Ch 8 Alkene Addition rxns
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
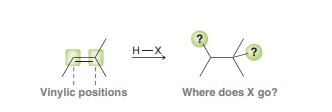
Hydrohalogenation
H-X is regioselective (mark +). IF carbocation RAR possible then a mix of products is obtainted. Not really super useful
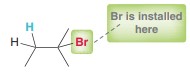
Hydrohalogenation 1
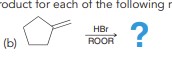
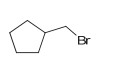
Hydrohalogenation 2 (Be careful peroxides)
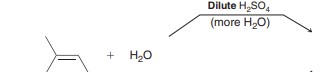
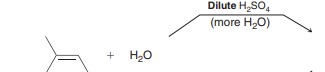
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration
Markovnikov + of H and OH over alkene. Synthetically very useful.
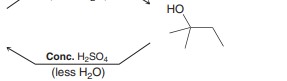
Reversal of alcohol to alkene. Elination reaction
Uses heat=less h2o or just a more concentrated acid
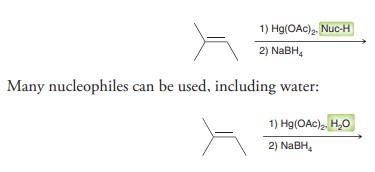
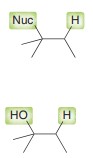
Oxymercuration-demurcuration
Markovnikov addition of H and OH across alkene without carbocation rar
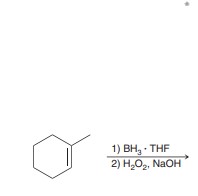
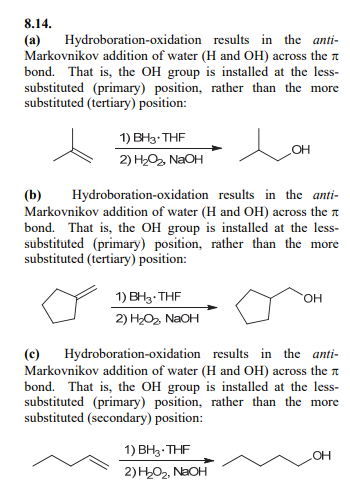
Hydroboration oxidation
Anti Markovnikov addition of H and OH across alkene. Syn addition.
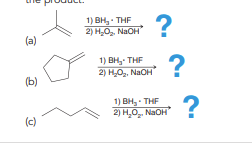
Hydroboration Oxidation
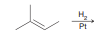
Hydrogenation
gives syn addition of H’s over alkene. Reduces double and triple bonds to single bonds. Only makes syn products in cases where stereo centers are formed
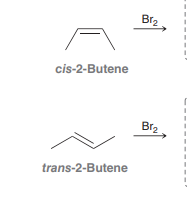
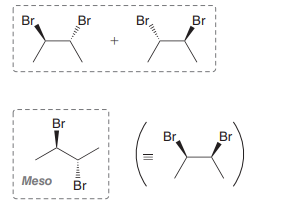
Bromination
Anti addition over alkene of Br and Br over alkene
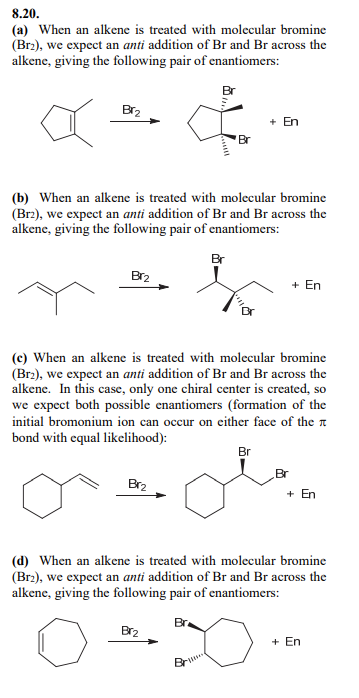
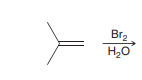
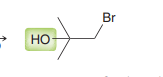
Halohydrin formations
anti addition of Br and OH across the alkene with OH being installed at the more substituted position. 3 ring bridged intermediate is attacked by OH.
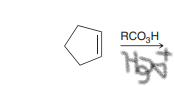
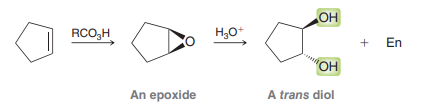
Anti dihydroxylation. MCPBA and Ch3CO3H (peroxyacetic acid) are both peroxy acids (strong oxidizing agents)
Epoxide intermeidate. Ring opening to form trans-diol via aqueous acid.
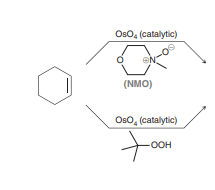
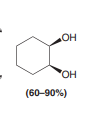
Syn Dihydroxylation: KMnO4, NaOH, Cold
Gives the same OH and OH over the alkene. KMnO4 is a strong oxidizing agent and can cause further oxidation of the diol so OsO4 is used more often
Ozonolysis
Cleavage of C=C sp2 bonds can open a ring or make two products with a c=o in place of the other Carbon in the C=C bond