Business exam
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Stakeholders
stakeholders are parties who have a stake in a company’s success or failure. They can influence or be influenced by the company’s decisions and actions.
Business Strategy
A business strategy is a long-term plan for how a company will create value for itself and its stakeholders by achieving its goals and gaining a competitive edge.
Revenue
Revenue is the amount of money a company receives from selling its goods or services to its customers. It is also called sales or the top line
Gross Profit
Gross profit is the amount of money a company earns from selling its products or services, after deducting the direct costs associated with producing them. Gross profit shows how efficiently a company uses its resources and materials. Gross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from the total revenue.
Net Profit
Net profit is the amount of money a company has left after paying all its expenses, including taxes, interest, and dividends. Net profit shows how profitable a company is after accounting for all its costs. Net profit is calculated by subtracting all expenses from the gross profit
Cash Flow
Positive cash flow is when a business receives more money than it spends in a given period. It means that the business can cover its expenses, save money, and invest in its growth. Positive cash flow indicates a healthy and profitable business.
Negative cash flow is when a business spends more money than it receives in a given period. It means that the business cannot pay its bills, debts, and obligations. Negative cash flow indicates a struggling and unprofitable business.
Competition / competitor
Competition in business is the rivalry among firms that offer similar products or services to the same customers. Competition aims to increase sales, revenue, and market share.
Competitive advantage
Competitive advantage is the edge a business has over its rivals in offering better value to customers. It can be based on cost, quality, differentiation, or specialization
Supply chain
A supply chain is a network of entities that produce, transport, and sell a product or service to customers. It includes raw materials, manufacturing, logistics, and distribution
Macro factors
Macro factors are the external factors that affect a business’s performance and decision-making. They include economic, political, social, technological, environmental, and legal forces
Micro factors
Micro factors are the internal factors that affect a business’s performance and decision-making. They include customers, suppliers, competitors, resellers, and the public
Brand recognition
Brand recognition is the ability of consumers to identify a brand by its features, such as logo or slogan, without seeing its name. It shows how familiar and memorable a brand is
Marketing
Marketing is the process of creating and delivering value to customers and stakeholders through various channels and methods. Marketing aims to increase sales, awareness, and loyalty for a business or a brand
Target audience
A target audience is a group of potential customers who share certain characteristics and needs that a business wants to reach with its marketing efforts
Market Share
Market share is the percentage of sales in an industry or product category that a company earns. It shows how well a company competes with other companies in the same market
Needs vs wants
Needs and wants in business terms are the desires and demands of customers and consumers for products or services that a business offers. Needs are the essential requirements for survival, such as food, water, shelter, and clothing. Wants are the preferences or wishes for things that are not necessary for survival, such as phone, computer, television, and car. A business aims to fulfill both the needs and wants of its target audience by creating and delivering value
Customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is how well a company meets or exceeds its customers’ expectations for its products or services1. It shows how happy and loyal customers are with a company.
Value proposition
A value proposition is a statement that summarizes why a customer should buy a product or service from a company. It highlights the benefits, value, and uniqueness of the offer
Price leader
A price leader is a company that can set the market price for a product or service, and influence other companies to follow it1. It usually has a large market share, low costs, or high demand
example of price leader
An example of a price leader in the tech industry is Apple, which has a dominant market share in the smartphone industry and can charge high prices for its iPhones. Other companies, such as Samsung and Google, have to match or lower their prices to compete with Apple.
8 roles of business
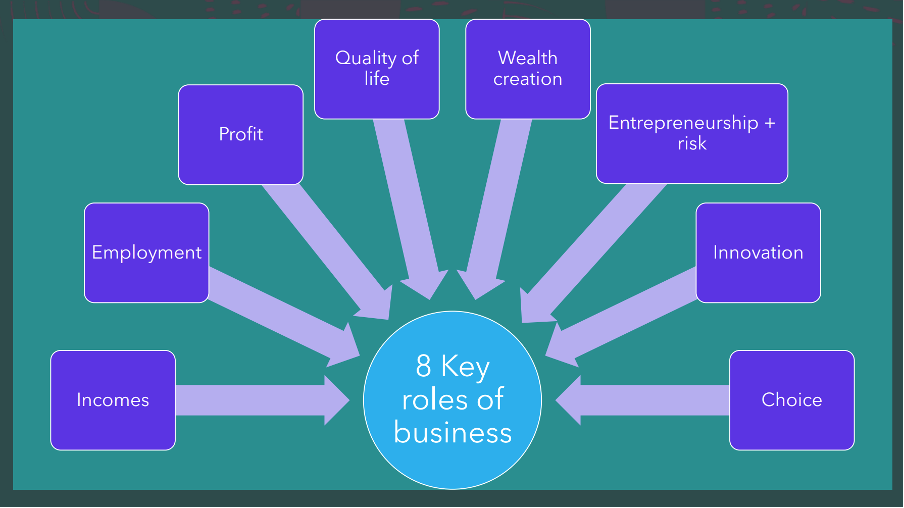
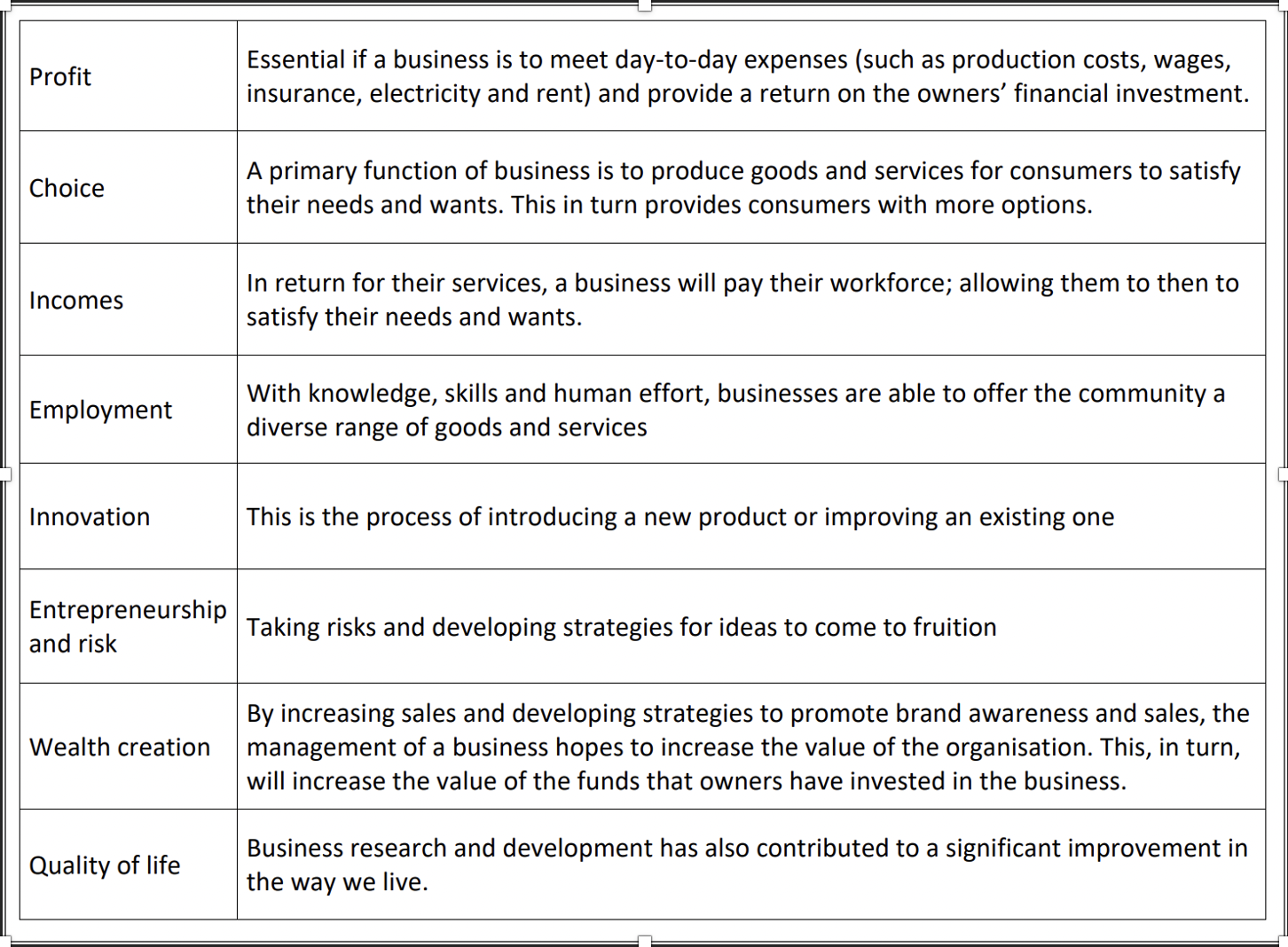
8 roles of business explanation
4 main functions of a business
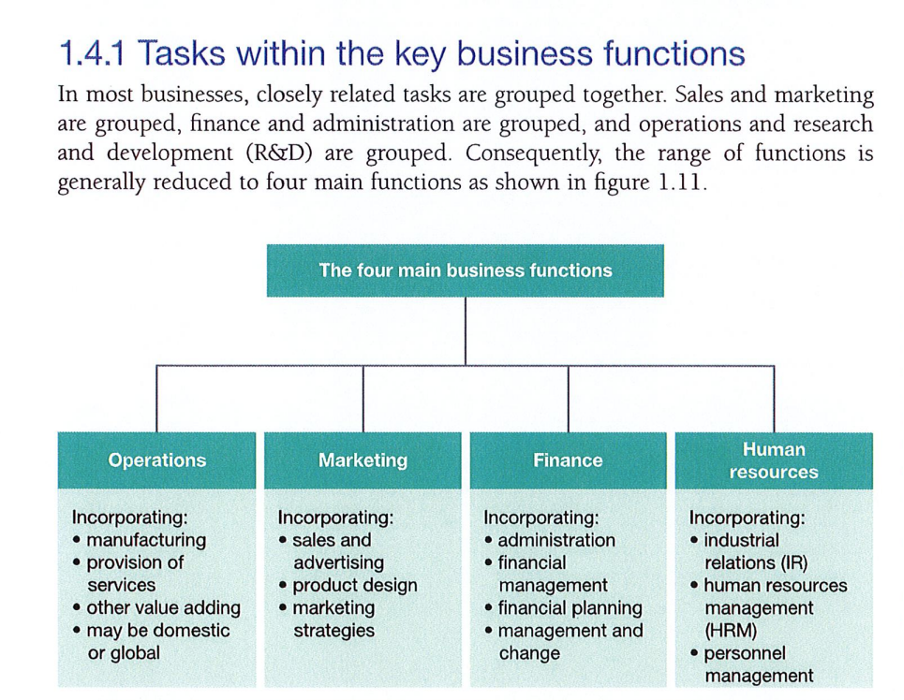
operations

marketing

finance

Human resources

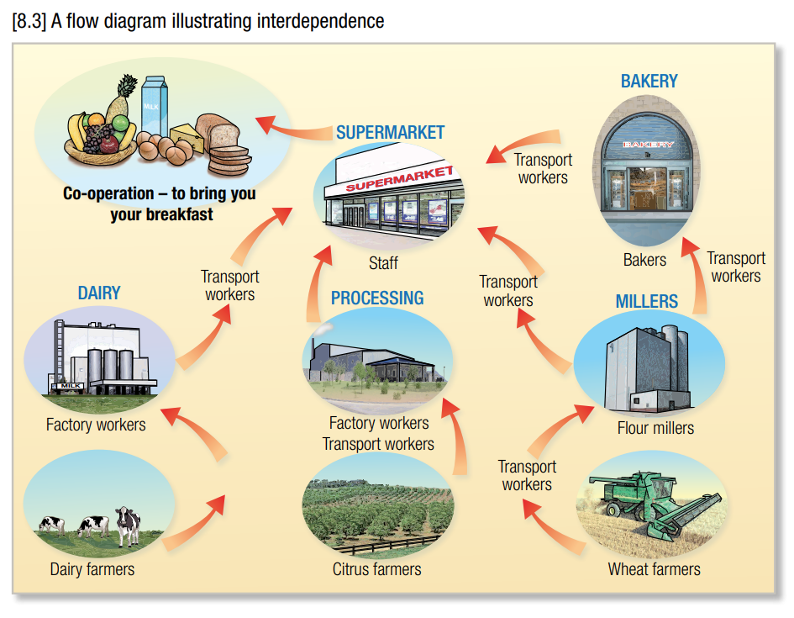
interdependance

interdependance diagram
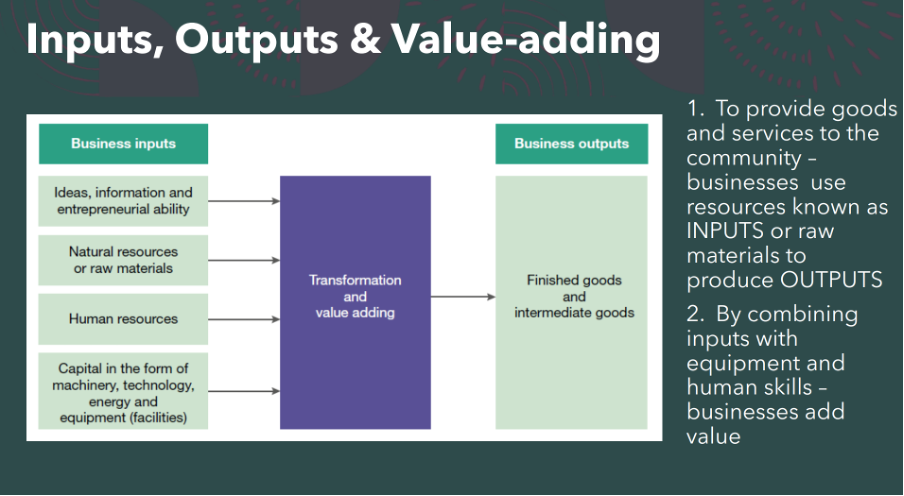
inputs outputs and value adding
- An example of inputs, outputs, and value-adding in business is a bakery that makes and sells bread. The inputs are the raw materials (such as flour, yeast, water, etc.), the labor (such as the baker, the cashier, etc.), and the services (such as electricity, rent, etc.) that the bakery needs to produce bread. The output is the bread that the bakery sells to customers. The value-adding is the difference between the revenue from selling the bread and the cost of the inputs. The bakery adds value by transforming the inputs into a product that customers want and are willing to pay for. The bakery can increase its value-adding by either increasing the price of the bread or reducing the cost of the inputs.
Circular Economy
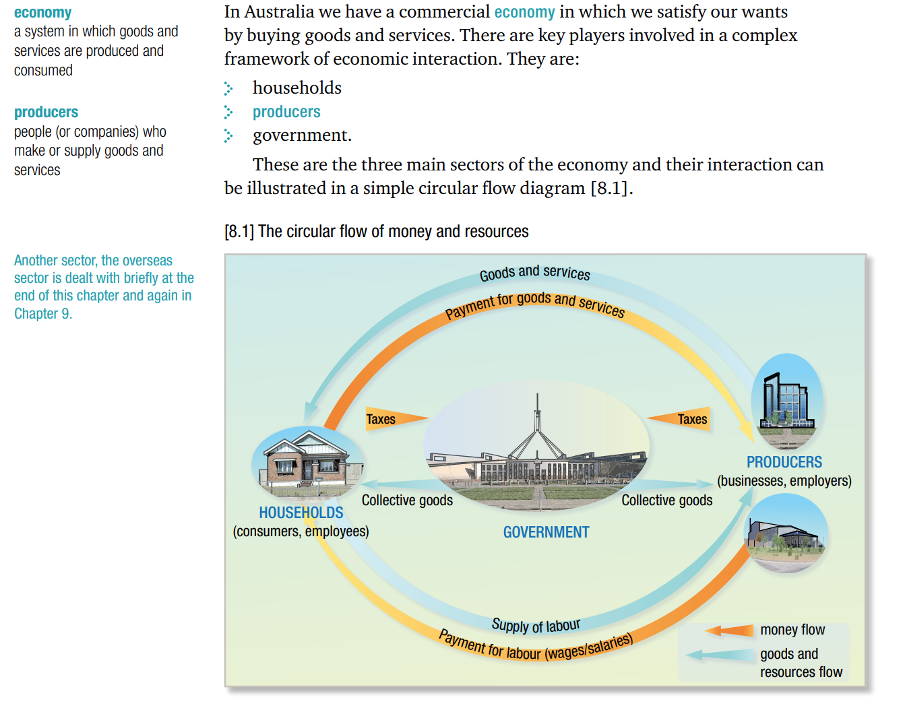
households

producers and the government

Employees

employers

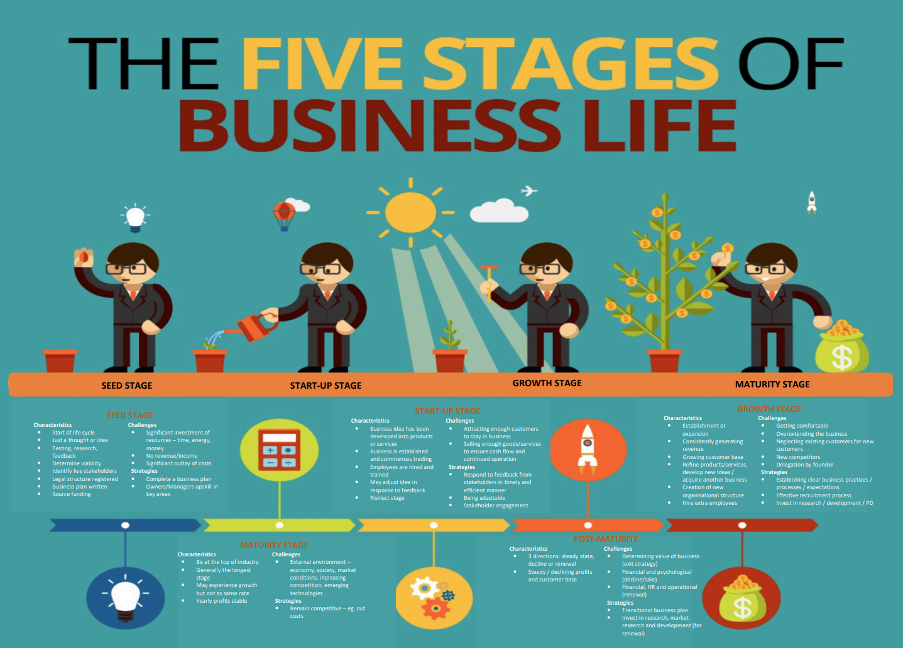
the five stages of business