Intro sensory systems
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
General concepts of sensory systems: Sensation is a ____ experience
Contact with external or internal environment occurs through _____ ____ - these can be ____, ____, or ____
General concepts of sensory systems - sensation is a conscious experience
Contact with external or internal environment occurs through sensory receptors - these can be exteroreceptors, proprioceptors, or interoreceptors
4 modalities of sensation?
Tactile
Proprioceptive
Thermal
Pain
A receptor neuron encodes stimulus from a restricted region of the receptive surface - this is the _____ ____
For any neuron in a sensory pathway, the ____ ____ consists of all ____ ___ that can influence activity.
A receptor neuron encodes stimulus from a restricted region of the receptive surface - this is the receptive field
For any neuron in a sensory pathway, the receptive field consists of all sensory receptors that can influence activity
There is orderly _____ arrangement between adjacent regions of the ___ ___ and this is projected onto central neural structures as ____
There is orderly topographic arrangement between adjacent regions of the receptive area and this is projected onto central neural structures as somatotopy
Sensation is perceived to be at the site of the ____ ___ regardless of where along the ___ ___ the stimulus is initiated. This is what produces ____ ____ sensation
Sensation is perceived to be at the site of the peripheral receptor regardless of where along the central pathway the stimulus is initiated
This is what produces phantom limb sensation
Sensory systems are both _____ and ____ pathways
Sensory systems are both series and parallel pathways
Receptors are biological ____ and convert some ___ or _____ into a transmitted ____ or ____ ____
Receptors are biological transducers and convert some physical or chemical energy into a transmitted signal or action potential
Adequate stimulus is the particular kind of ____ to which a receptor is ____ ___
Adequate stimulus is the particular kind of energy to which a receptor is most sensitive
Law of specific nerve energies says that the sensation that is felt depends on specific ___ ____ that is stimulated and the area of the ____ to which it is connected
The law of specific nerve energies says that sensation that is felt depends on specific nerve fibers that is stimulated and the area of the CNS to which it is connected
The intensity of sensation is coded in terms of ____ ___ ____ and not ___. Also depends on the ____ of ____ stimulated
The intensity of sensation is coded in terms of action potential frequency and not size. Also depends on the number of receptors stimulated
The receptor or generator potential is a ____ ____ potential that ____ with ____ - it is produced by an increased conductance to ___ ___ and causes ____ at the first ___ of ___ - if it is great enough, the ____ will initiate _____ _____
The receptor or generator potential is a local depolarizing potential that decays with time - it is produced by an increased conductance to small ions and causes depolarization at the first node of ranvier - if it is great enough, the depolarization will initiate AP generation
Receptor potentials are ___ with the stimulus. The amplitude of the receptor potential determines the _____ with which ____ ____ are generated. The duration of the receptor potential determines the ____ or the ____ of action potentials
Receptor potentials are graded with the stimulus. The amplitude of the receptor potential determines the frequency with which action potentials are generated. The duration of the receptor potential determines the duration or train of action potentials
Slowly adapting mechano receptors ____ _____ to a ____ ___
Rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors respond ____ at the _____ of a ____
Slowly adapting mechanoreceptors continue responding to a continuous stimulus
Rapidly adapting mechano receptors respond only at the beginning of a stimulus
Receptive fields of tract cells can have both ____ and ____ components - more complicated than ____
Tract cell characteristics are based on their ____ - can be ____ or _____
Receptive fields of tract cells can have both excitatory and inhibitory components - more complicated than receptors
Tract cell characteristics are based on their inputs - can be unimodal or polymodal
Modification of sensory information - convergence, divergence, direct inhib, presynaptic inhib
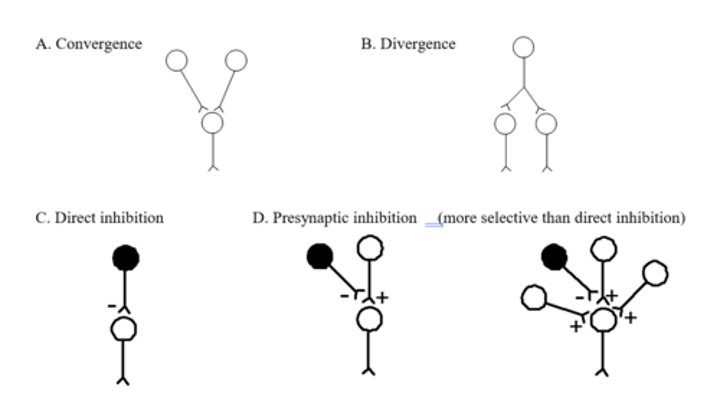
Convergence and divergence combine to increase the ____ _____ ____ of higher order neurons in a sensory pathway
Convergence and divergence combine to increase the receptive field complexity of higher order neurons in a sensory pathway
Convergence/divergence image
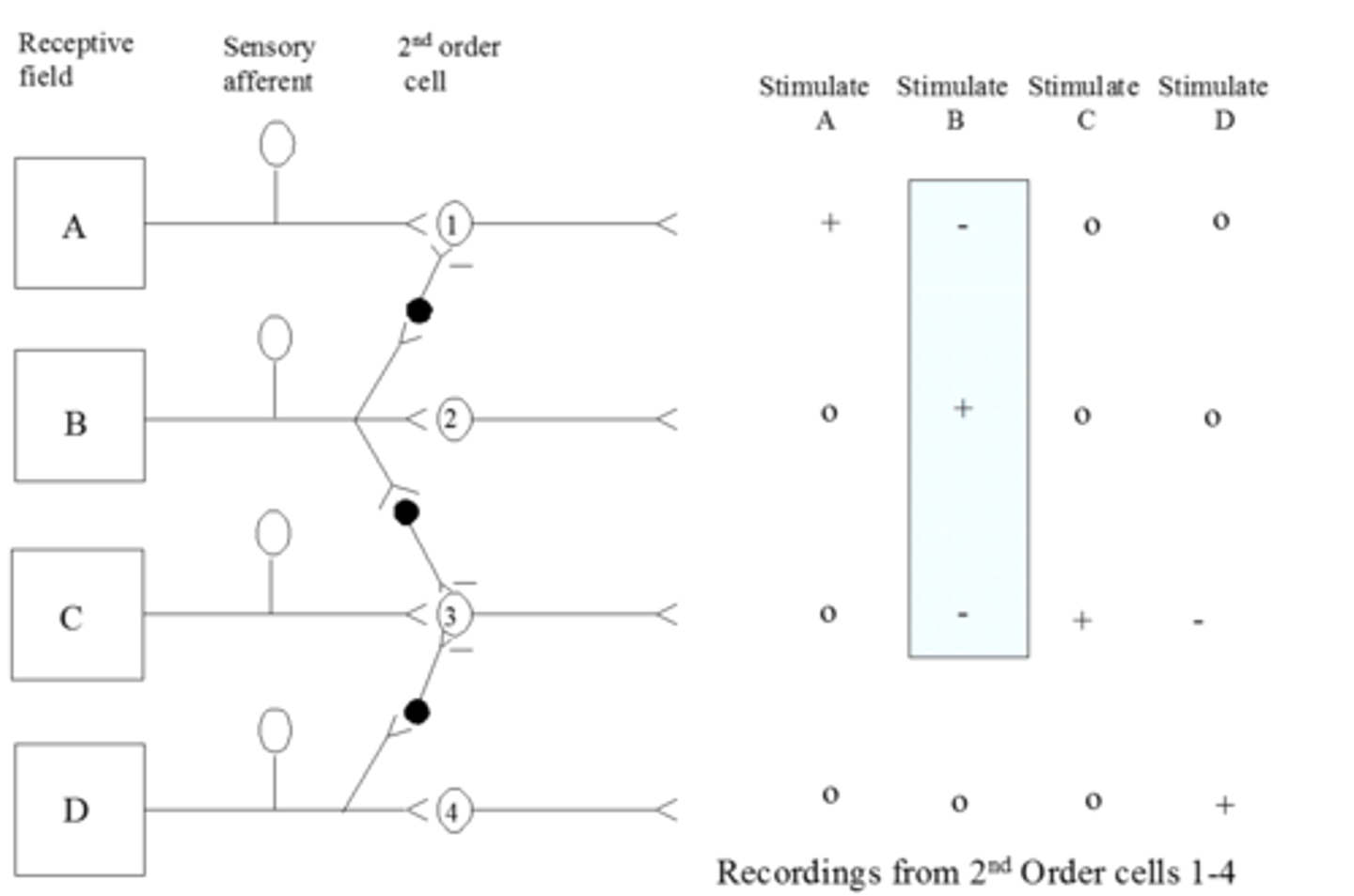
Surround (or lateral) ____ sharpens _____
Surround (or lateral) inhibition sharpens boundaries
Spatial resolution is the minimum separation needed for two stimuli to be _____ from a more intense ____ ____ - this is enhanced by ____ ____
Spatial resolution is the minimum separation needed for two stimuli to be distinguished from a more intense single stimulus - this is enhanced by lateral inhibition
Lateral inhibition is where a neuron may be excited to fire an action potential by stimulation of its _____ ___ but inhibited from activity by stimulation of the region surrounding its ___ ____
Lateral inhibition is where a neuron may be excited to fire an action potential by stimulation of its receptive field but inhibited from activity by stimulation of the region surrounding its receptive field
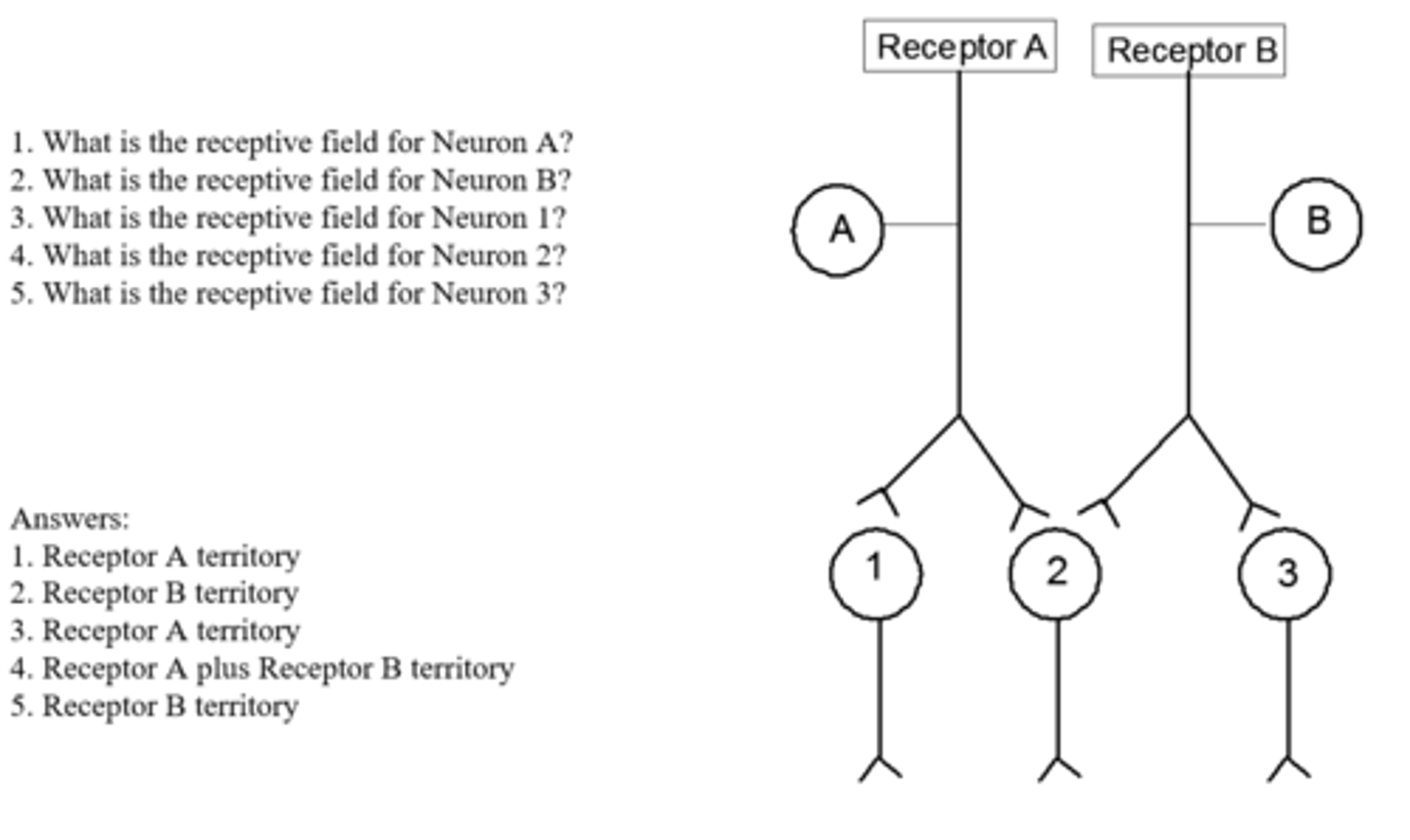
The starting point for the representation of a body form in neural space is the area of skin innervated by a ____ ____ ___ ie the ____ ____ of the ____ ___ - a ___ map is a composite of ____ ___
The starting point for the representation of a body form in neural space is the area of skin innervated by a single peripheral receptor ie the receptive field of the afferent fiber - a neural map is a composite of receptive fields
A dermatome is a composite of all ____ ____ of all the ____ ___ ___ cells that enter the ___ ___ at one ____ ____
A dermatome is a composite of all receptive fields of all the dorsal root ganglion cells that enter the spinal cord at one segmental level
the dermatomal map is converted to a ____ ___ by ____ ___ in the ___ ___ and _____ pathway
The dermatomal map is converted to a somatotopic map by fiber re-sorting in the dorsal columns and anterolateral pathway
The size of a cells receptive field is generally larger for cells ____ along the ____ ____
The size of a cells receptive field is generally larger for cells further along the synaptic relays
There is distortions in the ___ ___ due to the requirement of ____ _____ structures to be ____ ___ (like the ____ and ___)
There is distortions in the neural map due to the requirement of fine tactile structures to be densely innervated (like the digits and lips)
When dorsal root afferent fibers enter the spinal cord, different types of ____ each terminate in a ___ ___ in the ____ ____
That is to say, different ____ ___ _____ terminate in ____ ____
When dorsal root afferent fibers enter the spinal cord, different types of afferents each terminate in a specific form in the specific laminae
That is to say, different afferent fiber classes terminate in specific ways