biochem chp 2 water
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
physical properties of water
melting point - 0 C
boiling point - 100 C
heat of vaporization - 2260 J/g
bc of noncovalent interactions
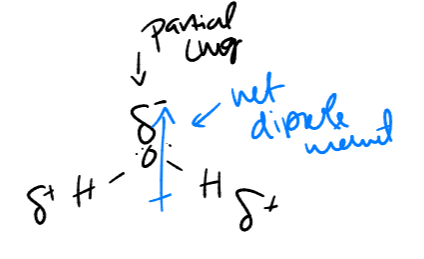
geometry of water / dipoles
e- geometry - tetrahedral (ish)
molecular geometry - bent
Noncovalent interactions
easy to break/ dynamic
always forming and breaking
salt bridges, H bonds, van der waals
Hydrogen bonds
between Hydrogen bonded to electronegative atom (O, N, S) and lone pair on an electronegative atom
longer than a covalent bond but much weaker
polar molecules bond well, charges do not
water structure in ice
goal: maximize H bonds
ice less dense than liq H20
will float to top so suff can live underneath
only prt that doesn’t maximize is top bc no other water so will be exposed and less stable
hydrogen bond functions
substrate recognition, enzyme binding
nucleic acid pairing
if lone pair involved in resonance cant accept H bond
most stable h bond geometry (energetically)
linear
(bent not as stable)
ionic bond
charge charge interaction
positive and negative charge => favorable
forms salt bridge
stabilizes different biological reactions
coulombic interactions
like charges
unfavorable
F
Q1Q2/Er²
Q = absolute value of charge
r = distance between charges
E = dielectric constant
Dielectric constant
ability of environment to reduce strength of electrostatic
EH2O = 80
high dielectric charge makes good for screening / can mitigate charges
universal solvent, will always have screening/shielding effect
Van der Waals/London Dispersion Forces
uncharged and uncharged
nonpolar/nonpolar
dipole-dipole interactions
induced dipole
highly dynamic
van der waals interactions components
attractive force (LDF) depends on polarizability
repulsive force (steric repulsion) depends on size of atoms
van der waal radii
larger VDWr —> weaker interaction
can plot
how do nonpolar molecules dissolve in water
carrier molecules
clathrates
gas channels
carrier molecules
enzymes adapted to carry gasses through the cell
gas channels
small hydrophobic channels for gasses
1 way
clathrates
ordered cage molecules around a guest molecule
guest molecule hydrophobic
higher entropic cost
enthalpy mildly unfavored because not maximizing H bonds
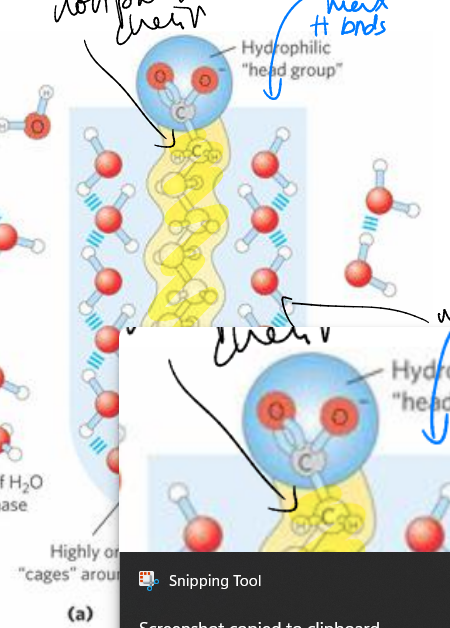
micelles
spherical macro shapes
form under favorable conditions (release of water clusters drives formation)
release of ordered water in biological interactions
when a nonpolar substrate comes into contact with enzyme (also np) ordered water is released as H2O clusters and disordered water is displaced by the interaction
enzyme-substrate interaction stabilized by H bonding, ionic and hydrophobic interactions
strong noncovalent interactions
hydrogen bonds
ionic interactions (attraction/repulsion)
weak noncovalent interactions
hydrophobic interactions
van de waals interactions
pH
=-log[H+]
log scale
pH water = 6.5-8
weak vs strong bases in aqueous solution
strong acid/base completely dissociates into H+ or OH- in aqueous solution
weak acids do not completely dissociate
proton and conjugate base
described by dissociation constant
acid dissociation constant (ka)
keq of HA ←→ A- + H+
-logka=pka
ka decrease, pka increase, pH increase
henderson hasselbach equation
calculate concentrations of the acidic and basic components of the mixture id the pH and pKa are known
pKa=pH-log[A-]/[HA]
weak vs strong titration curves
strong has sharp incr/decr (almost vertical)
weak has more gradual less steep incline
relationship between titration curve and pKa
pH=pKa at midpoint
buffers
aqueous solutions that can resist change in pH in if small amounts of acid or base are added
“buffering region” the change is very small as a function of added acid or base
pH in biology
enzymes catalysts have optimal pH (extremes can cause problems with metabolism)
low pH —> acidosis
caused by diabetes, fasting, starvation, etc
treated by treating underlying cause and/or IV bicarbonate