electron configuration
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
draw a diagram of how the waves look going down an EM spectrum
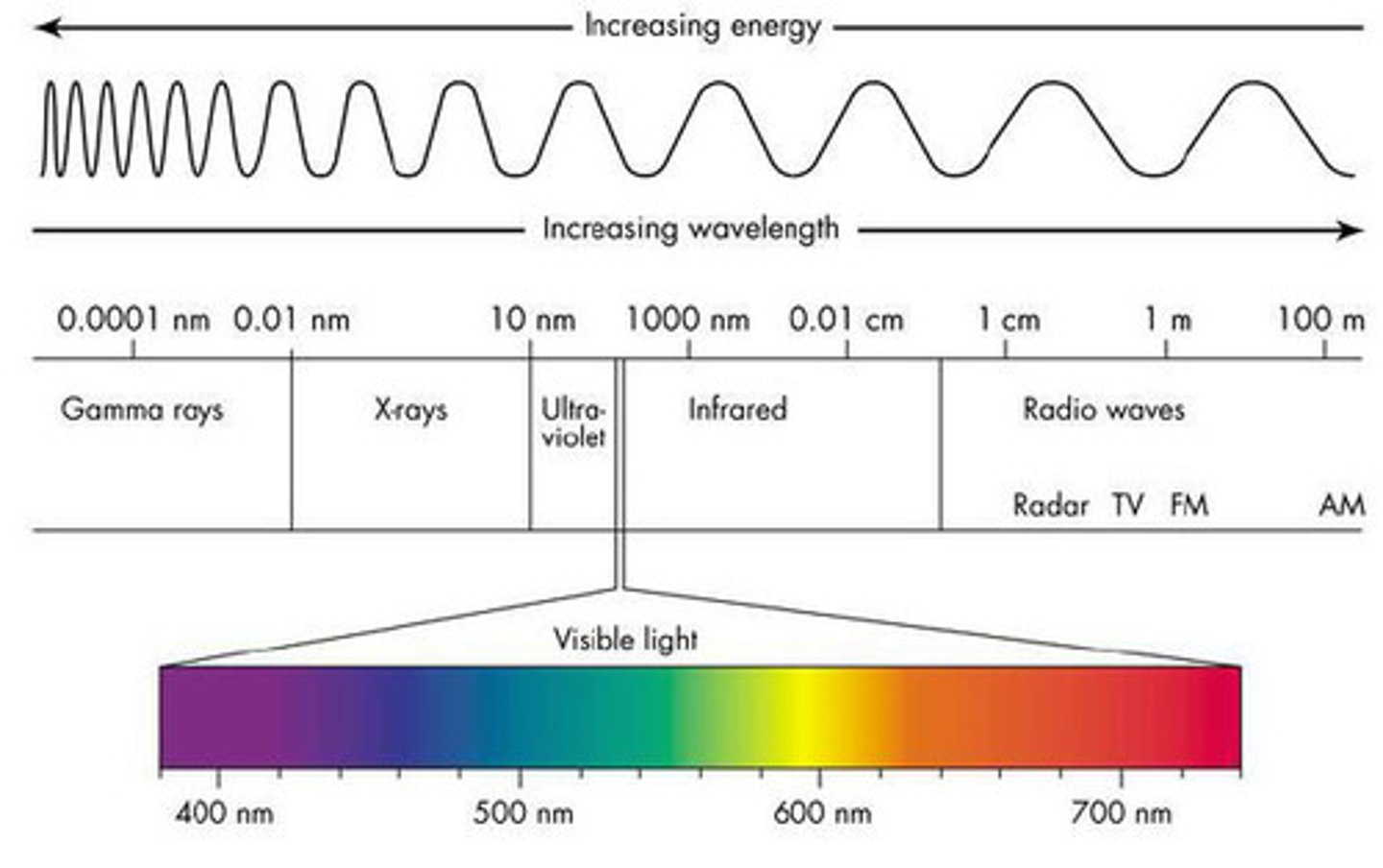
what side of the em spectrum has the longest wave length give colour and radiation
red, radiowaves
what side of the em spectrum has the shortest wavelength give colour and radiation
purple
gamma
if something has a short wavlength whats its frequency like
high frequenecy
so long wavelength =
low frequency
name the relationship between frequency and wavelength
inversely proportional
3 most damaging wavelengths
ultra violet
x rays
gamma rays
what is the speed of all EM waves
speed of light or c
3.00 x 10^-8
whats the equation linking wavespeed frequency and wavelength
c = fλ
what is a continuous spectrum
a spectrum which shows all the wavelengths/ frequencies/ energies of light
what does a continuous spectrum look like
RAINBOW (so like tom)
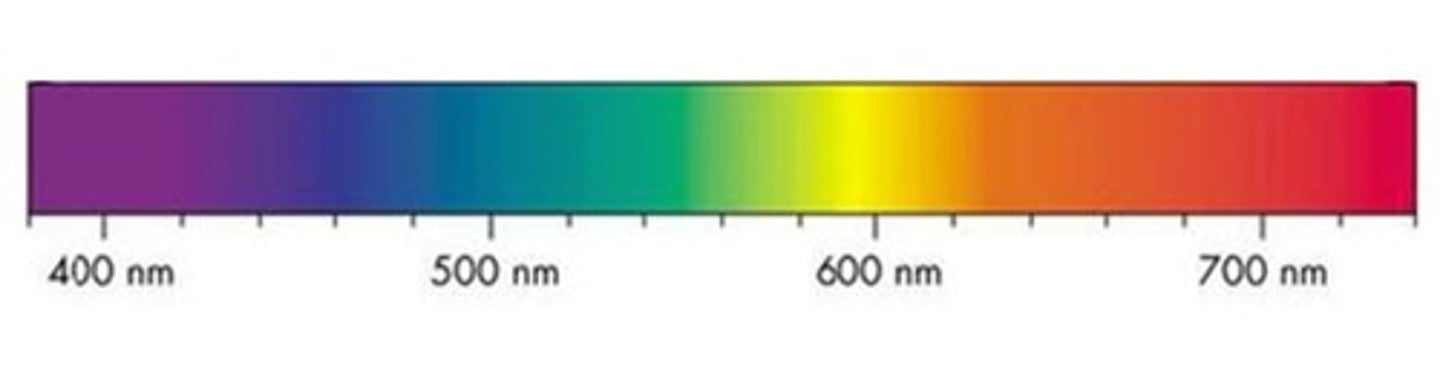
so what does a line spectrum show
specific wavelengths/frequencies of light
what are two types of line spectra
absorption and emission
what does an absorption spectrum show
frequency/wavelength shown when a substance (usually a gas) has white light shone through it to show us what wavelengths and frequencies of light it absorbs
what does an absorption spectrum look like
its all rainbow and it has black lines to show whats being absorbed

what does an emission spectrum show
the wavelegths/frequencies of light emitted when white light is shone on a substance
what does an emission spectrum look like
all black with rainbow lines

why do substances emit or absorb light
light is made up of photons = energy stores
when light shines on an object it will absorb certain photons of light
which excites the atom's electrons on the energy levels (shells) causing them to jump up one or more energy levels
when the electrons jump back down from the energy level it causes them to emit photons of light
why do the electrons jump back down
the atom is not stable
can electrons jump more than one shell
yes
the bigger the jump =
the greater the energy of the photon
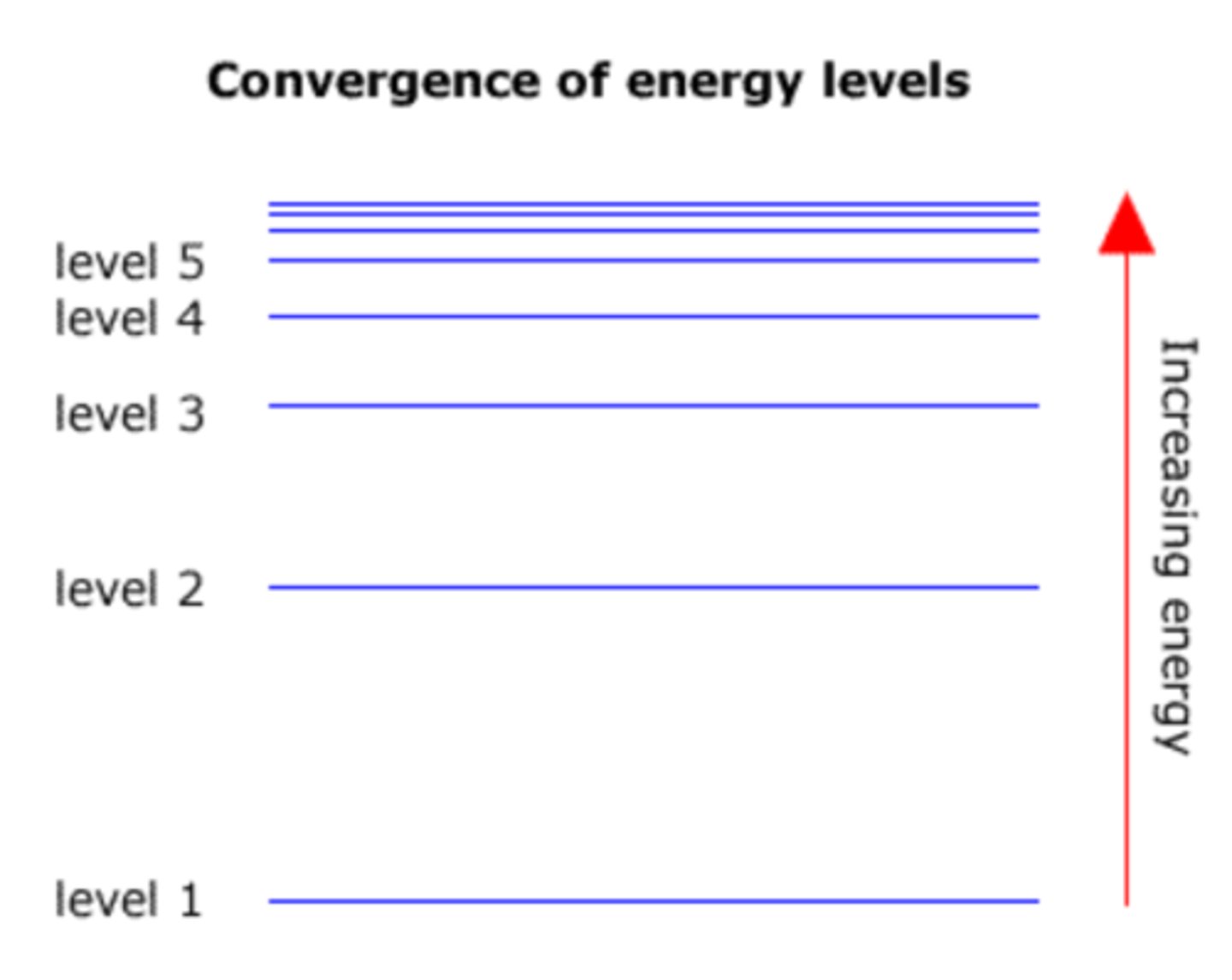
how is the line spectra of hydrogen specific to hydrogen
the lines converge the same as the energy levels
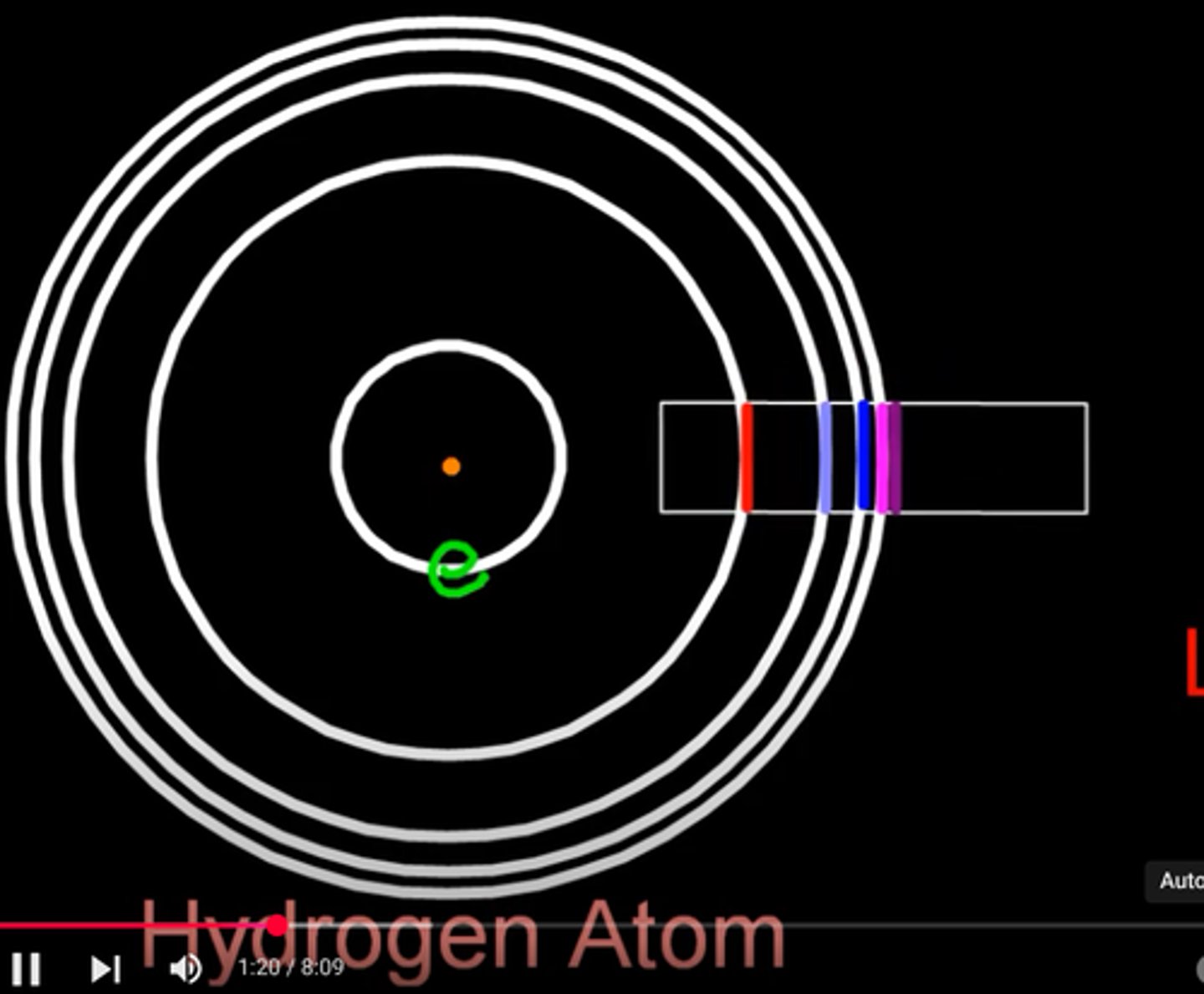
so how does the line emission spectrum of hydrogen come about
white light is shone at a hydrogen atom, exciting electrons causing them to jump energy levels, when they return to their original energy level they release a photon of light which is shown on the hydrogen emission spectrum
what are principle quantum numbers
the numbers on the energy levels of an atom
n = 1 first shell
n = 2 second shell
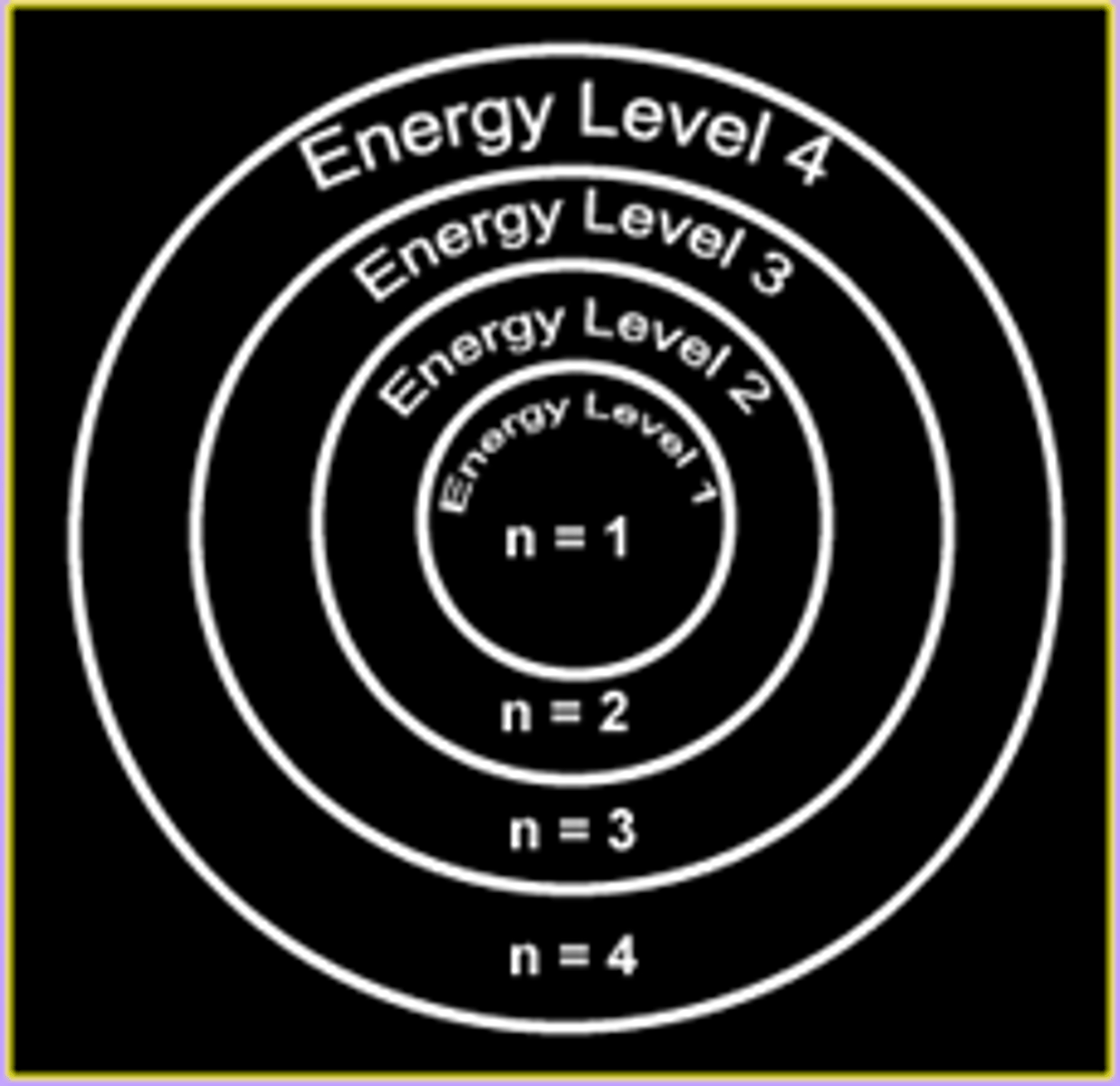
two key words to describe energy levels of atoms
1. converging: at higher energy levels (further from the nucleus) the shells get closer together
2. concentric: they are within one another
describe the lines on the emission spectra of hydrogen
converging at higher energies
how does the photon of light released differ when electrons jump back down
depending on which energy level it jumps BACK DOWN TO
e.g if it jumps down to n=1 its different photon of light then if it jumps back down to n=2
where does the electron jump back down to if its got the highest energy
or where does the highest energy jump come back down to
n=1
if an electron jumps back down to n=1 what kind of photon is it
it is a UV photon
why is UV the highest energy
not a damn clue - just learn it
if an electron jumps back down to the n=2 energy level what kind of photon is it
visible light
if an electron jumps back down to the n=3 energy level what kind of photon is it
infared
how do you ionise an atom
by exciting an electron enough to just pop off the atom
what two things can be worked out using the main energy levels
the maximum number of electrons
the number of orbitals
how to work out the maximum number of orbitals from main energy level number
n^2
e.g work out the orbital number of the 5th main energy level
n=5
5^2 = 25
how to work out the maximum number of electrons
2n^2
e.g work out the max number of electrons on the 4th main energy level
n=4
4x2 = 8
8^2 = 64
what are the 4 orbitals
s, p, d, f
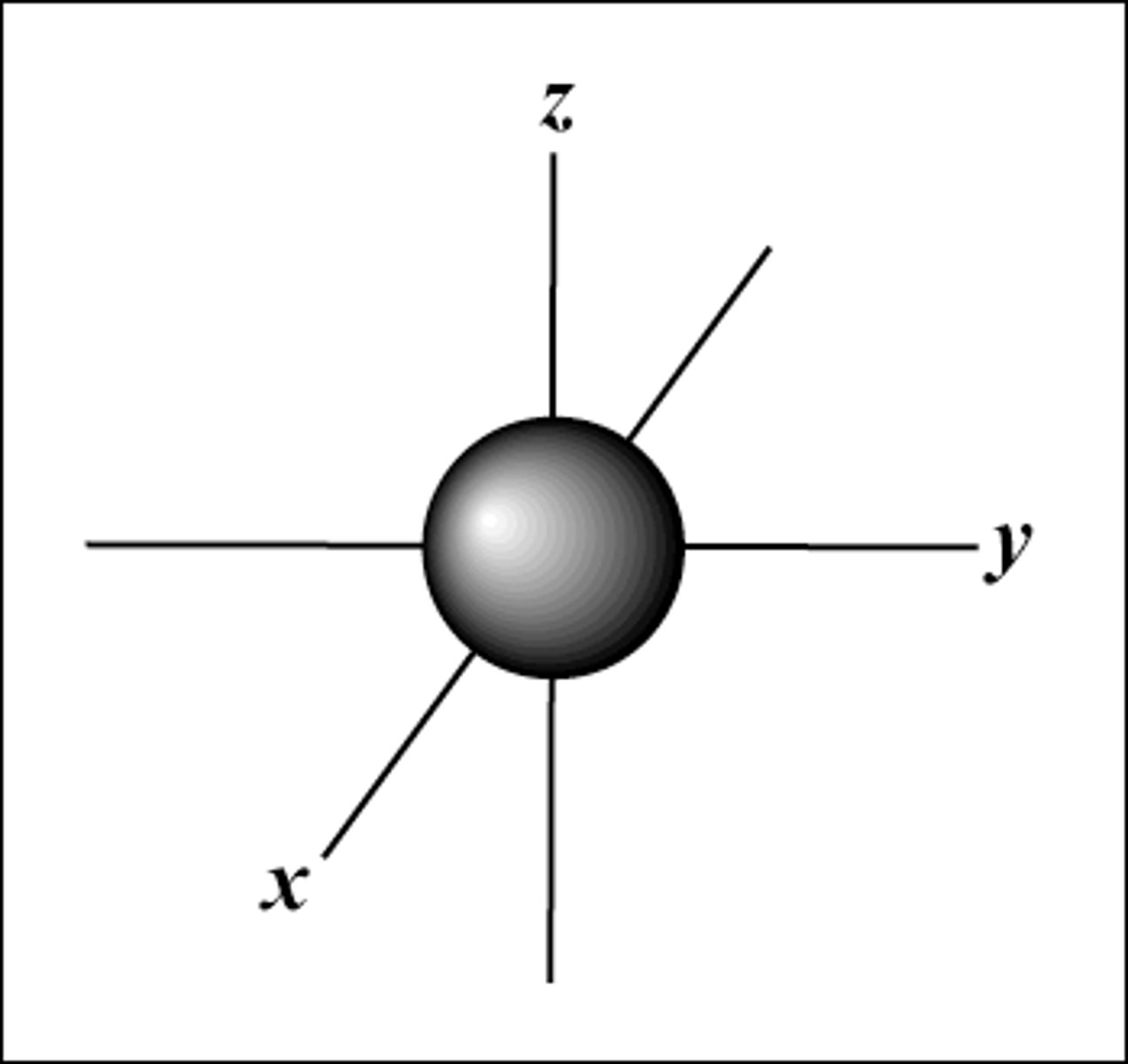
what is the lowest energy orbital of the 4
s orbital
shape of s orbital
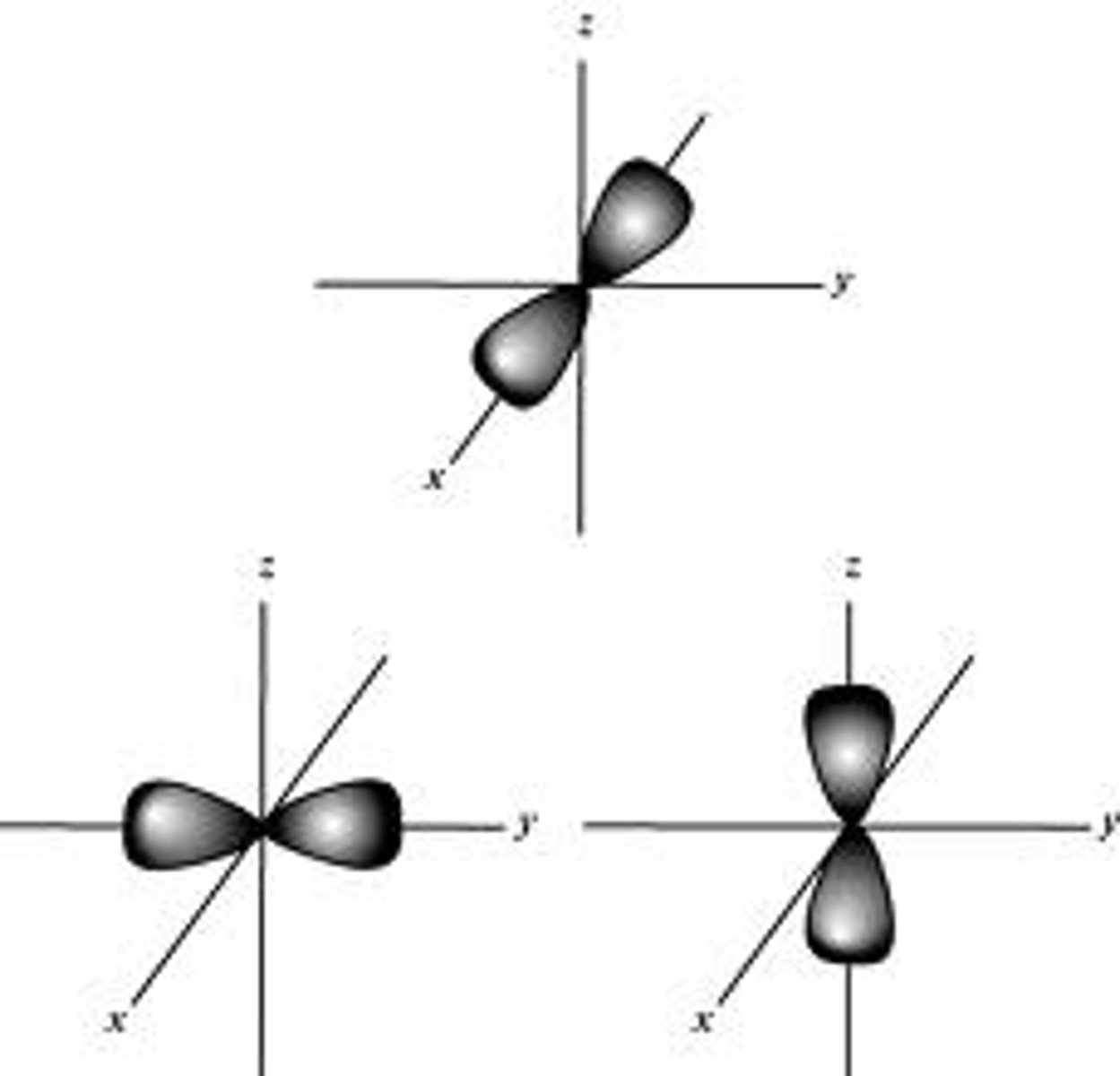
shape of the p orbital
how many are there
infinity shaped
three px py pz
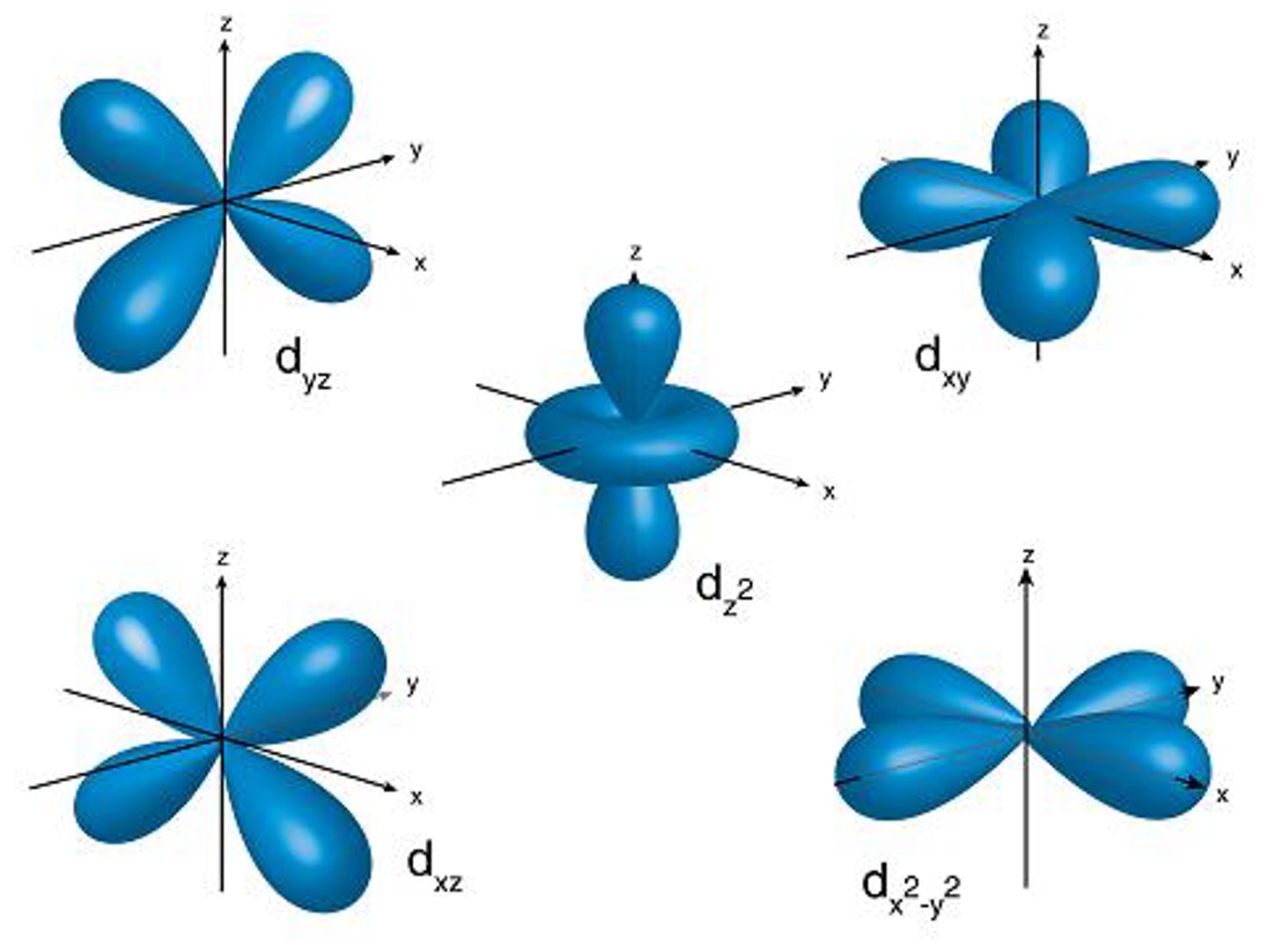
shape of d orbital and how many
each one is like a four leafed clover
D FOR DONUT
where is s block p block d block and f block on the periodic table
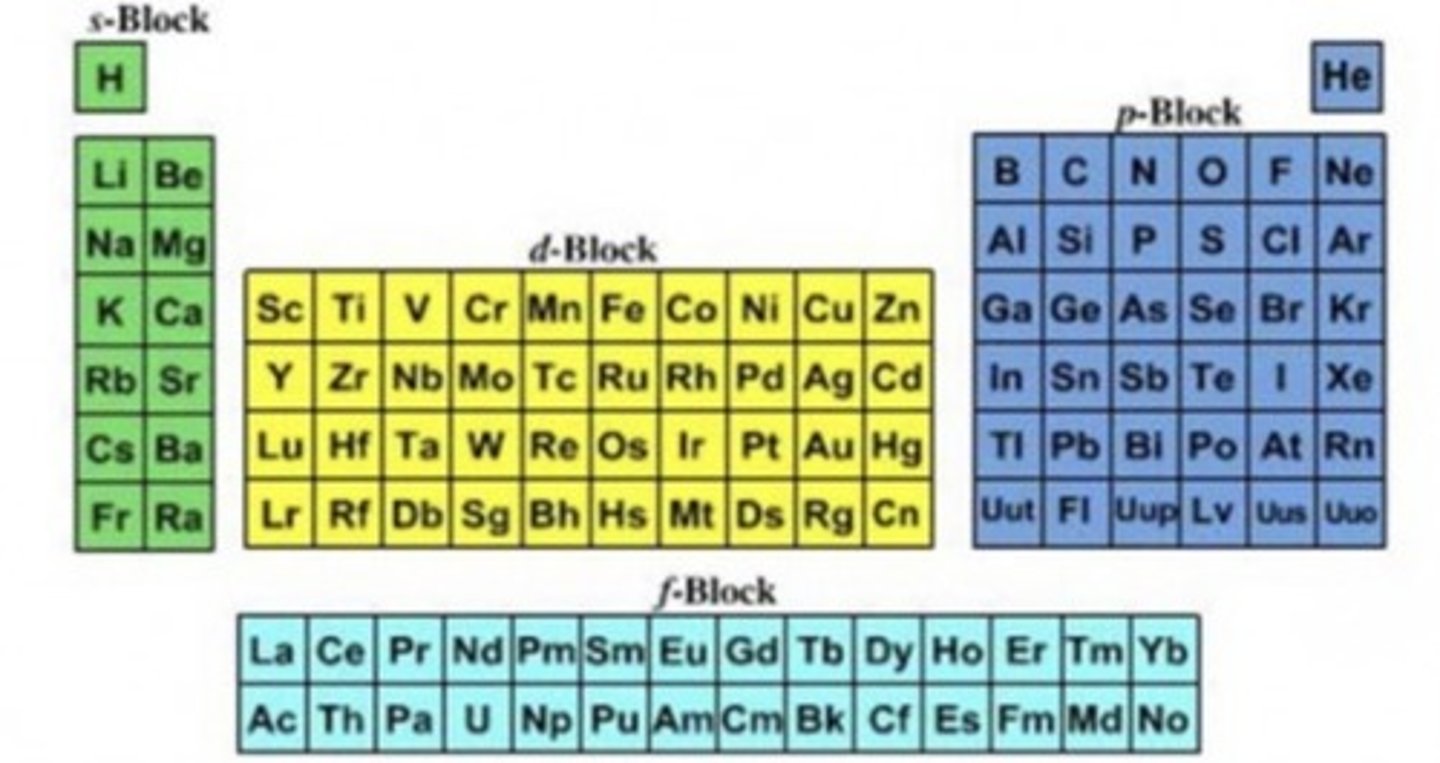
how to work out the electron configuration
find element on periodic table then go from hydrogen across and count in the orbitals e.g
C, 1s2 2s2 3p2
can figure out small number on end by counting along the p orbital to see how far in the element carbon is
how to know the coefficient of the line youre counting across
written on the side !!!!!!!! its the period number !!!!!
well up until the d block elements
whats special about the way we write the electron configuration of elements which have electrons occupying orbitals in the d block
the d block configuration starts from 3d instead of 4 like shown on the period number e.g the electron configuration of Mn is [Ar] 4s2 3d5
how can we shorten electron configuration
by using the nearest noble gas and wacking it in square brackets
what do you need to do when writing electron configuration for ONLY transition elements
swap the order so its 4s and 3d
why should you swap the order of 3d and 4s in transition elements
even though the 4s gets filled first then the 3d when theyre emptied, when ionised and lose electrons they actually lose their 4s ones first due to the similar energies between them
how to draw orbital box diagram (the order of the boxes)
same order as the periodic table
what do the whole number plus boxes represent
subshell
e.g 2p ■■■
is the 2p subshell
so what does one box represent
an orbital which makes sense because there was 3 p orbitals px pz py so it makes up p subshell
whats true about the number of electrons in one oribital
2 electrons
what is hunds rule
electrons fill all orbitals in a subshell singly before forming pairs
what is paulis exclusion principle
2 electrons occupying the same orbital must have opposite spins
whats 2 things to remember if asked to draw orbital box diagram
1. the 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s subshells all sit on one line so do the 2p 3p 4p subshells and 3d 4d
2. theres 1 orbital for s subshells, 3 for p subshells and 5 for d subshells
two exceptions in electron configuration
copper and chromium
Cu and Cr
why is chromium an exception and how does it work
half full/full or empty orbitals are the most stable and energetically favourable
if chromium stayed as it was it would have an electron in four out of the five 3d orbitals meaning its partially filled and the 4s orbital is fully filled however instead the 2nd 4s electron goes to the last orbital on the 3d subshell so theres instead a half filled 3d orbital and a half filled 4s orbital which is more stable and energetically favoured making its elec config 4s1 3d5
why is copper an exception and how does it work
copper's electron config is actually 3d10 4s1 instead of 3d9 4s2 this is because its more ENERGETICALLY FAVOURABLE for copper to fill each 3d orbital and leave the 4s orbital half filled as opposed to full 4s orbital and partially filled 3d orbital
what is the limit of convergence
where the lines on an emission spectrum converge
what are the two equations needed for a limit of convergence question
wave speed (given to you its the speed of light) = wavlength x frequency
ionisation energy = h (constant) x frequency
what do we work out using those equations
which of those things equates to the limit of convergence
the ionisation energy
what should you be worried about in these limit of convergence calcuations
it might ask you for it in moles not one atom so work out in atoms then times it by avogadros constant
if it asks for say 2 moles then you again work out atoms then times by avogadros constant then times 2