Immuno Lec 5: Vaccinations
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Define Active Immunisation
Stimulates the body’s own immune system
Activates innate and adaptive immune system
Define Passive Immunisation
Provides immunity by transfer of antibodies
Temporary protection
Active vs Passive Immunisation
Passive | Active | |
Source | Other human/animal | Own body |
Effectiveness | Low to Moderate | High |
Protection Duration | Days/Weeks | Years |
Development time | Immediate | Days/Weeks |
Use | Prevention/Treatment | Prevention/Treatment |
Purpose of Vaccination
Prophylatic/Preventative
Herd Immunity
Therapeutic
Eradicative
Describe the mechanism of a Live attenuated vaccine
Pathogen is weakened → can still replicate, cant cause diseases
Mild symptoms, occur after 7-21 days incubation period
Immune response similar to natural infection
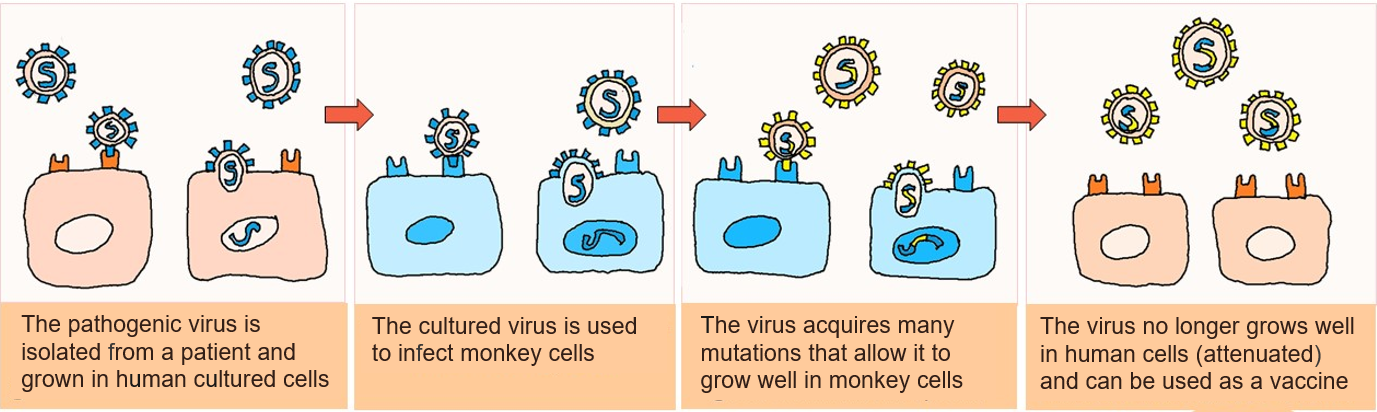
Creating live-attenuated vaccines by culturing in non-human cells
1) Pathogenic virus is isolated and grown in human cultured cell
2) Cultured virus infects monkey cells
3) Cultured virus mutates, allowig it to grow well in monkey cells
4) Virus no longer grows well in human cells after mutations (attenuated)
Using recombinant DNA tecnhiques in creating live-attenuated cells
1) Isolate pathogenic virus
2) Isolate virulence gene
3) Delete/mutate virulence gene
Describe the mechanism of an inactivated vaccine
Microbes killed by radiation/heat/chemicals
3D conformation of most epitopes preserved
Live-attenuated vs Inactivated
Attenuated | Inactivated | |
Effectiveness | Very effective
| Less effective
|
Induced immunity |
|
|
Side effects | May cause unexpected side effects in immunocompromised patients | Lower chance of causing side effects in all target patient groups |
Virulence | Possible to regain virulence due to mutations | No danger of regaining virulence |
Subunit vaccines
Components of pathogen that do not replicate
For highly immunogenic antigens
Require the use of adjuvants
Advantages of Subunit vaccines
Simpler production and QC
No worries of under-activation/reversion
Disadvantages of Subunit vaccines
Difficult and time consuming to identify good antigens
Less immunogenic
Requires boosters/adjuvants
May fail to stimulate cell-mediated immunity
Toxoid vaccines
Toxins from toxin-secreting pathogens are deactivated/treated with Formalin
Inactivated toxins (Toxoids) introduced to the body to stimulate immune response
Recombinant subunit vaccine
Gene encoding for immunogenic proteins are cloned and expressed in a host cell
Immunogenic peptides are synthesised by the cells
Immunogenic are used as antigens for vaccines and are processed by MHC-II Pathway
Adjuvants
Substances which are administered together with vaccine to enhance the immune response towards the vaccine
Induce inflammation
Accelerate antigen presentation
mRNA vaccines
mRNA sequence enclosed by lipid nanoparticle
enters humans cells via cell membrane
proteins are syntehsised by transcription/translation, and are broken down by proteasome/secreted out of the cell to be engulfed by antigen-presenting cell