Anti-Histamine Drugs
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
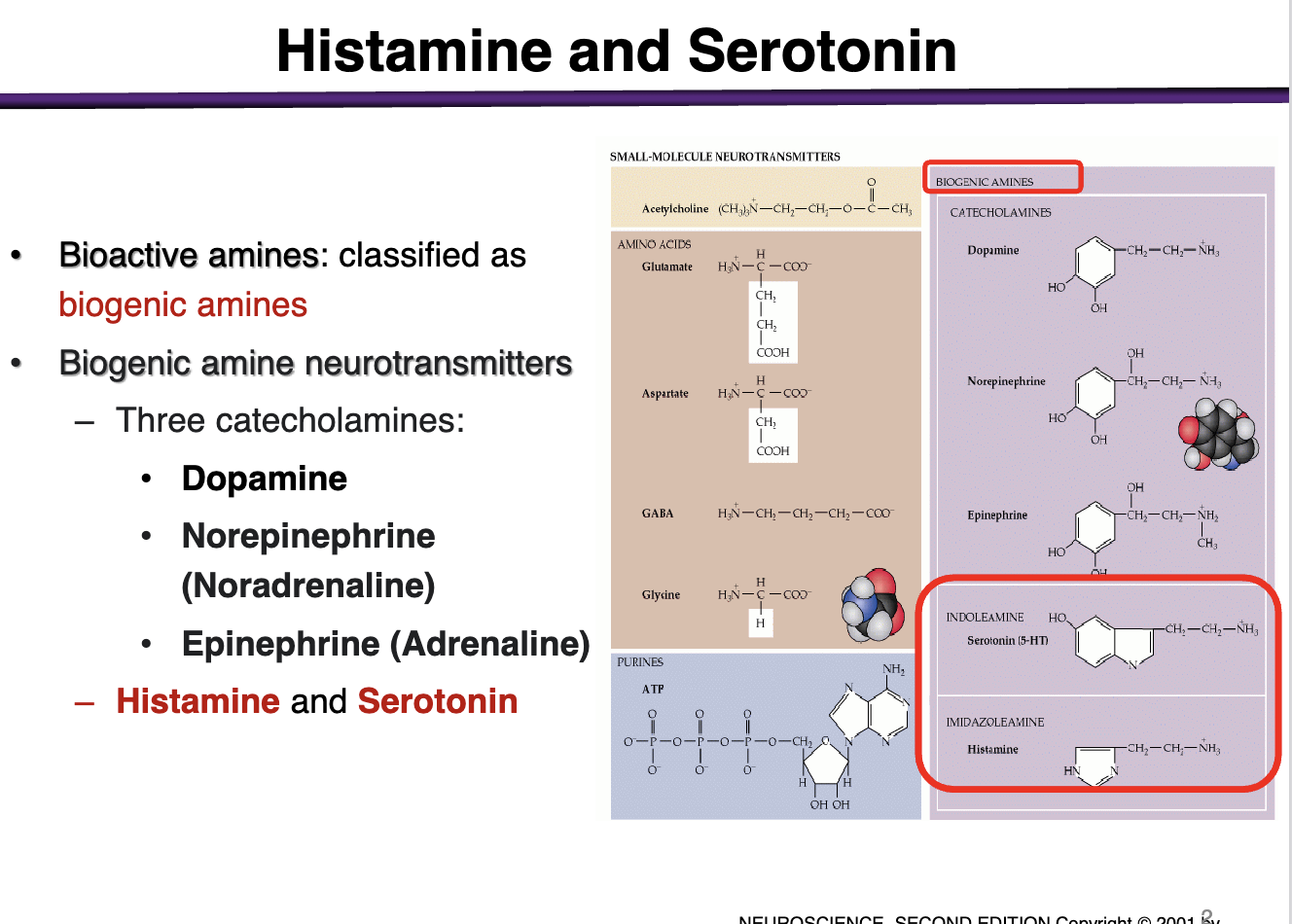
What are examples of biogenic amine NTs?
3 catecholamines:
Dopamine
Norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
Other biogenic amines include: histamine and serotonin
What is histamine?
Histamine is a biogenic amine that acts as a signaling molecule in the periphery but also as a NT in the CNS
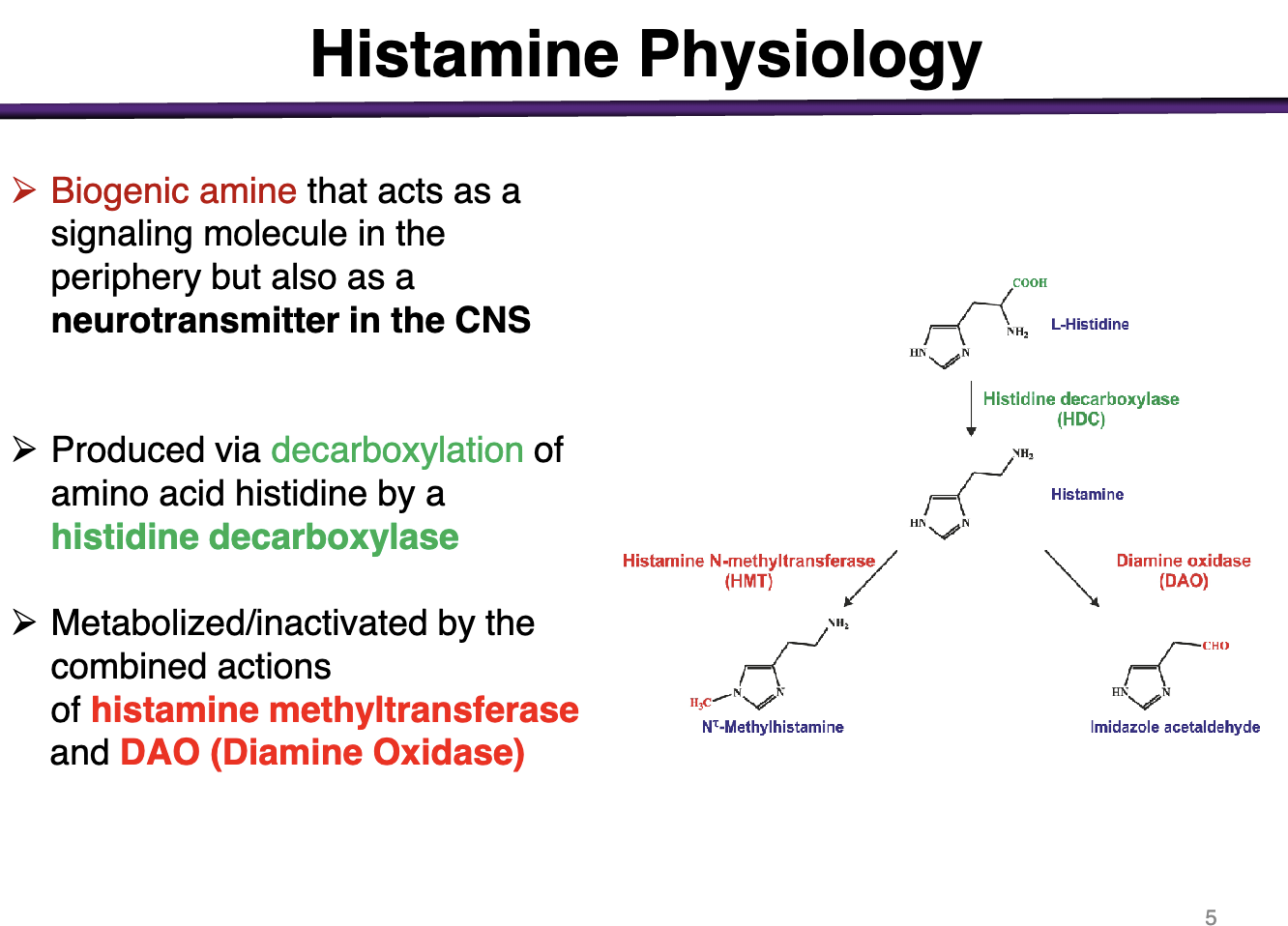
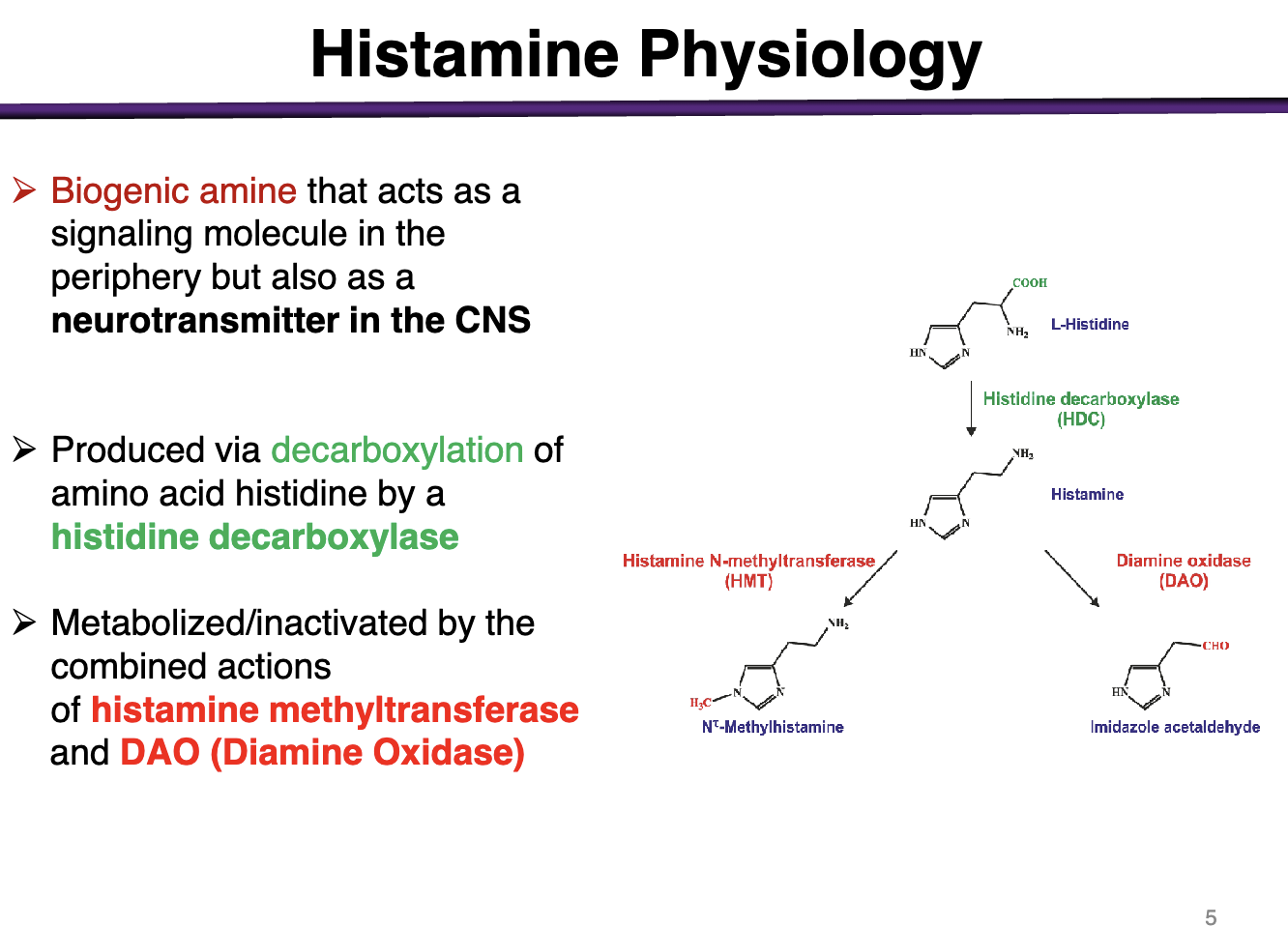
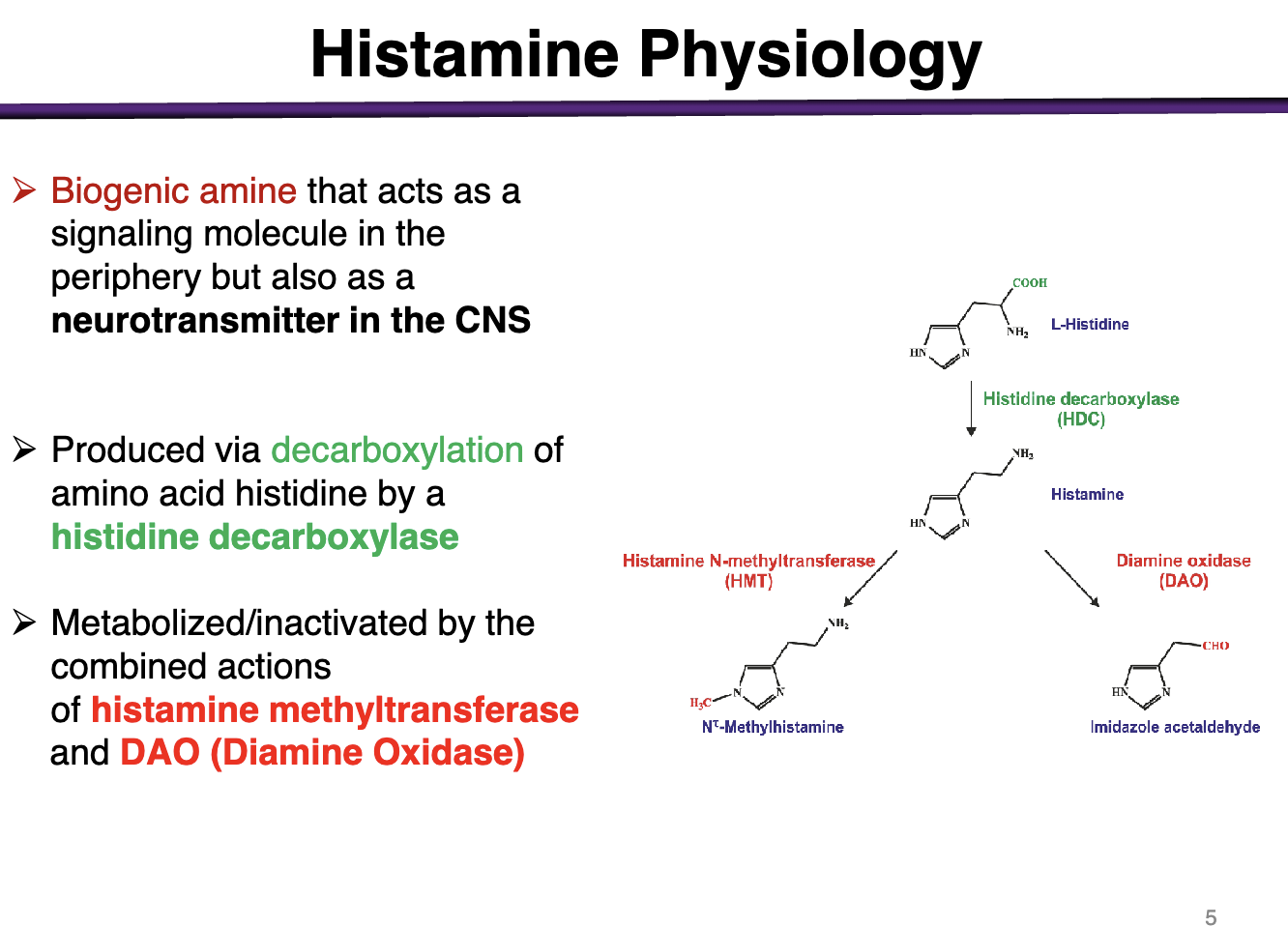
How is histamine produced? How is it metabolized/inactivated?
Decarboxylation of a.a. histidine by a histidine decarboxylase
Histamine methyltransferase and DAO
What class does histamine belong to?
Biogenic amine *test question
What produces histamine?
Produced by mast cells via allergic reactions or histaminergic neurons
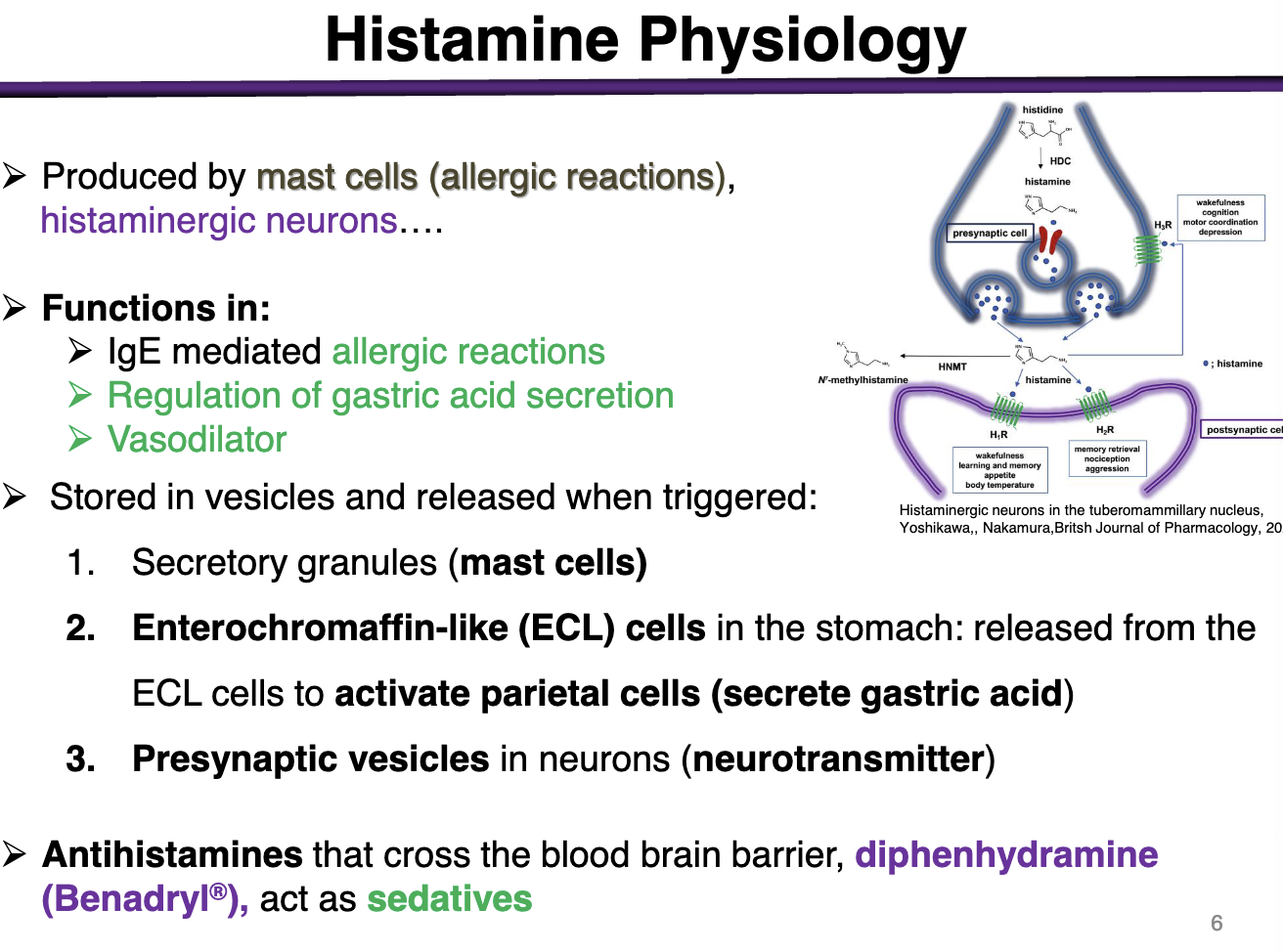
What are histamine’s functions?
IgE mediated allergic reactions
Regulation of gastric acid secretion
Vasodilator
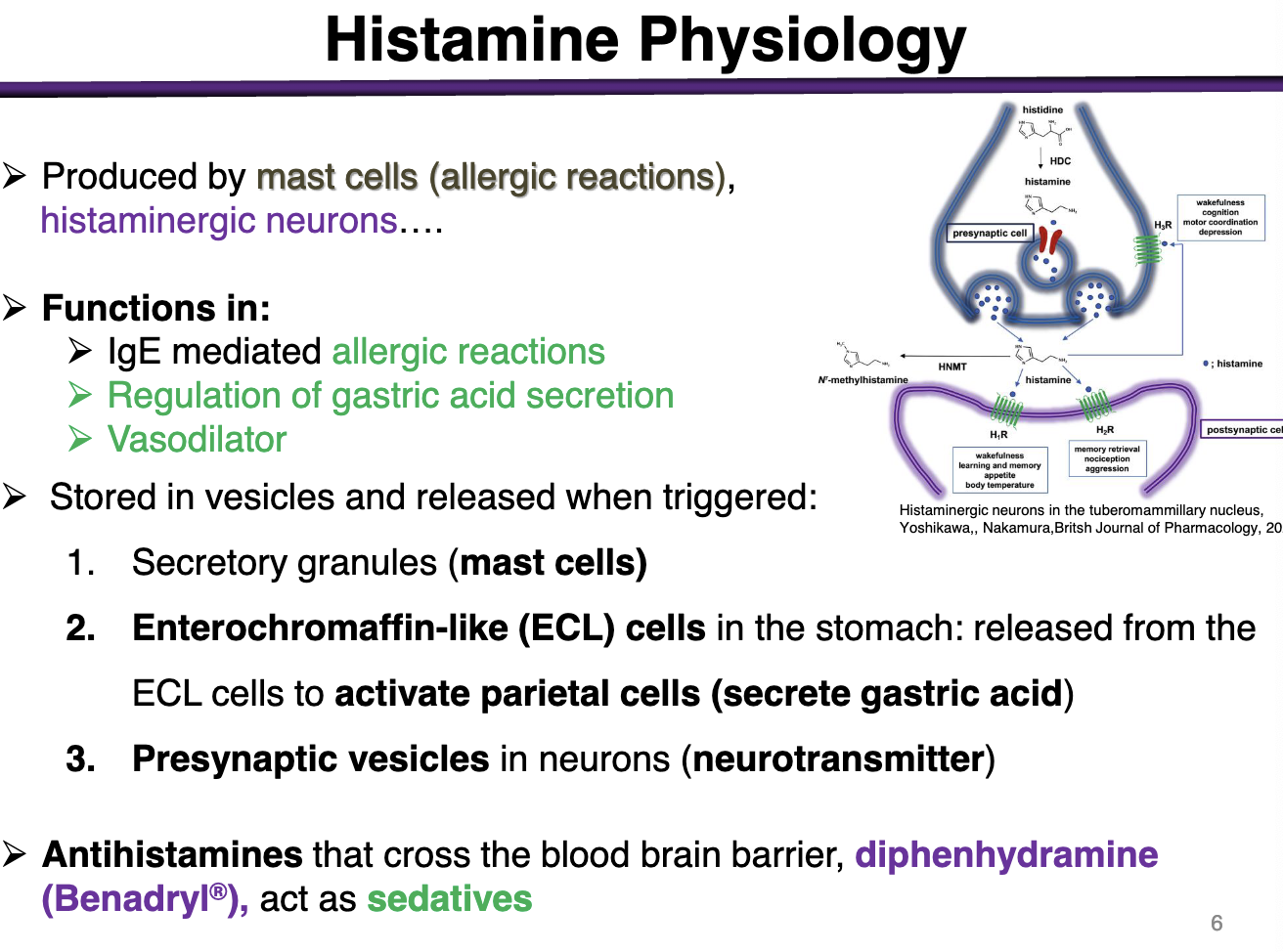
Where is histamine stored?
Secretory granules in mast cells
Enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells in the stomach: released from ECL cells to activate parietal cells (secrete gastric acid)
Presynaptic vesicles in neurons (neurotransmitter)
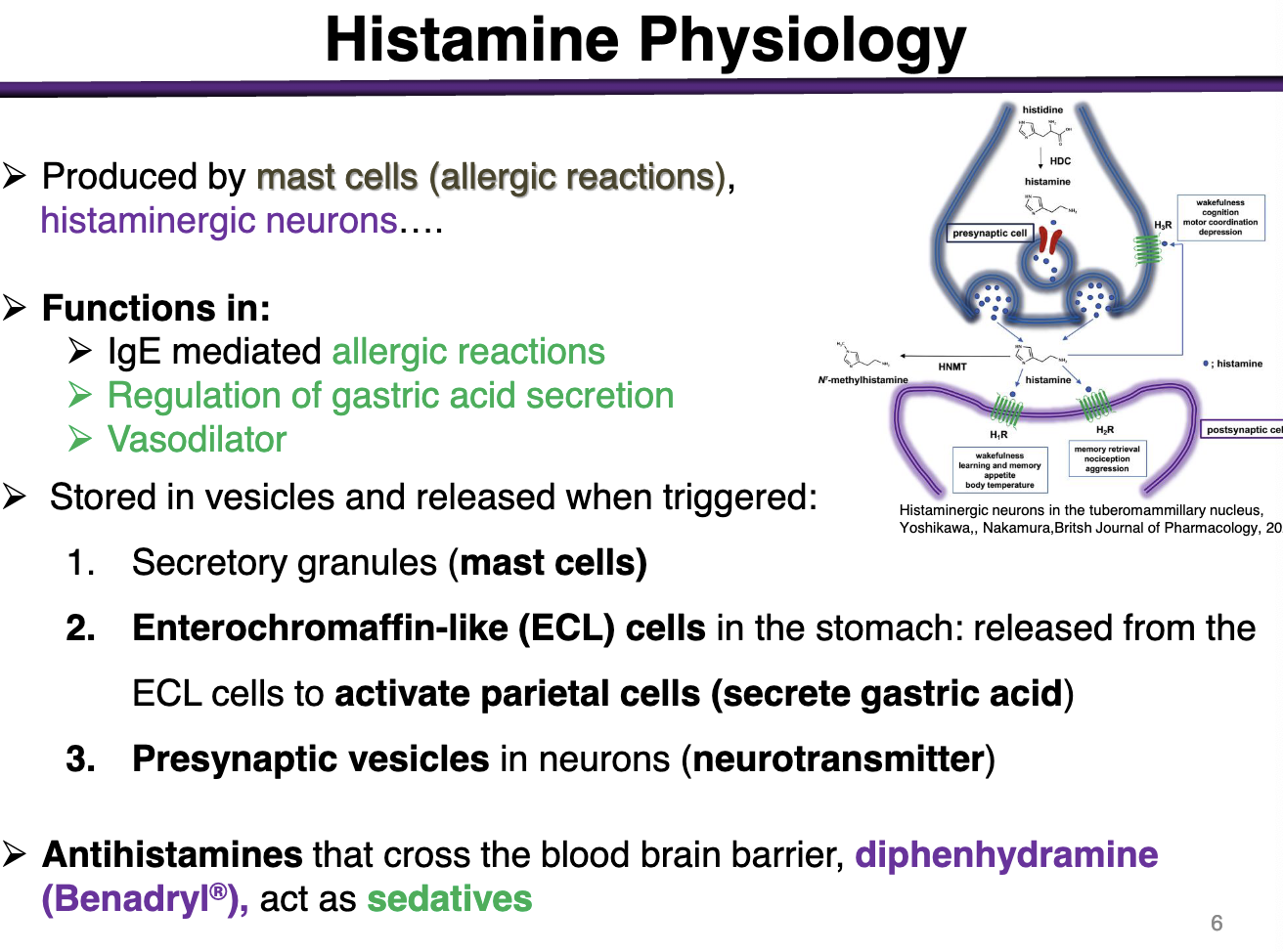
Histamine role in normal physiology
Released during injury: (wound healing)
Vasodilation leakage of inflammatory mediators
Recruitment of immune cells
Stimulate gastric acid secretion
Neurotransmitter
Controls neuroendocrine functions: body temperature, arousal, and cardiovascular regulation
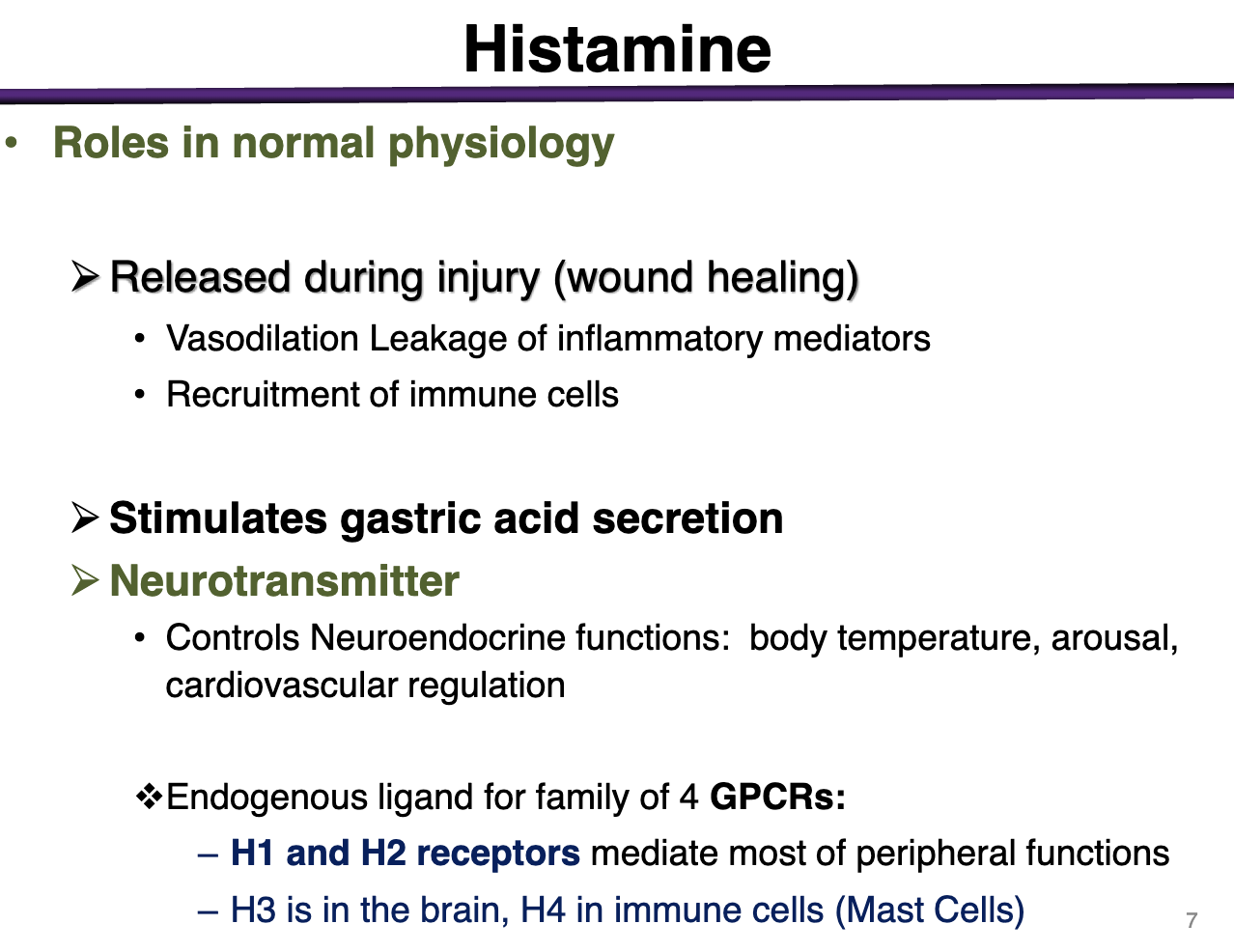
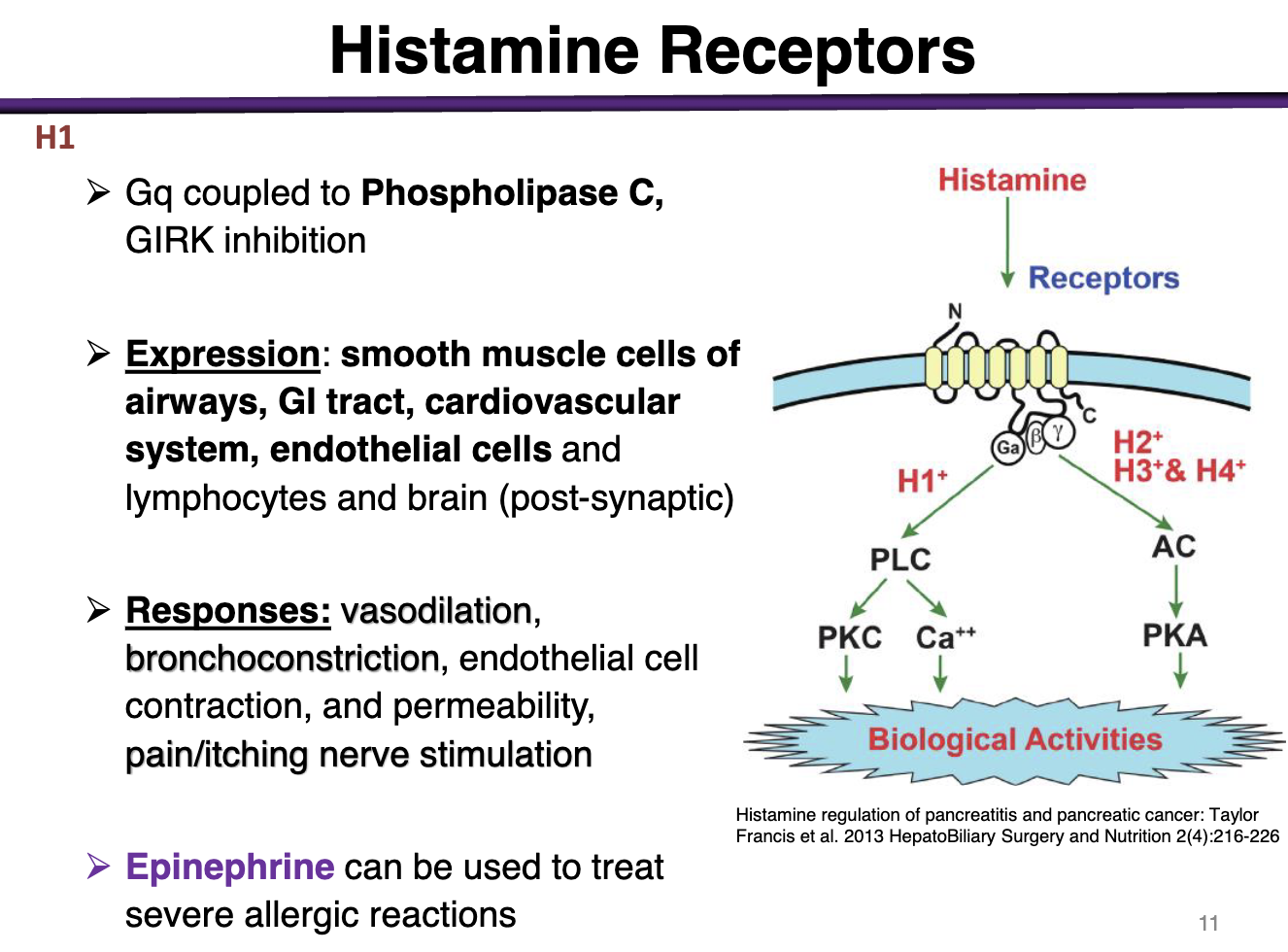
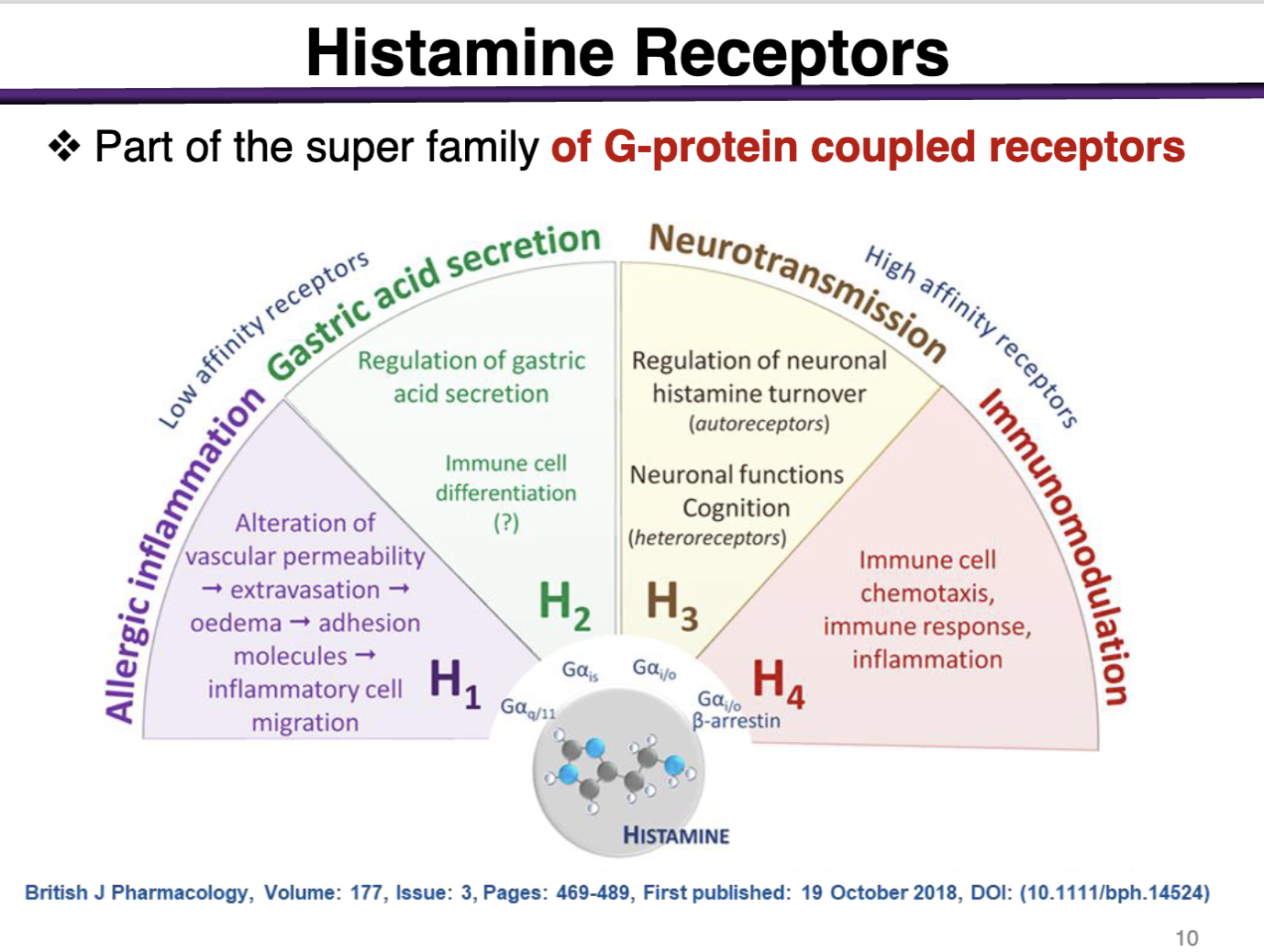
Histamine receptors location and types
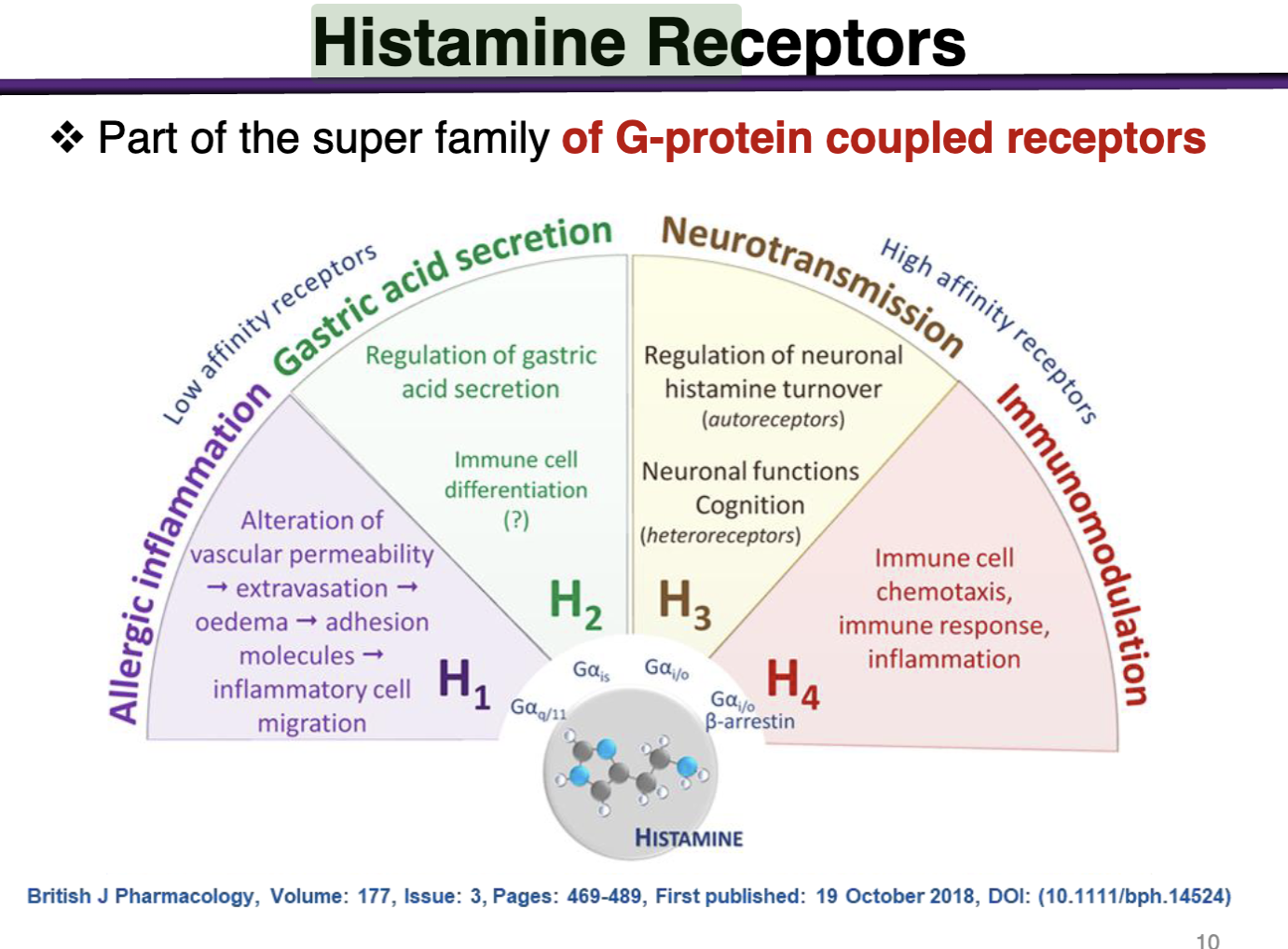
Endogenous ligand for family of 4 GPCRs
H1 and H2 mediate most peripheral functions
H3 is in the brain, H4 in immune cells (mast cells)
H1 receptor activation can lead to:
Type I hypersensitivities
Release of histamine from mast cells via H1
Histamine release in response to IgE mediated allergic reactions that is found in seasonal rhinitis (hay fever), urticaria (HIVES), angioedema
excessive gastric acid secretion
mechanism: H2 receptor activation
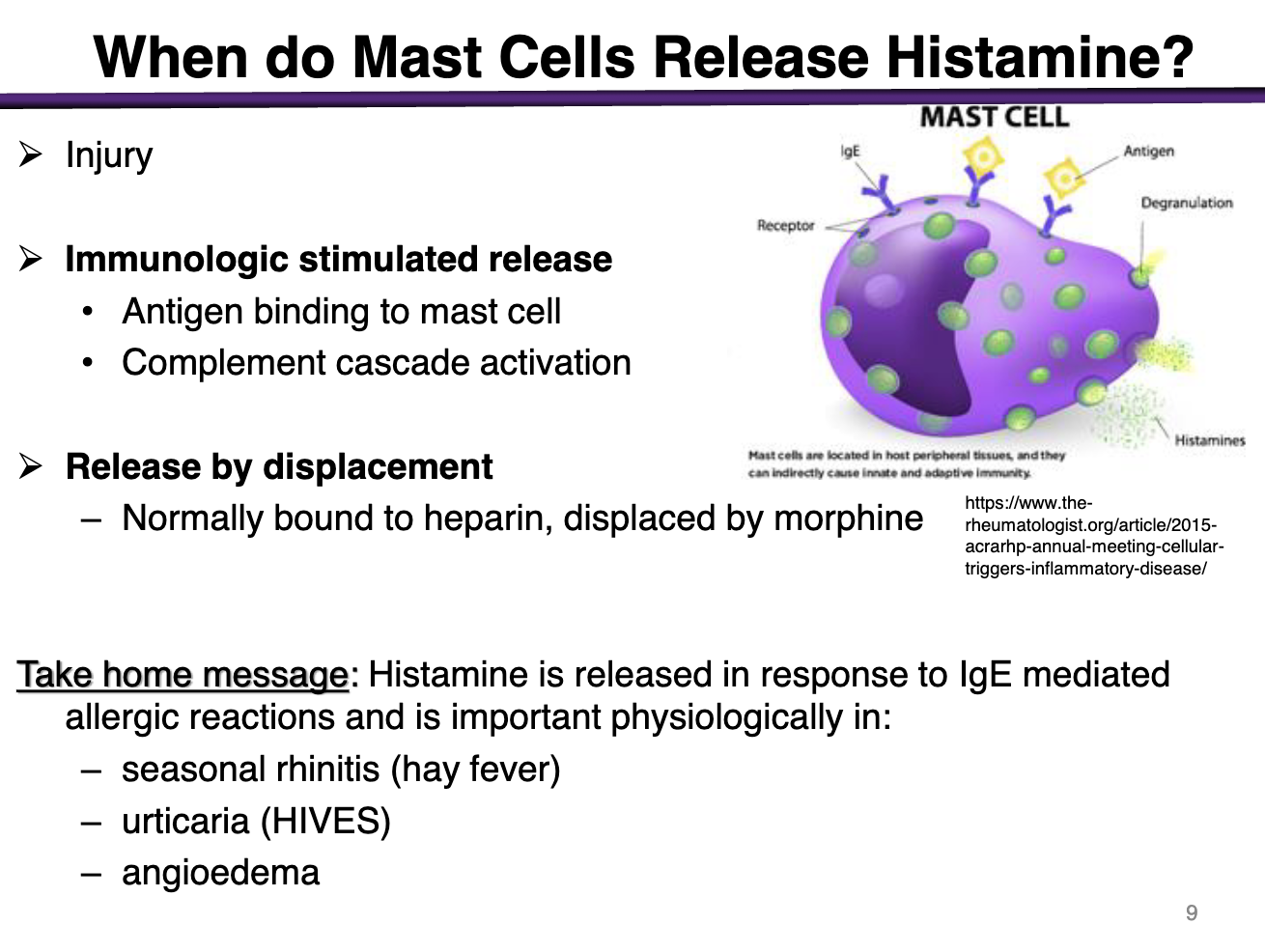
When do mast cells release histamine?
During injury
Immunologic stimulated release
antigen binds to mast cell
complement cascade activation
Release by displacement
bound to heparin, displaced by morphine
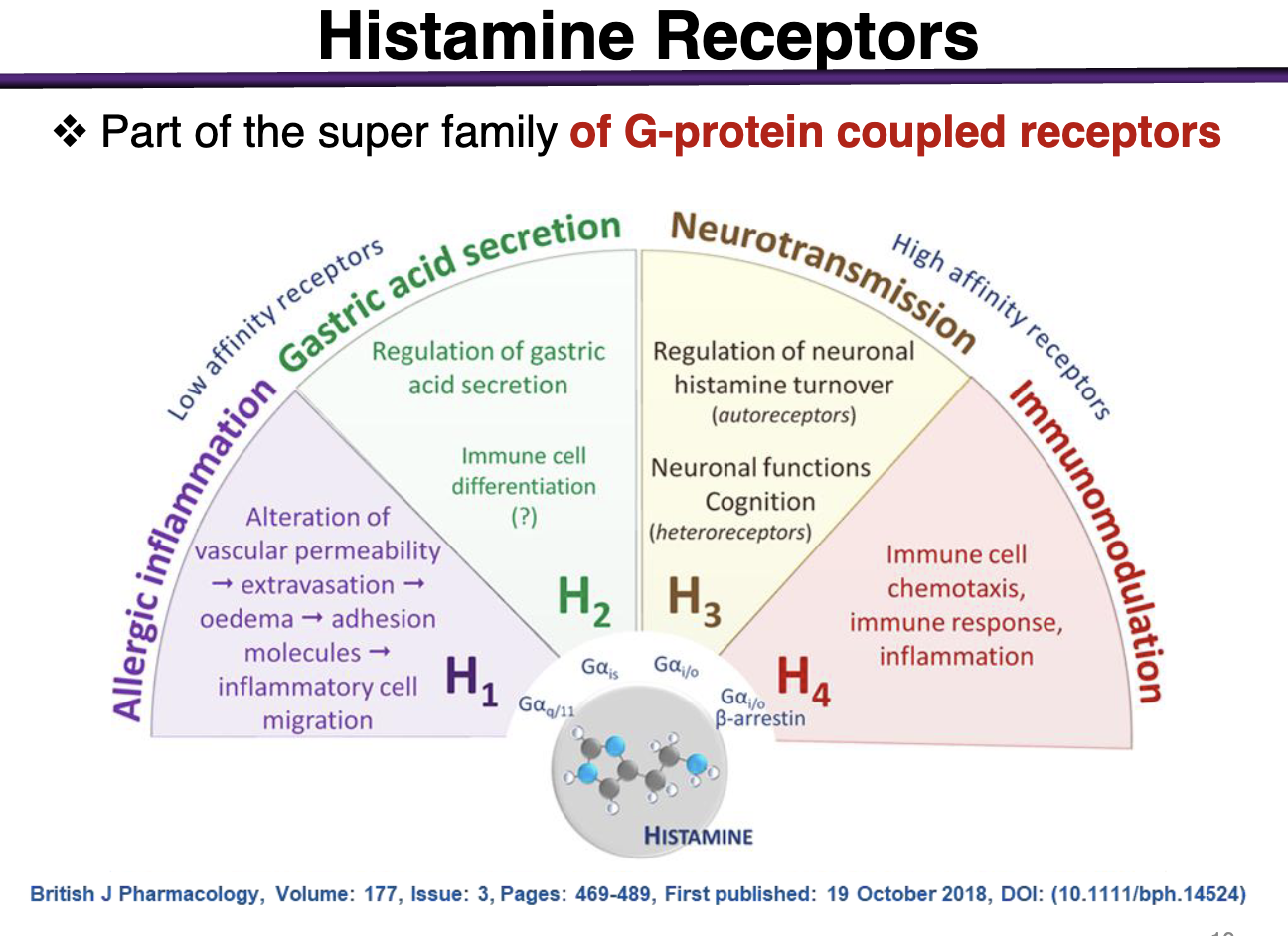
Histamine binds to what kind of receptors
All are coupled to G-proteins
Allergic Inflammation: H1 → Allergic Inflammation
Gastric Acid Secretion: H2 → gastric acid secretion
Neurotransmission: H3 → Neurotransmission
Immunomodulation: H4 → Immunomodulation
H1 receptor characteristics
H1 is a Gq coupled to PLC → Girk Inhibition
Expression: smooth muscle cells of airways, GI tract, cardiovascular system, endothelial cells
Responses: vasodilation, bronchoconstriction, endothelial cell, contraction, permeability, pain/itching nerve stimulation
epinephrine used to treat severe allergic rxns
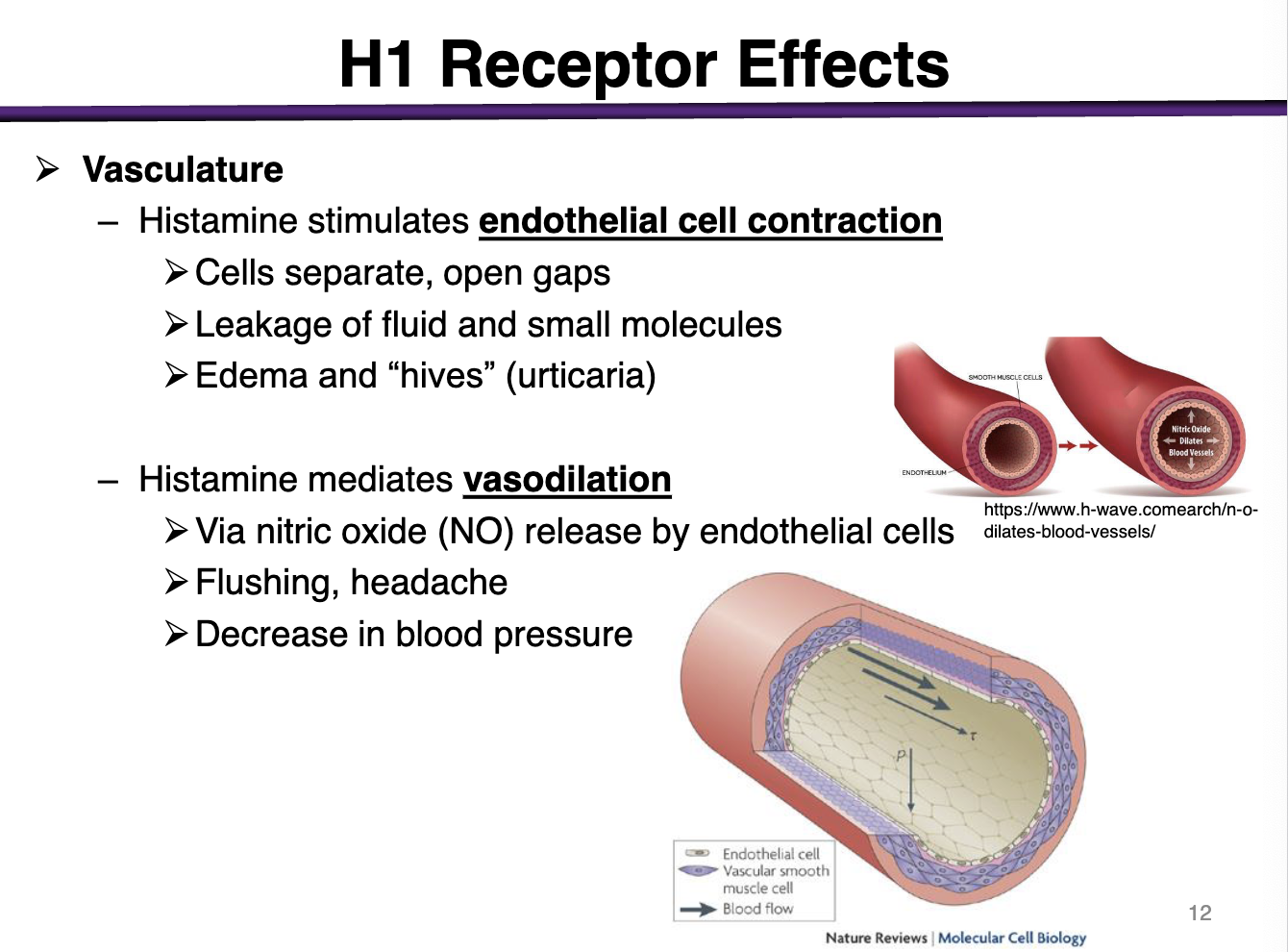
histamine effect on endothelial cells vs smooth muscle cells
H1 is expressed in endothelial and smooth muscle cells
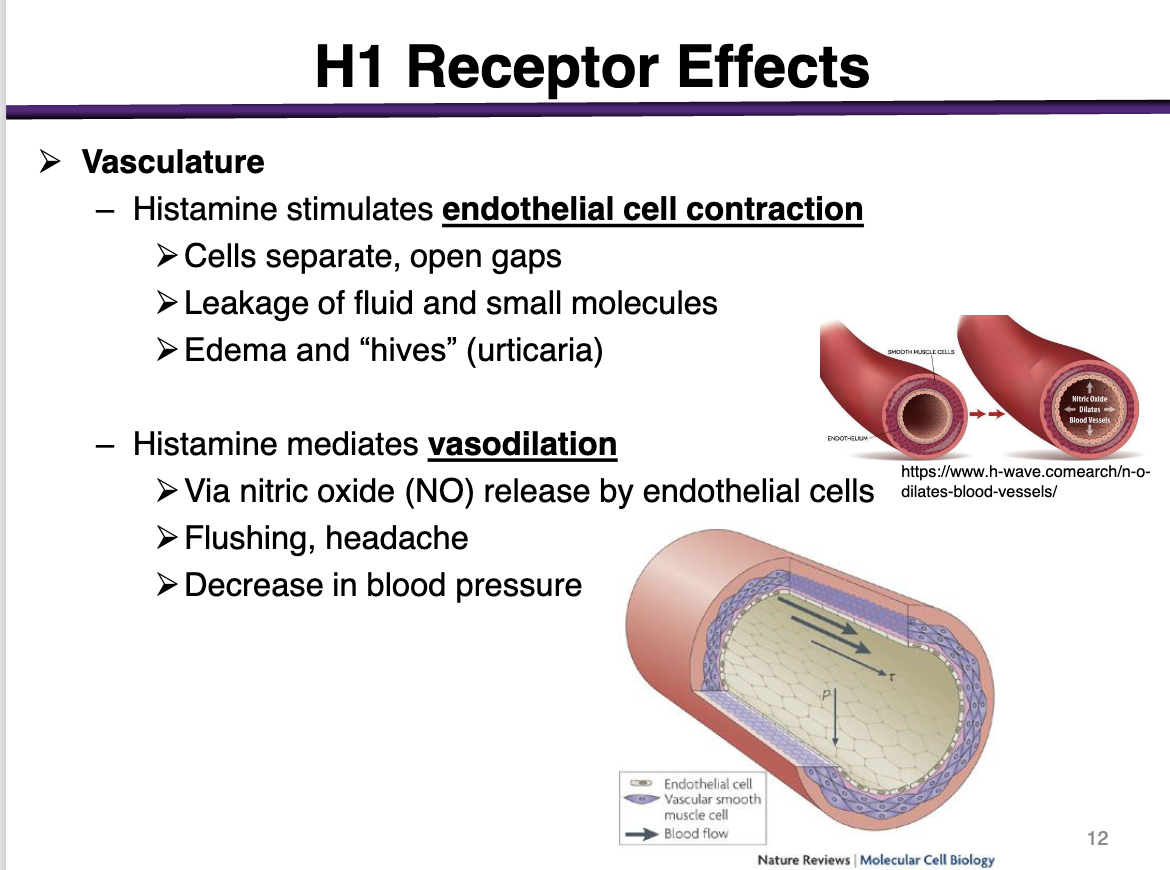
Histamine stimulates endothelial cell contraction
cells separate, open gaps
leakage of fluid and small molecules
edema and hives (urticaria)
this creates gaps so that inflammatory mediators can be released into the blood to recruit immune cells
Histamine mediates vasodilation in the smooth muscle
via nitric oxide (NO) release by the endothelial cells
flushing, headache
decrease in blood pressure
Why is a pt experiencing stimulation of pain and itchiness?
urticaria
Gq-mediated post-synaptic response (GIRK inhibition)
h1 receptor effects on respiratory system
bronchoconstriction
usually insignificant except: allergy induced asthma and anaphylaxis
H1 immunity/inflammation
leakage of inflammation mediators and antibodies
H1 receptor effects Gi tract smooth muscle
contraction (large histamine doses may cause diarrhea)
h1 receptor effects uterus
contraction (anaphylaxis: miscarriage)
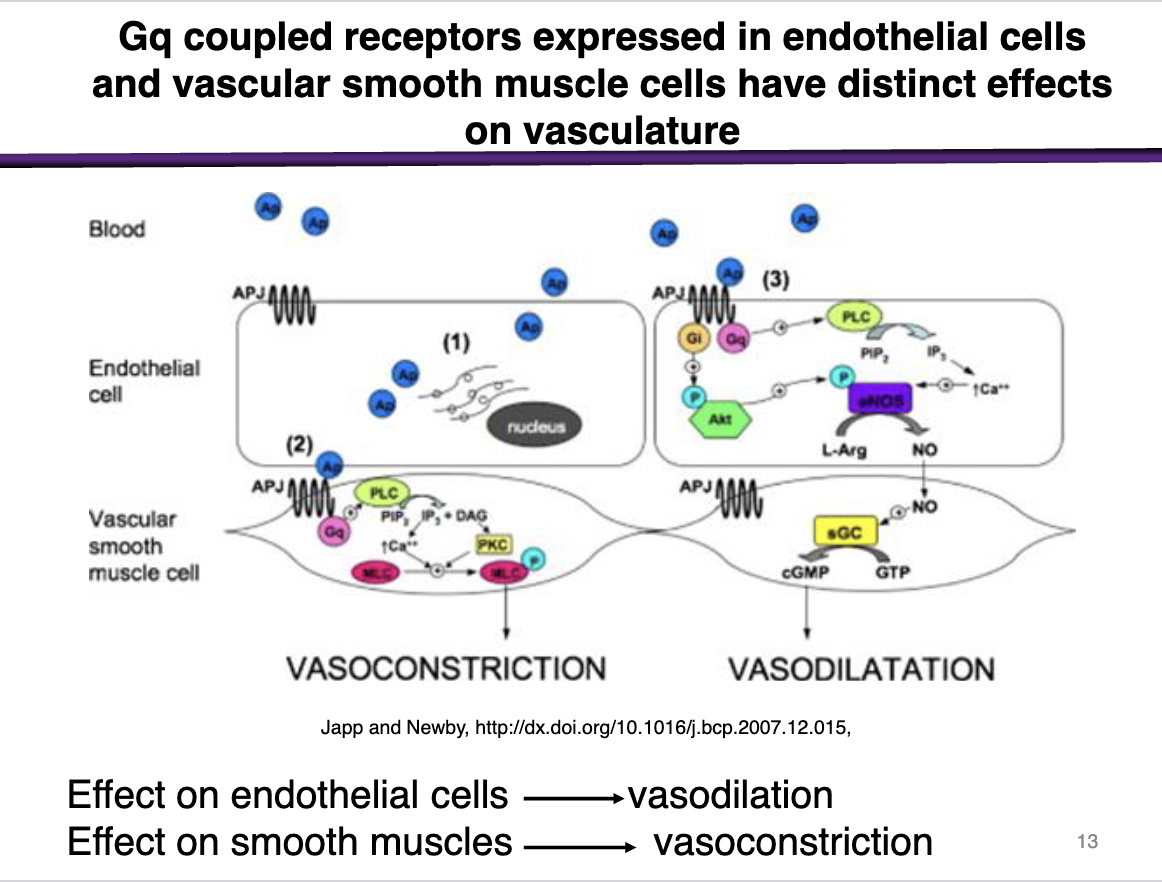
Describe
ON THE LEVEL OF ENDOTHELIAL CELLS
When histamine bind to receptors in the endothelial cells (closest layer to systemic circulation)
The endothelial cells will contract
Allows for the leakage for the inflammatory mediators (Like Nitric Oxide) to recruit more immune cells into the smooth muscle cells
Histamine stimulates endothelial cell contraction
and
Mediates Vasodilation
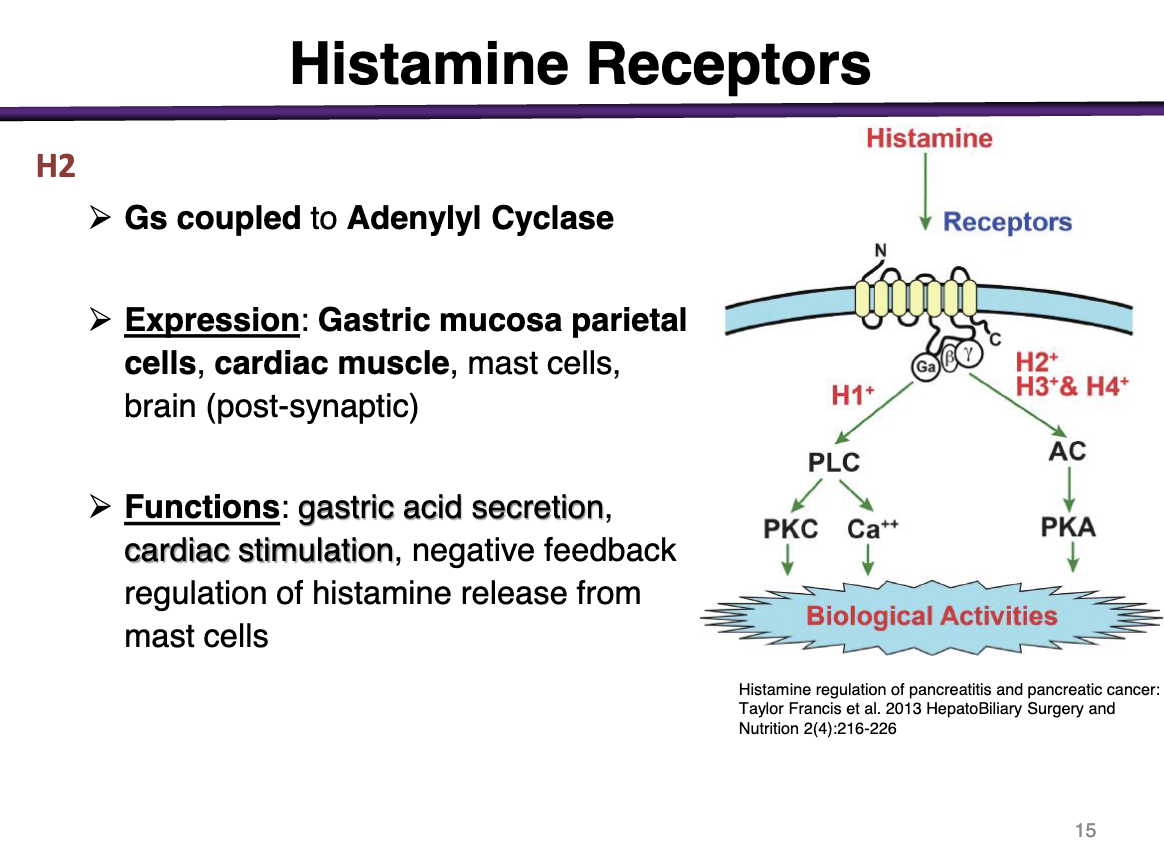
H2 receptor
effector; second messenger
expression
and function
Gs coupled to Adenylyl Cyclase
Expression: Gastric mucosa and parietal cells, cardiac muscle, mast cells, brain (post-synaptic)
Functions: gastric acid secretion, cardiac stimulation, negative feedback regulation of histamine release from mast cells
Cardiovascular H2 receptor effects
increase heart rate
contributes to anaphylaxis
direct stimulation, increased contractility, increased rate
Secretory tissue H2 receptor effects
secretion of gastric acid (enterochromaffin-like ECL cells —> parietal cells —> acid secretion)
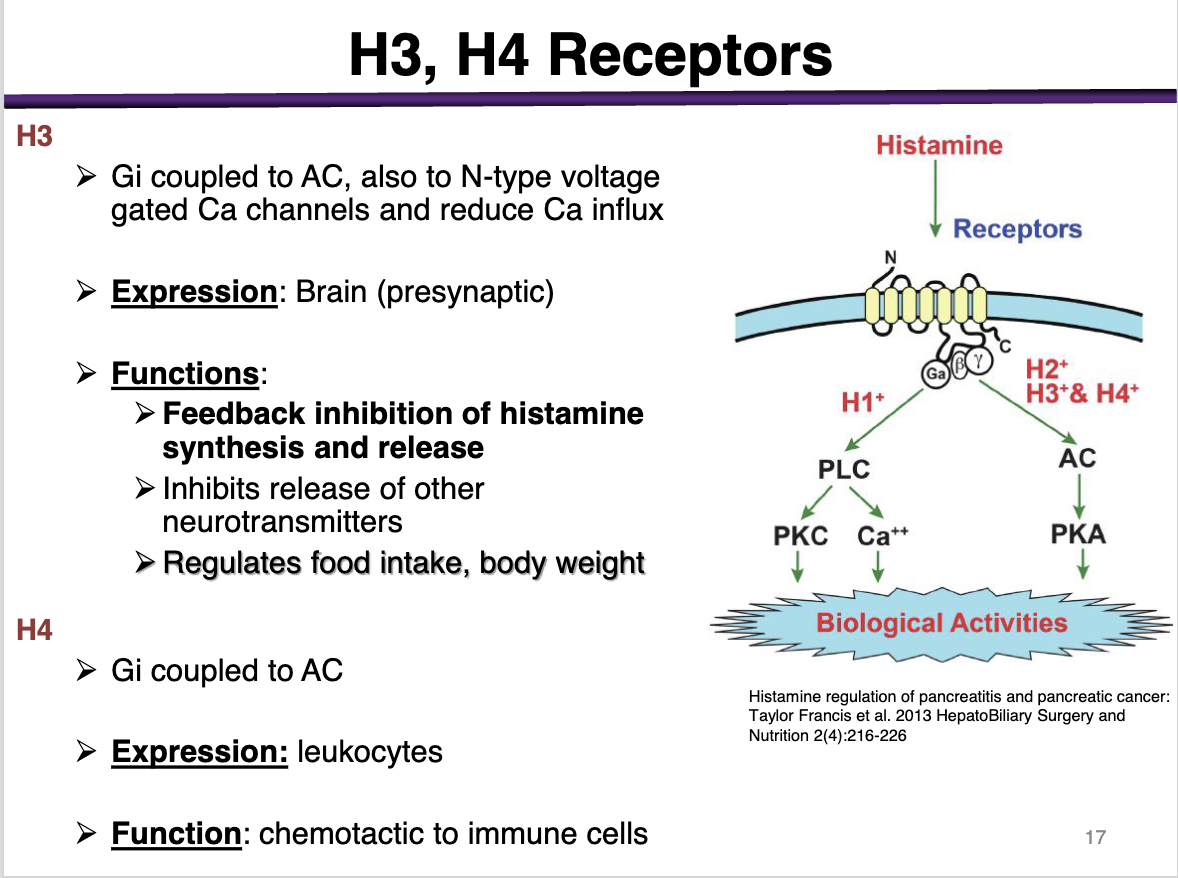
H3
effector and second messenger
expression
functions
Gi coupled to AC
Also to N-type voltage gated Ca channels and reduce Ca influx
Expression: Brain (presynaptic)
Functions: Feedback inhibition of histamine synthesis and release; inhibits release of other neurotransmitters'; regulates food intake, body weight
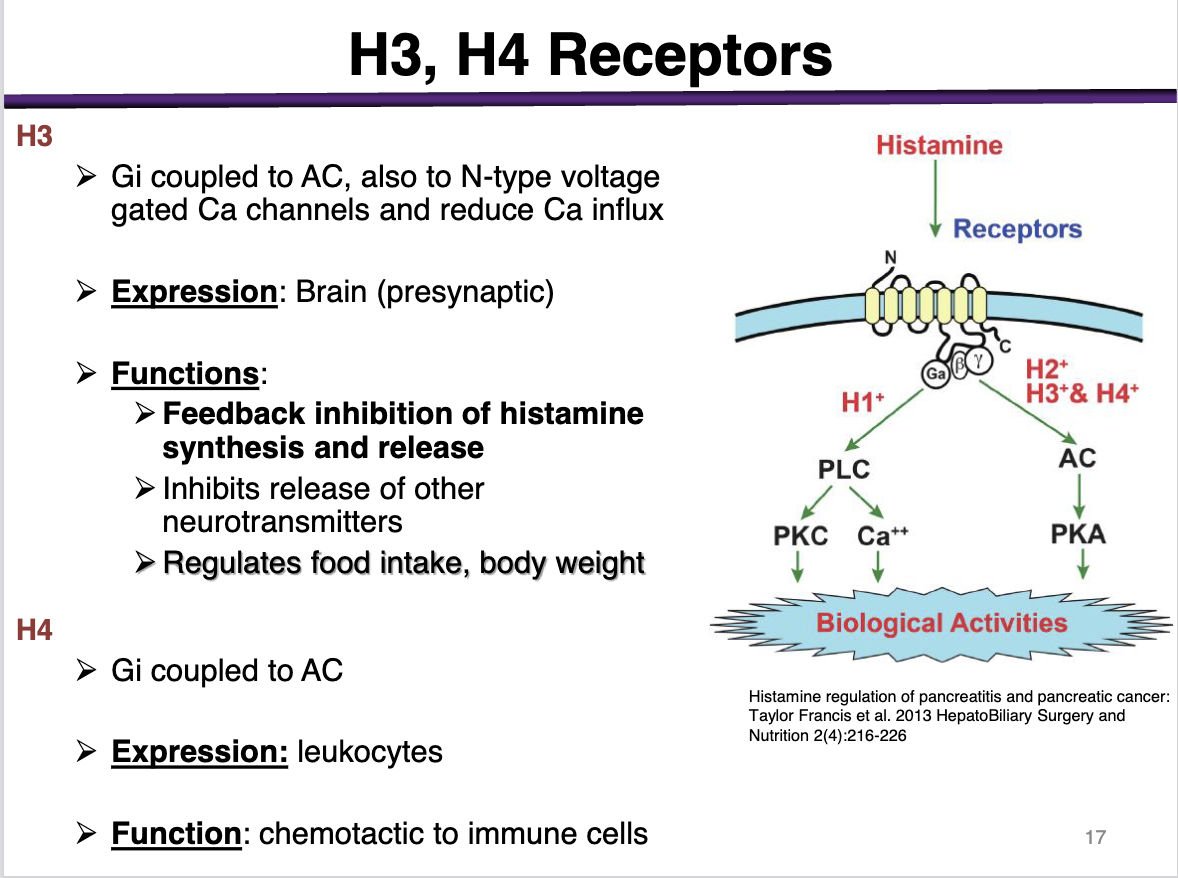
h4
effector and second messenger
expression
function
Gi coupled to AC
expression: leukocytes
Function: chemotactic to immune cells
H1 antagonists would be used for
immediate allergic responses

h2 antagonists would be used for
gastro-intestinal disorders such as
Ulcers, heartburn, GERD

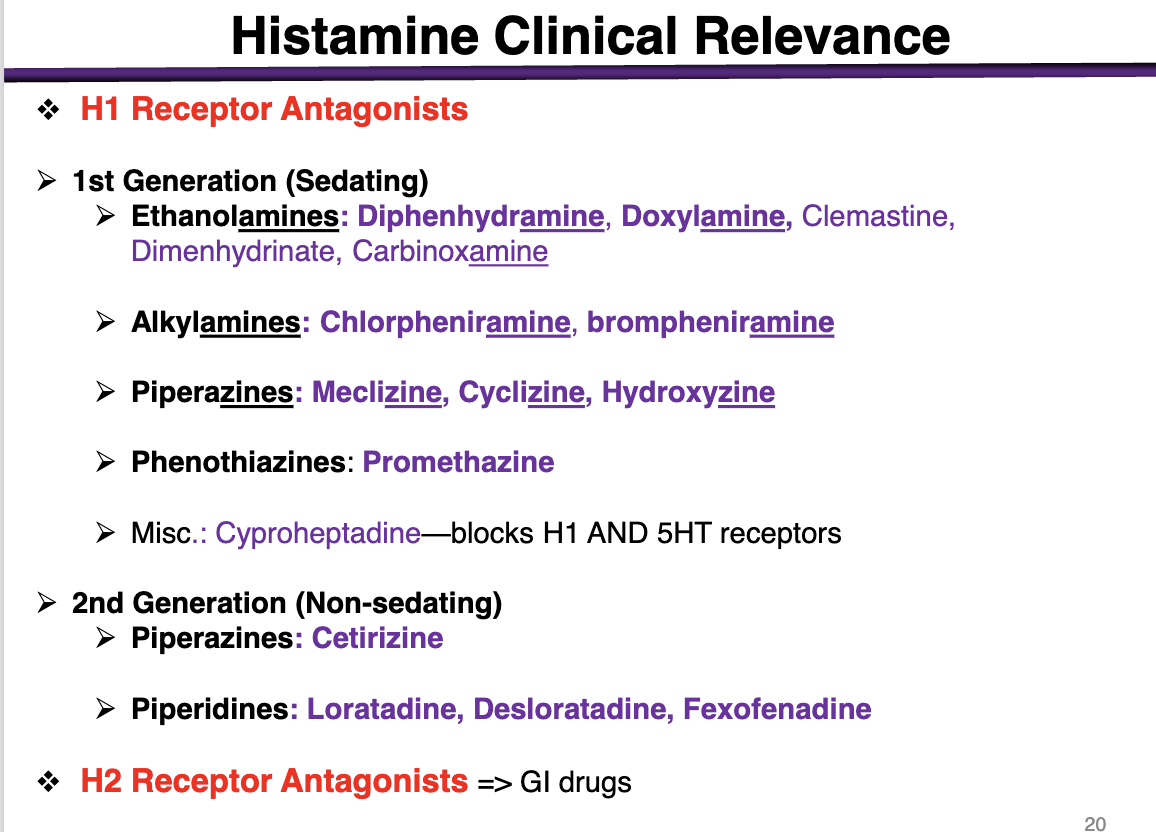
1st generation antihistamines are:
sedating or non-sedating
sedating
These cross the BBB and get into the brain
*exception is alkylamines; minimal sedation alongside 2nd gen
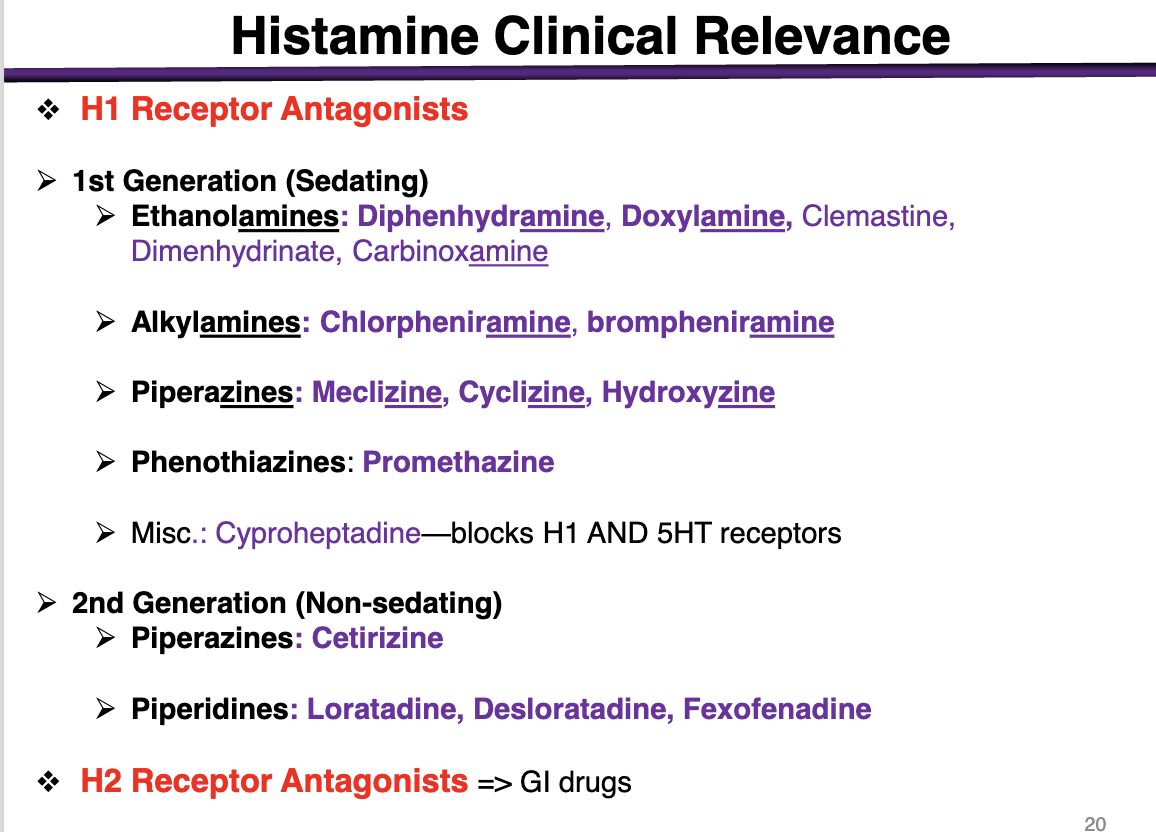
examples of ethanolamines
These are 1st generation (sedating histamines)
diphenhydramine, doxylamine, Dimenhydrinate, Carbinoxamine
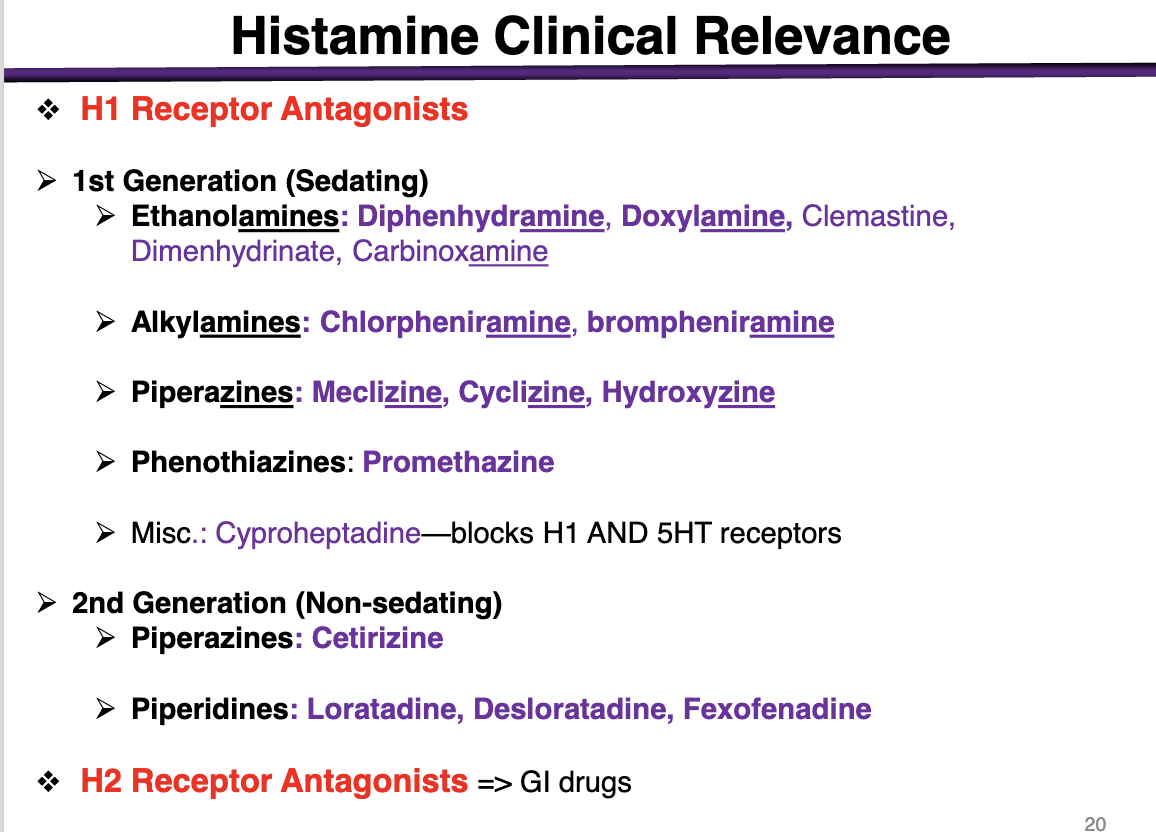
examples of alkylamines
1st generation sedating histamines
Chlorpheniramine, brompheniramine
Alkylamines have the lowest BBB penetration
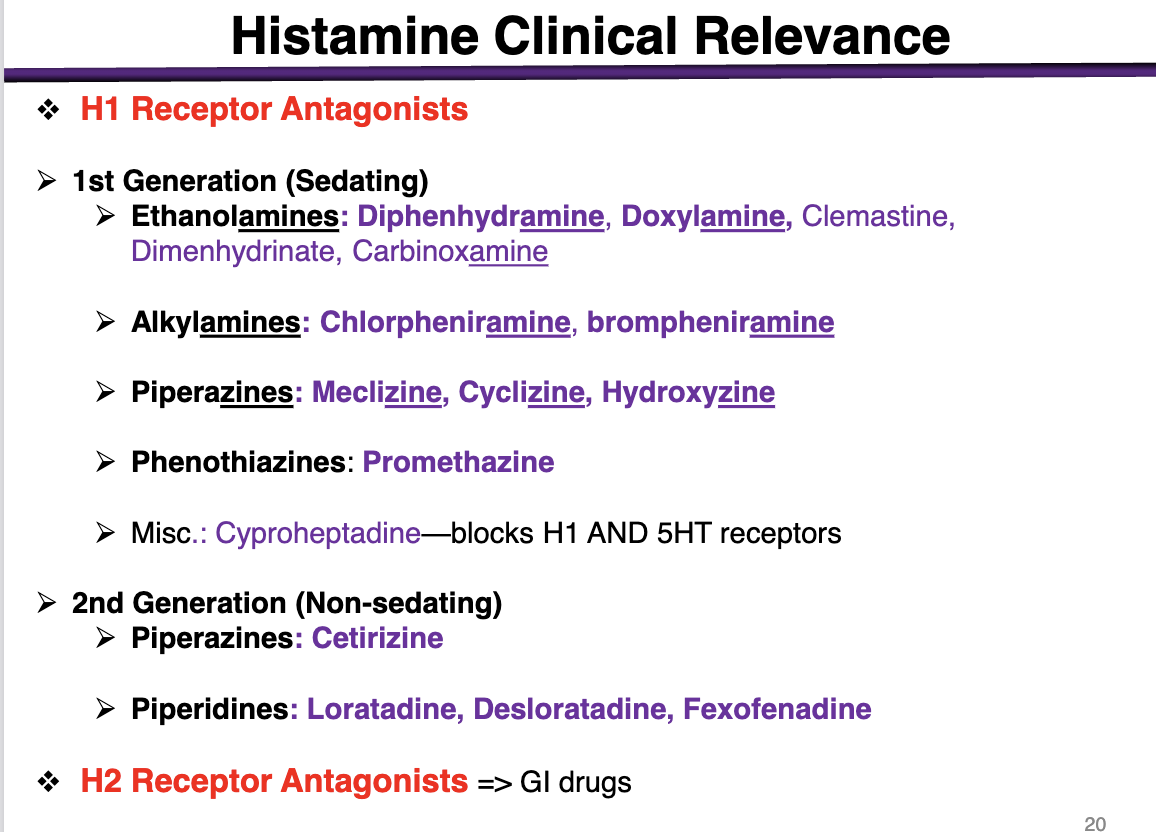
examples of piperazines in 1st generation
1st generation sedating histamines
meclizine, cyclizine, hydroxyzine
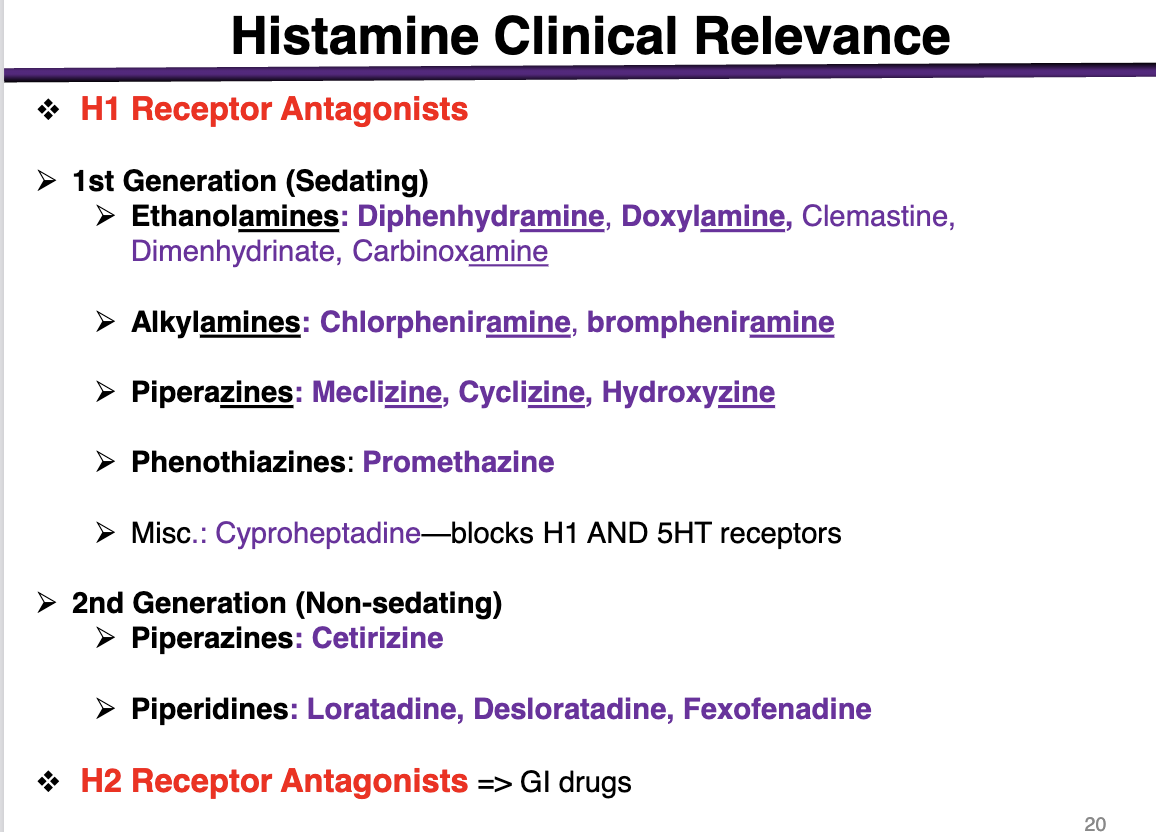
phenothiazines example
1st generation antihistamine (sedating)
promethazine
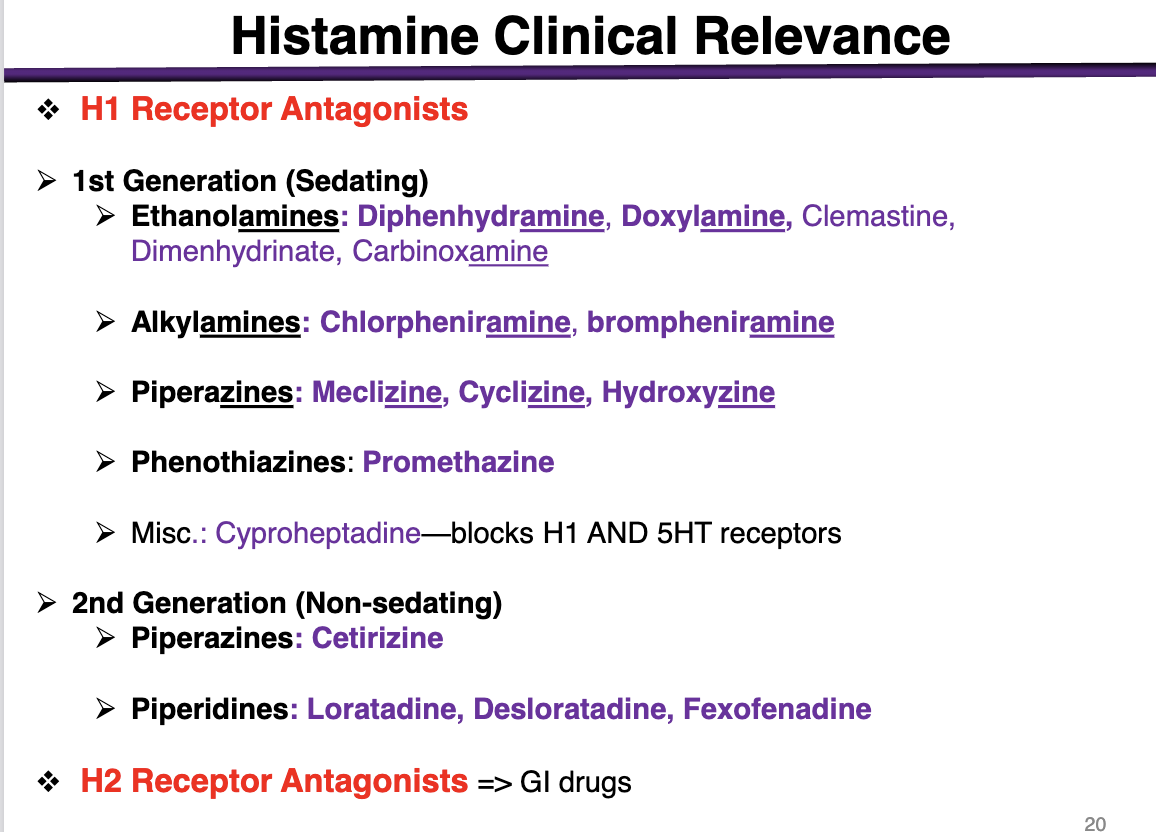
What is special about cyproheptadine
blocks H1 and 5HT receptors
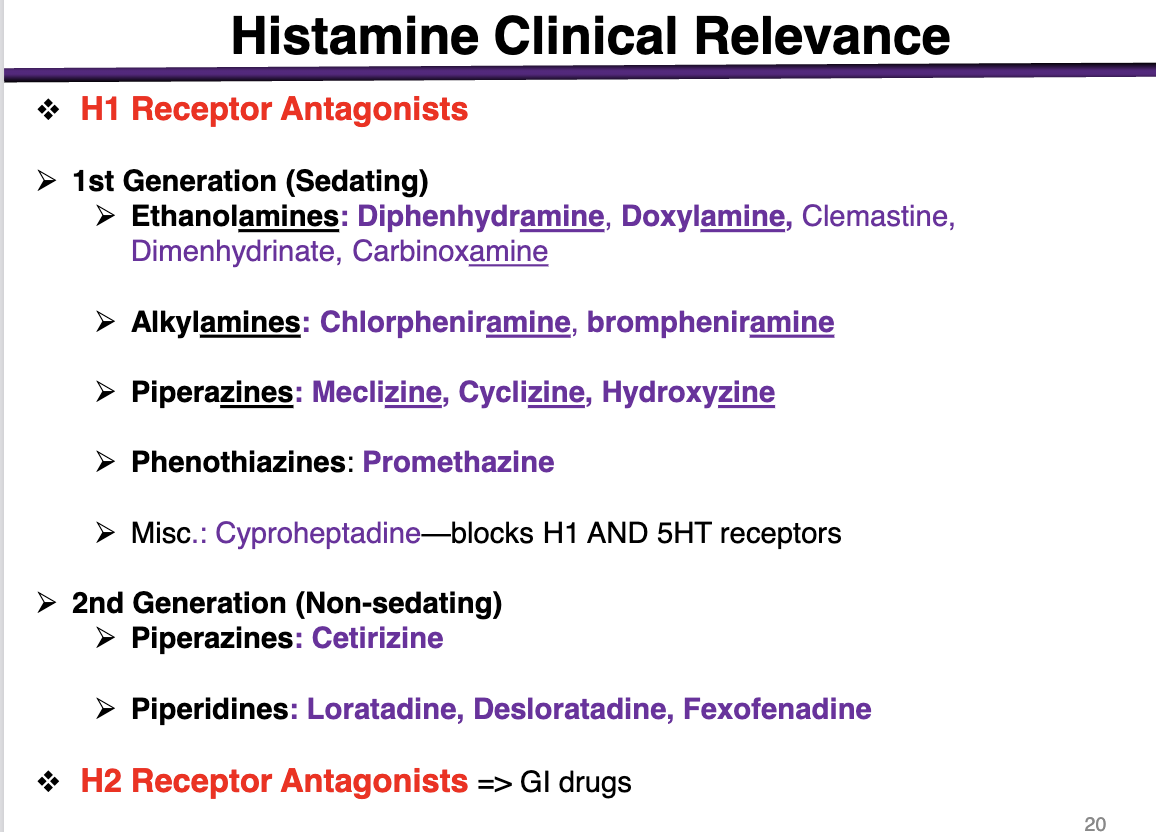
2nd generation (non-sedating) examples
Piperazines: Cetirizine (different from the other 1st generations); cannot cross the BBB
Piperidines: Loratadine, Desloratadine, Fexofenadine
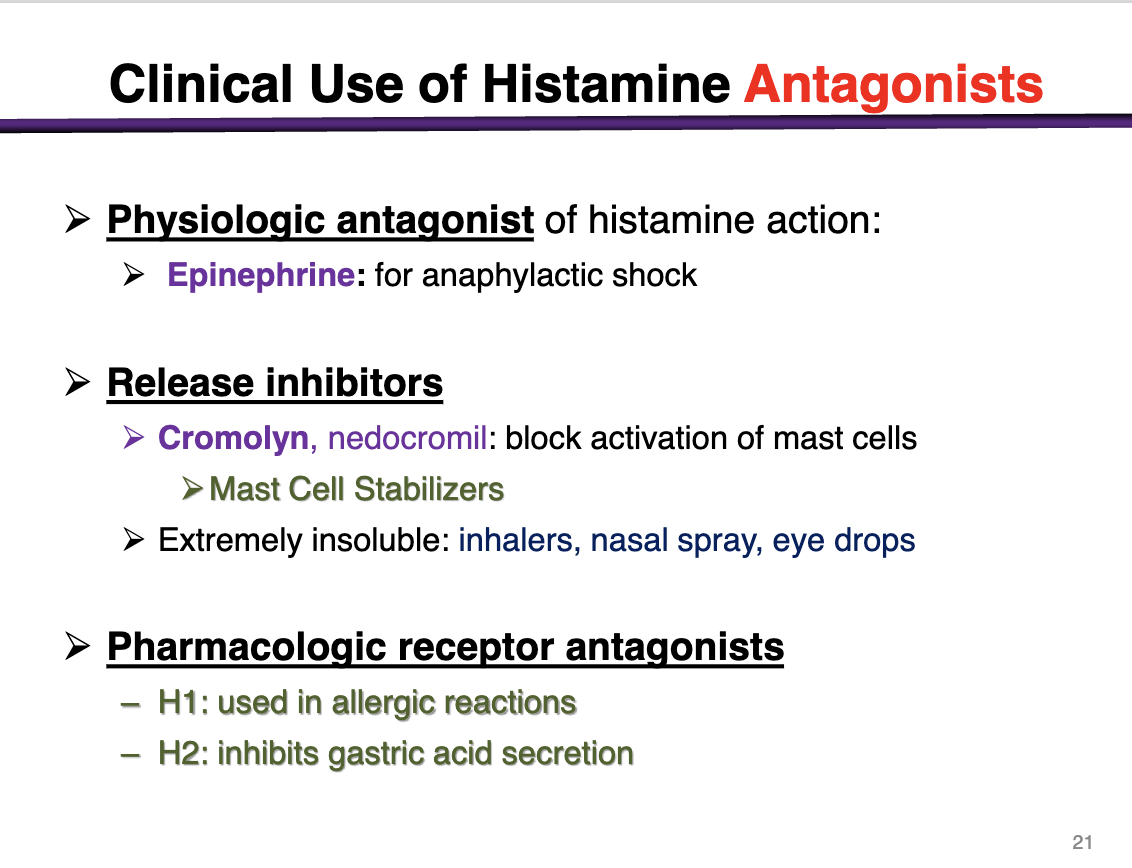
physiologic antagonist of histamine action
epinephrine for anaphylactic shock
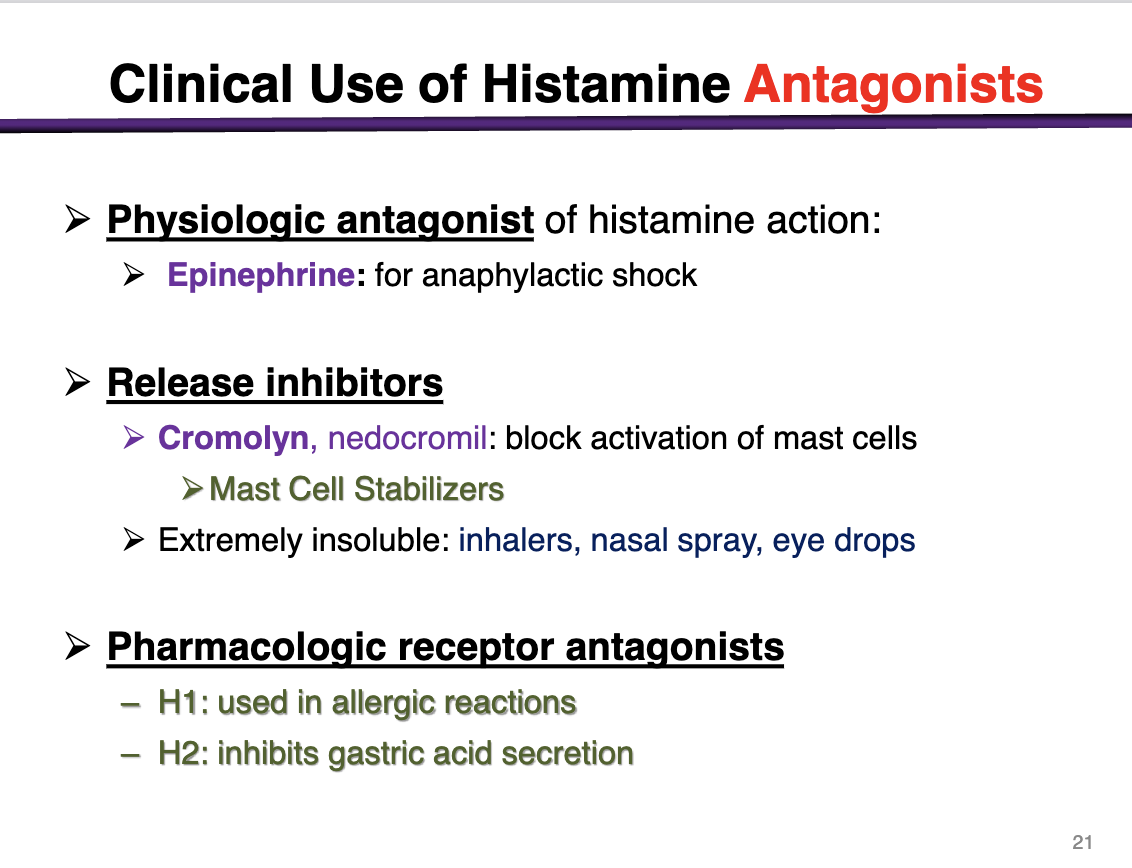
Release inhibitors
Cromolyn, nedocromil: block activation of mast cells
Mast cell stabilizers
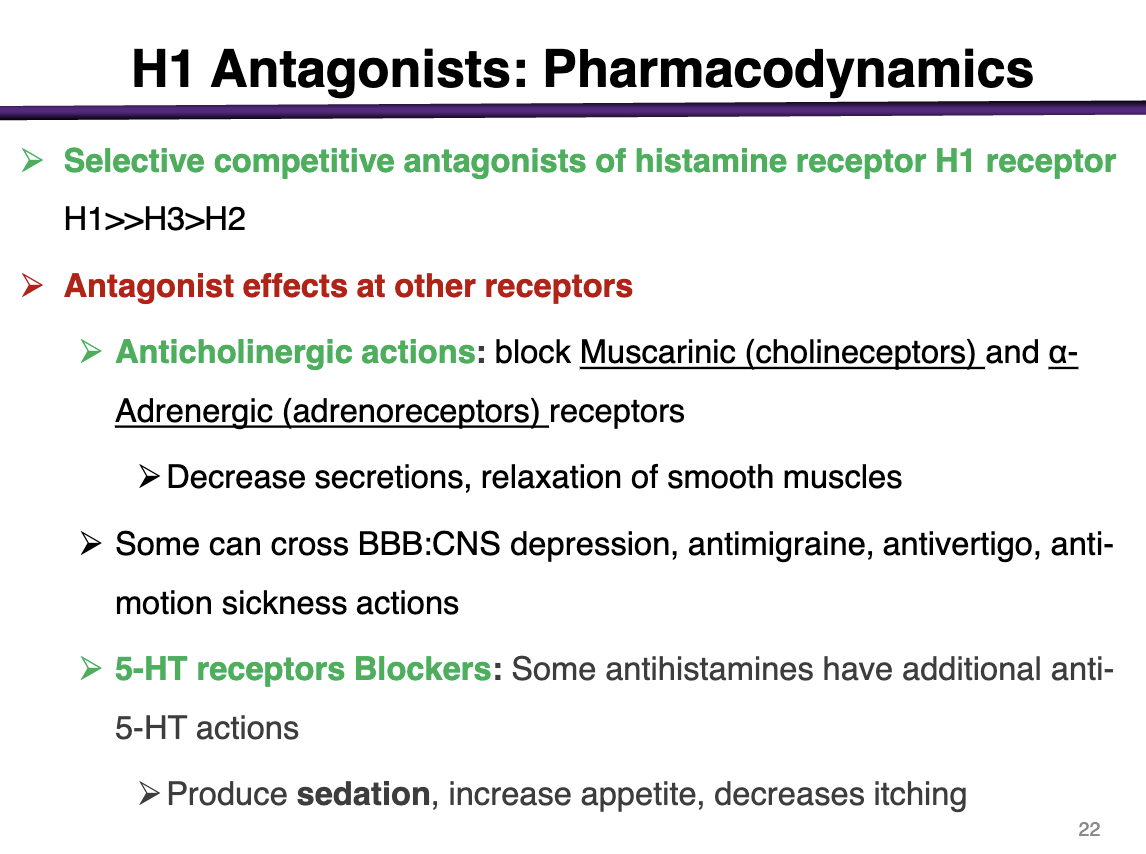
Selective competitive antagonists of histamine receptor H1 receptor
H1> > H3> H2
at a low dose of h1 antagonist, the drug will bind to H1 receptors
At a higher concentration, the drug will bind to h3 (brain) and H2 (GI)
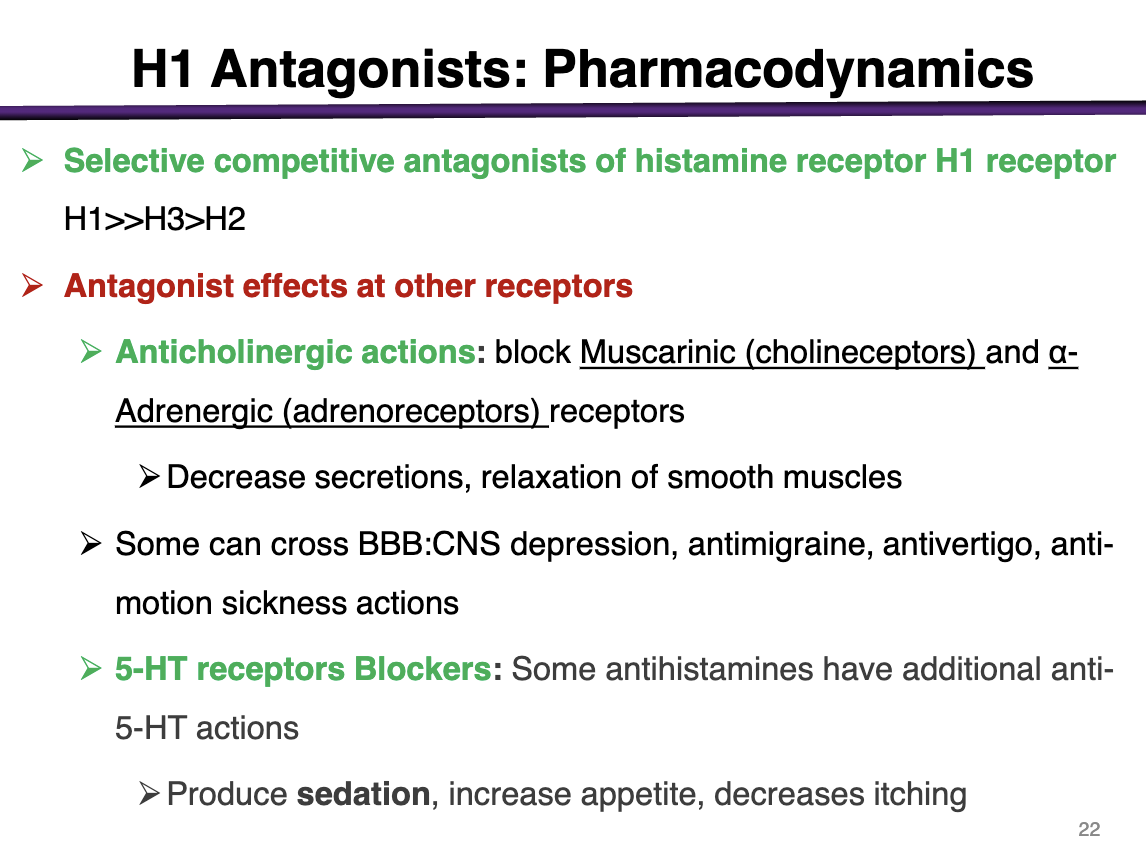
What other effects do H1 receptors have
Antagonist effects at other receptors:
Anticholinergic Actions: Can block muscarinic (cholinoceptors) and a-adrenergic (adrenoreceptor) receptors
Decrease secretions, relaxation of smooth muscles
Some can cross BBB: CNS depression, antimigraine, antivertigo, anti-motion sickness actions
5-HT receptor blockers: some antihistamines have additional anti-5-HT actions and can produce sedation, increase appetite, decrease itching
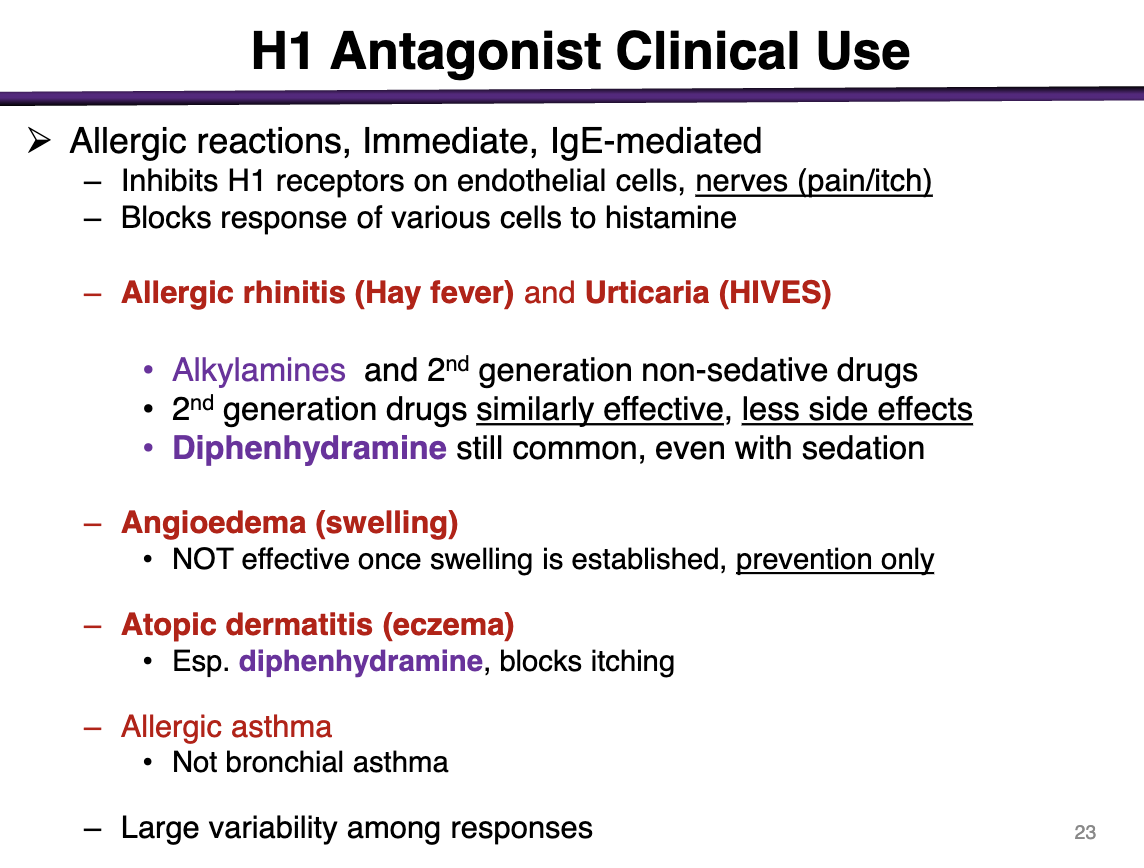
indications for H1 antagonist
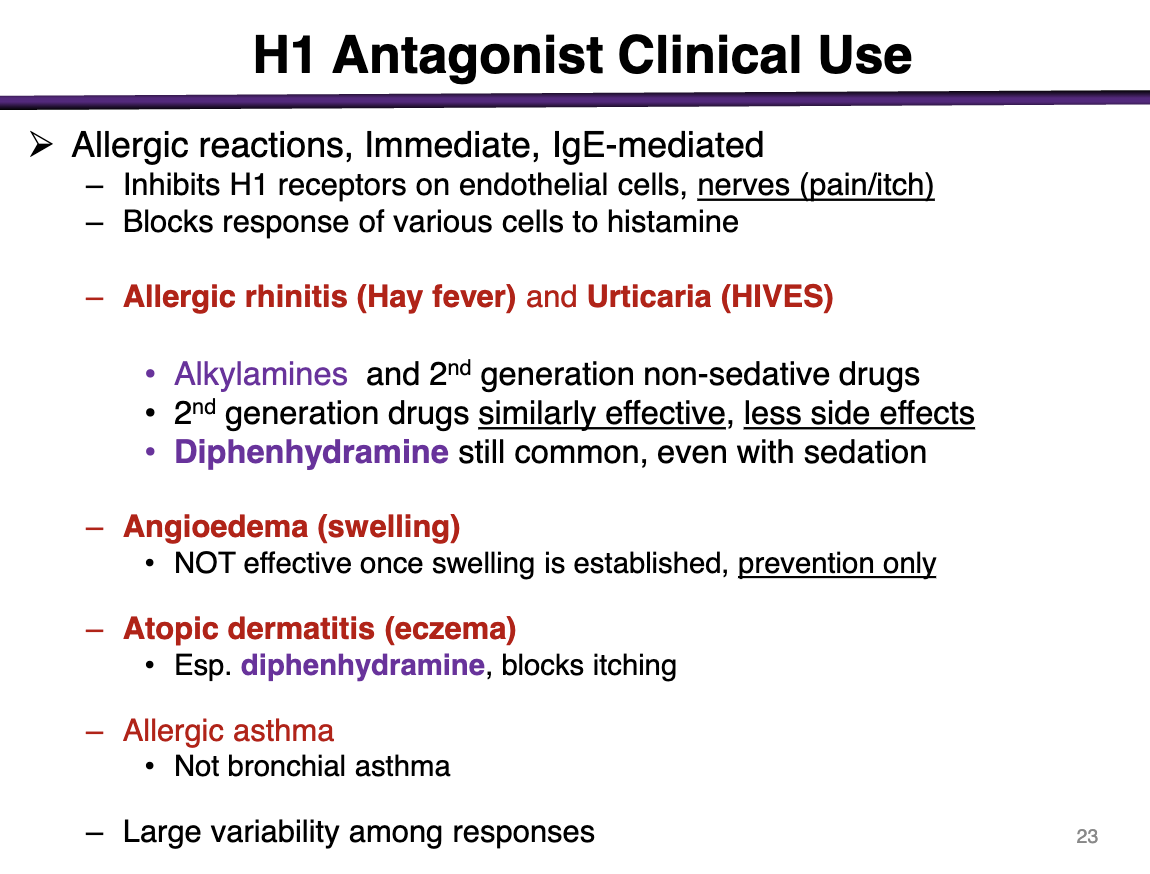
Allergic reactions, immediate, IgE-mediated
Inhibit H1 receptors on endothelial cells, nerves (pain/itch)
Blocks response of various cells to histamine
drugs for
For allergic rhinitis (hay fever), urticaria (HIVES)
Alkylamines (chlorpheniramine, brompheniramine; lowest of the 1st)
and 2nd generation non-sedative drugs
2nd generation are just as effective with less side effects
Diphenhydramine is common even with sedation
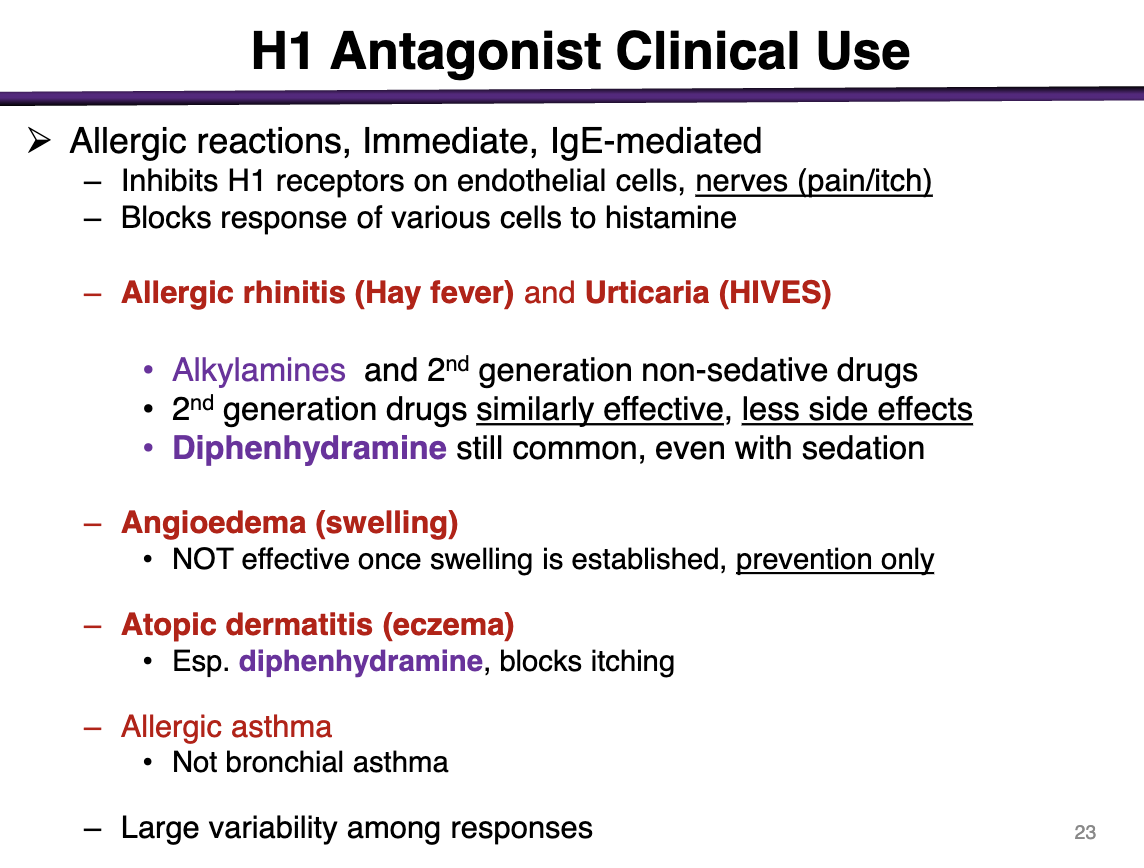
can you use an h1 antagonist for angioedema?
Not effective when swelling is established; preventative only
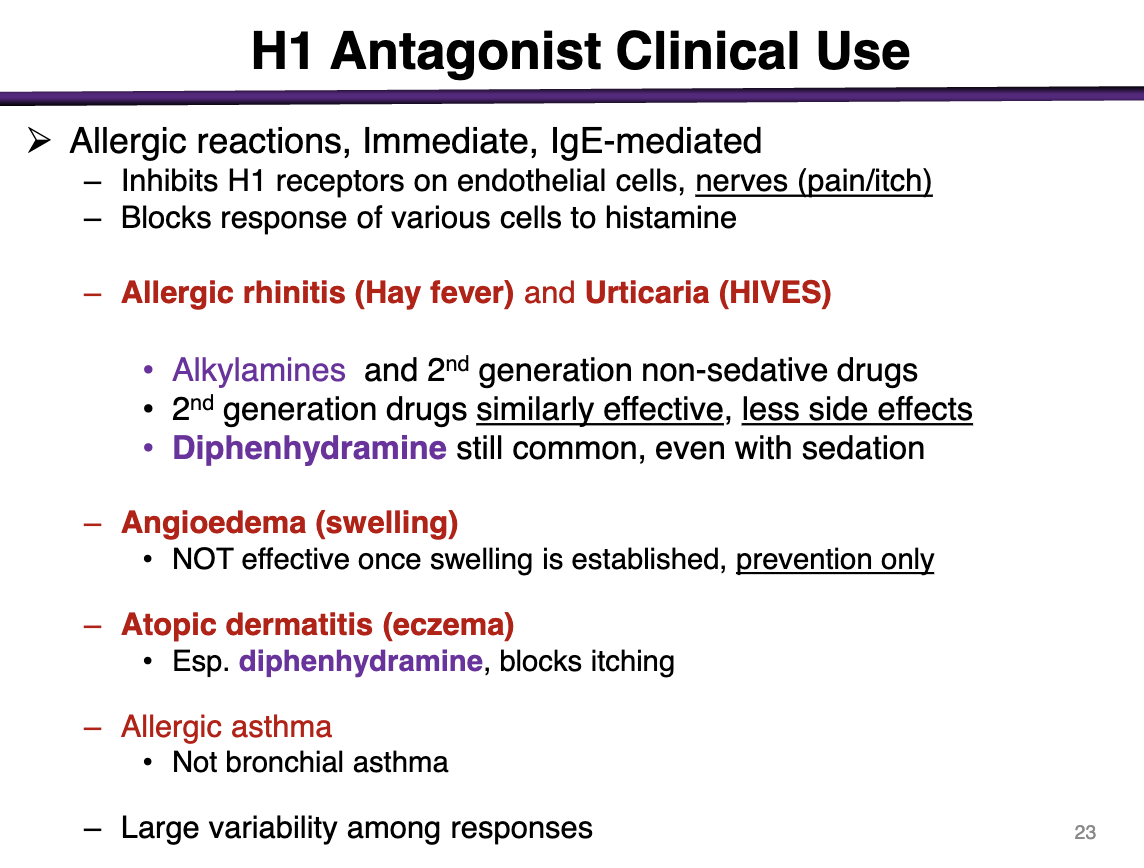
h1 antagonist use for atopic dermatitis (eczema)
diphenhydramine, blocks itching
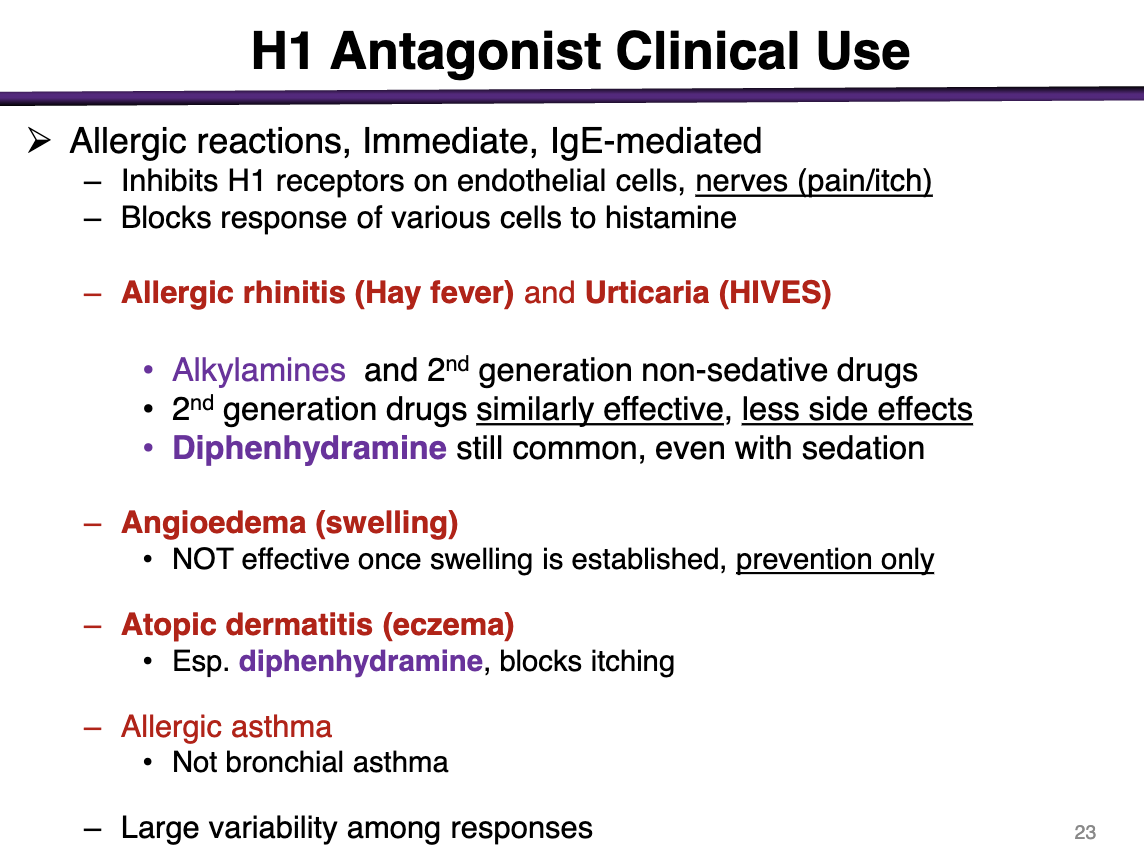
t/f h1 antagonists can be used for bronchial asthama
false; only allergic asthma
off-target effects from H1 antagonists are predominately mediated by
muscarinic blockade
Sedation is a signifiant side effect that is mediated in the CNS
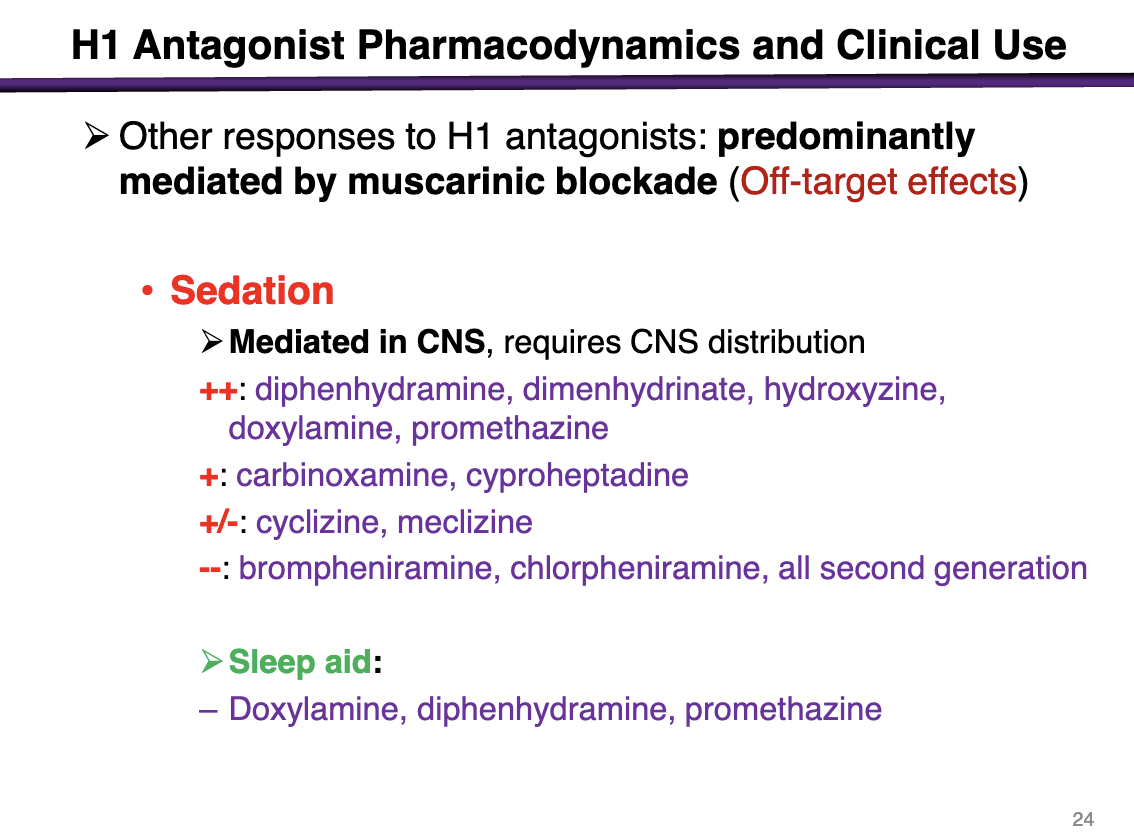
sedation effects of diphenhydramine, dimenhydrinate, hydroxyzine, doxylamine, promethazine
++ sedation potential
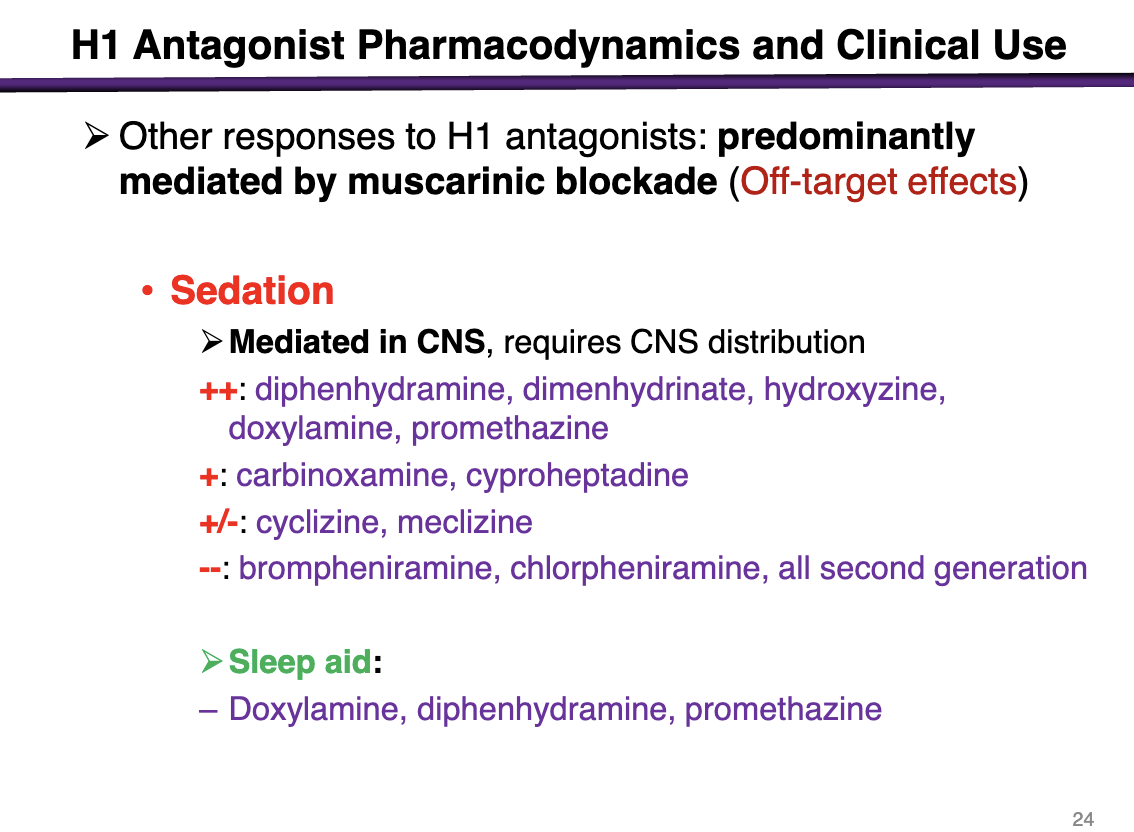
sedation effects of carbinoxamine, cyproheptadine
+
sedation effects of cyclizine, meclizine
+-
sedation effects of brompheniramine, chlorpheniramine, all second generation
- -
H1 antagonists that can be used as sleep aids
doxylamine, diphenhydramine, promethazine
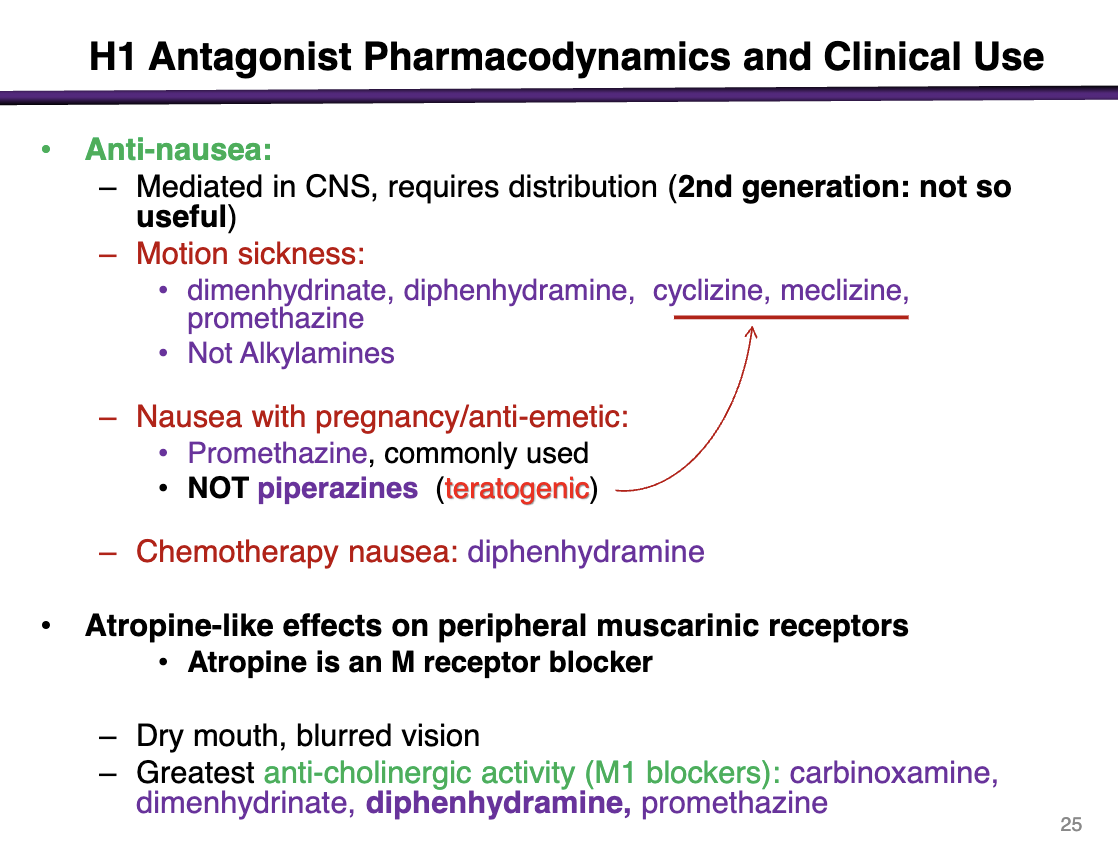
what h1 antagonists can you use for as anti-nausea medications
2nd generations are not useful due to limited CNS penetration
can be used for motion sickness, nausea with pregnancy/anti-emetic, chemotherapy nausea
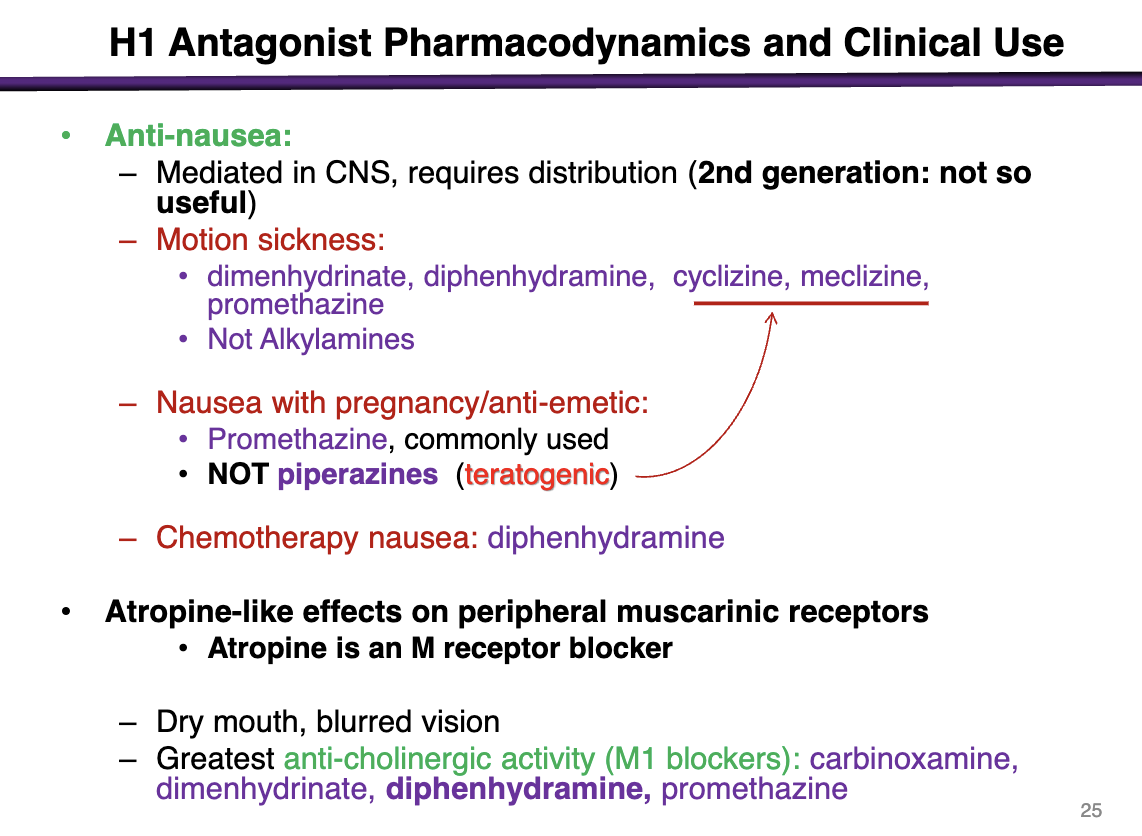
medications used for motion sickness
Can use these for motion sickness:
dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, cyclizine, meclizine, promethazine
Not alkylamines
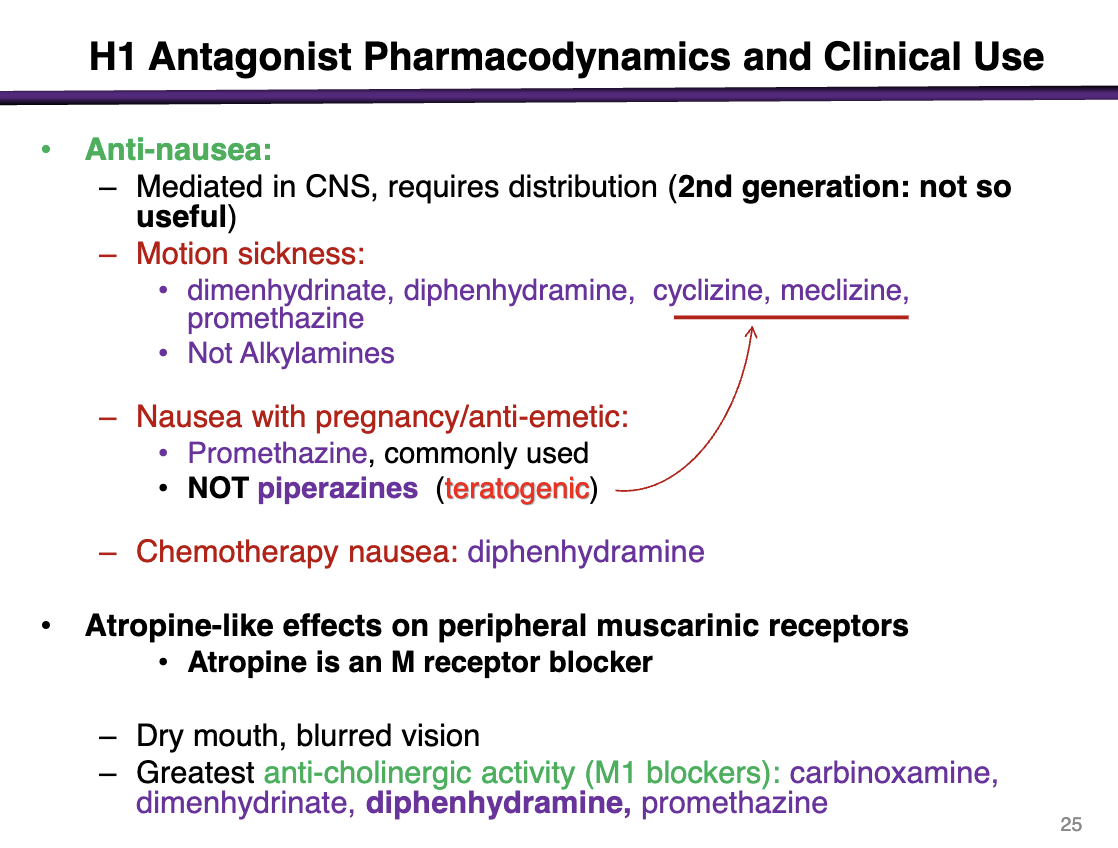
medications used for nausea with pregnancy
promethazine
NOT piperazines (teratogenic): cyclizine and meclizine
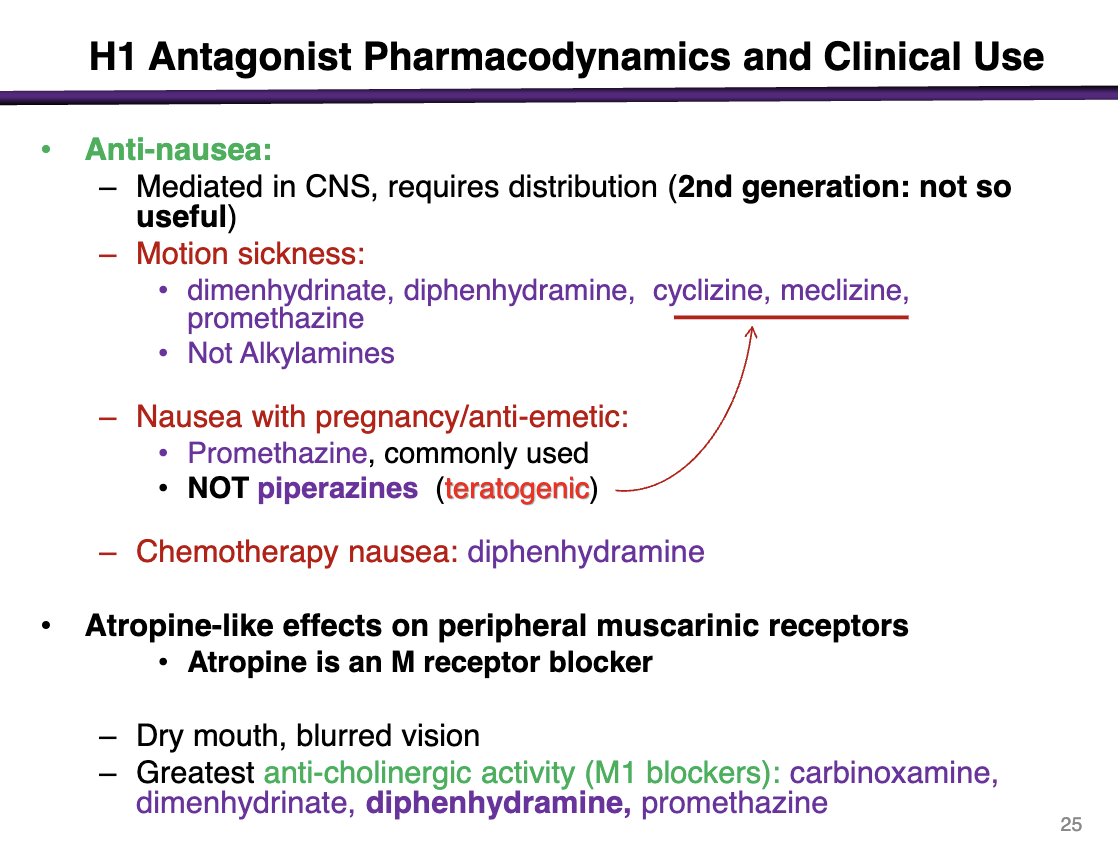
contraindication of cyclizine and meclizine
pregnancy; these are teratogenic
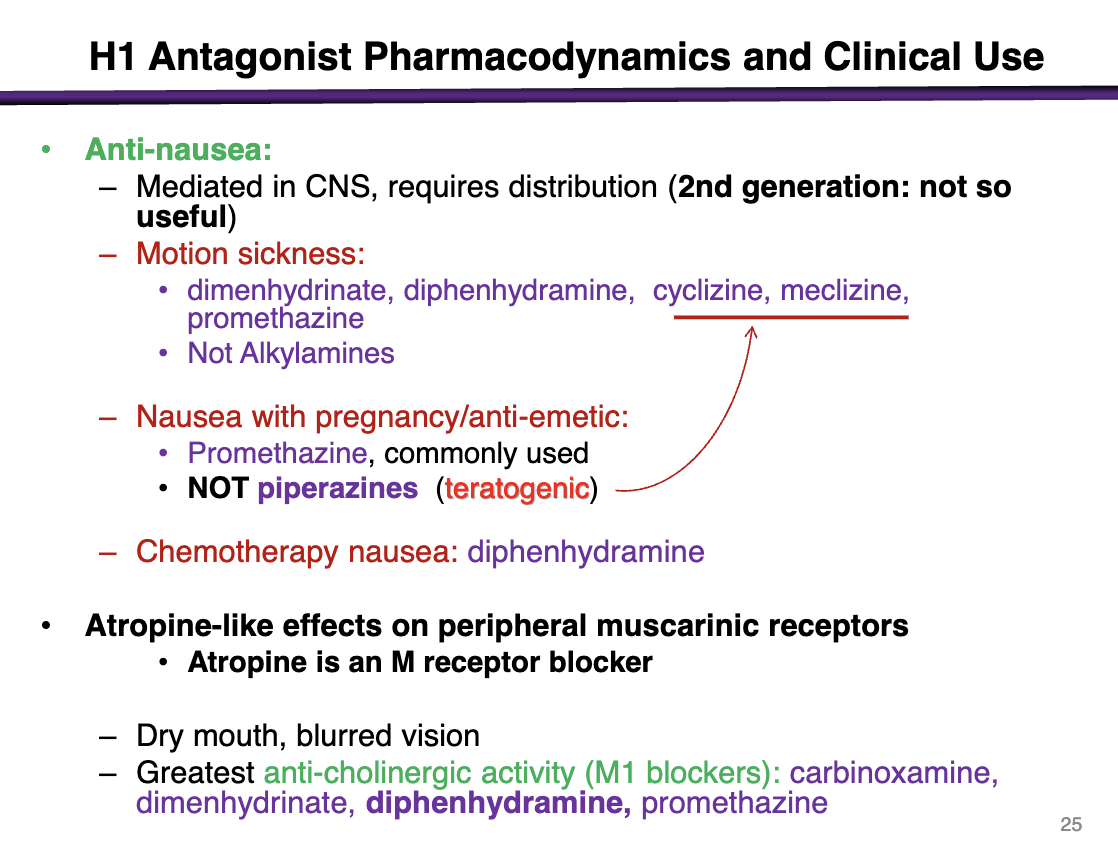
what are atropine-like effects on peripheral muscarinic receptors from H1 antagonists
Dry mouth, blurred vision
Greatest anti-cholinergic activity (M1 blockers)": carbinoxamine, dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, promethazine
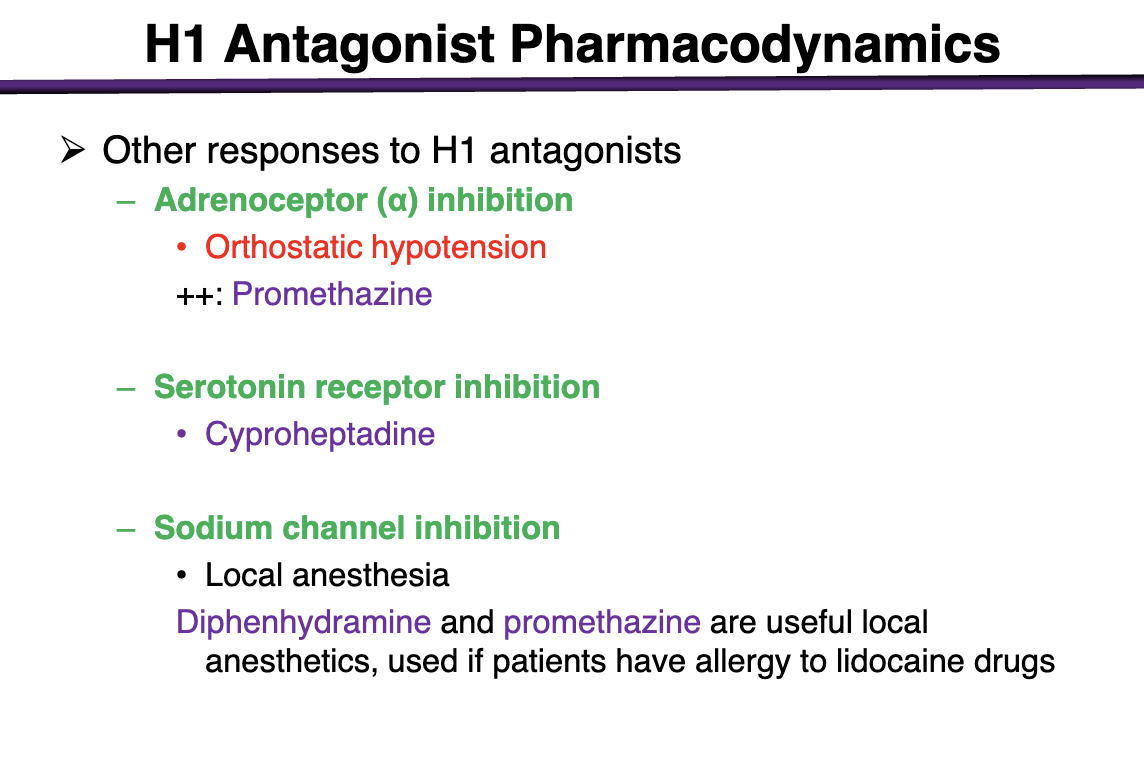
what drug has adrenoceptor a inibition
promethazine ++
can cause orthostatic hypotension
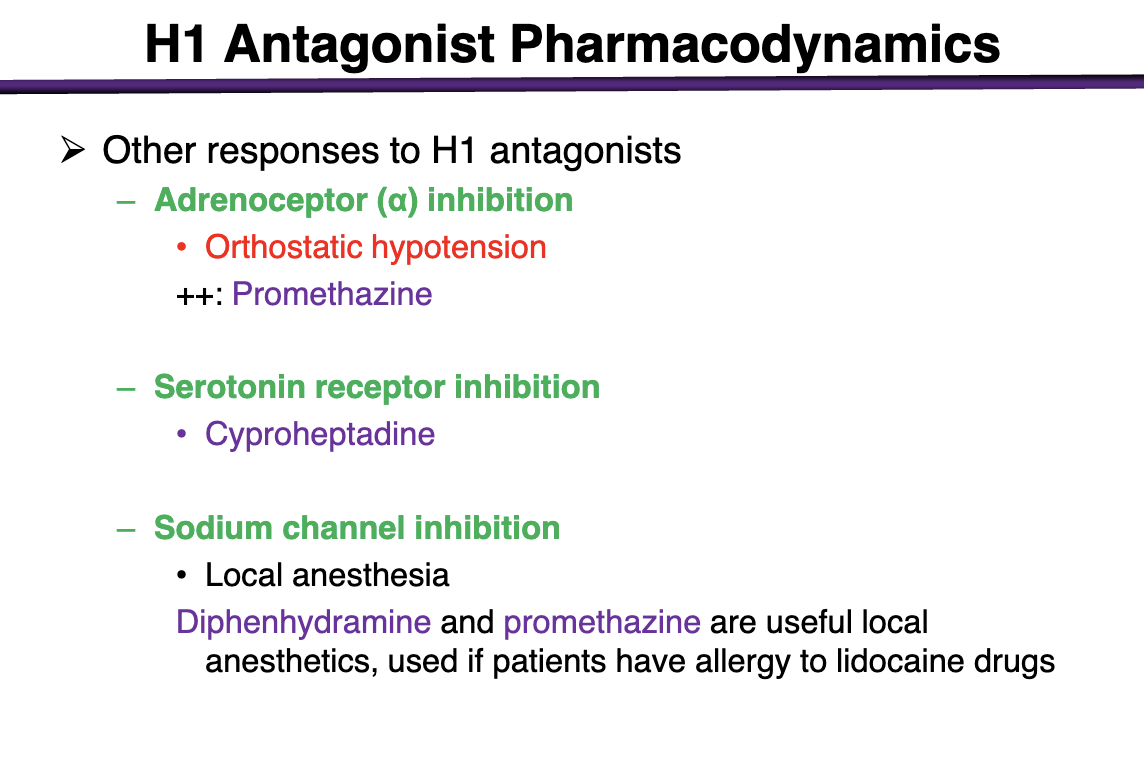
what can cause serotonin receptor inhibition
cyproheptadine
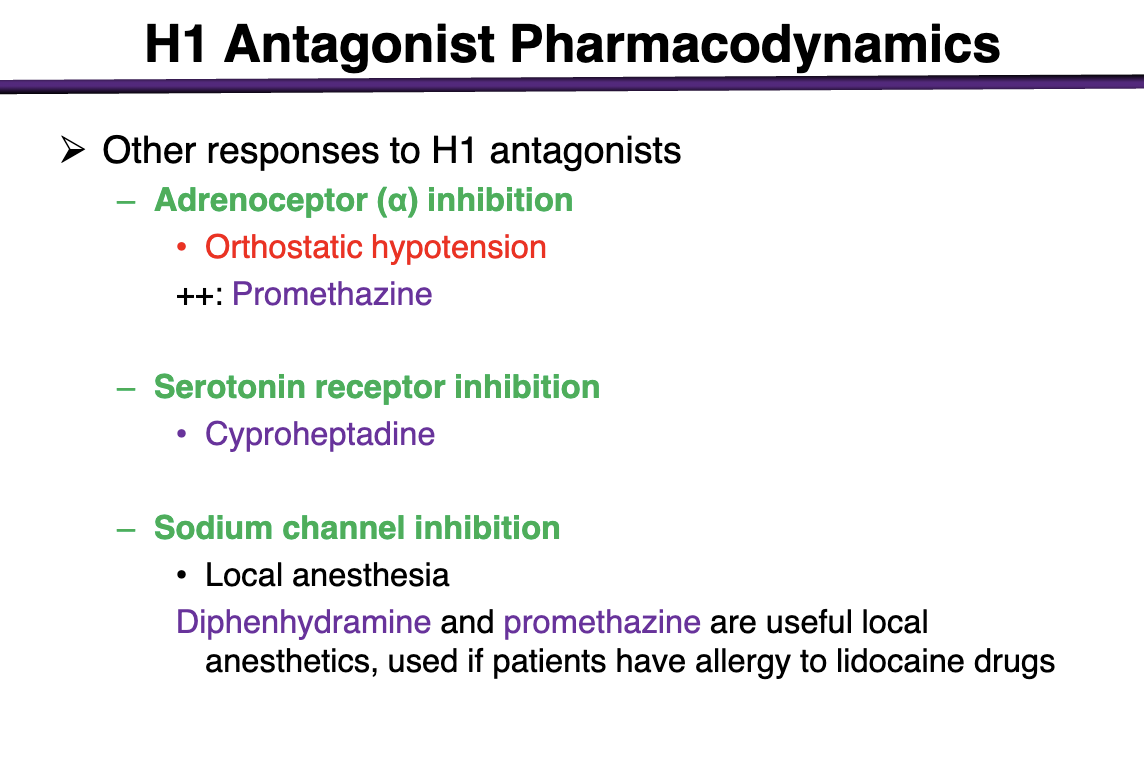
what h1 antagonist can cause sodium channel inhibition
local anesthesia
diphenhydramine and promethazine are useful local anesthetics if ppts have allergy to lidocaine drugs
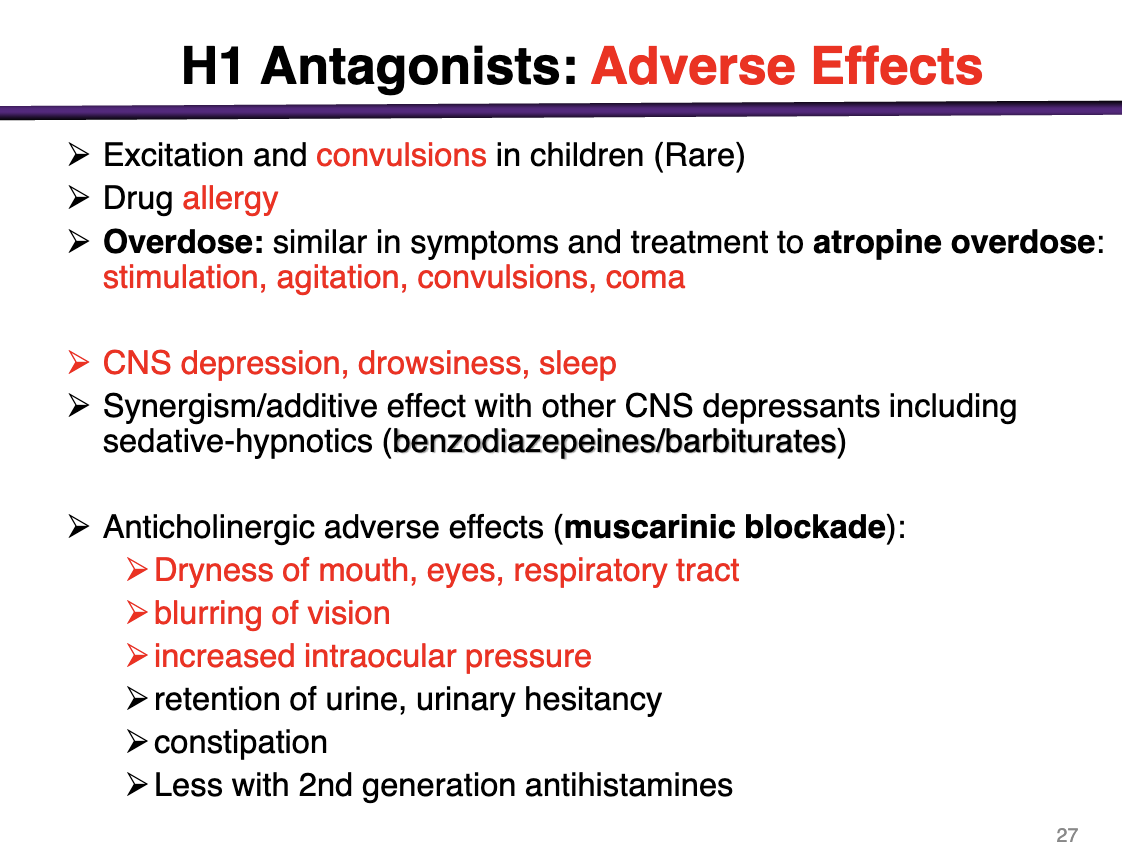
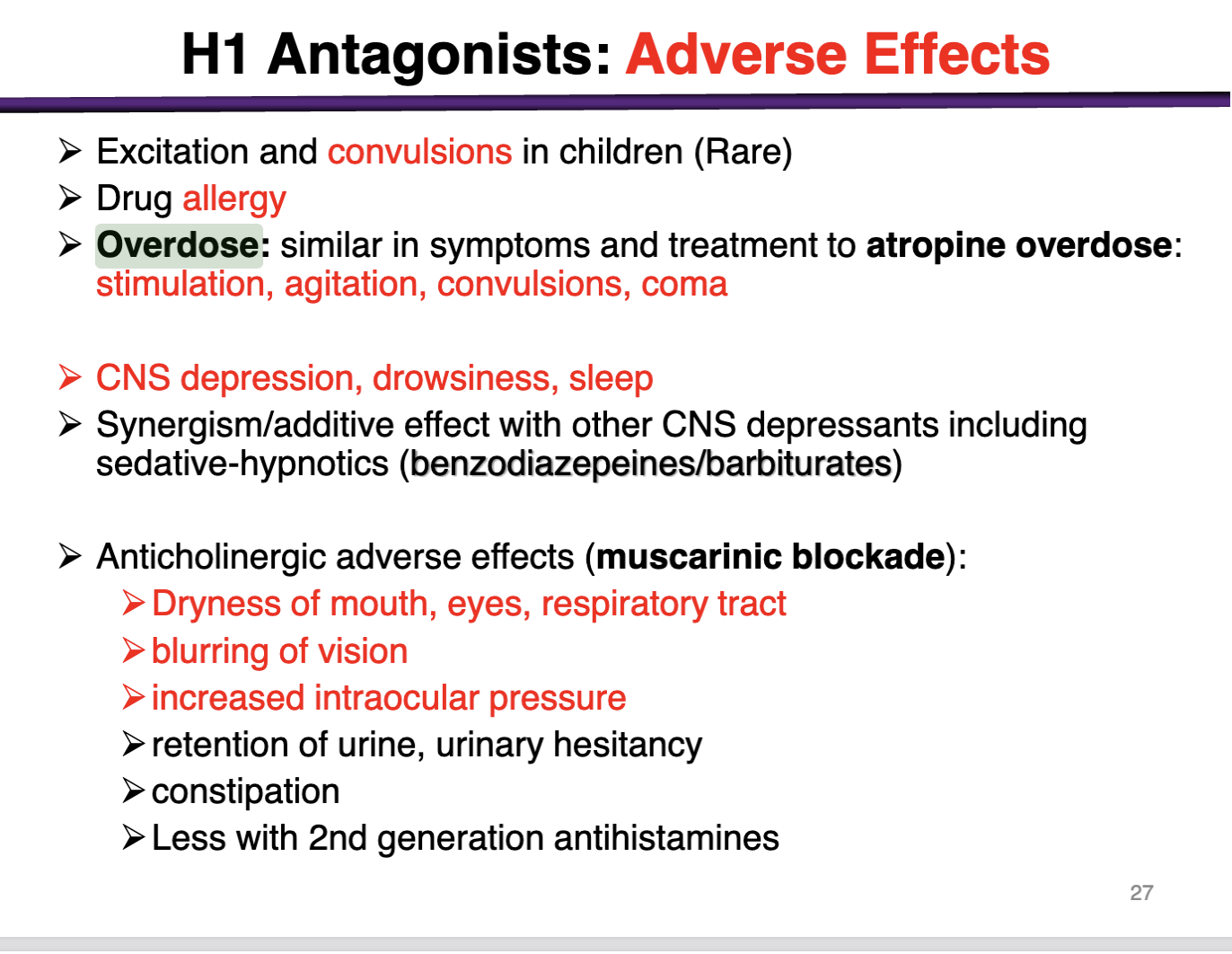
Adverse effects of H1 antagonists
excitation and convulsions in children (rare)
Drug allergies
Overdose: similar to atropine overdose: stimulation, agitation, convulsions, coma
CNS depression, drowsiness, sleep
synergism/additive effect seen with other CNS depressants
Anticholinergic adverse effects (muscarinic blockade)
Dry mouth, eyes, and respiratory tract, blurring vision, increase IOP, urinary retention, constipation
*less common with 2nd generation antihistamines
Histamine receptors are all
A. Ligand gated ion channels
B. G-protein coupled receptors
C. Expressed only in the periphery
D. Expressed only in the central nervous system
E. Activated by allergy drugs
B) G-Protein Coupled Receptors
Activation of beta-adrenergic receptors cause...?
A. Sedation
B. Vascular smooth muscle contraction
C. Heart muscle contraction
D. Bronchiolar smooth muscle contraction
E. Gastric acid secretion
A. Sedation
B. Vascular smooth muscle contraction
C. Heart muscle contraction (BETA)
D. Bronchiolar smooth muscle contraction
E. Gastric acid secretion
Which is not a normal physiologic function of histamine?
A. Wound healing
B. Control of gastric acid secretion
C. Neurotransmitter
D. Control immune response
E. Mood stabilization
E) Mood stabilization is NOT a function of histamine; it is a function of serotonin
The mechanism of anti-histamine overdose is....
A. Activation of H1 receptors
B. Inhibition of H1 receptors
C. Inhibition of H2 receptors
D. Inhibition of muscarinic receptors
E. Inhibition of adrenergic receptors
D. Inhibition of muscarinic receptors
Physiologic responses to H1 receptor activation following an injury include:
A. Vasoconstriction
B. Bronchodilation
C. Secretion of gastric acid
D. Activation of pain and itch sensory nerves
E. All of the above
D. Activation of pain and itch sensory nerves
C) Gastric acid is H2
Which of the following H1 antagonists has the lowest level of CNS distribution?
A. Diphenhydramine
B. Doxylamine
C. Promethazine
D. Fexofenadine
E. Dimenhydrinate
D. Fexofenadine
2nd generation