Knee and Distal Femur
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the longest, strongest, and heaviest bone in the body?
femur
Explain the shape of the femur
slightly convex anteriorly; slants medially 10-15o, placing medial condyle lower than the lateral
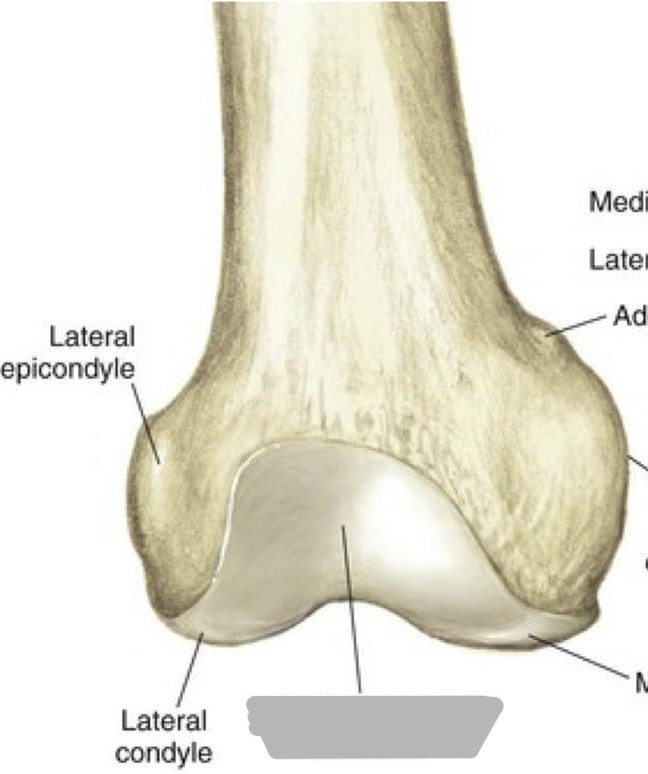
Explain the location of the condyles of the femur
distal, rounded, non-palpable aspect of the bone
medial is larger and more inferior
Explain the location of the epicondyles of the femur
palpable prominences above the condyles
medial is larger
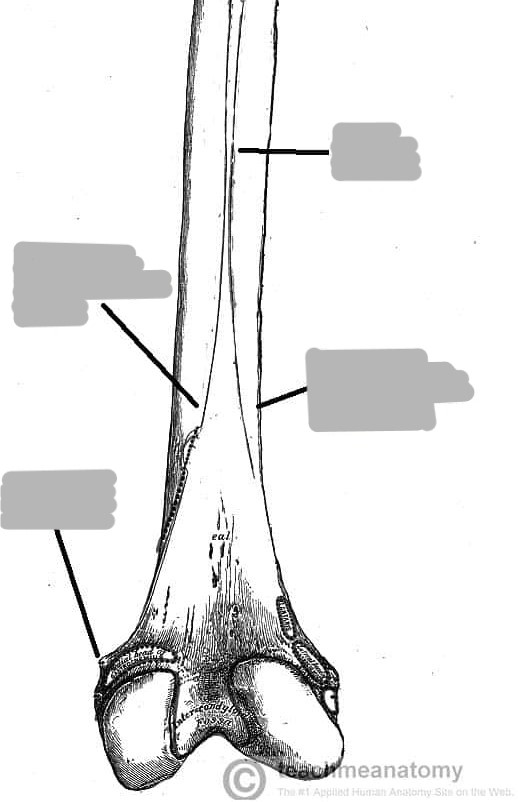
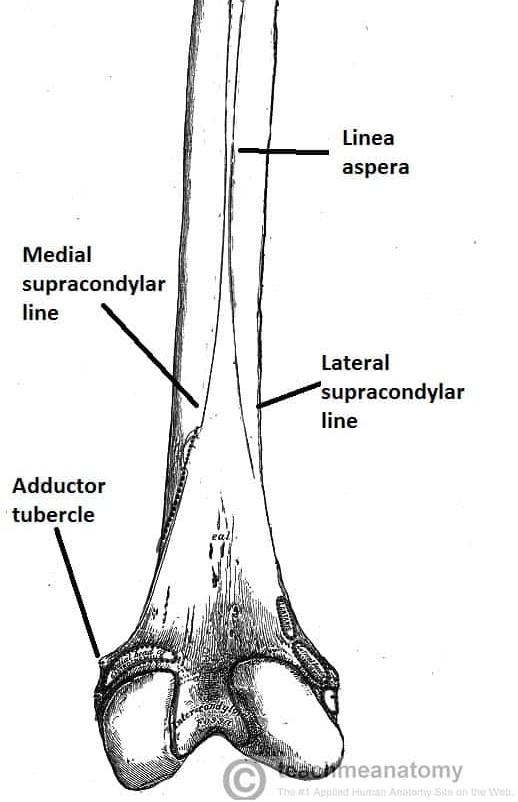
Explain the location of the adductor tubercle
non-palpable prominence on the superior posterolateral aspect of the medial epicondyle
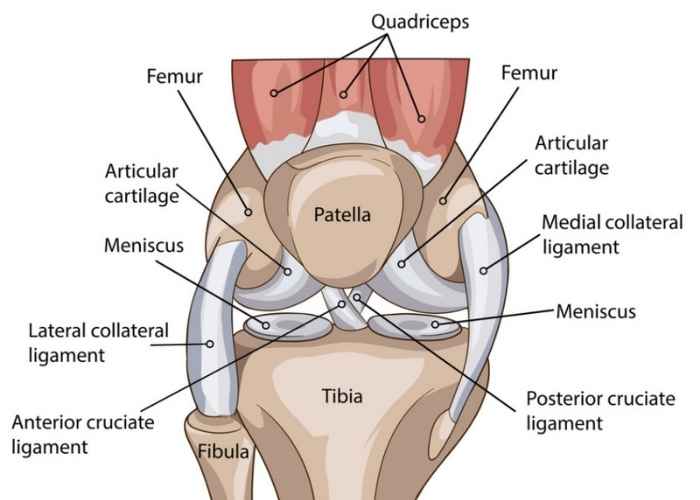
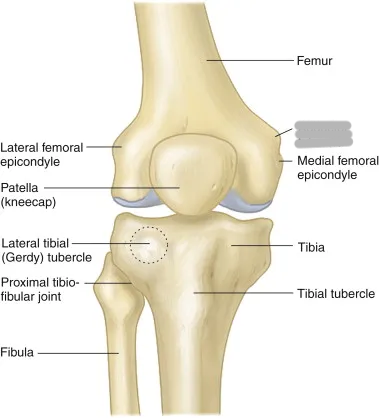
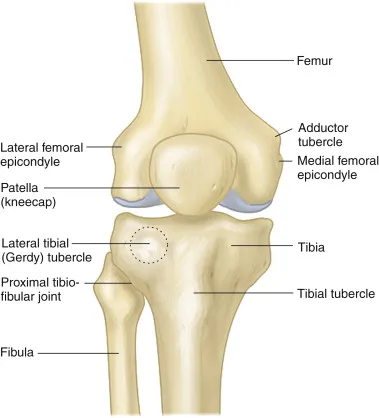
Explain the intercondylar fossa/notch (location and what it is)
deep depression on the posterior distal surface of the femur between the condyles
Explain the linea aspera (location and what it is)
bony ridge on posterior femur that divides into the medial and lateral supracondylar lines
Explain the popliteal surface (location and what it is)
triangular surface superior to the intercondylar fossa on the posterior distal femur
margin formed by medial and lateral supracondylar lines
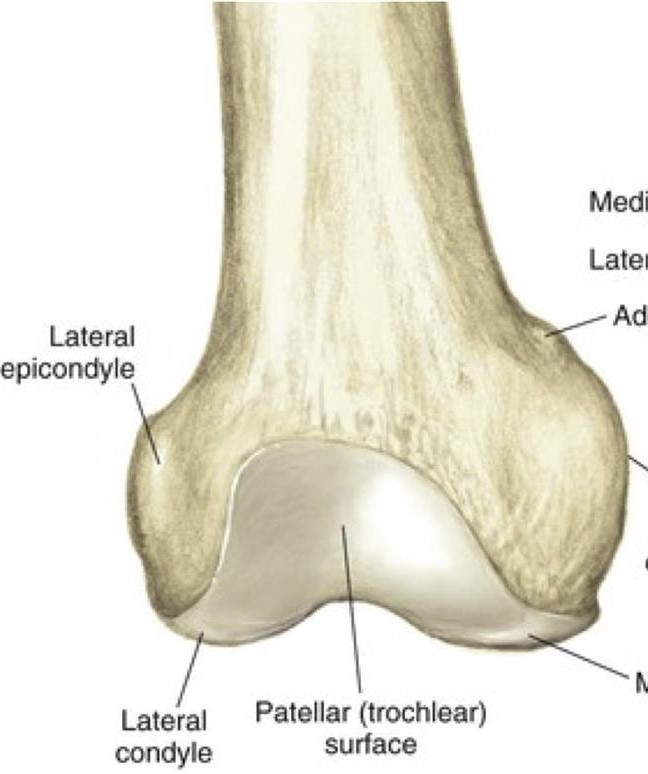
Where does the patella sit on the femur?
the patellar surface/intercondylar sulcus/trochlear groove
Which condyle of the femur has a more anterior projection (appears higher in sunrise view)?
lateral
What is osteoarthritis?
joint degeneration due to age; causes pain, stiffness, swelling, limited movement; treated by arthroplasty
Why should the leg be flexed only 20-30o for a lateral knee?
to open the patellofemoral joint space as much as possible
Why is a 5-7o cephalic angle used for a lateral knee?
to superimpose the condyles
What causes distal condylar rotation?
lower leg parallel to IR or not using cephalic angle
What causes anterior/posterior knee rotation?
condyles not superimposed
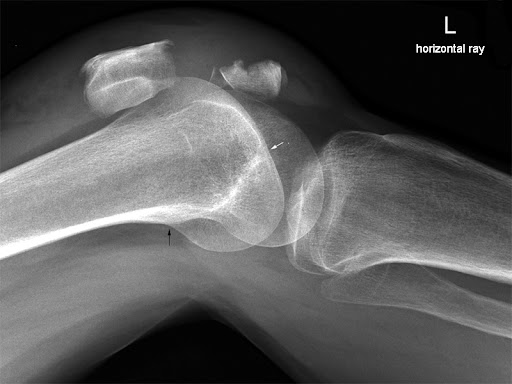
What kind of rotation is this?
distal condylar rotation
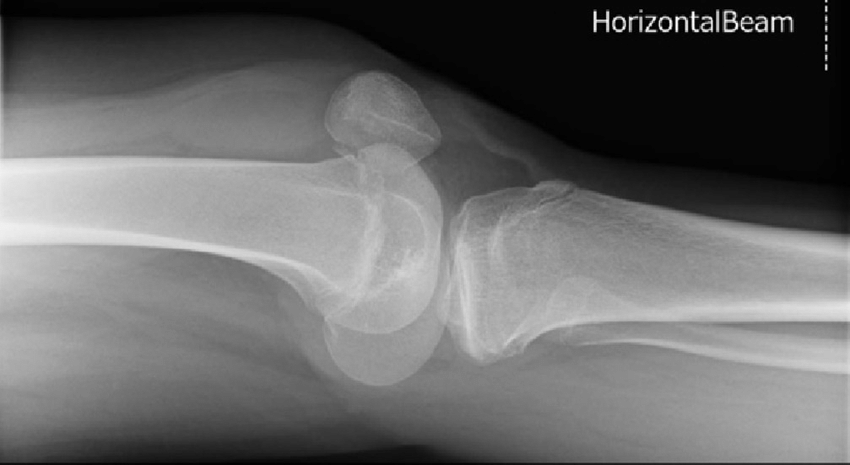
What kind of rotation is this?
anterior/posterior rotation
What does a trauma lateral knee demonstrate?
air fluid levels and effusion into the joint space
The external oblique of the knee demonstrates:
patella slightly off lateral aspect of femur
fibula superimposed over lateral aspect of tibia
demonstrates medial side
The internal oblique of the knee demonstrates:
patella slightly off medial aspect of femur
proximal tibiofibular joint is demonstrated
demonstrates lateral side
What does the Settegast method demonstrate?
the patellofemoral joint
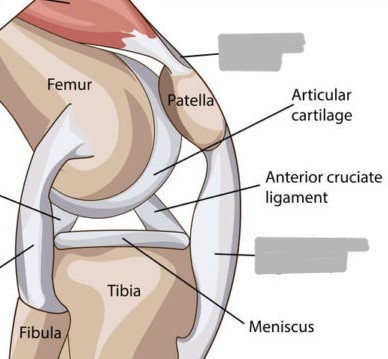
What are the 4 ligaments of the knee and their functions?
medial collateral ligament (MCL): prevents lateral sliding
lateral collateral ligament (LCL): prevents lateral sliding
posterior cruciate ligament (PCL): prevents anterior sliding
anterior cruciate ligament (ACL): prevents posterior sliding
What type of joint is the femorotibial joint?
diarthrodial, synovial, hinge
What type of joint is the patellofemoral joint?
diarthrodial, synovial, gliding
What are the 2 major bursae of the knee joint?
suprapatellar (anterior femur)
infrapatellar (anterior tibia)
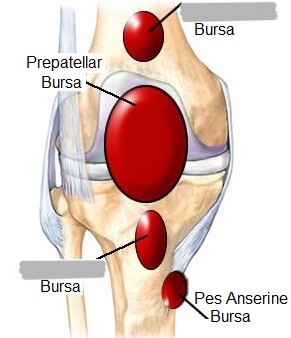
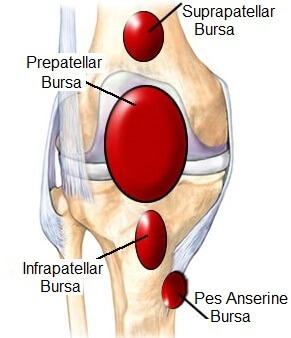
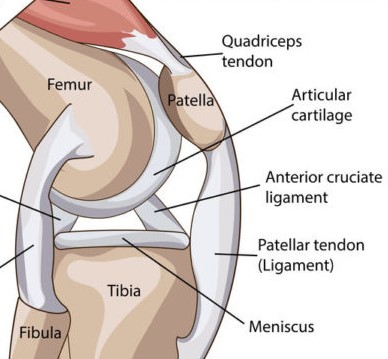
What are the anterior tendons/ligaments that connect the patella to the leg?
patellar ligament extends from apex of patella to tibial tuberosity
quadriceps tendon attaches to the base of the patella and the quadriceps femoris muscle
Explain Osgood Schlatter’s disease
patellar ligament becomes inflamed and pulls away from the tibial tuberosity due to overuse
occurs most commonly in in athletic, adolescent boys
Explain the Baker’s cyst
popliteal cyst found in conditions where there is a chronic swelling of the semimembranous bursa (arthritis, meniscus injuries, ligamentous injuries)
Explain varus
lower leg points medially (bow legged) due to narrowing of the medial joint space
Explain valgus
lower leg points laterally (knock kneed) due to narrowing of the lateral joint space
What is the flabella?
sesamoid bone located in the knee area (varies in size and shape, and occurs in 25% of people)