10. Binomial Distribution
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
A ________ __________ is a variable (typically represented by X, or another capital letter) that takes on a different value for each outcome of a random phenomenon, and is determined by chance
random variable
A _______ variable is a variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon
random
The two broad types of random variables are _______ random variable and __________ random variable
discrete
continuous
A ______ random variable is a random variable that has a countable set of distinct values
Examples:
→ X = number of heads from a coin toss
→ Y = the result of a single die roll
→ the number of smokers in a random sample
discrete
A _________ random variable is a random variable that has infinitely many values. A variable is _________ if between any two possible values of the variable, there exists another possible value for the variable
Examples:
→ X = height
→ Y = serum creatinine level
→ Z = volume
continuous
A __________ __________ is a graph, table, or formula that gives the probability of a given outcomes’s occurance
probability distribution
A _________ ___________ ________ (pdf) is any mathematical relationship between each possible value and the probability of that value
P(x) = P(X = x)
probability distribution function
Requirements for a probability distribution:
1) All of the individual probabilities must be between ___ and ___ (, inclusive);
2) The sum of all probabilities must be equal to _
0 and 1
1
When dealing with probability distributions, a _______ is the set of all possible outcomes for a random variable
→ it refers to a hypothetical ________ of numbers, not a ________ of people
population
_________ ________ have shapes, centers, and variability
probability distributions
The _____, or expected value, of any discrete random variable X represents the average value of the outcomes
(each observed X value is multiplied by its respective probability)
mean
A __________ random variable is a particular type of discrete random variable with the following characteristics:
→ There is a ______ number of identical trials
→ There are only ___ possible outcomes for each trial. One success (S) and one failure (F).
→ The probability of S remains the _____ from trial to trial (denoted as p)
→The outcomes of the trials are __________
binomial
fixed
two
same
independent
When working in a binomial setting, the number of successes X out of n trial has a binomial distribution with parameters n and p
→ the parameter _ is the total number of trials
→ the parameter _ is the probability of a success on any one observation (the possible values of X are the whole numbers from 0 to n | the choice of what we call a success is ______)
n
p
arbitrary
In order to work with binomial random variables, we must first define the _______ _______ which is the number of ways we can choose k objects from a total of n objects
binomial coefficient
we usually think of the ________ ________ as the number of ways we can arrange k successes among n observations
binomial coefficient
x! is called
x factorial
( n ) =
k
n!/k!(n-k)!
x! = 1 × 2 × 3 x . . . x ___
x
2! =
1 × 2 = 2
(7 - 3)! =
4! = 1 × 2 × 3 × 4 = 24
0! =
1
Consider 5 letters (A, B, C, D, E). How many different combinations of 3 letters can we choose?
( 5 ) = 5!/3!(5-3)!
3

How to calculate binomial coefficient on calculator?
top number input
press nCr
bottom number input
ENTER
( n ) can be denoted as…
k
Ckn or nCk or nCk
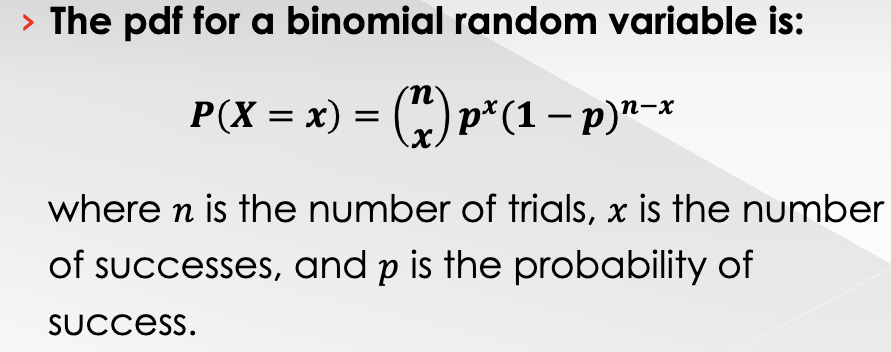
A __________ ________ ________ (pdf) is any mathematical relationship between each possible value and the probability of that value
→ the pdf for a binomial random variable is:
______________________________________
where n= # of trials, x = # of successes, and p = is the probability of success
Shorthand to denote a binomial random variable: X~Bin(n, p), where n = # of trials and p = the probability of a success on any one trial
→ X~Bin(10, 0.5) signifies that X is a binomial random variable with n = _ trials and p = __ probability of success on any one trial
10
0.5
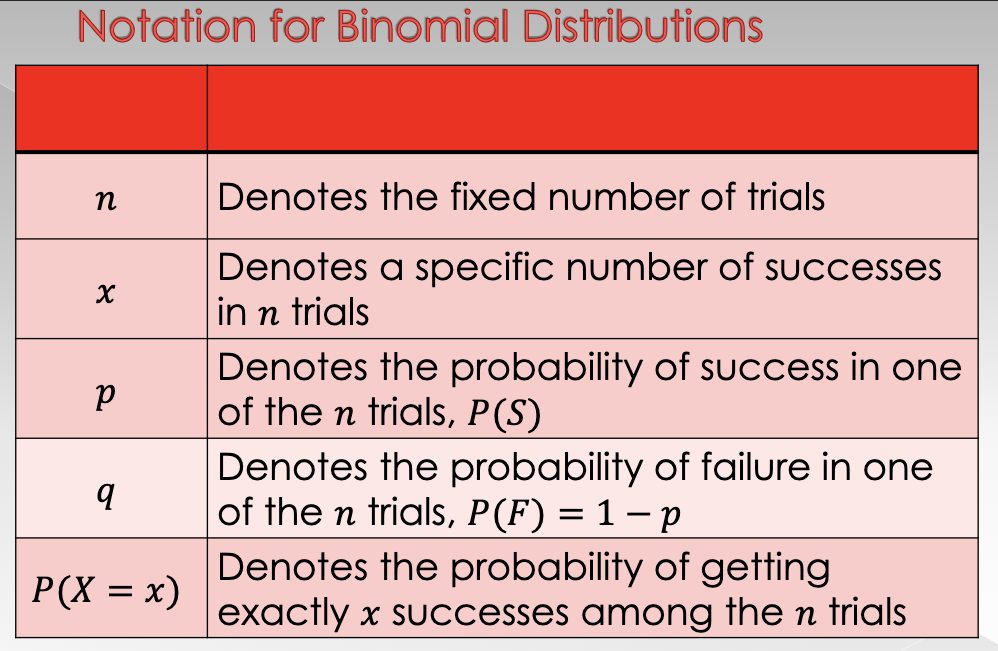
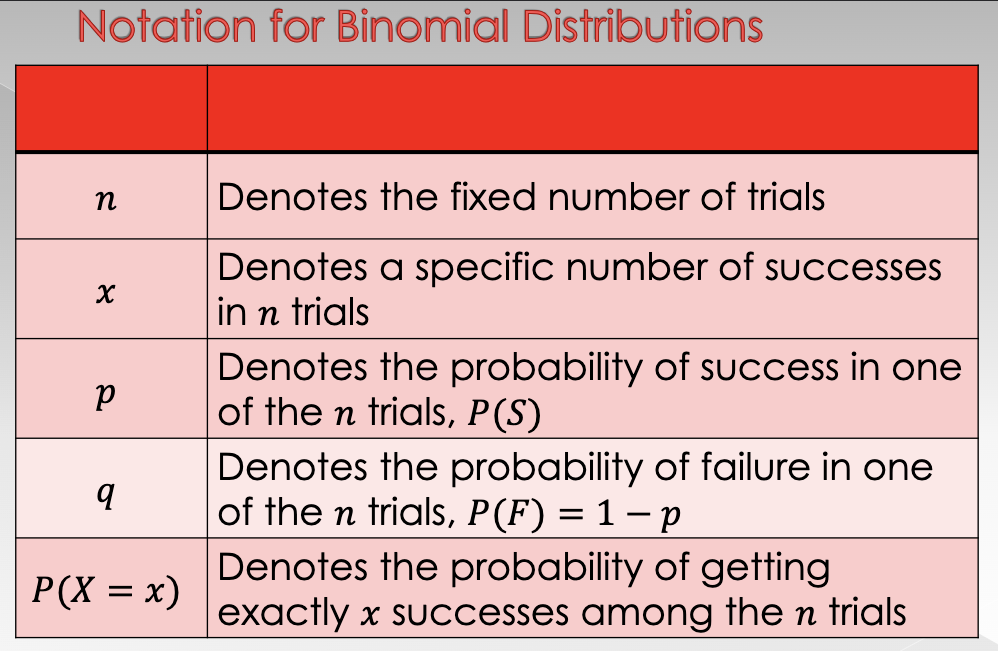
Since there are a fixed number of trials n, when you are interested in the probability of x successes, the number of failures is automatically determined to be __ - __
→ The probability of success is the same for each of the x successes, and the probability of failure is the same for each of the __ - __ failures
n (# of fixed trials) - x (number of specific number of successes in n trials)
Since all the n trials are __________, the probability of the intersection of any single combination of events is simply the product of their corresponding probabilities
→ However, there are more than just the one way to choose which trials are successes and which are failures . . . “n chooses x” different ways
independent
The complement of getting at least one item of a particular type is you get __ items of that type
no