Chapter 6, Lesson 4: Skin Disorders
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 6, Lesson 3 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Skin cancer
Cancer caused by exposure to the UV rays of the sun, most often on the head, neck, and hands of fair-skinned people and the elderly; one of the most common and easily treated cancers
Types of skin cancer
Basal cell carcinoma (stratum basale)
Squamous cell carcinoma (stratum spinosum)
Malignant melanoma (melanocytes)
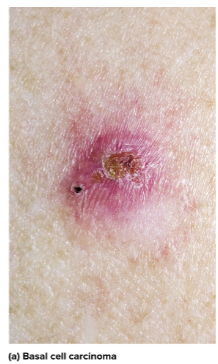
Basal cell carcinoma
The most common type of skin cancer in the stratum basale; forms a small shiny bump with central depression and is the least dangerous because it seldom metastasizes
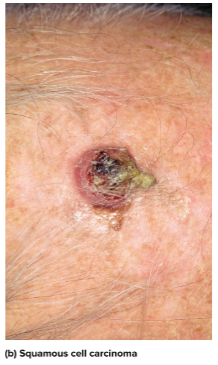
Squamous cell carcinoma
Arises from the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum on the scalp, ears, lower lip, or back of hand and can form a concave ulcer; early detection and removal can allow recovery but if untreated can spread to lymph nodes and become lethal
Malignant melanoma
Skin cancer that arises from melanocytes and is less than 5% of all skin cancer; can be removed if caught early but is fatal when metastasized—greatest risk is genetics in men, redheads, and severe sunburn victims in childhood
Burns
The leading cause of accidental death from extreme tempreatures, radiation, electricity, or acids; fluid loss, infection, or toxic eschar cause most deaths
Eschar
The burned, dead tissue that forms over a burn
Debridement
The removal of eschar
Burn classification
Made to the depth of tissue involvement; first, second and third degree
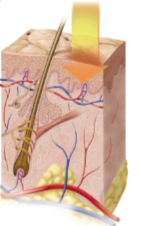
First-degree burn
Burns that only involve the epidermis that can cause redness, slight edema, and pain but heal within days
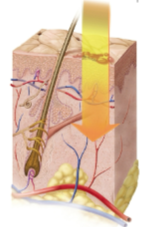
Second-degree burn (partial-thickness burn)
Burns that can involve part of the dermis and may appear red, tan, or white with blisters and pain; these take several months to heal and may leave scars
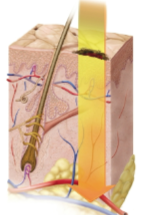
Third-degree burn (full-thickness burn)
Burns that involve all of the dermis and deeper tissue; they require skin grafts and need fluid replacement, infection control, and nutrition to recover
UV Rays
Rays from the sun that have the potential to cause cancer; sunscreens may provide protection but may provide a false sense of security and damage DNA through their chemicals
Skin graft
Taking skin and putting it on a burn (usually of the third degree)
Autograft
Skin grafts taking tissues from another location on the same person’s body
Split-skin graft
Taking the epidermis and part of the dermis from an undamaged area and grafting it elsewhere; is an autograft
Isograft
Using tissue from an identical twin in a skin graft
Homograft (allograft)
Using tissue from an unrelated person in a skin graft
Heterograft (xenograft)
Using tissue from another species in a skin graft
Other graft options
Using the amnion from afterbirth and artificial skin from silicone and collagen