibits glucagon Secretion
Stimulators:
↓Serum glucose
↑Serum amino acids* (arginine, alanine)
Sympathetic stimulation (via β2‐AR)
Glucocorticoids
Prolonged fasting
Exercise
Inhibitors:
↑ Serum glucose
Somatostatin
Insulin
GLP1
Describe what happens to Plasma glucose, glucagon and insulin level after a meal and after an overnight fast
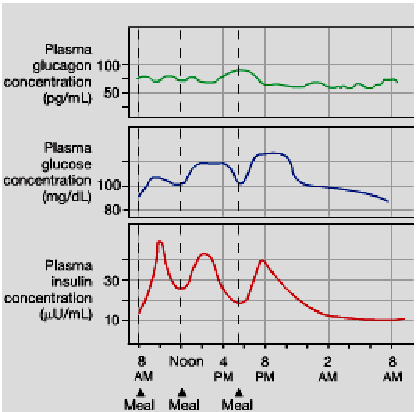
How does Insulin and Glucagon interact w/ each other?
Describe I/G ratio of:
Large carb meal
Small meal
low-carb diet
Overnight fast
Starvation
Hormonal integration
Insulin inhibits glucagon secretion
Glucagon stimulates insulin secretion
I/G ratio:
Large carb meal (10 or higher)
Small meal (7) vs. low-carb diet (1.8)
Overnight fast (2.3)
Starvation (0.5 or less)
Differeneitate between mTORC1 vs AMPK pathways
mTORC1
promoting anabolic processes & suppressing catabolism.
Activation:
nutrients, insulin, and growth factors
AMPK:
promotes catabolic pathways
Activation:
energy stress (e.g., high AMP levels, low oxygen
Glucagon
What are the two types of Diabetes?
What are the mechanism of Hyperglycemia
Types of Diabetes:
Type I: Insulin deficiency (low synthesis)
Type II: Insulin resistance (defective insulin/receptor interaction or intracellular signaling pathway)
Mechanism of hyperglycemia:
Increased hepatic glucose output
Decreased glucose uptake via insulin-dependent transport (GLUT4)
Describe what happens to glucose levels Postprandial in a normal vs diabetic person
In a diabetic, higher peak in glucose levels and slower decline compared to a normal patient
What are the Metabolic results of DM?
Complications of constant hyperglycemia?
what are macrovascular complications?
Microvascular complications
Metabolic results of DM:
Chronic hyperglycemia (most common)
Dyslipidemia
Skeletal muscle wasting
Complications of constant Hyperglycemia:
cellular damage → athophysiological mechanisms:
Mitochondrial dysfunction
Oxidative stress
Inflammation
Memorization Tip: “DSI” → Don’t Saturate It (glucose)
plasma hyperosmolality and osmotic diuresis
May cause hyperosmolar coma (severe loss of intracellular fluid in the brain)
Macrovascular Complications:
atherosclerosis
hypertension
Microvascular (angiopathy):
neuropathy (nerve damage)
nephropathy (renal failure)
retinopathy (micro aneurysms, retinal hemorrhage)
Differentiate between the causes of Hypo/Hyper Glycemia
Causes of hypoglycemia:
Overproduction of insulin in response to a meal
(may indicate high risk for diabetes or early stage of type II DM)
Some medications (insulin and antidiabetic drugs)
Alcohol intake
Liver, kidney, or heart disorders
Eating disorders
Pregnancy
Causes of hyperglycemia:
Insulin deficiency or insulin resistance
Medications (steroids)
Illness or infection (stress-induced hyperglycemia)
Being inactive
Differentiate the Early/Late (sever) clinical manifestations of hypo/hyper glycemia
Hypoglycemia:
Early Manifestations:
Weakness
Shakiness
Palpitation, tachycardia
Hunger
Nausea
Diaphoresis
Anxiety, hyperventilation
Prolonged or severe
Hallucinations
Seizures
Hypothermia
Neurologic symptoms
Coma
Hyperglycemia
Early manifestations:
Weakness
Polyuria, polydipsia, dehydration
Altered vision
Weight loss
Prolonged or severe:
Diabetic (keto)acidosis
Kussmaul hyperventilation (deep and rapid breathing)
Hypotension, arrhythmias
Stupor
Coma (hyperosmolar)
Describe how these hormones affect plasma glucose levels and how:
Growth Hormone:
Glucocorticoid
Catecholamines
Growth Hormone:
↑ Plasma glucose via:
Stimulating insulin gene expression
Inducing insulin resistance (↓ glucose uptake)
↑ Gluconeogenesis
↑ Intestinal glucose absorption
May cause hyperinsulinemia
Glucocorticoids:
↑ Plasma glucose via:
↓ Insulin sensitivity (diabetogenic)
↑ Gluconeogenesis
Enhance glycogenolysis (permissive to glucagon, catecholamines, in response to acute stress)
↑ Calorigenic effect
Promote glycogen synthesis (high insulin/glucagon ratio in chronic excess of glucocorticoids)
Catecholamines:
↑ Plasma glucose via:
Stimulating glycogenolysis (liver & muscle)
↑ Muscle glucose supply & glycolysis → lactate for gluconeogenesis
Direct gluconeogenesis via α₁ and β2 receptors
Inhibit insulin secretion via α₂ receptor;
Stimulate insulin secretion via β2 receptor
Describe the two strageties for Hyperglycemia prevention and management
Diet modifications
Limit carbohydrate intake
Focus on balanced nutrition to reduce postprandial glucose spikes
Exercise:
Promotes exercise-dependent glucose uptake
Muscle contraction → enhance GLUT4 transporter expression → increases glucose uptake
Insuline-independent effect.