BIO with David Exam I
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
An example of a testable scientific hypothesis about Ebola virus might be:
A) Ebola hemorrhagic fever is the most horrific disease to emerge in the past 30 years.
B) Ebola virus is not transmitted by aerosol droplets during the early stages of infection.
C) The National Institute of Health should fund efforts to construct portable field clinics in Africa.
D) When an effective vaccine is developed, it should be administered immediately to healthcare workers, but not yet to most individuals in West Africa.
B
One important difference between a mathematical theorem and a theory in the physical sciences is that a scientific theory:
A) is not based on quantitative data.
B) incorporates metaphysical philosophy.
C) is always true once formally, logically deduced.
D) can be rejected if later experiments do not support it.
D
What is not a universal characteristic of all living organisms?
A) They are capable of independent movement.
B) They have a complex structure.
C) They have metabolism.
D) They reproduce their structure.
A
Viruses, like living things:
A) consist of several, complex cells.
B) can transform matter and energy in complex pathways outside their host cells.
C) can actively grow and develop outside their host cells.
D) have genes which code for proteins
D
Life can be considered an emergent property of:
A) molecules
B) organelles
C) cells
D) an organism
C
Replicates in a scientific experiment:
A) receive identical experimental treatments
B) receive different doses of the dependent variable
C) are randomly assigned experimental treatments
D) are used solely to determine qualitative, not quantitative, data
A
Unlike living organisms, viruses:
A) do not replicate their structure
B) lack metabolism outside their host cells
C) lack genes made of nucleic acids
D) do not contain any proteins
B
This domain of living things has single, simple, prokaryotic cells and superficially resembles Bacteria in appearance, but differs in molecular biology and often lives in extreme habitats:
A) Amoebozoa
B) Fungi
C) Prions
D) Archaea
D
In this kind of chemical bond, two atoms share valence electrons
a. electrostatic
b. covalent
c. hyrophobic
d. hydrolytic
b
The kind of chemical bond in which one atom donates an electron to another atom, making the atoms positively and negatively charged, is called a ____ bond.
a. hydrophilic
b. covalent
c. nuclear
d. ionic
d
This element is often found as an ion in solution, or ionically bonded to chloride atoms, forming square crystals. It often preserves the ionic balance inside and outside of cells, and functions in nerve impulses in animals.
a. ammonium
b. sodium
c. lead
d. iodine
b
This element has atoms with the smallest mass (one atomic mass unit) and is a highly reactive gas. It is found in nearly all cellular molecules, as well as water.
a. helium
b. hydrogen
c. nitrogen
d. argon
b
This element makes up 78% of the atmosphere, and is found in many cellular molecules, especially amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It is NOT found in water, or in most carbohydrates.
a. nitrogen
b. oxygen
c. argon
d. bromine
a
Iron and zinc are metallic elements which are
a. found in some proteins, especially enzymes
b. not found in living cells, but are abundant in rocks
c. found in nearly all cellular molecules, such as carbohydrates and lipids
d. toxic to living cells, even at very low concentrations
a
Isotopes of the same element have atoms that differ from each other in the number of
a. protons
b. neutrons
c. electrons
d. neutrinos
b
Many properties of water, such as its cohesion, efficacy as a solvent, and high heat of vaporization result from
a. hydrogen bonds between molecules
b. spontaneous, hydrolytic release of protons
c. differences in mass between hydrogen and oxygen atoms
d. dissolution of non-polar compounds dissolved in water
A
pH measures the _____ in water or a solution made with water.
a. neutron
b. proton
c. hydride
d. electron
B
The pH of an alkaline solution, such as ammonia, might be
a. 4.5 to 5.5
b. 1.5 to 4.5
c. 9.0 to 12.0
d. 6.5 to 7.5
C
The pH of blood and many cells is about ____ only slightly higher than neutral pH.
a. 9.5
b. 5.5
c. 7.5
d. 3.5
C
Some hydrophilic compounds, like _____, have relatively many atoms connected by polar covalent bonds, especially between ______ and _______.
a. carbohydrates, O, H
b. oils, C, H
c. terpenoids, C, C
d. fats, P, N
A
Hydrophobic compounds, which mix poorly with water, have almost entirely non-polar covalent bonds between ___ and ___ or between ____ and _____ atoms.
a. C and C, C and H
b. S and H, P and H
c. C and O, N and H
d. O and H, O and N
A
Found in alcohols or carbohydrates, what is the name of this functional group, which has (–OH)?
a) methyl
b) ethyl
c) carboxyl
d) hydroxyl
D
What is the name of this functional group (–NH₂), often found in proteins and bases of DNA and RNA? It can act as a base in water.
a) aldehyde
b) amino
c) keto
d) methyl
B
What is the name of this functional group (–HC=O), found in some carbohydrates like glucose?
a) aldehyde
b) methoxy
c) amino
d) keto
A
What is the name of this functional group (–C=OOH), which is found in many organic acids, such as acetic acid (vinegar)?
a) aldehyde
b) ethyl
c) amino
d) carboxyl
D
What is this functional group (–C=O–C–), often found in carbohydrates?
a) amino
b) carboxyl
c) keto
d) aldehyde
C
What is the name of this functional group (–PO₄), often found in DNA and RNA?
a) sulfhydryl
b) phosphate
c) carboxyl
d) keto
B
Which functional group can have a positive charge when it picks up a proton from water?
a) amino
b) carboxyl
c) aldehyde
d) ethyl
A
Which functional group is non-polar, having no N, P, S, or O?
a) amino
b) sulfhydryl
c) methyl
d) keto
C
Viruses, like living organisms, always have
a. An external cellular membrane
b.Genetic material of nucleic acids
c. Their own ribosomes for protein synthesis
d.Metabolic pathways to produce energy
B
Prions, such as the one causing bovine spongiform encephalopathy,
a. Contain a small RNA genome
b. Are incorrectly folded proteins
c. Exhibit homeostasis
d. Are parasitic bacteria
e. Have a plasma membrane
B
This is NOT a property of ALL living things.
a. Their cells have nuclei and organelles
b. They show homeostasis and regulation
c. They have growth and development
d. They have genes composed of DNA
A
A scientific Theory
a. Is based on metaphysical evidence
b.May be falsified by new data
c. Is tested by qualitative, not quantitative, data
d.Represents an ethical or esthetic statement
B
Which element is not associated with most living cells?
A. Nitrogen
B. Phosphorous.
C. Copper.
D. Lithium
D
Which element is essential for most living things, but not abundant in cell molecules (a micronutrient)?
A. Boron
B. Carbon
C. Magnesium
D. Aluminum
C
Which element is a major constituent of nearly all cellular molecules?
A. Strontium.
B. Zinc
C. Silicon.
D. Hydrogen
D
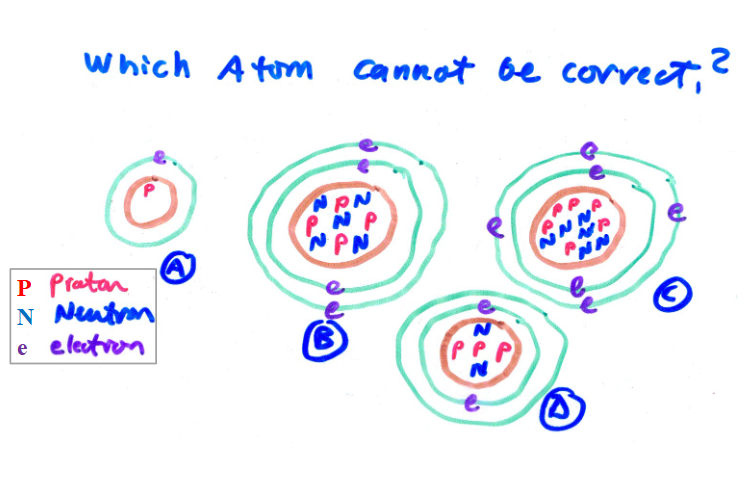
D

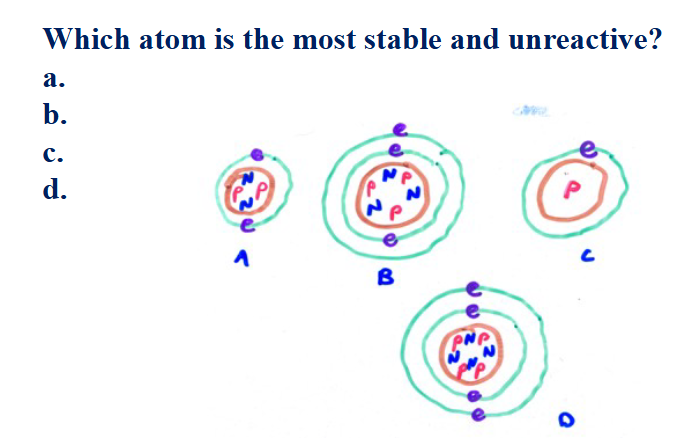
A
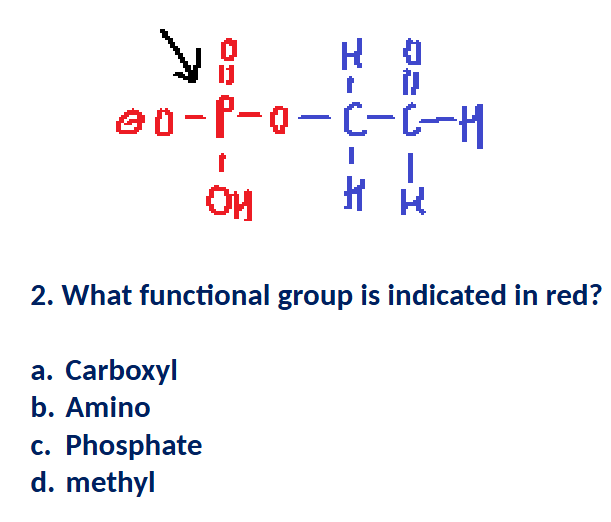
When dissolved in solution, molecules containing a _____ functional group can increase the pH of water by removing protons.
a. Amino
b. Nitrosyl
c. Carboxyl
d. Suflhydryl
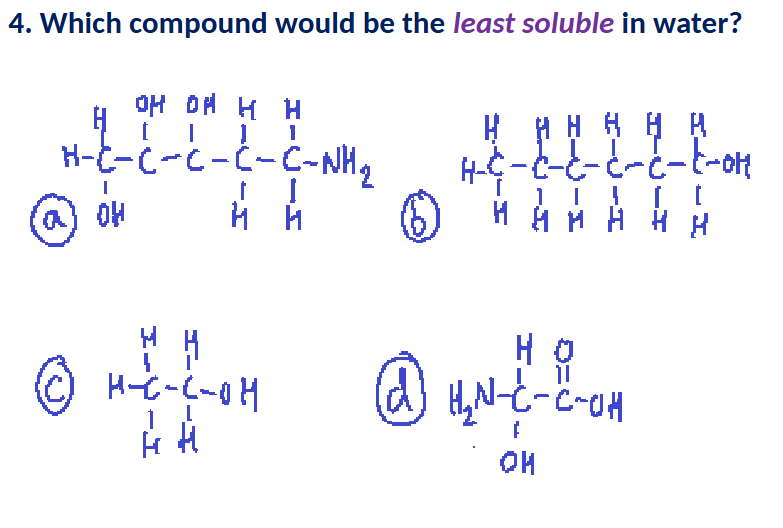
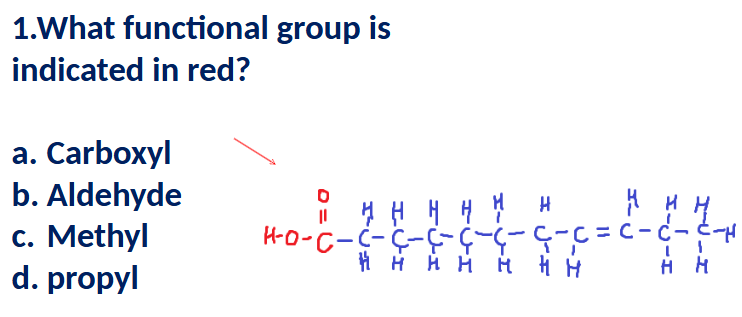
A
This functional group, consisting of just an oxygen
and a hydrogen atom, is found in all alcohols and
carbohydrates.
a. Aldehyde
b. Hydroxyl
c. Carboxyl
d. Keto
B
C
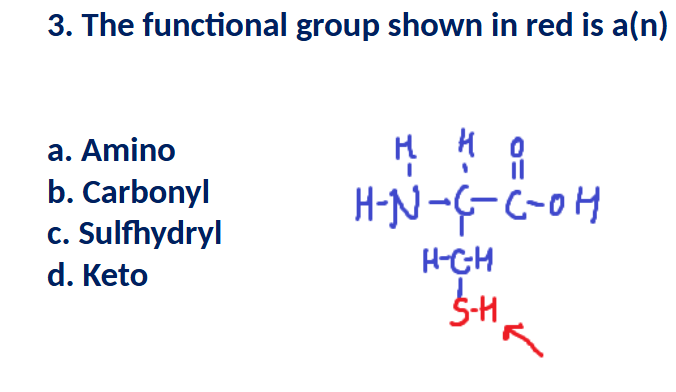
When dissolved in solution, molecules containing a
_____ functional group can decrease the pH of water by adding protons.
a. Amino
b. Nitrosyl
c. Carboxyl
d. Suflhydryl
C
C
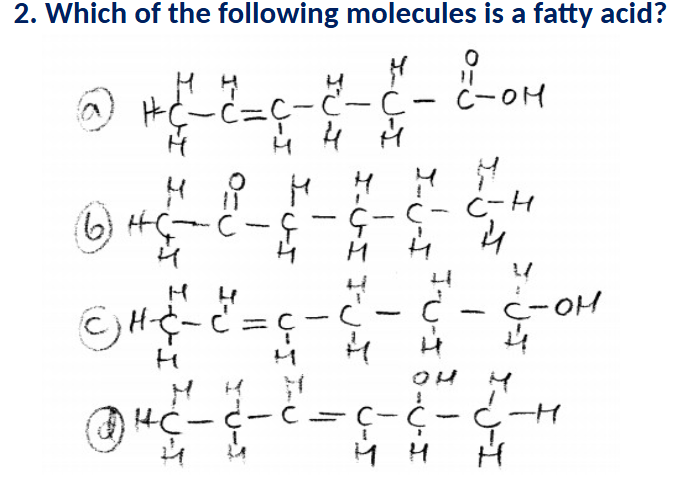
A (has a carboxyl on the end)
Which of the following functions is directly
performed by RNAs? (More than one possible).
a. Forming permeability barrier around cell
b. Transporting instructions to make a protein
c. Long-term energy storage in cells
d. Forming core of ribosome structure
e. Carrying amino acids during protein synthesis
f. Long-term storage of genetic information
B, D, E (A,C: lipids, E:DNA)
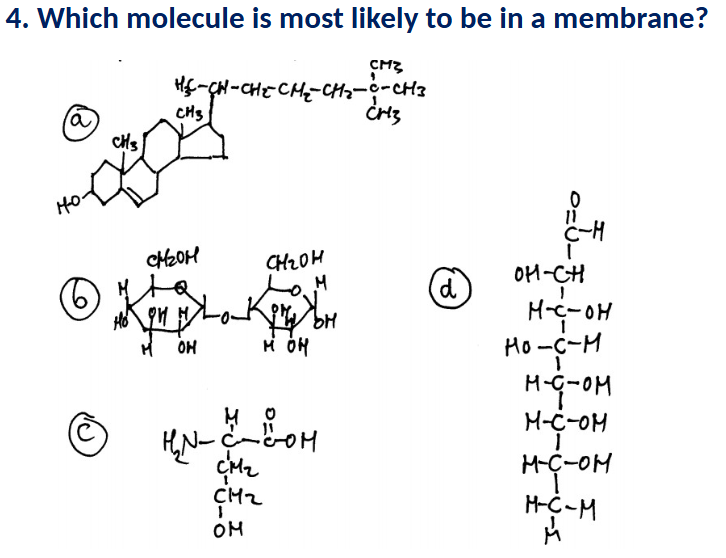
A (sterol)
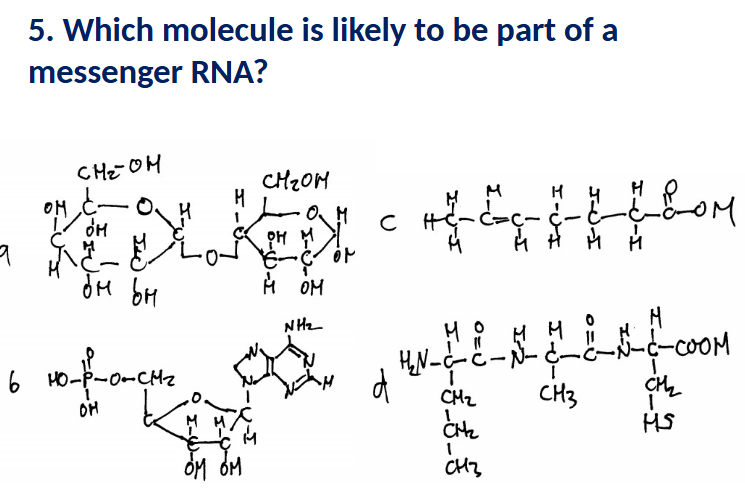
B
Two or more amino acids can be joined together by ------ linkages in a dehydration
synthesis reaction.
• A. glycosidic
• B. ester
• C. peptide
• D. hemiacetal
C
Proteins are constructed from amino acids in these structures in the cell.
• 1. Lysosomes
• 2. Nucleoli
• 3. Ribosomes
• 4. Mitochondria
3
What sorts of functional groups can be present in the side chains of various amino
acids? More than one apply.
A. Hydroxyl
B. Phosphate
C. Sulfhydryl
D. Carboxyl
E. Halide
F. Amino
G. Non-polar
H. Steroid
A, C, D, F, G
The secondary structure of a protein, such as alpha-helices and beta sheets, is formed by
• A. Hydrogen bonding between peptide amino and carboxyl
groups.
• B. Hydrophobic interactions of non-polar side chains
• C. ionic bonding between opposite charged side-chains
• D. Van der Waals interactions between several polypeptides.
A
A typical prokaryotic cell, such as a bacterium, might be _____ micrometers in diameter.
a. 0.025
b. 1.0
c. 25.0
d. 250.0
Which structures would be present in a prokaryotic cell
(bacterium)? (More than one.)
a. Chromosome
b. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
c. Plasma membrane
d. Nuclear envelope
e. Golgi complex
f. Ribosomes
g. Cilia
h. microfilaments
i. Flagella
A, C, F, I

B

D

A

B
Highway 299 is a major route for trucks
carrying manufactured goods throughout
the state.
a. plasma membrane
b. smooth ER
c. microtubules
d. peroxysome
C
Edgar just ate a slice of pizza, which is now being digested in his stomach.
a. Mitochondrion
b. Lysosome
c. Rough ER
d. microfilaments
B
SJ remediation service receives potentially toxic chemicals from factories and treats them chemically to render them non-toxic.
a. Smooth ER
b. Golgi complex
c. Microtubules
d. Plasma membrane
A
Allegrata Inc. has a system of gargantuan warehouses “gratification centers” where goods from manufacturers are shipped to various destinations by an overworked staff.
a. Rough ER
b. Mitochondria
c. Chloroplasts
d. Golgi
D
Within the records department of Newco, Inc. are the designs for all the company’s products and standard operation procedures.
a. Chromosomes
b. Mitochondria
c. Peroxysomes
d. Apicoplasts
A
These non-cellular, infectious, replicating entities consist of a nucleic acid genome surrounded
by proteins.
a. Ribozymes
b. Bacteria
c. Viruses
d. Prions
C
A mathematical theorem, unlike a scientific theory,
a. Cannot be falsified once it is logically proved
b. Must be tested in a laboratory experiment
c. Can be refuted if later experimental observations do not support it
d. Is not based on logical deduction
A
Living cells have this in common with viruses.
a. Genes made of nucleic acids
b. A complex cellular structure
c. Metabolism
d. Ribosomes
A
A scientific hypothesis, unlike an informal guess,
a. Must be accepted as true
b. can be inferred logically from mathematical definitions
c. is testable in an experiment
d. is unlikely to be true
C
Bacteria and _____ are examples of prokaryotic cells.
a. Fungi
b. Eukarya
c. Merokarya
d. Archaea
D
These are infectious, protein, disease agents which lack genes or metabolism. Some cause fatal spongiform encephalopathies of humans, sheep, cattle, and deer.
a. Bacteria
b. Apicomplexa
c. Microsporozoa
d. Prions.
D
In these chemical bonds, two atoms exchange an electron, one becoming negatively charged,
the other positive.
a. Covalent
b. Dipolar
c. Divalent
d. Ionic
D
The term “_______” would best describe the kind of chemical bond between the atoms of
oxygen and hydrogen in a water molecule.
a. Polar covalent
b. Diatomic
c. Ionic
d. Hydrophobic
A
Approximately 20% of the atmosphere is composed of this reactive gas, which also comprises much of the mass of carbohydrates.
a. Carbon
b. Nitrogen
c. Sulfur
d. Oxygen
D
This macronutrient element is often included in plant fertilizer, and it is especially abundant
in the “backbone” of DNA and RNA.
a. Potassium
b. Phosphorous
c. Iron
d. Calcium
B
As you write the answer with your graphite pencil, consider this element, which graphite is
made of , which found in nearly all cellular molecules, whose atoms can form four covalent
bonds, often to itself, forming chains or rings.
a. Carbon
b. Nitrogen
c. Sulfur
d. Hydrogen
A
Hydrophobic molecules have mostly atoms of these elements.
a. O, H
b. S, O
c. C, H
d. P, H
C
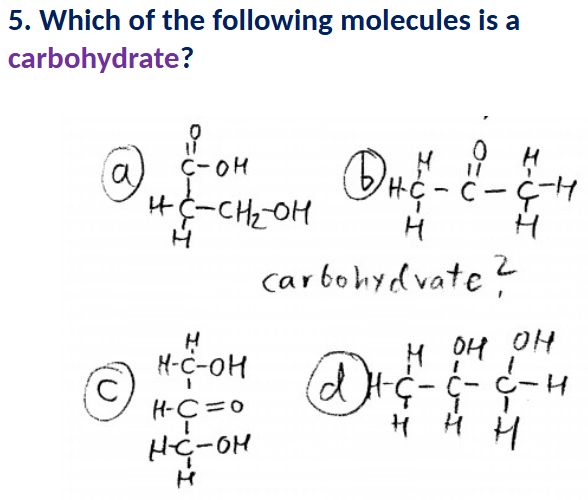
Carbohydrates have many of these functional groups, which tends to make them quite
hydrophilic.
a. Phosphate
b. Hydroxyl
c. Sulfhydryl
d. Amino
B
The nuceleotide base thymine in DNA is replaced by the base ____ in RNA.
a. Cytosine
b. Guanine
c. Alanine
d. Uracil
D
These rancid-smelling molecules have a long (10-25 atom) chain of carbon and hydrogen
atoms, with a carboxyl group at one end.
a. Fatty acids
b. Nucleotide bases
c. Mercaptans
d. Monosaccharides.
A
This polysaccharide is found in the cell walls of plants. Ruminant mammals which consume
plant matter enriched in it have bacteria which produce enzymes to digest it. Otherwise, it is not
directly digestible to mammals.
a. Glycogen
b. Chitin
c. starch
d. cellulose
D
This object would be slightly larger (less than twice the distance) than the limit of resolution
of a light microscope.
a. An amoeba cell 240 m in diameter
b. A viral cell 70 nm in diameter
c. A bacterial cell 0.3 m in width
d. A ribosome 25 nm in diameter
C
Microfilaments, made of _______, are found in muscle cells, and also
a. Actin, support the plasma membrane
b. Filamentin, move chromosomes during cell division
c. Spectrin, join cell membranes together in seamless junctions
d. Ankyrin, move eukaryotic flagella in a rotating motion.
A
This cytoskeletal structure, also found in cilia, serves as tracks for the movement of vesicles
within cells.
a. Intermediate filaments
b. The desmoglea
c. Microtubules
d. Smooth endoplasmic reticula
C
Cells of all living things contain this structure.
a. Nucleus
b. Lysosome
c. Mitochondria
d. Plasma membrane
D
The lysosome serves directly to
a. Digest material brought into the cell
b. Provide a source of ATP for growth
c. Synthesize proteins from amino acids
d. Store fats an polysaccharides
A
To directly see sub-cellular structures less than 0.1 m is size, it is best to use a ____
microscope.
a. Epifluorescence light
b. Bright-field light
c. Scanning x-ray
d. Transmission electron.
D
This structure in some eukaryotic cells is the site of energy production during photosynthesis
and of carbon dioxide fixation.
a. Chloroplast
b. Mitochondrion
c. Nucleolus
d. Peroxisome
A
This structure is involved in the finishing and sorting of glycoproteins which are destined to
be exported (secreted) from the cell.
a. Smooth ER
b. Golgi complex
c. Peroxisome
d. Lysosome
B
This sub-cellular structure, found in all life, is the site where polypeptides are constructed
from amino acids. It is composed of two subunits, ach made of proteins and RNA.
a. Ribosomes
b. Carboxysomes
c. Desmosomes
d. Nucleoli
A
Entropy is best described as
a. Energy held in chemical bonds
b. Ability of a compound to release heat
c. The temperature of a molecules in solution
d. Relative disorder
D
The separation of positive and negative charges across the plasma membrane of neurons,
which occurs during nerve impulses, is a kind of
a. Diffusion
b. Electrical work
c. Mechanical work
d. Biosynthetic work
B
The main function of ATP in living organisms is to
a. Transport energy within cells to endergonic reactions
b. Serve as a long-term depository for energy
c. Serve as a short term energy source for exothermic reactions
d. Carry energy between tissues of plants and animals
A catalyst, such as an enzyme, can speed up a chemical reaction by
a. Reacting directly with the substrate and becoming permanently converted into a product
b. Reducing the overall free energy change of the reaction
c. Increasing the overall free energy change of the reaction
d. Reducing the activation energy of the reactio
In phagocyctosis,
a. The plasma membrane folds inward around a particle outside the cell
b. Small molecules flow directly through a pore in the membrane
c. A transporter spins within the membrane like a revolving door
d. Molecules pass directly through the membrane phospholipids
A
This molecule can pass through a cell membrane by direct diffusion
a. Sodium ions
b. Oxygen
c. Proteins
d. DNA
B
Diffusion always moves molecules
a. From high to lower concentration
b. By using ATP hydrolysis to power the process
c. From the inside of a cell to the outside
d. Suspended within a gaseous matrix
A
Molecules can be moved across a membrane from low concentration on one side to higher
concentration on the other side by
a. indirect diffusion
b. channel-mediated diffusion
c. active transport
d. indirect transport
C
This process occurs in vigorously exercising skeletal muscle, which may lack adequate
oxygen, producing lactate. It regenerates the NAD+ required for glycolysis.
a. lactogenesis
b. fermentation
c. gluconeogenesis
d. product-level phosphorylation
B