Lecture 15: Initial cash flows, operating cash flows, ending cash flows, taxes & depreciation (CCA), NPV
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is the capital expenditure decision?
They determine future direction of company & are critical:
often involve significant outlay of money & time
take many years to demonstrate returns
are irrevocable
due to size & long-term nature, can alter risk of entire firm
What is the capital budgeting process?
Where a firm makes capital expenditure decisions
search for & identify growth opportunities (+ NPV projects)
estimate cost of potential projects (verify if it is a + NPV by estimating cost)
estimate the magnitude & timing of cash flows
estimate WACC
compute project’s NPV (using the WACC/discount rate)
accept/reject project
What is an incremental cash flow?
(a - b) → difference = incremental cash flows
a) What will this cash flow be with the project?
b) What will this cash flow be without the project?
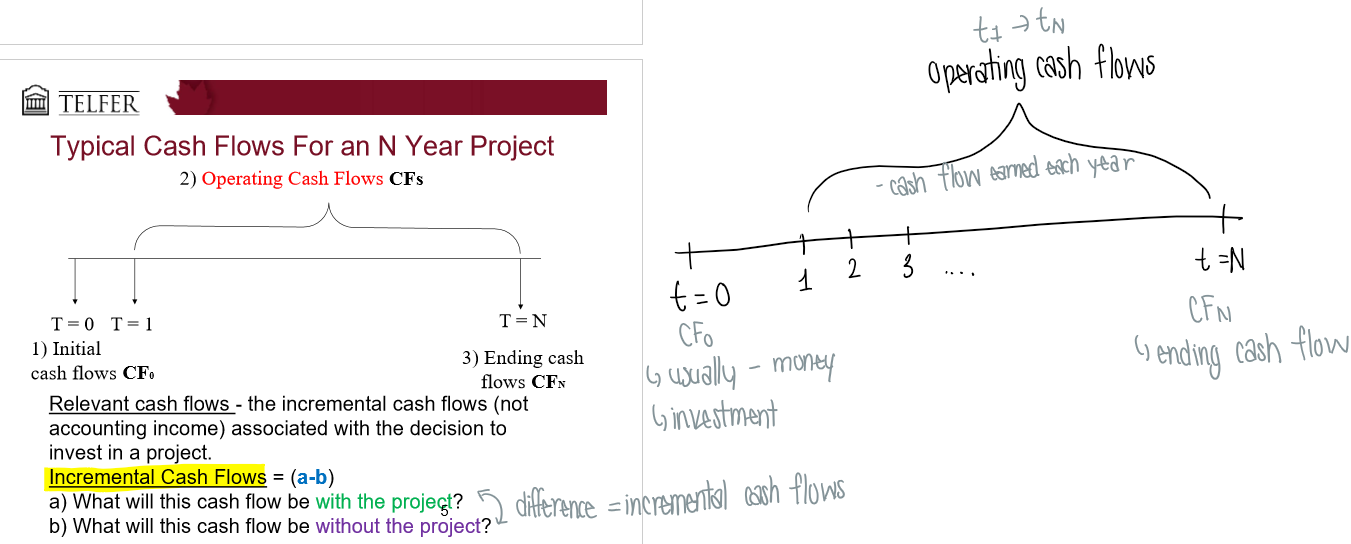
What is 1. initial investment (initial cash flows at T=0/CF0)
Cost of equipment → price paid for machinery (cash flow at beginning - costs, negative money, opportunity cost)
Related costs → shipping, set-up, installation
Opportunity costs → cash flow forgone as result of investment
Changes in net working capital
→ NWC = current assets - current liabilities
- firms need to keep certain amount of cash
usually remake your initial investment (NWC) at the end
*do not include sunk costs! (unrecoverable, spent costs) → not incremental
How do you 2. estimate operating cash flows?
Equivalent definitions of operating cash flows:
Bottom-up approach
OCF = Net operating profit after taxes + depreciation (add back depreciation bc it is non-cash flow expense)
Top-down approach
OCF = sales revenue - costs - taxes
Tax shield approach
OCF = (Sales revenue - costs) x (1 - T) + (depreciation x T)
→ must account for depreciation taxes
What are other considerations in estimating cash flows: Side effects (erosion vs. synergy)?
Side effects matter → negative/positive
→ included in calculation because they are incremental cash flows
Erosion/cannibalism (negative) - Apple introduces iPad which decrease MacBook sales
Synergies (positive) - Apple introduces iPhone which increases iTune sales
What are other considerations in estimating cash flows: allocated costs?
Be cautious about allocating costs to projects → incremental or not?
Should be accounted for in cash flows if:
creates additional incremental cost
Should not be accounted for in cash flows if:
allocations of overhead costs should not affect project’s incremental cash flows unless project actually increases overhead expenses
What are other considerations in estimating cash flows: interest expense?
Interest payments for loans can be large
Free-cash flow → don’t need to incorporate interest expenses because they are already included in the WACC
interest expenses (cash flows to debtholders) should not be subtracted!
What are other considerations in estimating cash flows: adjusting for inflation?
Rule is to be consistent
if it is a nominal cash flow, adjust with nominal rate
if it is a real cash flow, use the real interest rate
Use fisher’s equation

What is the capital cost allowance?
Depreciation is not a cash flow item, but indirectly impacts cash flows by lower taxes
Canada uses the capital cost allowance (CCA) → allows asset classes with different depreciation rates
Undepreciated capital cost (UCC) → balance of asset that still needs to be depreciated
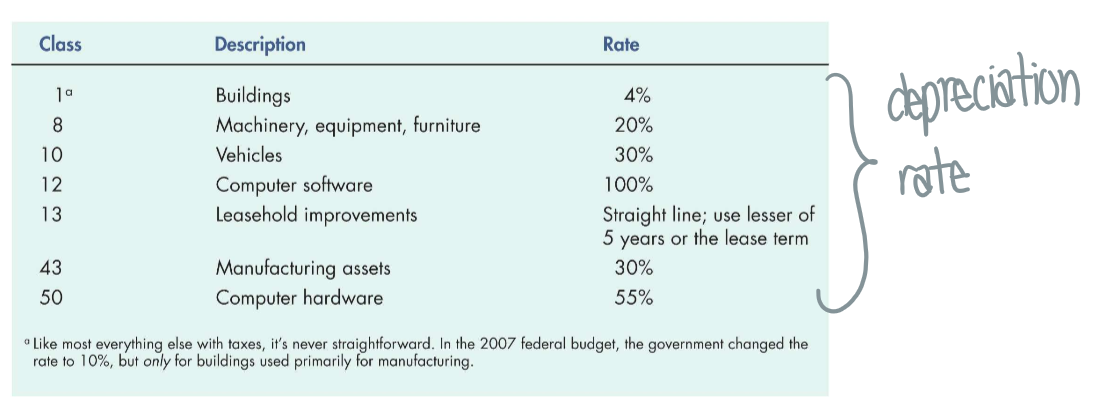
What is the 50% rule?
in 1st year, depreciate based on only 50% of the asset’s value (this is because asset is not always bought in the beginning of the period)
in 2nd year, can depreciate 100% (rest of asset value)
Undepreciated capital cost (UCC) → balance of asset that still needs to be depreciated
* straight line depreciation depreciates value of asset by the same amount each year

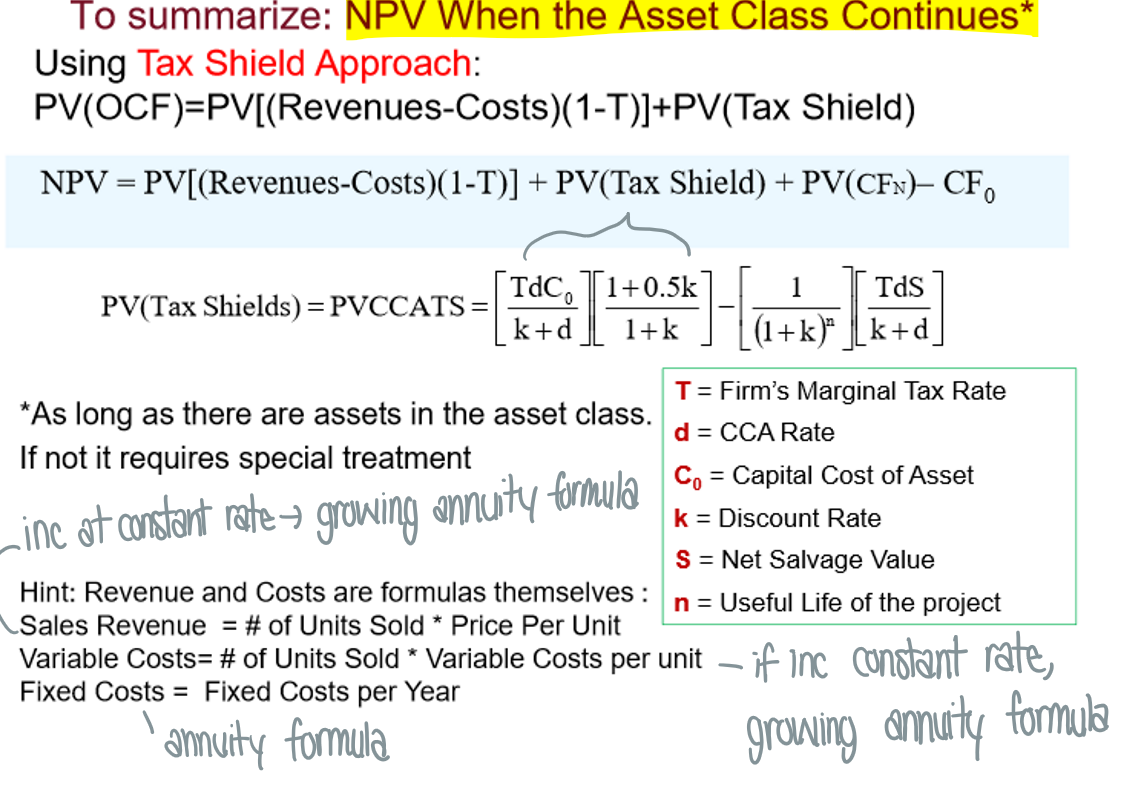
How do you calculate the present value of a capital cost allowance tax shield?
Tax shields from CCA continue in perpetuity as long as there are assets in the asset class
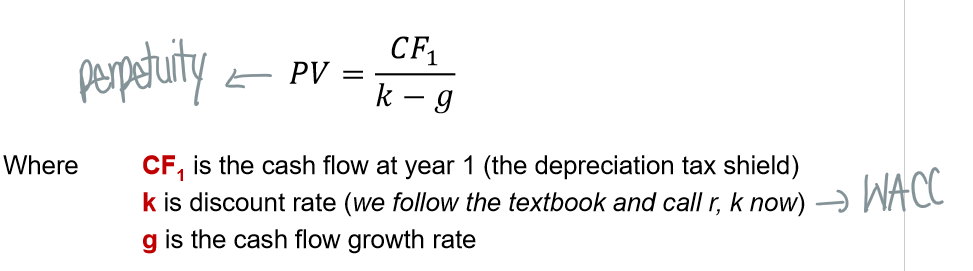
What happens to the tax shield over time?
Depreciates/decreasing at a constant rate
perpetuity if it continues forever/long time

What is the tax shield formula?
The present value of a perpetuity decreasing at a rate of d (CCA rate)

What happens to the tax shield if you sell the asset?
There is a loss of tax shield due to the asset sale
need to remove depreciation tax shield that you lose from selling the asset
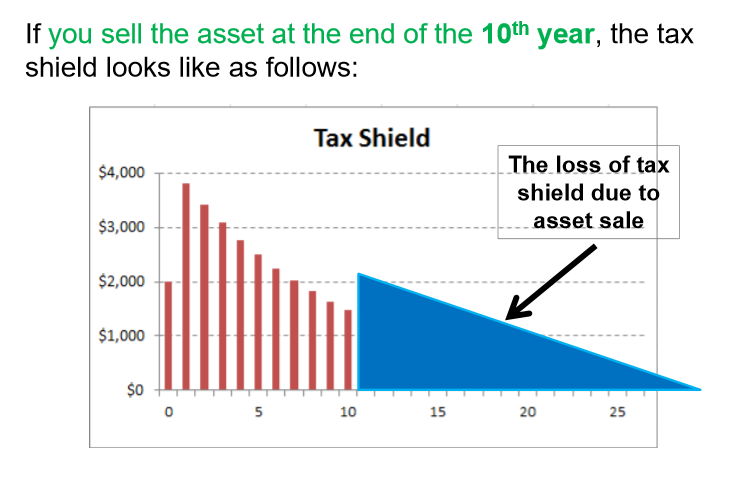
What is the formula for if you sell the asset (formula that removes depreciation tax shield from selling asset)?
What do 3. ending cash flows include?
Salvage value when you sell the asset (the money you make from selling the asset)
Open asset class: don’t need to consider tax consequences
closed asset class: if depreciated too much/too little
Compute UCC balance every year to check!
→ if UCC > salvage value (sold equipment at loss) → tax savings
→ UCC < salvage value (sold at gain) → tax losses