Ethnocentrism and Statistical Analysis in Research
1/488
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
489 Terms
Ethnocentrism
Belief in the superiority of one's culture.
Multiculturalism
Policy promoting equal cultural traditions.
Quantitative Approach
Focus on numerical data and statistical analysis.
Qualitative Approach
Focus on understanding subjective experiences.

Nomothetic Research
Study of general laws applicable to groups.
Hypothetico-Deductive Process
Testing hypotheses through empirical observation.
Proposition
Statement predicting relationships between variables.
Survey Method
Data collection through questionnaires or interviews.
Operationalization
Transforming concepts into measurable variables.
Instrumentalization
Creating tools for measuring variables.
Empirical Deduction
Process of deriving conclusions from observations.
Class
Social stratification based on economic status.
Gender
Social roles associated with being male or female.
Education
Formal instruction and learning experiences.
Ethnocentric Attitude
Prejudice against other cultures based on one's own.
Hypothesis
Expected relationship between variables in research.
Instrument 1
Survey questionnaire for data collection.
Scale (0-10)
Measurement scale for assessing ethnocentrism levels.
Literate
Ability to read and write.
Illiterate
Inability to read and write.
Annual Family Income
Total income of a family in a year.
Years of Schooling
Total years spent in formal education.
Measurement
Applying an instrument to quantify attributes.
Instrumentalization
Process of defining and measuring variables.
Codebook
Document detailing the coding plan for data.
Data
Results from observations across multiple cases.
Dataset/Database
Matrix of variables and cases with numerical data.
Statistics
Numbers used to analyze and summarize data.
Descriptive Statistics
Summarizes data without generalizing beyond the sample.
Inferential Statistics
Makes generalizations from a sample to a population.
Parametric Statistics
Assumes specific population parameters for analysis.
Non-parametric Statistics
Does not assume population parameters for analysis.
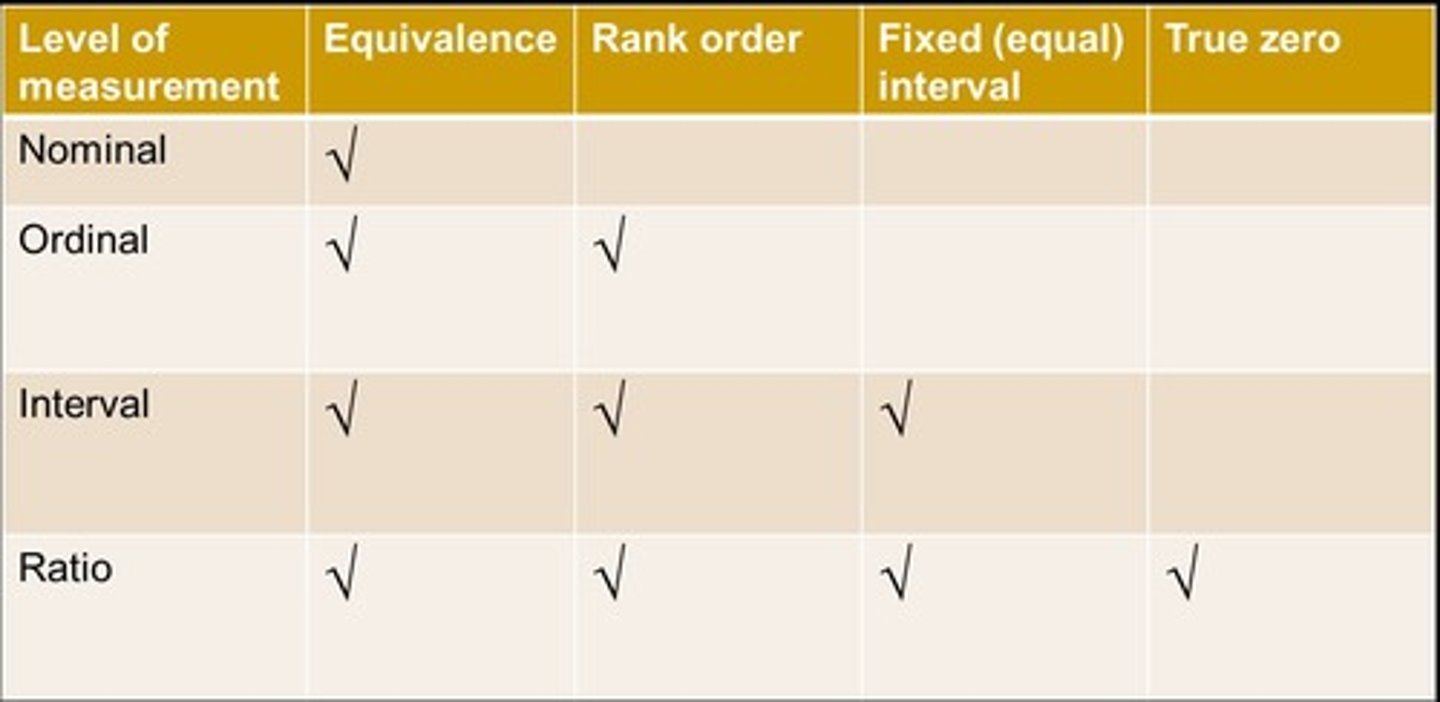
Levels of Measurement
Hierarchical classification of data measurement types.
Nominal Variables
Qualitative categories without numerical value or order.
Ordinal Variables
Ranked qualitative categories without precise measurement.
Interval Variables
Quantitative data with defined intervals but no absolute zero.
Ratio Variables
Quantitative data with defined intervals and absolute zero.
Aggregation
Combining multiple observations into a single dataset.
Quantitative Research
Research focused on numerical data and statistical analysis.
Variables
Attributes or characteristics measured in research.
Observations
Data collected from respondents or cases.
Statistical Techniques
Methods used for analyzing and interpreting data.
Frequency Distribution
Summary of how often each value occurs.
Data Matrix
Organized structure of variables and cases.
Summary Statements
Concise descriptions derived from large data sets.
IQ Test Score
Not a ratio; cannot perform multiplication.
Interval Measurement
Allows mathematical operations without true zero.
Ratio Level of Measurement
Includes true zero; allows all arithmetic operations.
Nominal Variables
Categorical; no order or interval; discrete categories.
Ordinal Variables
Categorical; ordered but no fixed interval.
Interval Variables
Ordered; fixed intervals; no true zero.
Continuous Variables
Can take any value within a range.
Categorical Variables
Classify observations by qualities or characteristics.
Discrete Variables
Distinct values; cannot be divided further.
Descriptive Research
Focuses on summarizing data characteristics.
Inferential Research
Draws conclusions from sample data.
Key Question 1
Descriptive or inferential issue in research?
Key Question 2
How many variables are analyzed simultaneously?
Key Question 3
What is the measurement level of variables?
Equivalence in Measurement Levels
All levels confirm equivalence of observations.
Ordered in Measurement Levels
Ordinal, interval, and ratio levels show order.
Fixed Interval
Only interval and ratio levels have fixed intervals.
Real Zero
Only ratio level of measurement has real zero.
Qualitative Variables
Another term for categorical variables.
Quantitative Variables
Another term for continuous variables.
Arithmetic Operations
Applicable to interval and ratio levels only.
Nominal
Categorical variables with no inherent order.
Ordinal
Variables that can be ranked in order.
Interval/Ratio
Variables with meaningful intervals and ratios.
Descriptive Statistics
Summarizes data without generalizing beyond sample.
Inferential Statistics
Makes generalizations about a population from a sample.
Single Nominal Variable
Analyzed descriptively or inferentially in various situations.
Single Ordinal Variable
Analyzed descriptively or inferentially in various situations.
Single Interval/Ratio Variable
Analyzed descriptively or inferentially in various situations.
Two Nominal Variables
Analyzed descriptively or inferentially simultaneously.
One Nominal and One Ordinal Variable
Analyzed descriptively or inferentially.
One Nominal/Ordinal and One Interval/Ratio Variable
Analyzed descriptively or inferentially.
Two Interval/Ratio Variables
Analyzed descriptively or inferentially.
Three or More Nominal Variables
Analyzed descriptively or inferentially.
Nominal and Two Ordinal Variables
Analyzed descriptively or inferentially.
Nominal/Ordinal and Two Interval/Ratio Variables
Analyzed descriptively or inferentially.
Statistics
Mathematical language for analyzing and summarizing data.
Data Presentation
Organizing data using charts, tables, and graphs.
Hypothesis Testing
Method to determine statistical significance in inferential statistics.
Exhaustiveness
All possible categories are represented in nominal measures.
Mutual Exclusiveness
Categories in nominal measures cannot overlap.
Rank-ordering
Establishing a sequence in ordinal measures.
Ordinal measures
Rank-order attributes beyond nominal qualities.
Education
Highest level of formal education completed.
Income
Individual income from all sources in last 12 months.
Interval measures
Rank-ordered with equal distances between attributes.
True zero
A meaningful zero point indicating absence.
Ratio measures
Includes nominal, ordinal, interval, and true zero.
Continuous variables
Can take any value between two points.
Discrete variables
Have distinct, separate values like 1, 2, 3.
Descriptive statistics
Summarizes data characteristics without inference.
Inferential statistics
Makes predictions or inferences about a population.
One variable analysis
Analyzing a single variable at a time.
Two variables analysis
Analyzing two variables simultaneously.
Three or more variables
Analyzing multiple variables at once.