effects of the boundary - water
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
how do flowing fluids exhibit viscous effects?
- stick to solid surfaces
- have stresses within their body
what is shear stress in a fluid proportional to
the velocity gradient, ie the rate of change of velocity across the flow
what is μ for a newtonian fluid?
the coefficient of dynamic viscosity
describe the features of laminar flow
- motion of fluid particles is very orderly
- move in straight lines
- parallel to pipe wall
describe the features of turbulent flow
- motion is locally completely random
- over all direction in one way
what is reynold's number?
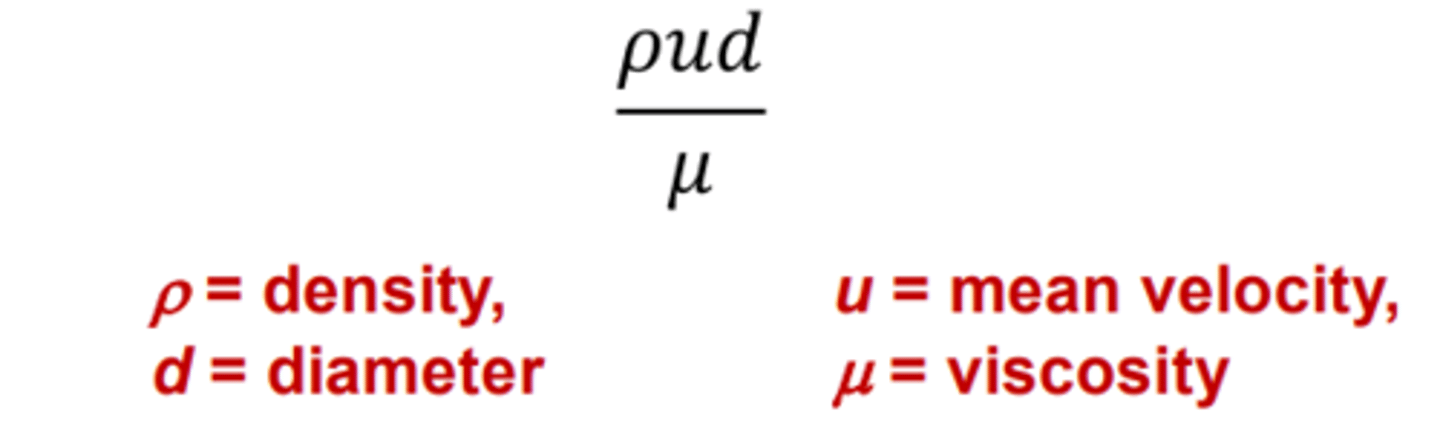
what can reynold's number predict?
change from laminar to turbulent flow for any fluid
what are the reynold's numbers for laminar flow?
Re < 2000
what are the reynold's numbers for transitional flow?
2000
what are the reynold's numbers for turbulent flow?
Re>4000
what are the SI units for reynold's number?
it is a non-dimensional number
what would limiting velocities be in a typical central heating system pipe (diameter 0.015m)?
0.0733 and 0.147 m/s (very slow)
where does laminar flow rarely occur?
in piped water systems
where does laminar flow more commonly occur?
in fluids of greater viscosity (eg in bearing with oil)
what does the Reynold's number mean?
Re = inertial forces / viscous forces
where do inertial forces dominate?
in faster flow
larger Re = turbulent flow
where do viscous forces dominate?
in slower flow
smaller Re = laminar flow
summarise the key features of laminar flow?
- Re<2000
- low velocity
- dye does not mix with water
- fluid particles move in straight lines
- simple analysis possible
- rare in practice in water systems
summarise the key features of transitional flow?
- 2000< Re < 4000
- medium velocity
- dye stream wavers - mixes slightly
summarise the key features of turbulent flow?
- Re>4000
- high velocity
- dye mixes rapidly and completely
- particle paths completely irregular
- average motion is in flow direction
- cannot be seen by naked eye
- must measure using laser
- analysis difficult
what is the most common type of flow?
turbulent flow
how do the effects of friction present in fluids?
as a pressure loss
what does shear stress do in a real flowing fluid?
slows the flow
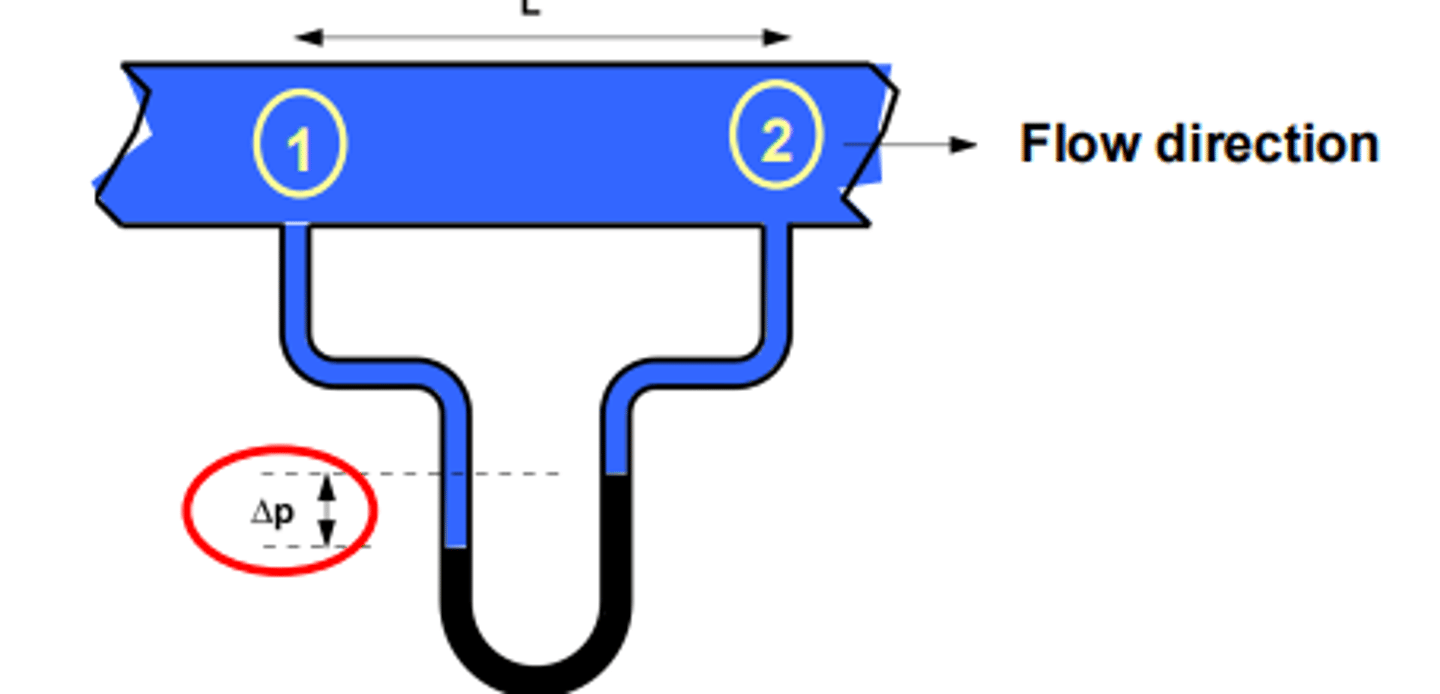
how can we view pressure loss?
attach a manometer
pressure at 1 is greater than pressure at 2
difference is Δp
how can we find driving force due to pressure?
driving force = upstream force - downstream force
= pA - (p-Δp)A=ΔpA
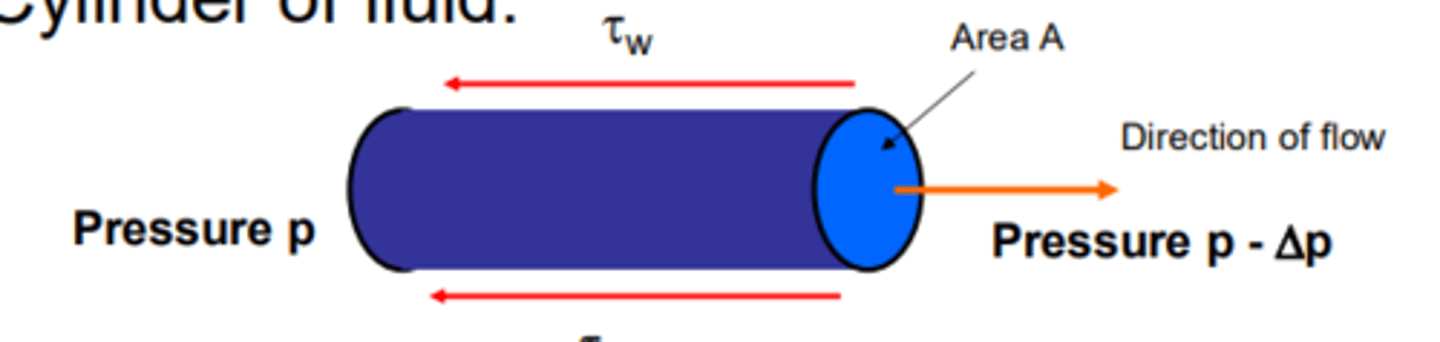
how can we find retarding force due to shear stress at wall?
retarding force = shear stress x area acts
= τw x area of pipe wall
what does driving force equal?
retarding force
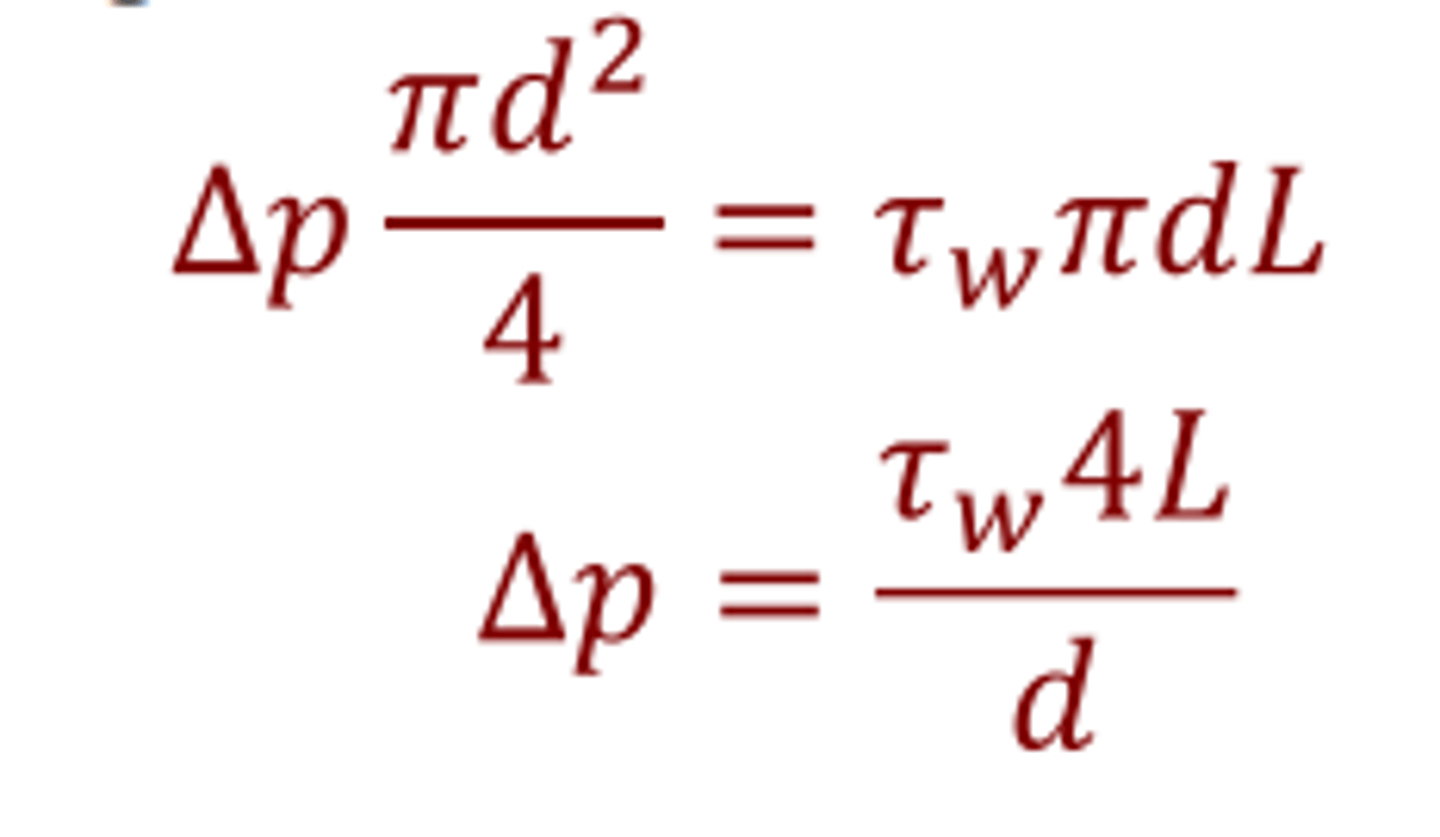
what is pressure loss proportional to?
velocity and laminar flow
pressure loss is proportional to velocity and laminar flow, what does this confirm?
- fluid does not slip past a boundary
- newton's law of viscosity
what is the Hagen-Poiseuille equation?
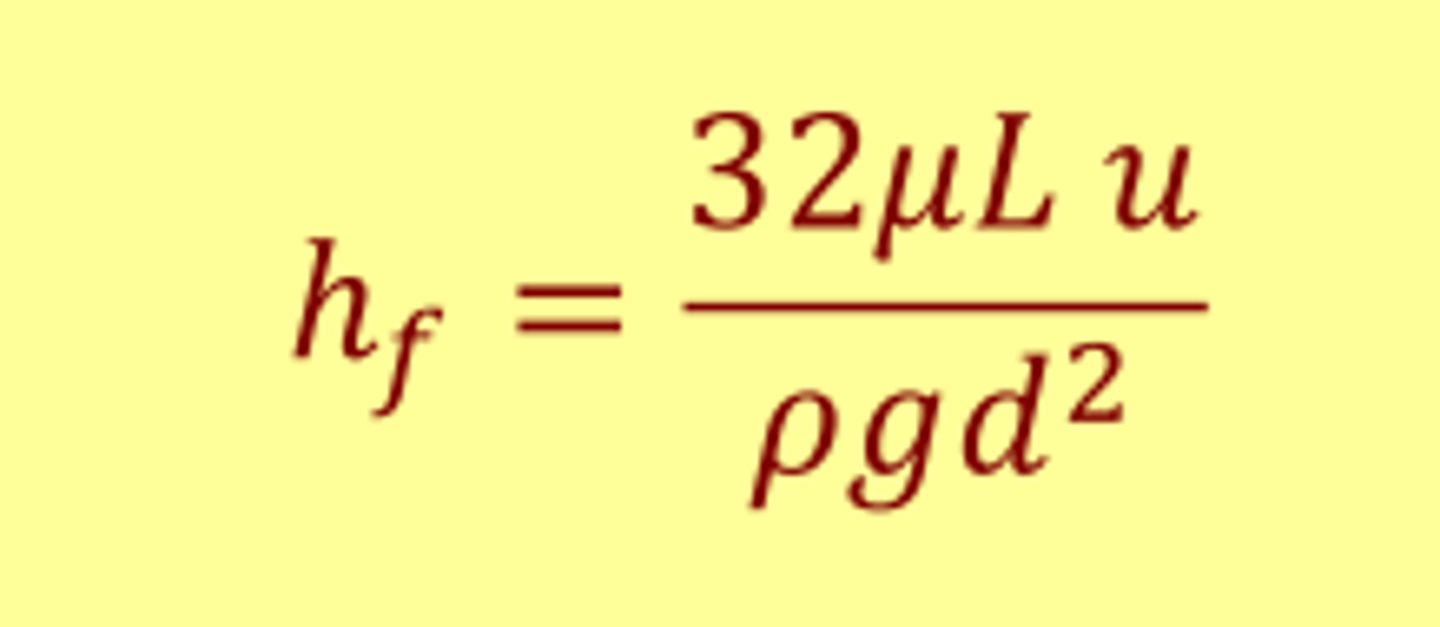
fluid flowing over a stationary surface is brought to rest by what?
shear stress τo
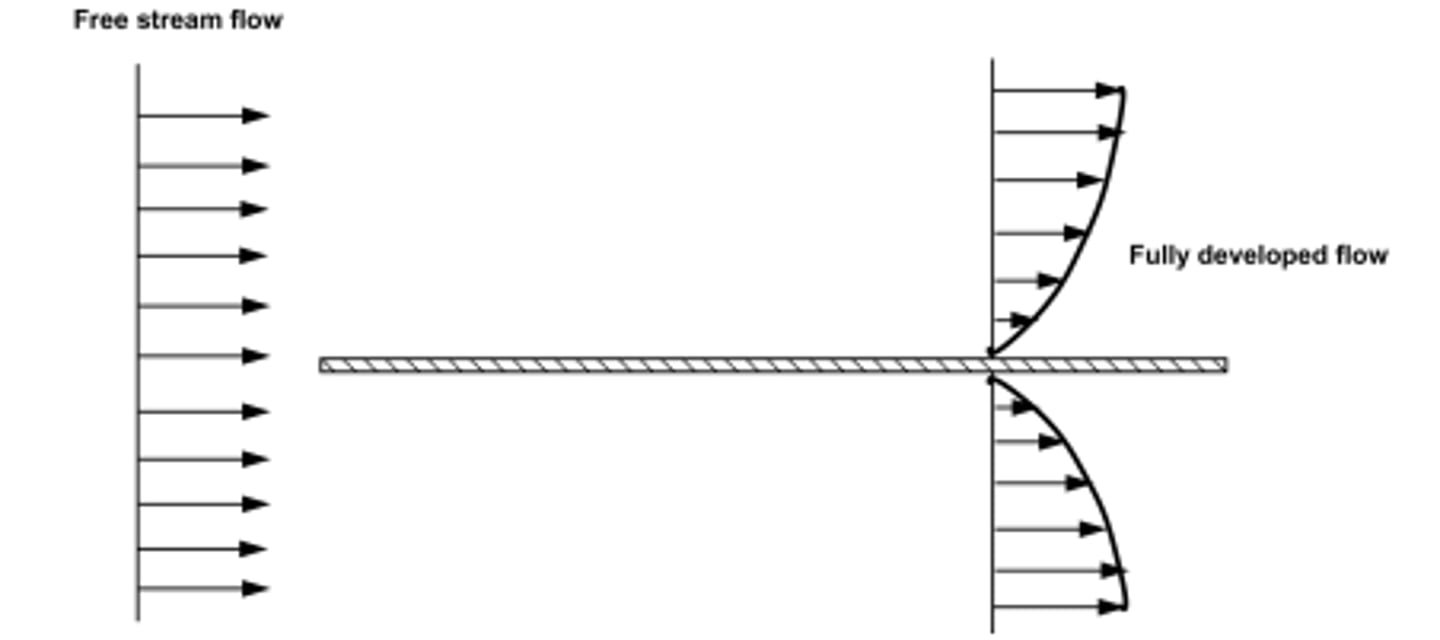
describe typical flow over a flat plate
upstream, before plates have free stream and constant velocity
downstream after flowing along the plate, the velocity profile that exists does not change - fully developed