5 - Major plant lineages and bryophytes
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
List the 7 main divisions of land plants
liverworts
mosses
hornworts
lycophyted
ferns
gymnosperms
angiosperms
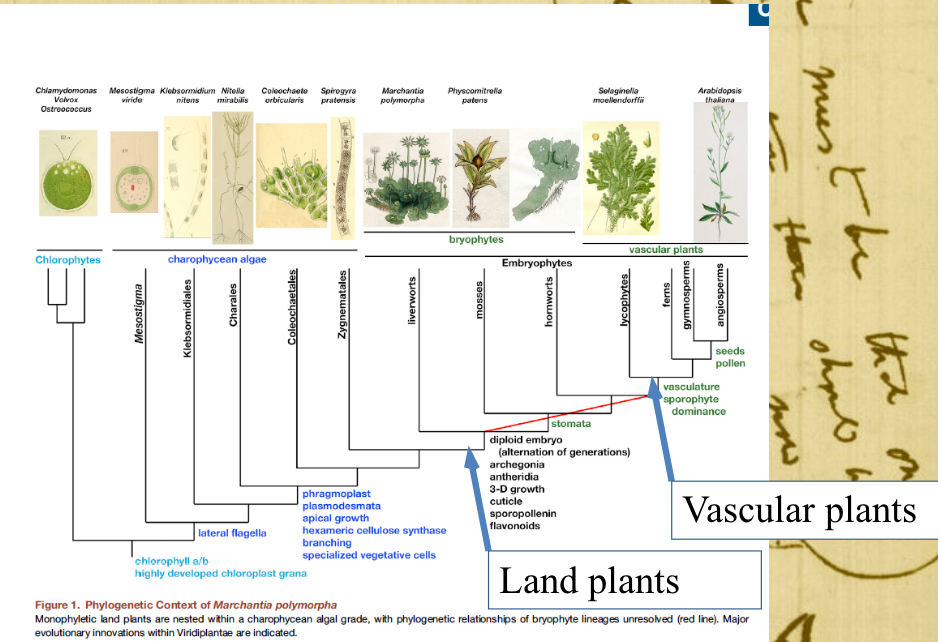
What did the earliest land plants descend from and where did they live?
streptophyte green algae that lived in shallow water margins
When did the earliest land plants descend?
the end of the Silurian
State one major selection event of land plants
periodic drying selected for those best able to tolerate periods without water, eventually accumulating adaptations that allowed them to live permanently above water
List 5 features shared by all terrestrial plants
alteration of generations
waxy cuticle
stomata for gas exchange
chlorophyll a and b
cellulose cell walls
List 3 major bryophyte lineages
mosses
hornworts
liverworts
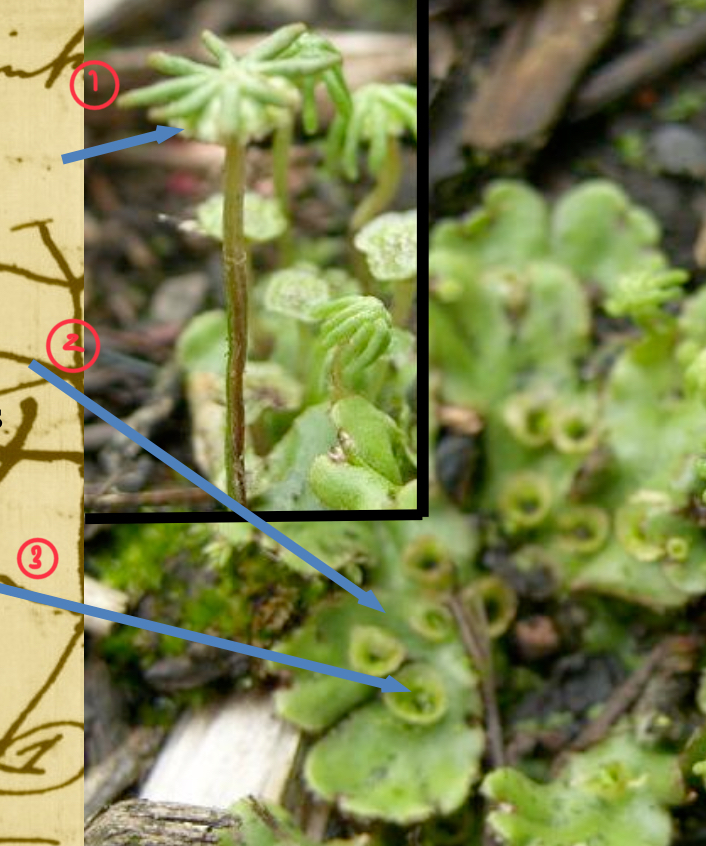

List these 3 structures of a liverwort and state whether they’re haploid or diploid
sporophyte (diploid)
gametophyte (haploid)
gemmae (haploid)
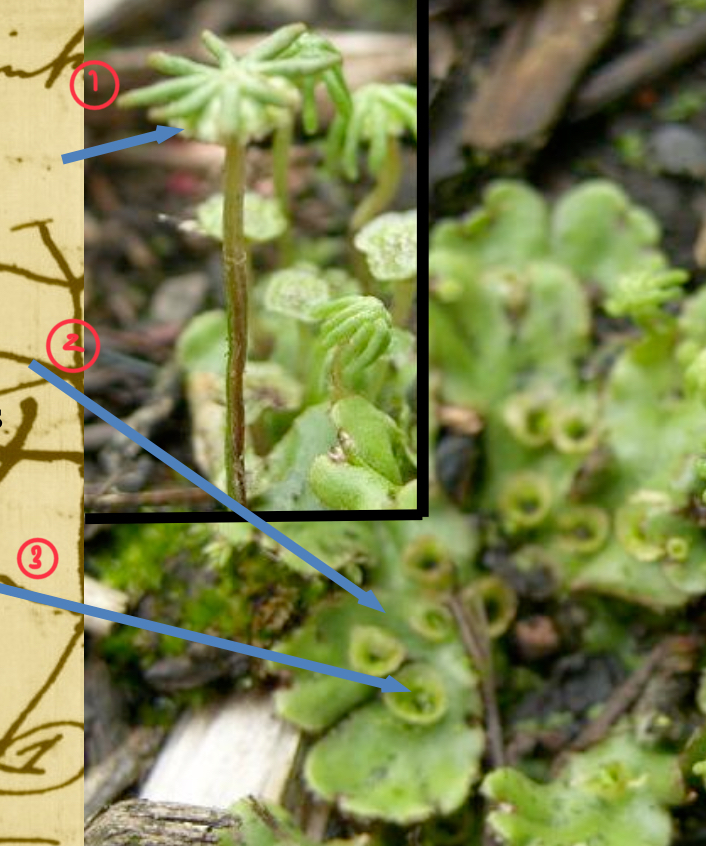

Discuss the diploid region of liverworts
the sporophyte undergoes meiosis to make haploid spores
Discuss the haploid region of liverworts (gametophytes) (2 points)
gametophyte produces gametangia which are motile sperm and non motile eggs
when mature and in wet conditions the sperm are released and swim to fertilise the eggs to form a zygote
Discuss the haploid region of liverworts (gemmae) (2 points)
undergoes vegetative (asexual) reproduction
during rainfall small liverworts get splashed out
List the correlating structures between mosses and liverworts
sporophyte is comprised of capsule and seta
gametophyte is comprised of the stem and leaves

State one difference between bryophytes and all other terrestrial plants
in bryophytes the gametophyte individual is the dominant part of the life cycle
Within bryophytes, what is the sporophyte dependent on?
the photosynthesising gametophyte
List 2 identifications of bryophytes
small, lacking lignin and support structures
mostly limited to moist environments
Describe tissue structure in byrophytes (3 points)
little tissue differentiation in stems
water can be absorbed directly through the underside of leaves/thallus as they lack waxy cuticle
rhizoids at the base of the stem which penetrate the substrate which has no role in absorbing water/minerals
Describe sporophyte structure in byrophytes (3 points)
developing zygote forms a “foot” which attaches to the gametophyte and absorbs sugars, minerals and water
the upper part grows by division and expands to form a capsule
cells inside the capsule undergo meiosis to produce haploid spores
How do sporangium behave in dry conditions?
unfurls to release spores
Why are bryophytes vulnerable to drying out?
they’re small and can’t readily store or transport water
List 4 environments that sphagnum moss can be found in
acidic tundra bogs
mountains
moorlands
peatlands
Why are peatlands ecologically important?
significant carbon stores, emitting sizeable quantities of methane
Why do peatlands act as carbon reservoirs?
the rate of plant production exceeds the rate of organic matter decomposition
What is poikilohydry within mosses and what are they adapted to?
mosses that are unable to maintain storage of water
adapted to drying and becoming inactive in dry conditions
What are poikilohydry mosses tolerant to during their dry phase (2 points)
extreme temperatures and UV light
What state do poikilohydry mosses undergo when dry and what does this allow them to do?
quiescent state
allows them to grow in inhospitable places like bare rock and deserts