(p4-p6) Integumentary system , skeletal system , and joints.
1/291
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
292 Terms
What are joints/articulation?
A joint or articulation is the place where two or more bones come together.
Job of the joints?
to hold the skeleton together and allow mobility.
The 3 classifications of joints
(what they're made of)
fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial.
Fibrous joints functions
Synarthrosis (immovable)
Does NOT allow movement
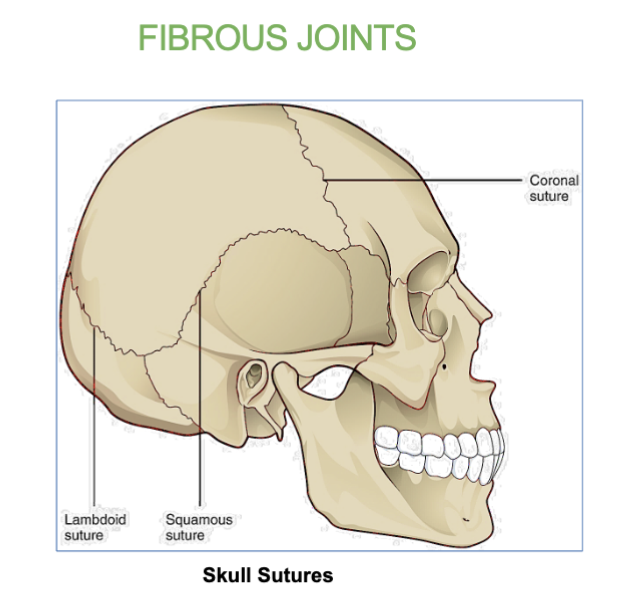
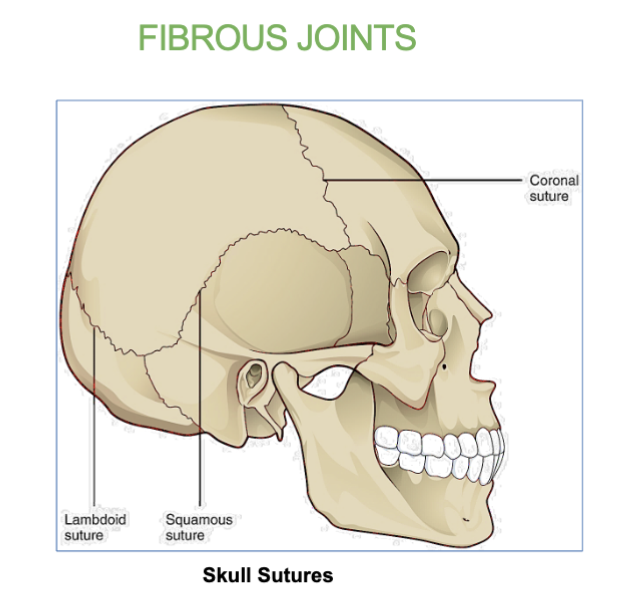
Example of a fibrous joint
Skull
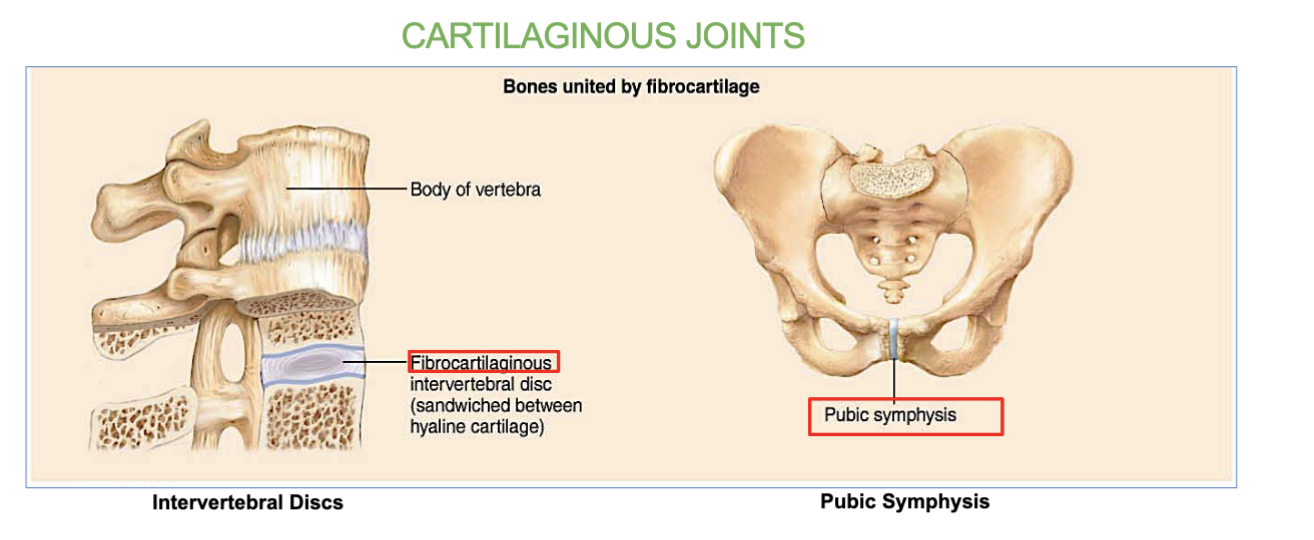
Cartilaginous joints functions
Amphiarthrosis (slightly movable)
allos for SOME movement, very little
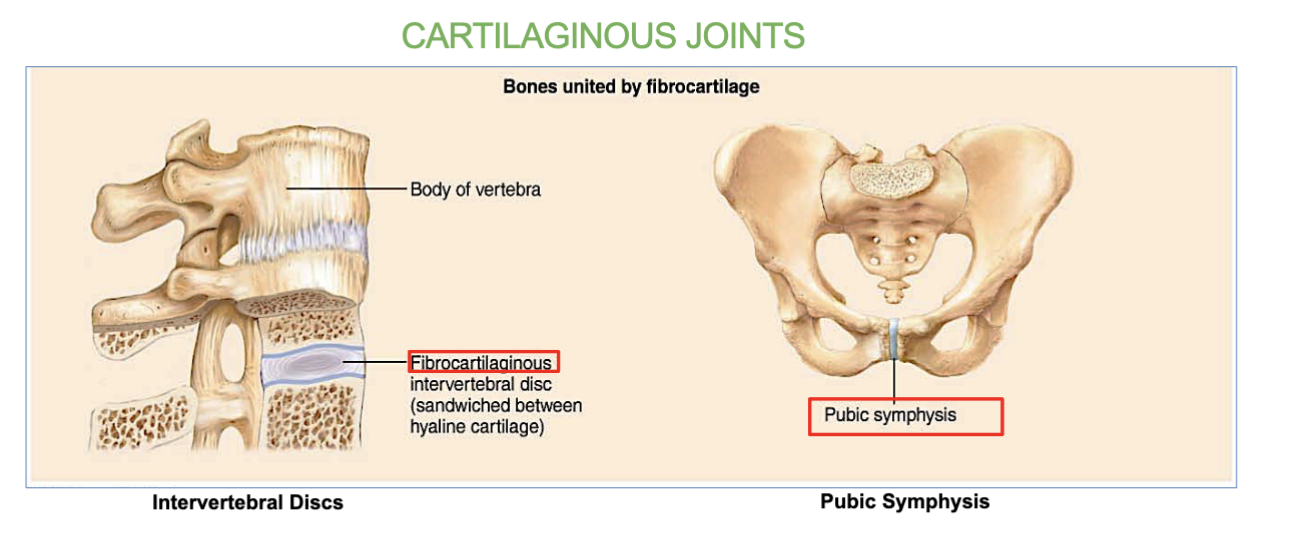
2 Examples of a cartilaginous joint
intervertebral discs (between the vertebrae in the spine)
Symphysis pubis (joint located between the left and right pubic bones at the front of the pelvis)
allows for limited movement
2 Examples of synovial joints
the shoulder and hips
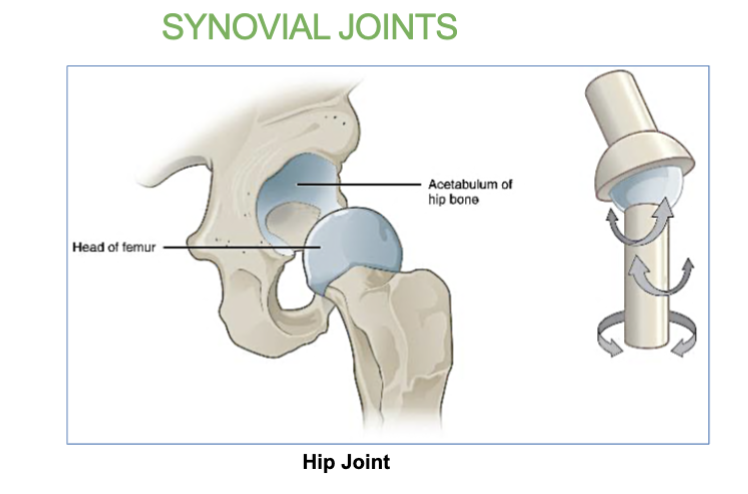
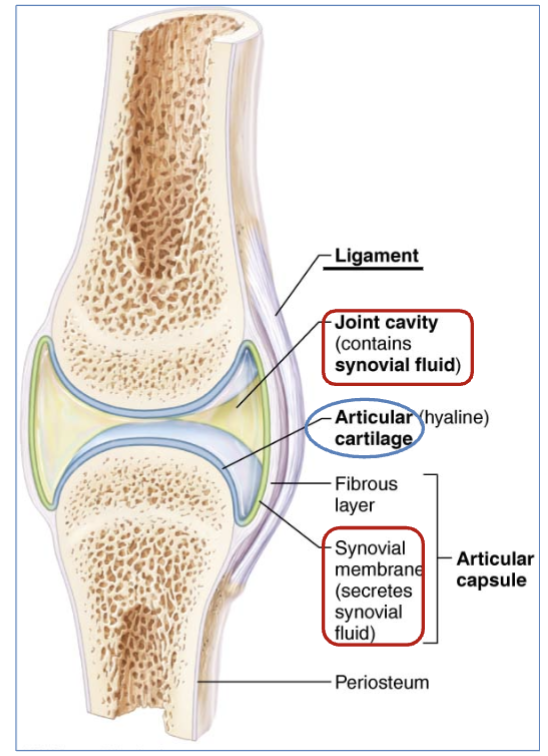
4 Structures of a synovial joint
Articular cartilage - end of long bones. covered in thin layer of hyaline cartilage
Synovial (joint Cavity) - filled with synovial fluid.
(synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid)
Articular Capsule- the joint is enclosed by a protective, fibrous structure called the articular capsule, which forms a joint cavity.
Reinforcing ligaments - Ligaments that support the joints by holding bone to bone and resisting excess or abnormal joint movements
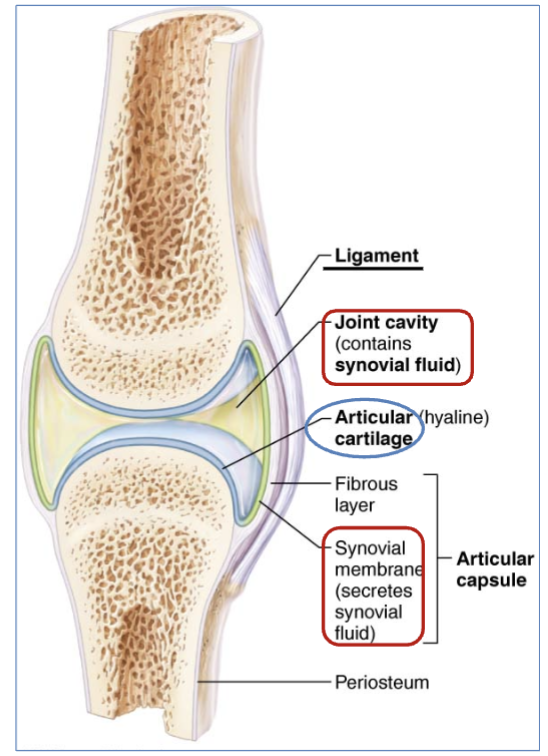
definition of Articular cartilage
(structure in synovial joint movement)
end of long bones, covered in thin layer of hyaline cartilage.
(reduces friction and allows for smooth movement of the joint)
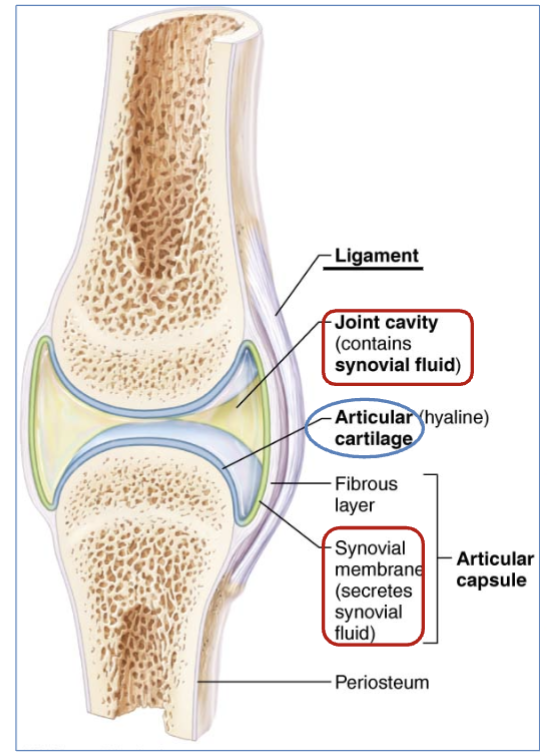
definition of Synovial (joint) cavity)
(structure in synovial joint movement)
cavity filled with synovial fluid.
(synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid)
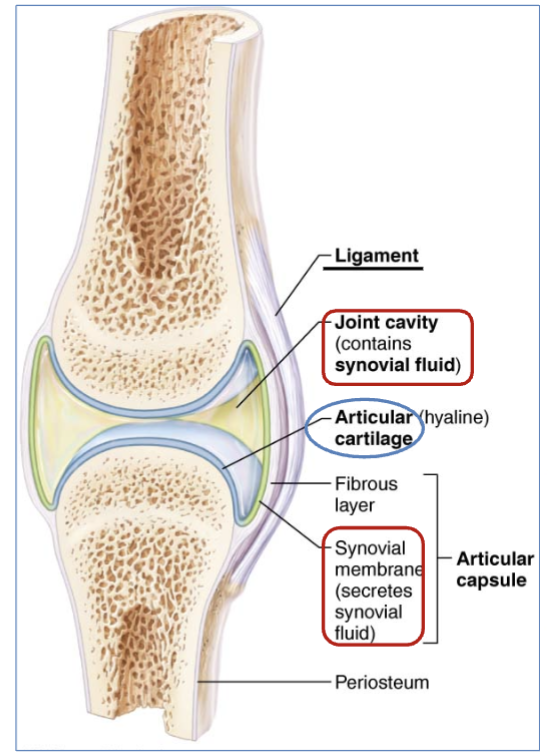
What secretes synovial fluid?
the synovial membrane
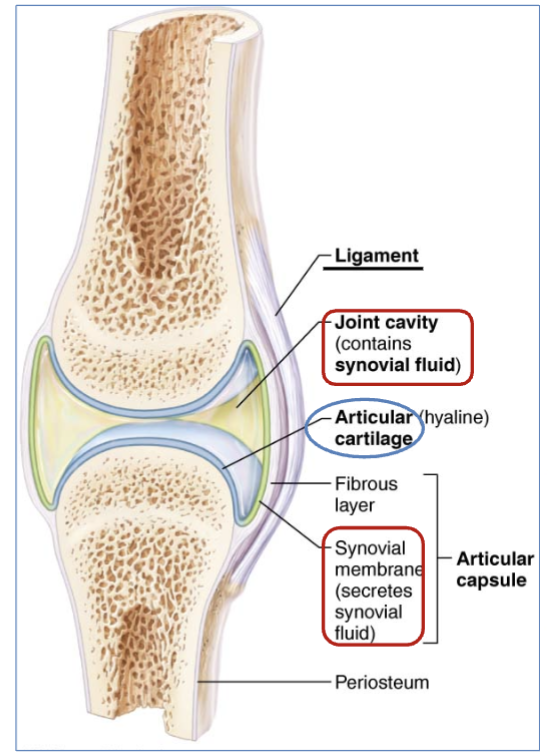
definition of Articular capsule
(structure in synovial joint movement)
the joint is enclosed by a protective, fibrous structure called the articular capsule, which forms a joint cavity.
JOB - a double-layered structure that surrounds and encloses a synovial joint, providing stability and flexibility )
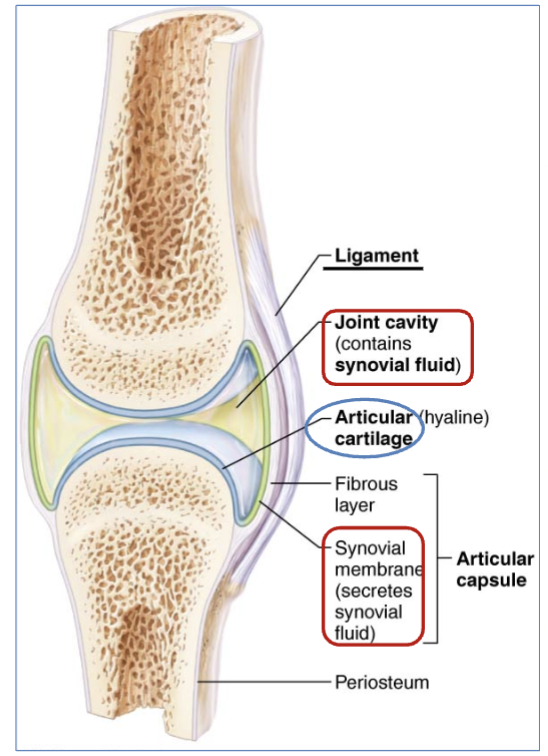
definition of Reinforcing ligaments
(structure in synovial joint movement)
are Ligaments that support the joints by holding bone to bone and resisting excess or abnormal joint movements.
3 factors that can influence joint stability
Articular surfaces - Joints with deeper sockets, like the hip, are more stable because they securely hold the bone in place.
Ligaments- More ligaments provide more stability.
Muscle tone- Strong muscle tone makes joint more stable
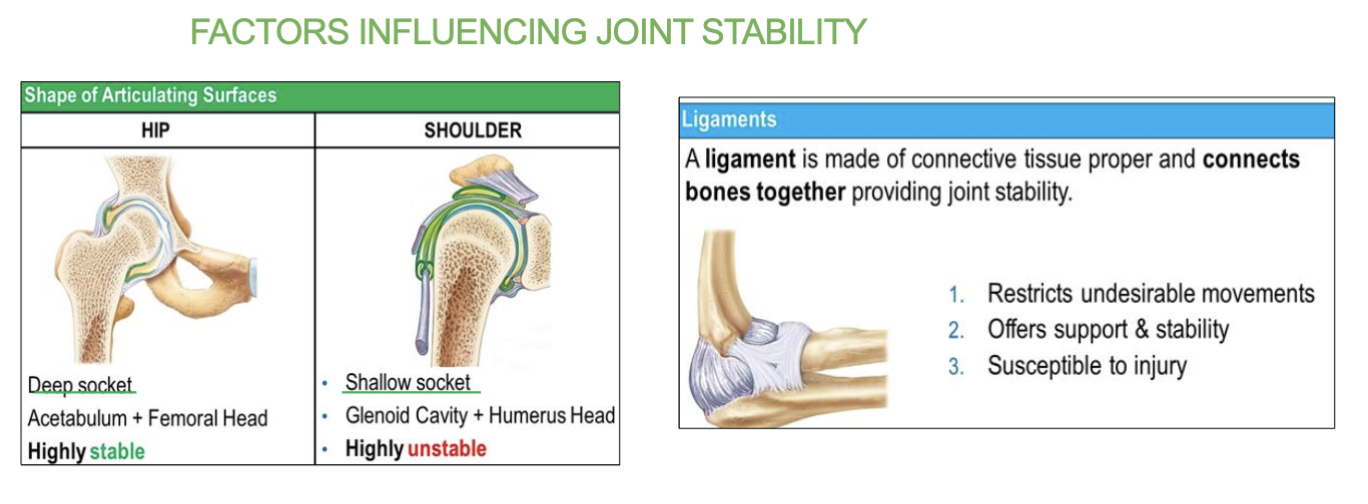
Whats a ligament and where are they?
a tough, fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones at a joint, providing stability.
on the outside of bones
3 jobs of the ligament
restricts undesirable movements
offers support & stability
but IS susceptible to injury
2 shapes/examples of articulating surfaces (2 sockets)
Deep socket and Shallow socket
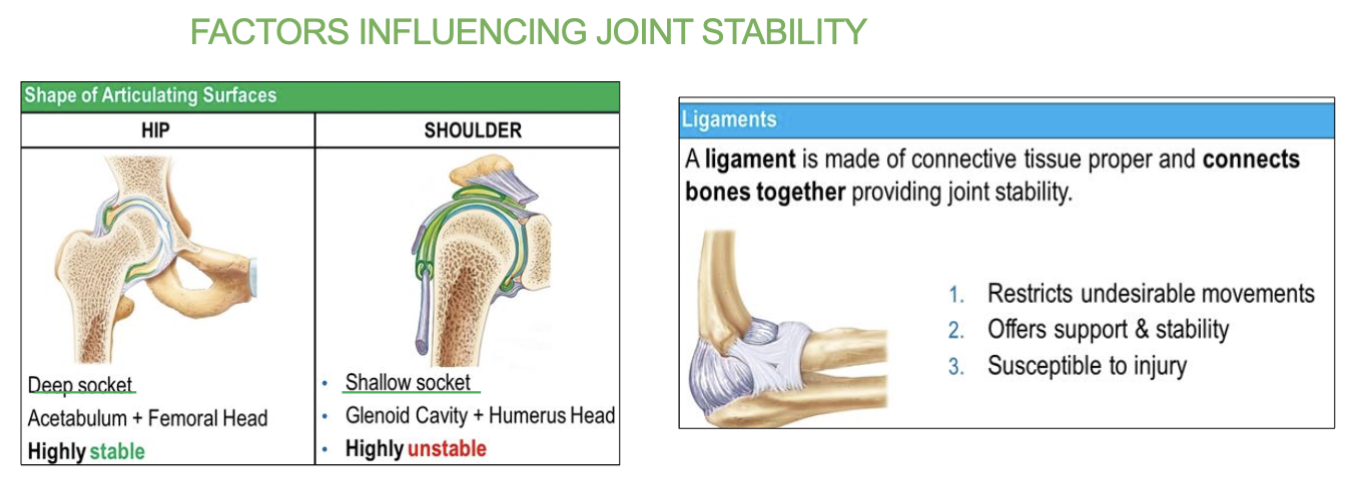
what does “articulating surfaces” mean?
& two examples?
where bones come into contact and interact with each other at a joint.
These surfaces are often covered with cartilage
EX- deep + shallow sockets
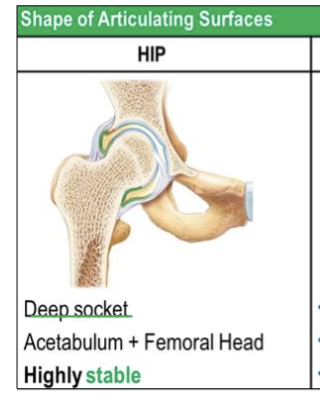
Job of deep socket
Provides more stability and less mobility.
(ex- hip joint (acetabulum)a + femoral head)
Highly stable
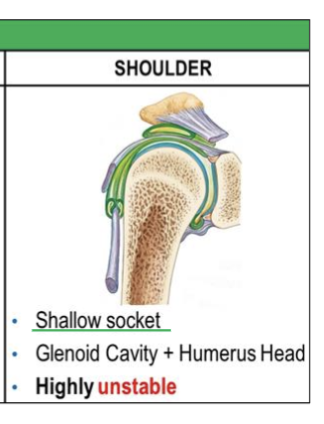
job of shallow socket
Allows greater mobility but less stability.
(ex- shoulder joint (glenoid cavity), + humeral head)
highly unstable
3 Friction reducing structures within joints
bursa
tendon sheath
meniscus
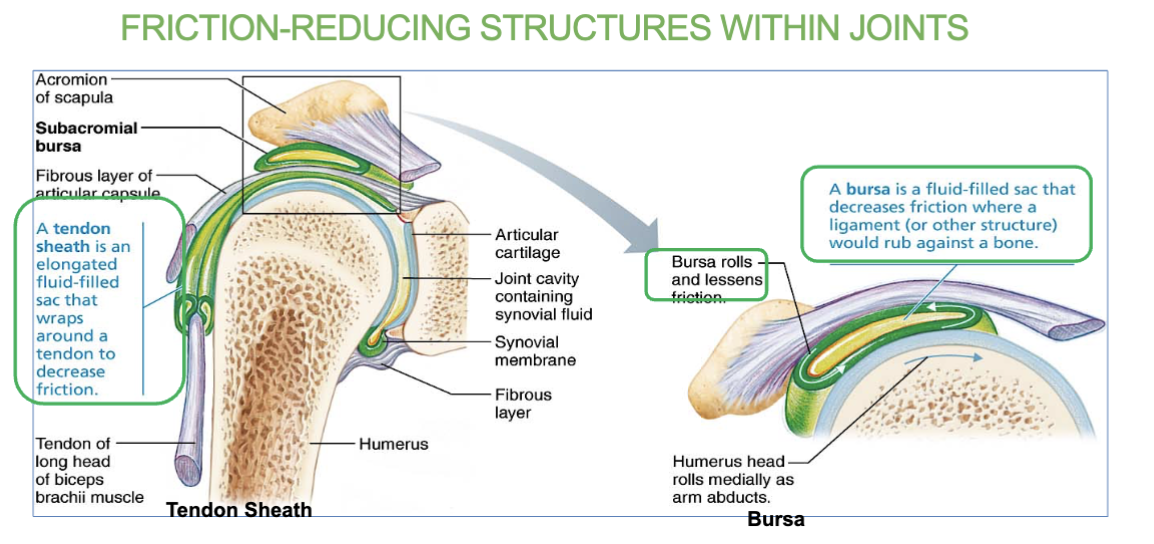
Bursa definition/job
(a friction reducing structure within joints)
Sac filled with synovial fluid that prevents friction between muscle, or tendon and underlying bone.
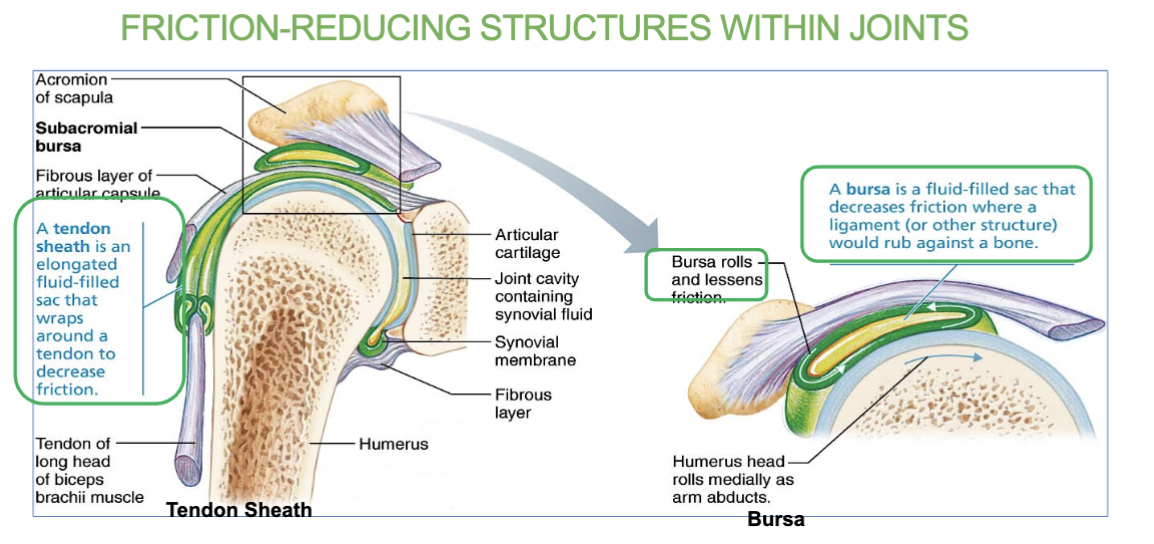
What’s a bursa?
Sac filled with synovial fluid that prevents friction between muscle, or tendon and underlying bone.
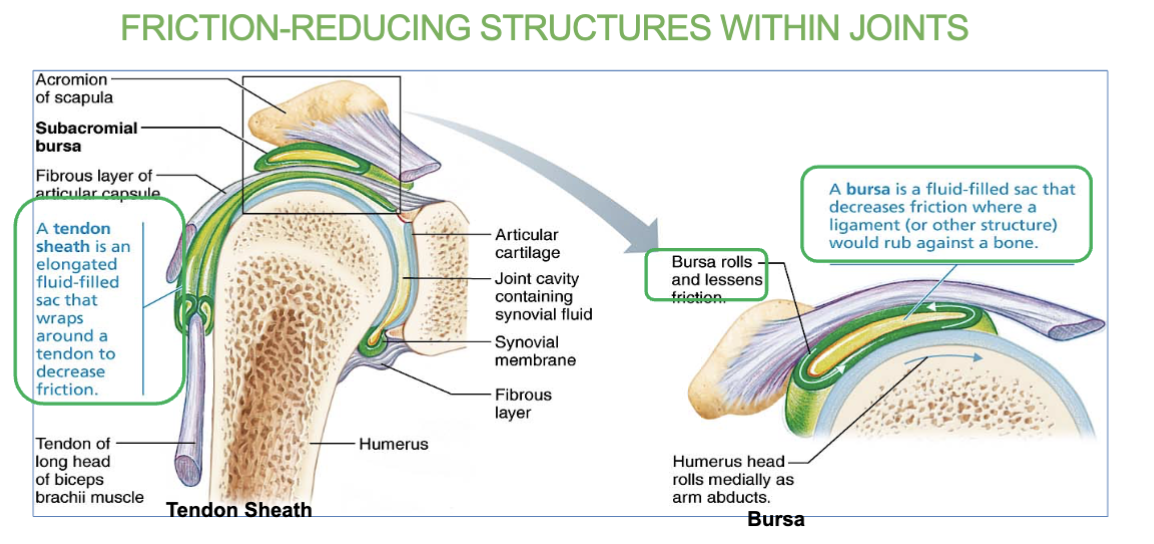
Tendon sheath definition/job
(a friction reducing structure within joints)
An elongated bursa that wraps around tendon.
decreases friction.
Meniscus definition/job
(a friction reducing structure within joints)
a C shaped cartilage between two bones.
two types - lateral and medial meniscus
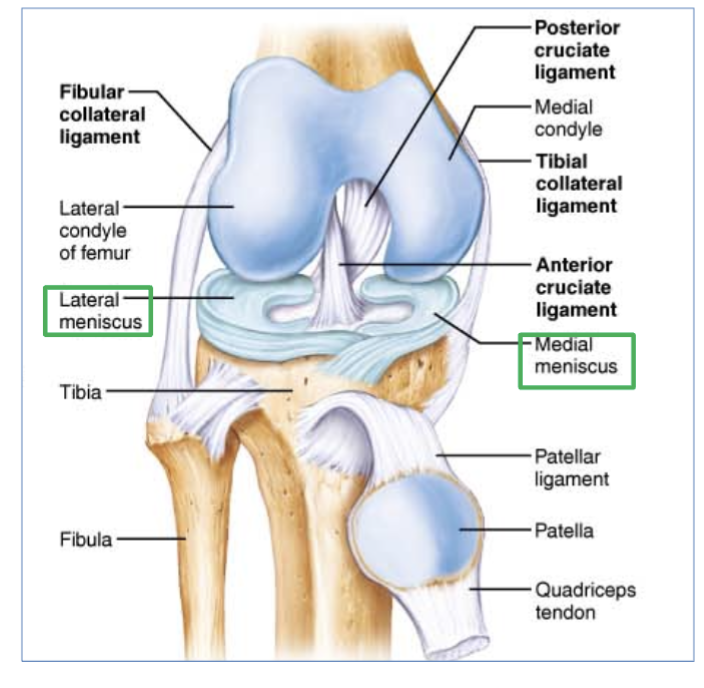
the 2 types of “meniscus” and where can you find them?
lateral and medial meniscus
in the knee joint
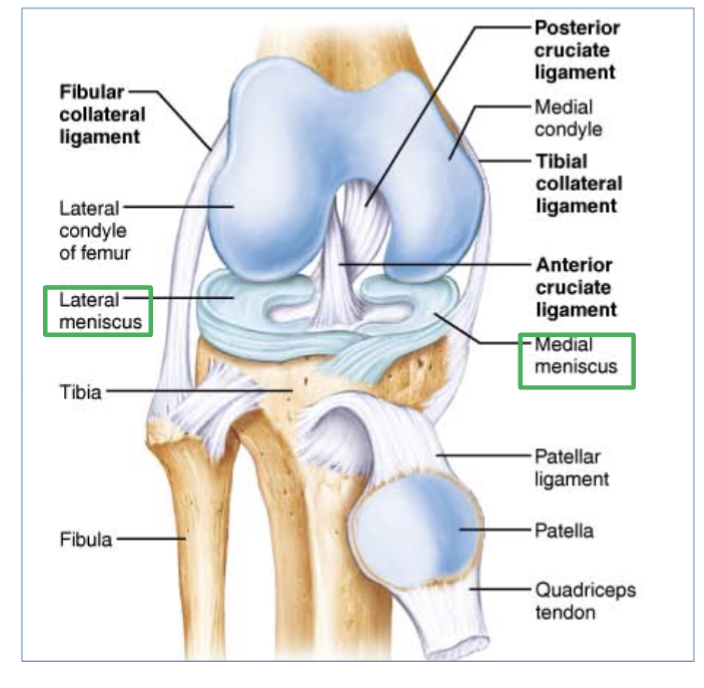
3 structures of knee joint (ligaments)
Tibial & Fibular collateral
Anterior & posterior cruciate ligaments
Medial & lateral menisci
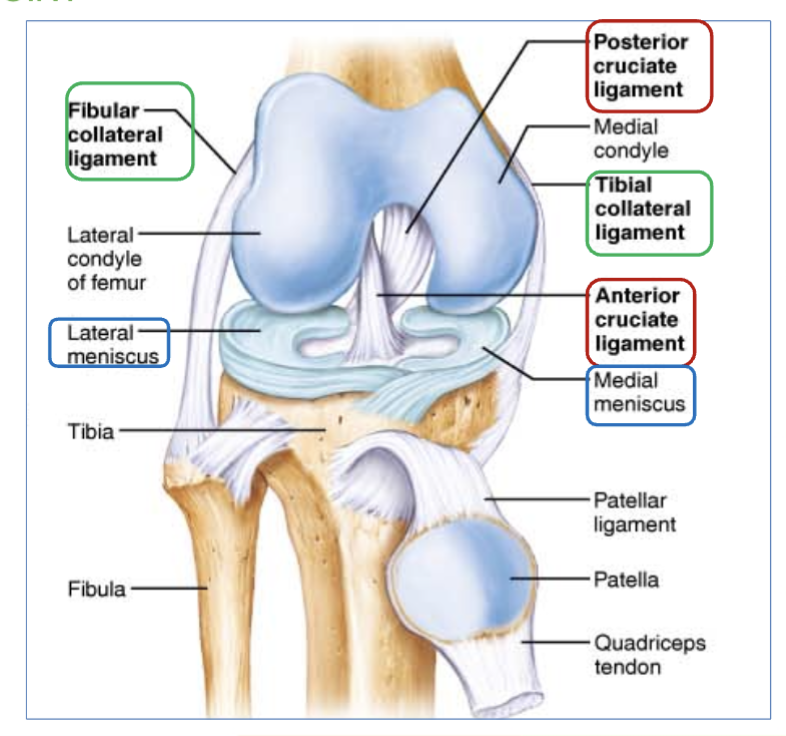
Tibial & Fibular collateral ligaments location
located on the sides of the knee outside of the articular capsule
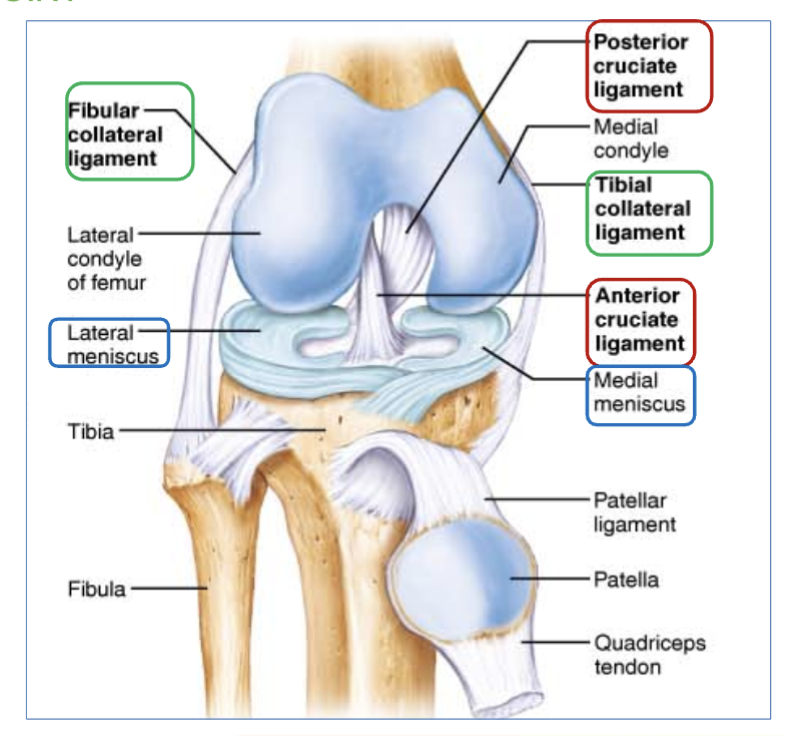
Anterior & posterior cruciate ligaments location
found inside the capsule, in the front and back of knee.
(ex- ACL, most common injury of ligament in knee, takes long time to heal)
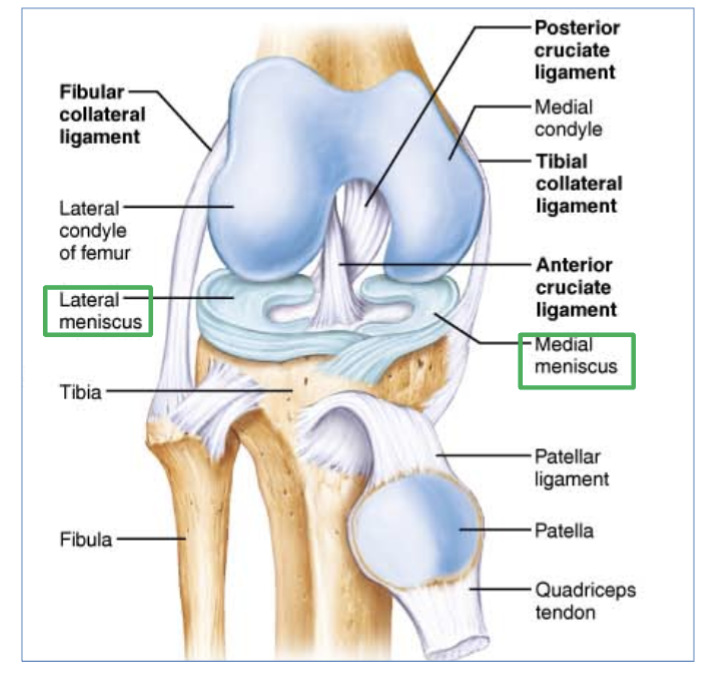
Medial & lateral menisci ligaments location
C shaped ligaments that provide padding and support between the femoral condyles and tibial condyles.
(right and left side of knee, inside articular cartilage)
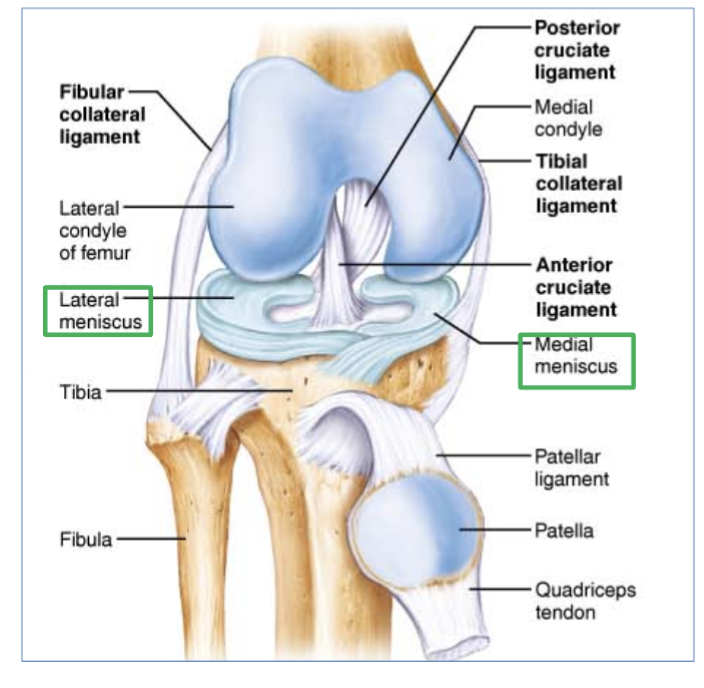
Most common ligament in the knee that is torn?
the AnterioR cruciate ligament ( ACL )
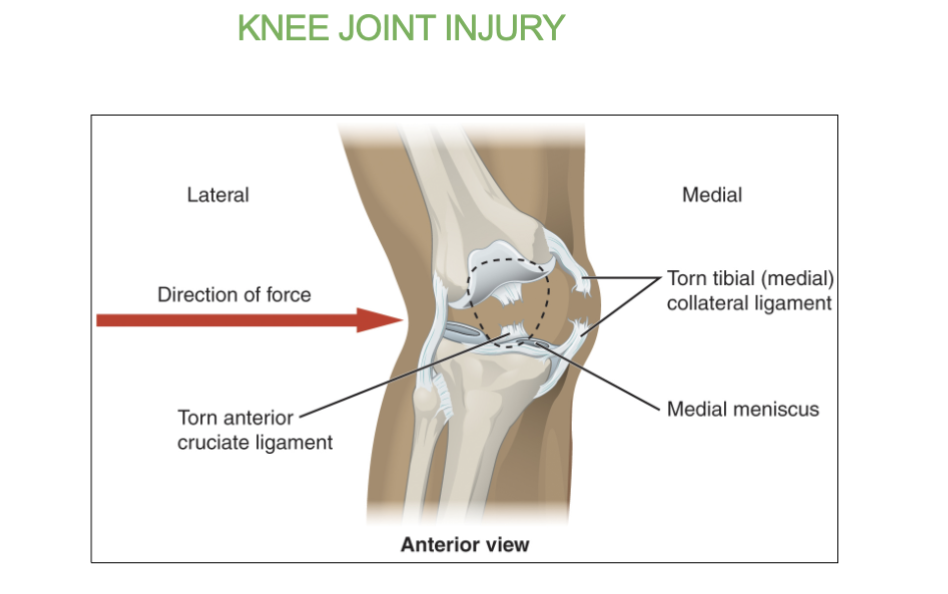
which joint is the largest joint of the body?
the knee joint
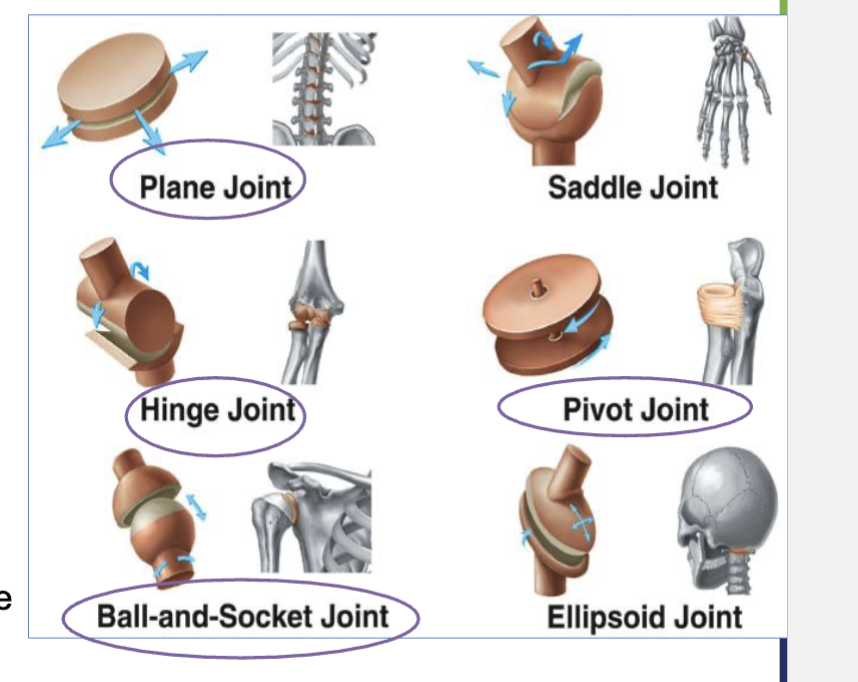
4 types of synovial joints?
pivot joints (doesn’t move, allows for rotation around its axis)
hinge joints ( ex - door hinge, angular movement)
planar joints (gliding movement ← →)
ball and socket (360 movement)
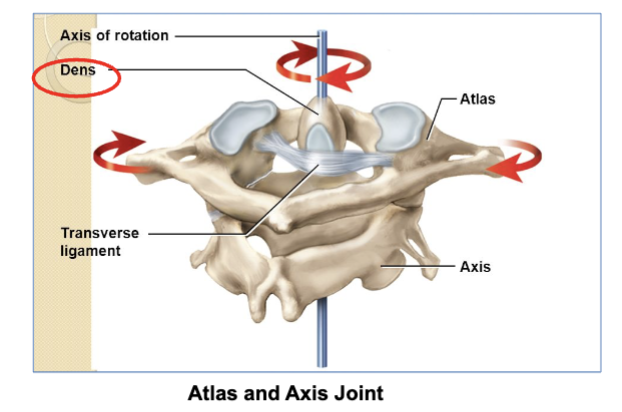
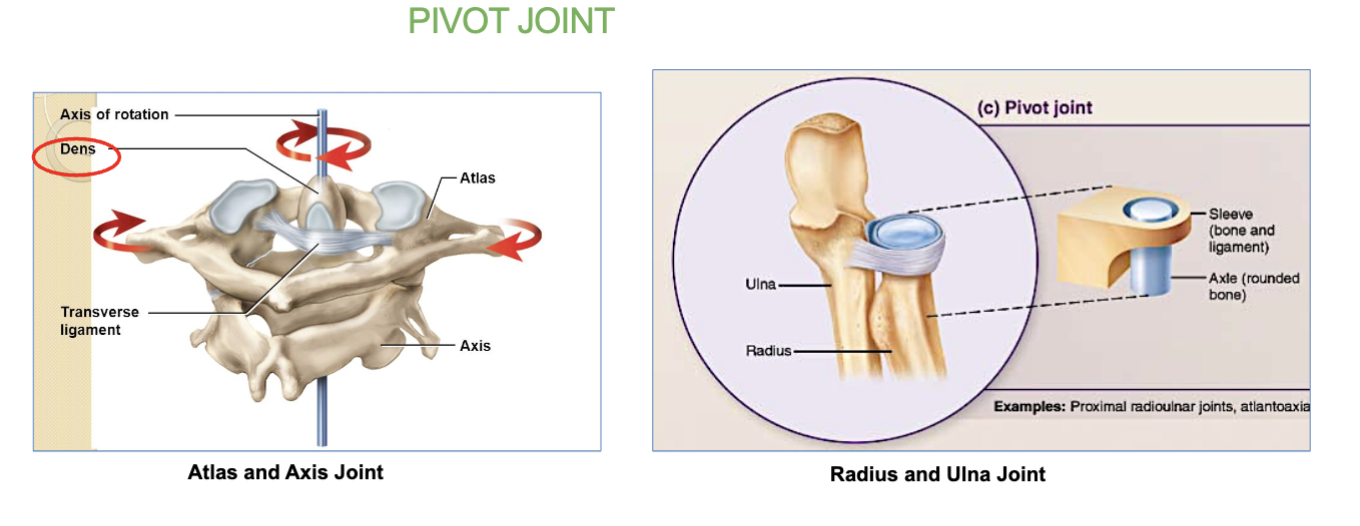
Pivot joints job/definition & 2 examples
let bones rotate around a central point (axis).
2 examples (remember) -
the atlantoaxial joint is where the C1 vertebra (atlas) and C2 vertebra (axis) meet. This joint lets your head rotate side-to-side (like shaking your head "no").
The radius (forearm bone) rotates around the ulna (another forearm bone), allowing your wrist and forearm to rotate
2 examples of pivot joints?
the atlantoaxial joint.
( where the C1 vertebra (atlas) and C2 vertebra (axis) meet. This joint lets your head rotate side-to-side )
- the Radius & Ulna .( The radius (forearm bone) rotates around the ulna (another forearm bone ) allowing your wrist and forearm to rotate )
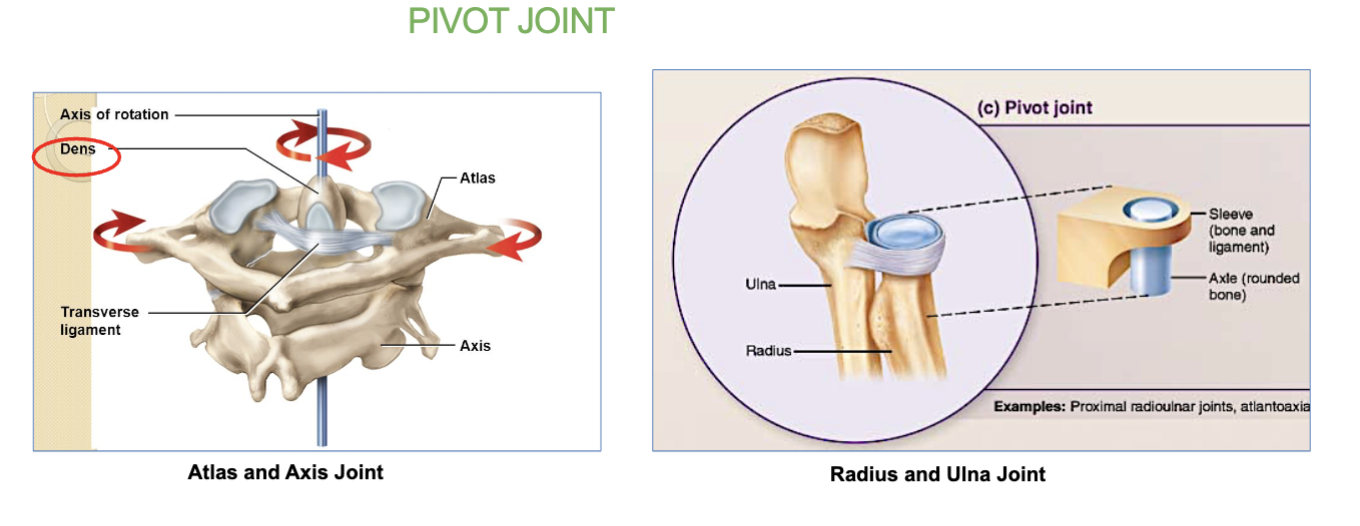
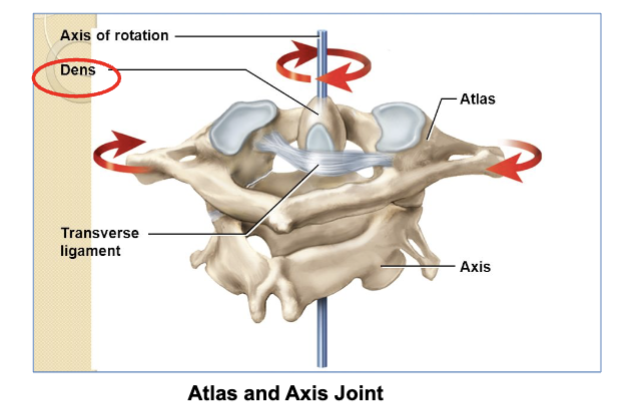
whats the atlantoaxial joint? (and its job)
a pivot joint.
its where the C1 vertebra (atlas) and C2 vertebra (axis) meet.
This joint lets your head rotate side-to-side (like shaking your head "no").
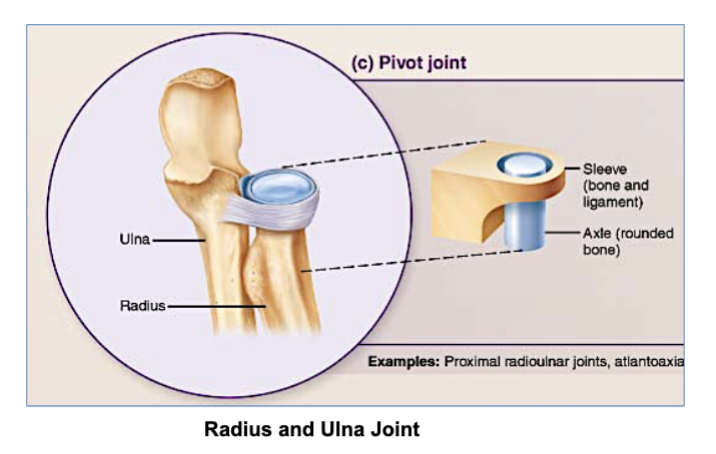
“The radius (forearm bone) rotates around the ulna (another forearm bone), allowing your wrist and forearm to rotate”
which joint is this an example of?
pivot joints
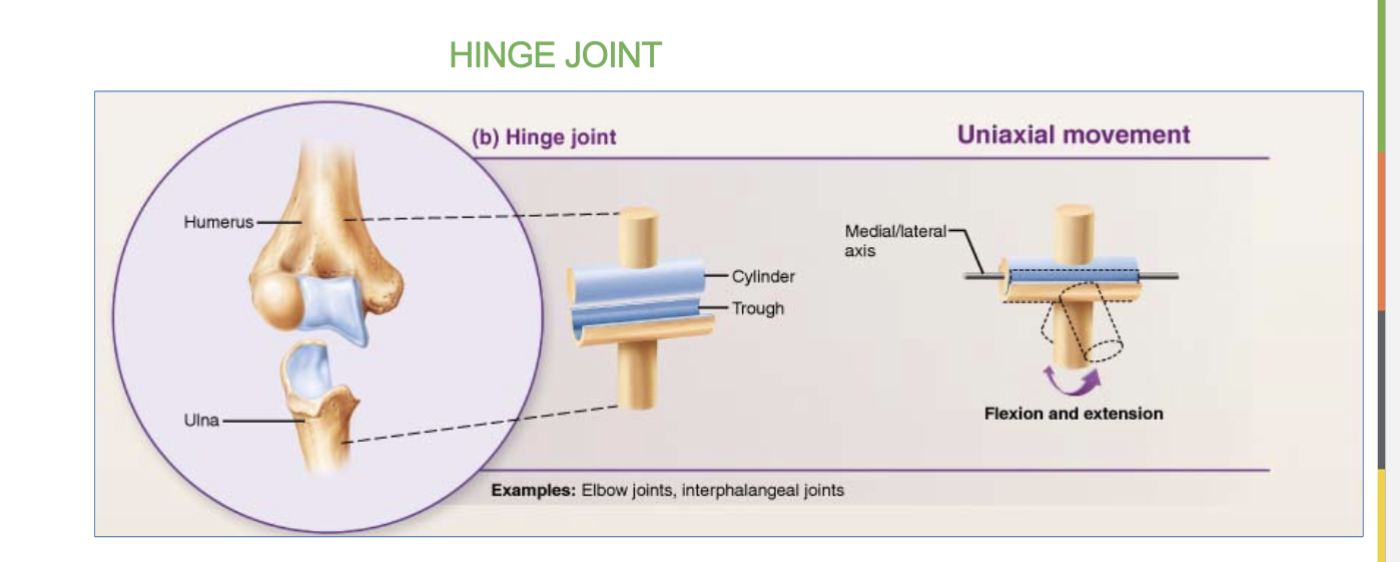
Hinge joint definition/job
& 2 examples
works like a door hinge, allowing flexion and extensions.
EX- elbow & knee
which joint allows for flexion and extensions?
the hinge joint.
Which joint allows for bones to rotate around a central point (axis)?
pivot joints
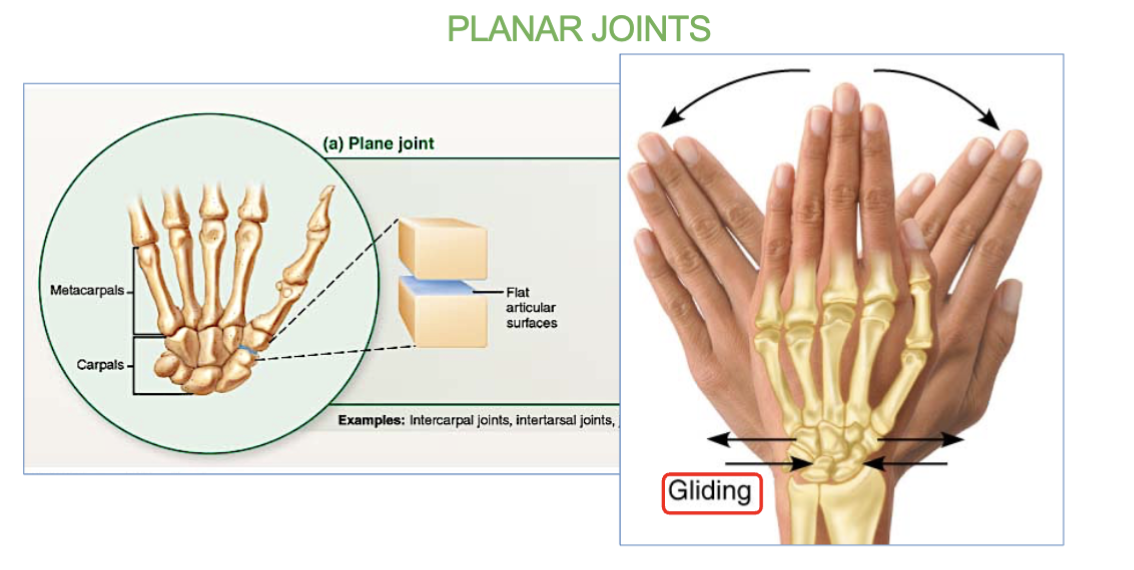
Planar joint definition/job
& 2 examples
allow for limited gliding movements ← →
ex- carpal bones (wrist) and tarsal bone (ankles)
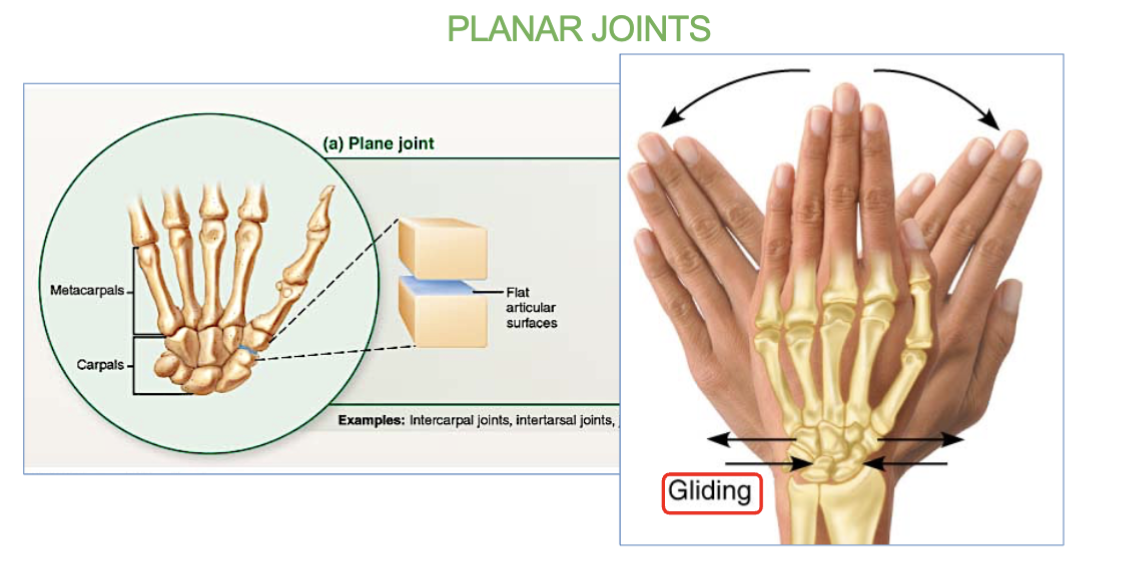
which joints allows for limited gliding movement?
Planar joints
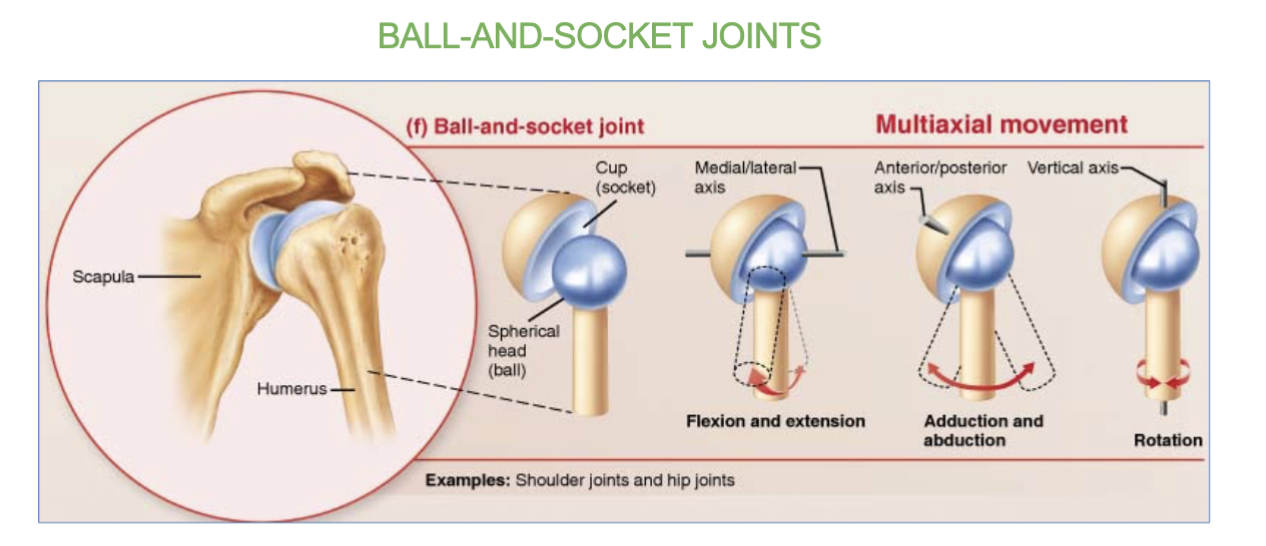
Ball & socket joints definition/job
& 2 examples
allow for multi-axial (360) movement
ex- only the hip and shoulder joints
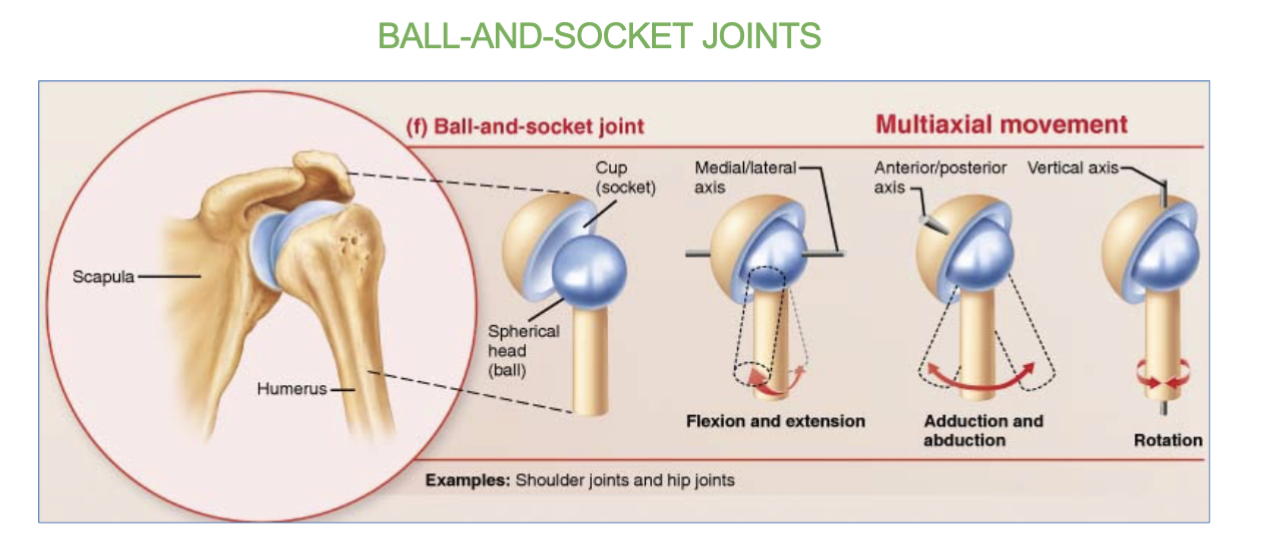
which joints allow for multi-axial (360) movement?
the ball and socket joints.
10 Types of Joint movements
flexion & extension (bending up and down)
abduction & adduction (limbs/fingers opening and closing)
depression/elevation (opening/closing mouth and up and down of shoulders)
protraction/retraction (pushing forward/pulling back of chin)
circumduction (circular pattern of limb , 360 degrees)
medial & lateral rotation ( turning head or limbs towards midline or away from midline )
pronation & supination (involves palms facing either posterior or anterior)
Dorsiflexion & Plantar Flexion (toes pointing up or pointing down)
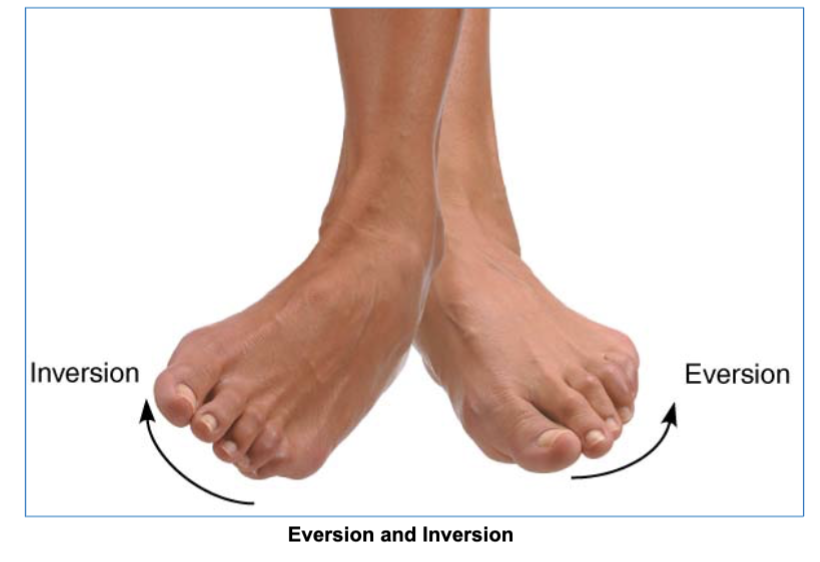
Eversion & Inversion (sole of foot either outward or inward)
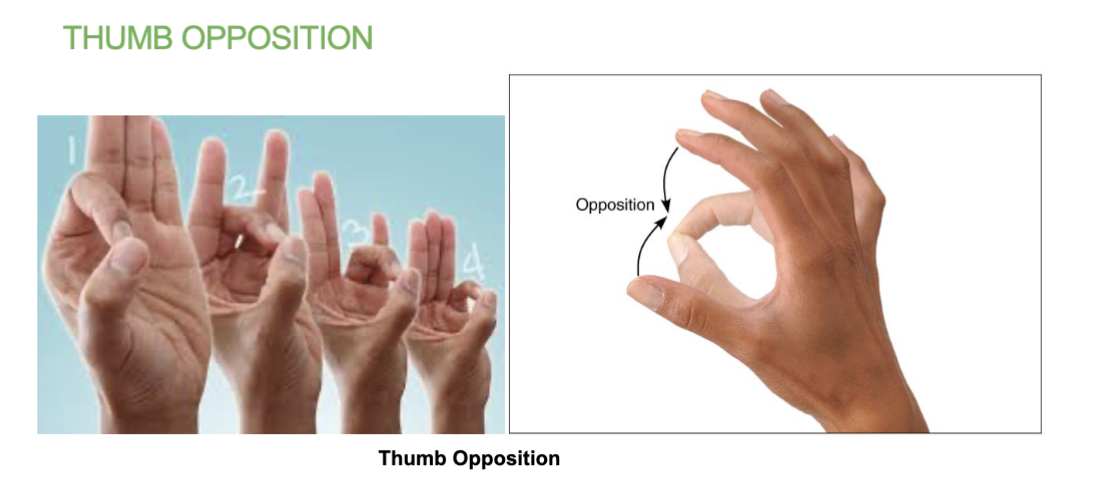
thumb opposition (tip of thumb to tip of other fingers)
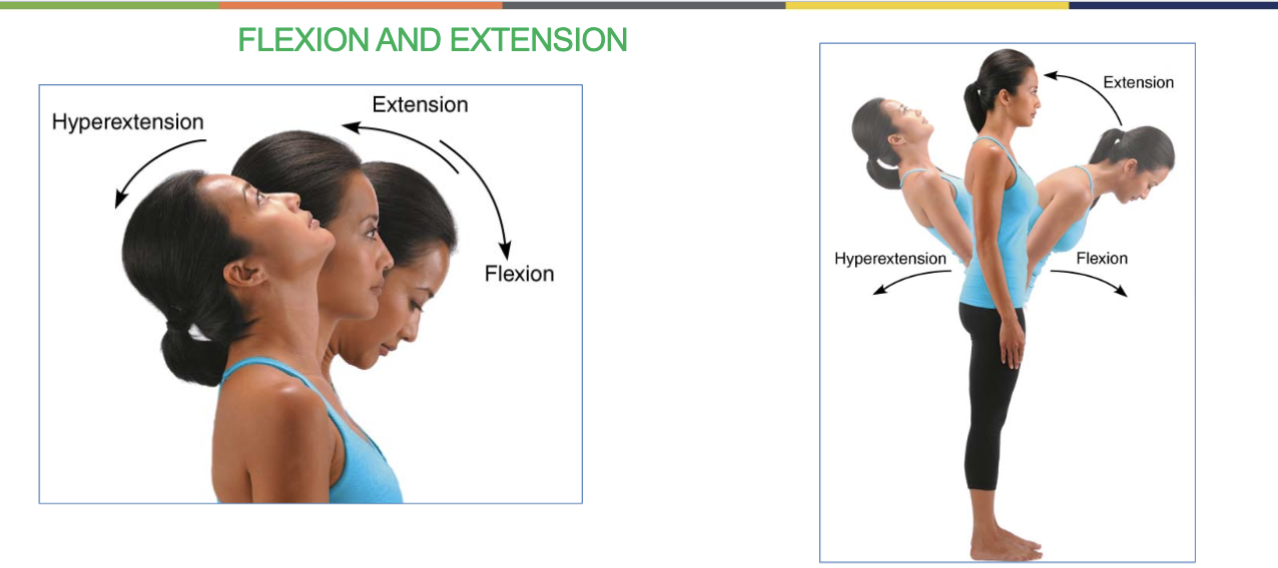
flexion & extension joint movement
(& hyper extension)
-bending up (being straight) and bending down (90º angle)
(hyper extension is bending back)
-at shoulder, hip, elbow, knee, wrist, and interphalangeal joints
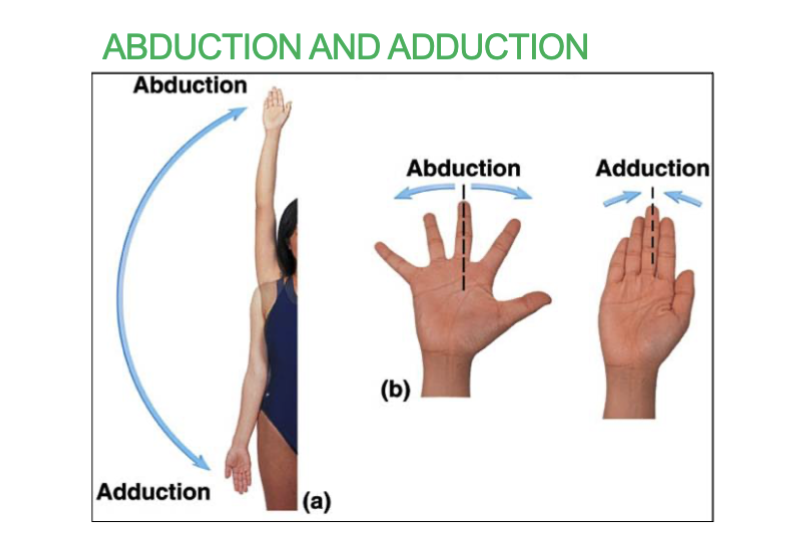
abduction & adduction joint movement
abduction - moving limb/fingers away from body
adduction - moving limb/fingers closer to body
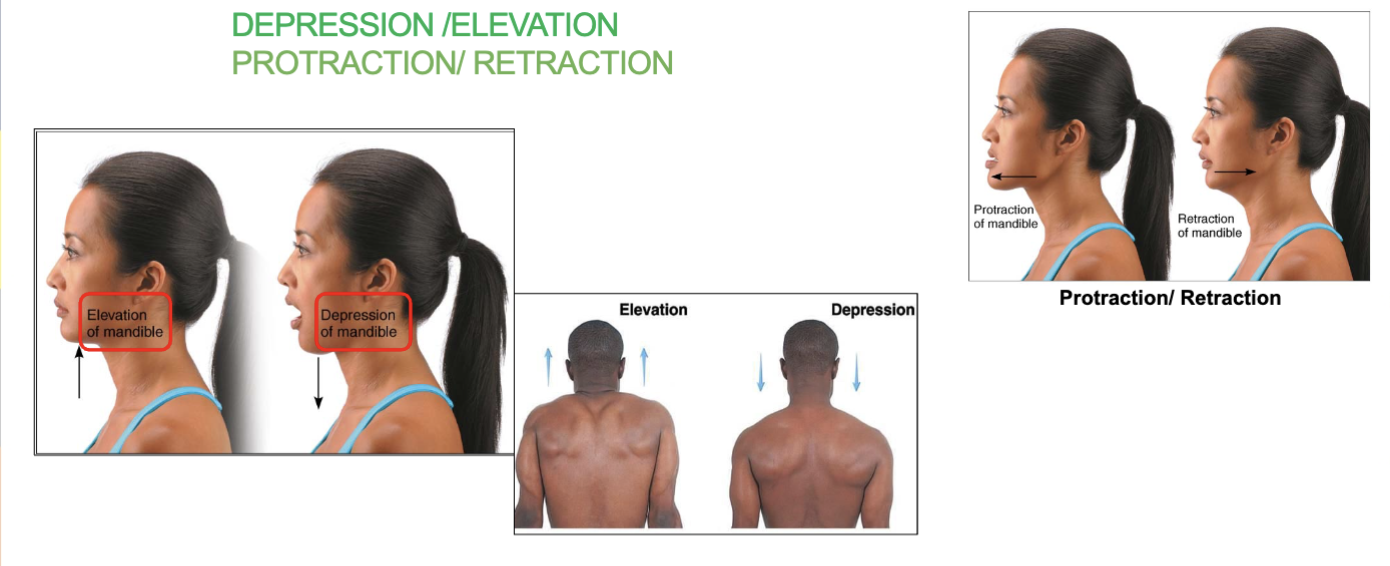
depression/elevation joint movement
depression/elevation - opening/closing mouth and shoulder
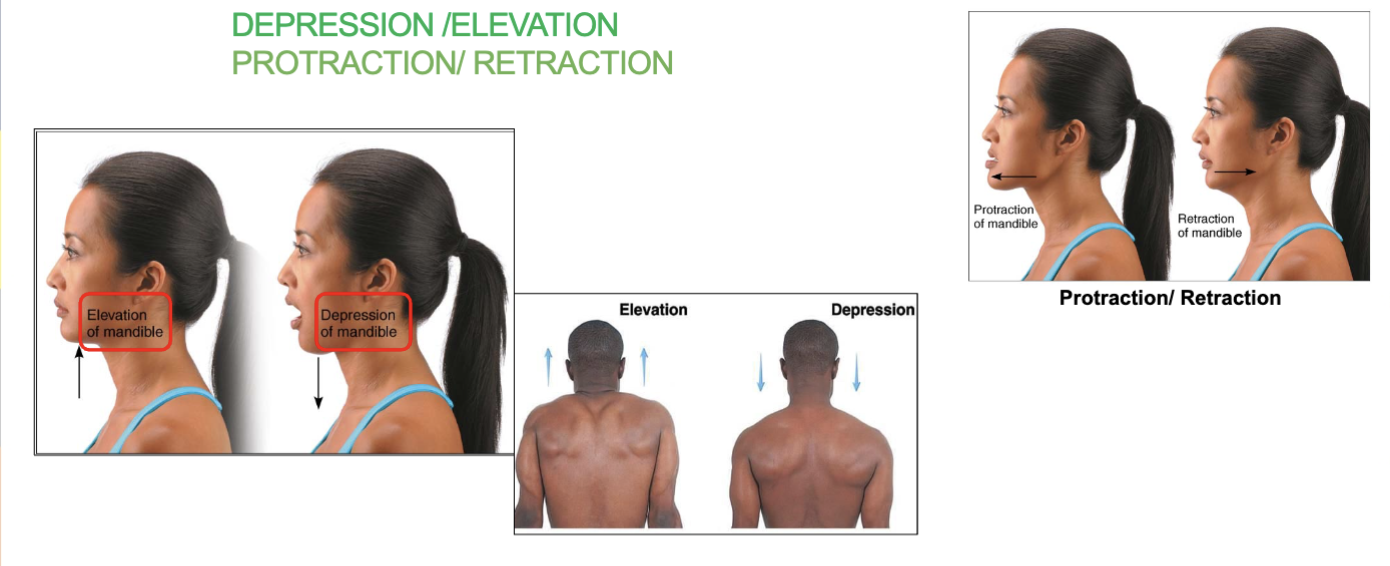
protraction/retraction joint movement
pushing chin forward and pulling chin back
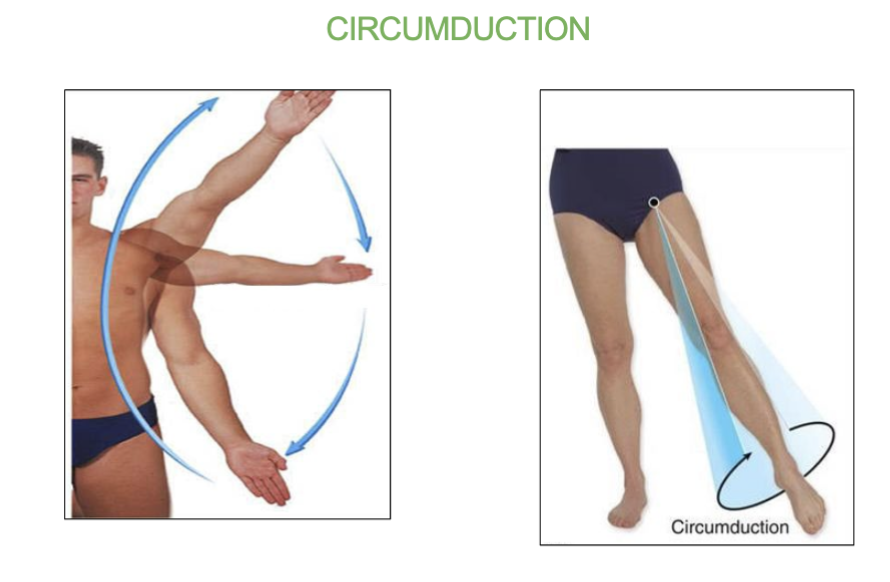
Circumdation joint movement
the movement of the limb in a circular pattern (360 degrees)
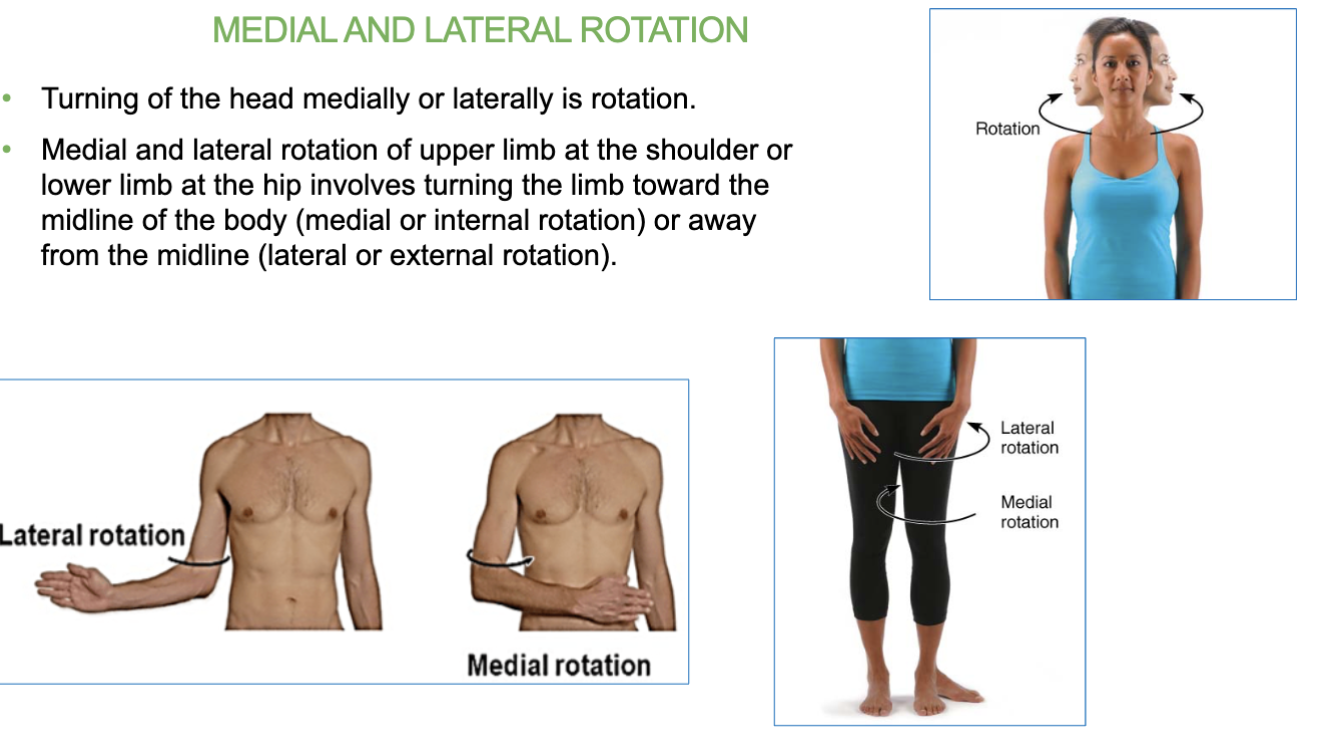
Medial/later rotation joint movement
turning limbs towards midline of body (medial) or away from body (lateral)
- Turning of the head medially or laterally is rotation.
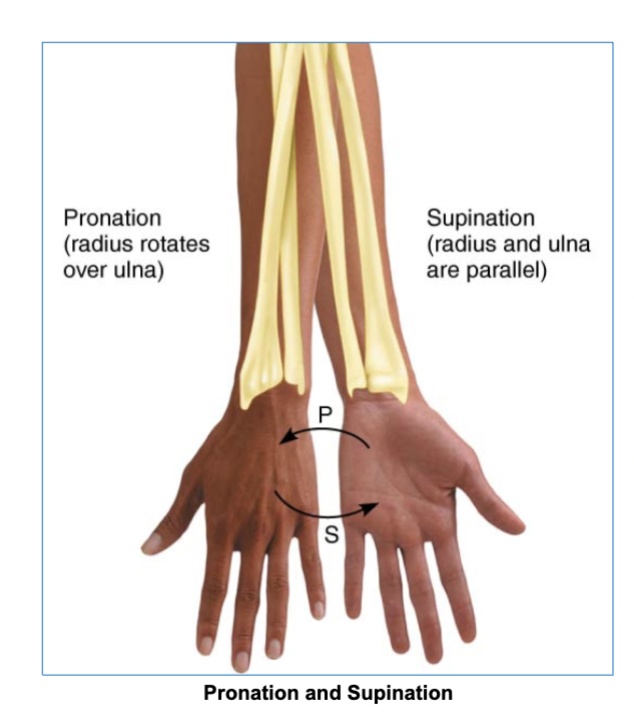
pronation and supination joint movement
forearm pronation/supination involves turning the hands so the palms facing either posterior or anterior
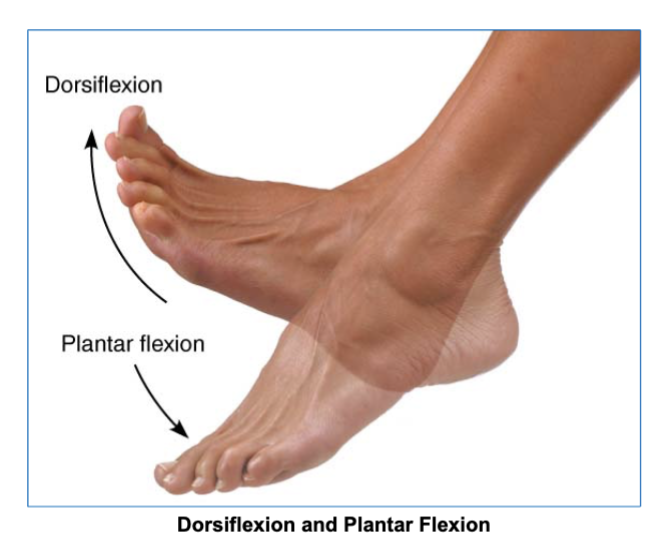
dorsiflexion and plantar flexion (at the ankle) joint movement
makes toes point up or down
eversion and inversion joint movement
moves the soles of foot either outward or inward
thumb opposition joint movement
brings the tip of thumbs into contact with the other finger tips of the same hand.
5 functions of skeletal system
1. Support
2. Protection
3. Movement
4. Mineral storage: Calcium and phosphorous
5. Hematopoiesis (Blood cell formation)
Protection (skeletal system function)
Bones Protect the brain
The cranium completely surrounds and protects the brain from injury.
What does hematopoiesis mean?
blood cell formation
hematopoiesis (skeletal system function)
blood cell formation
Red marrow is responsible for hematopoiesis.
Yellow marrow stores fat
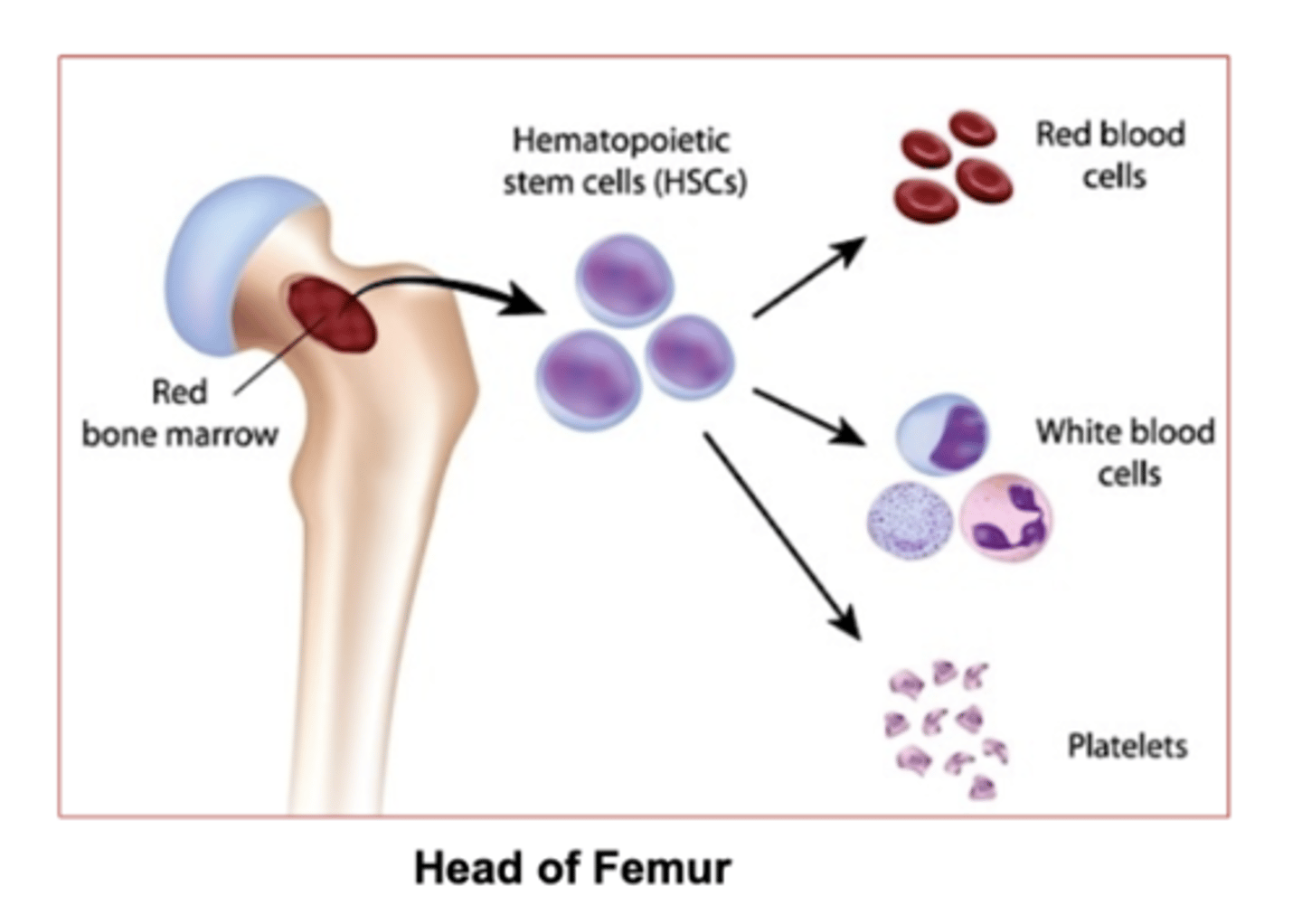
Which marrow is responsible for hematopoiesis (red blood cell formation) ?
red bone marrow
which marrow stores fat?
yellow bone marrow
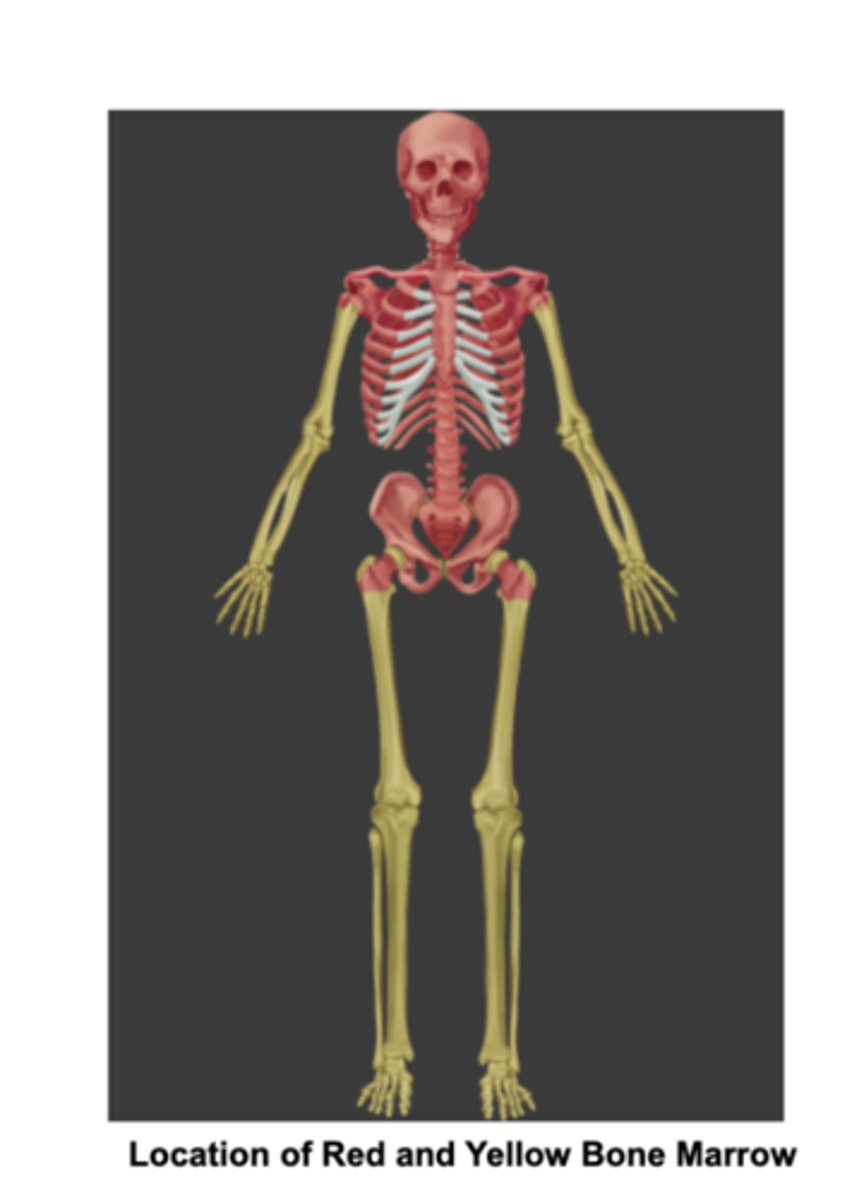
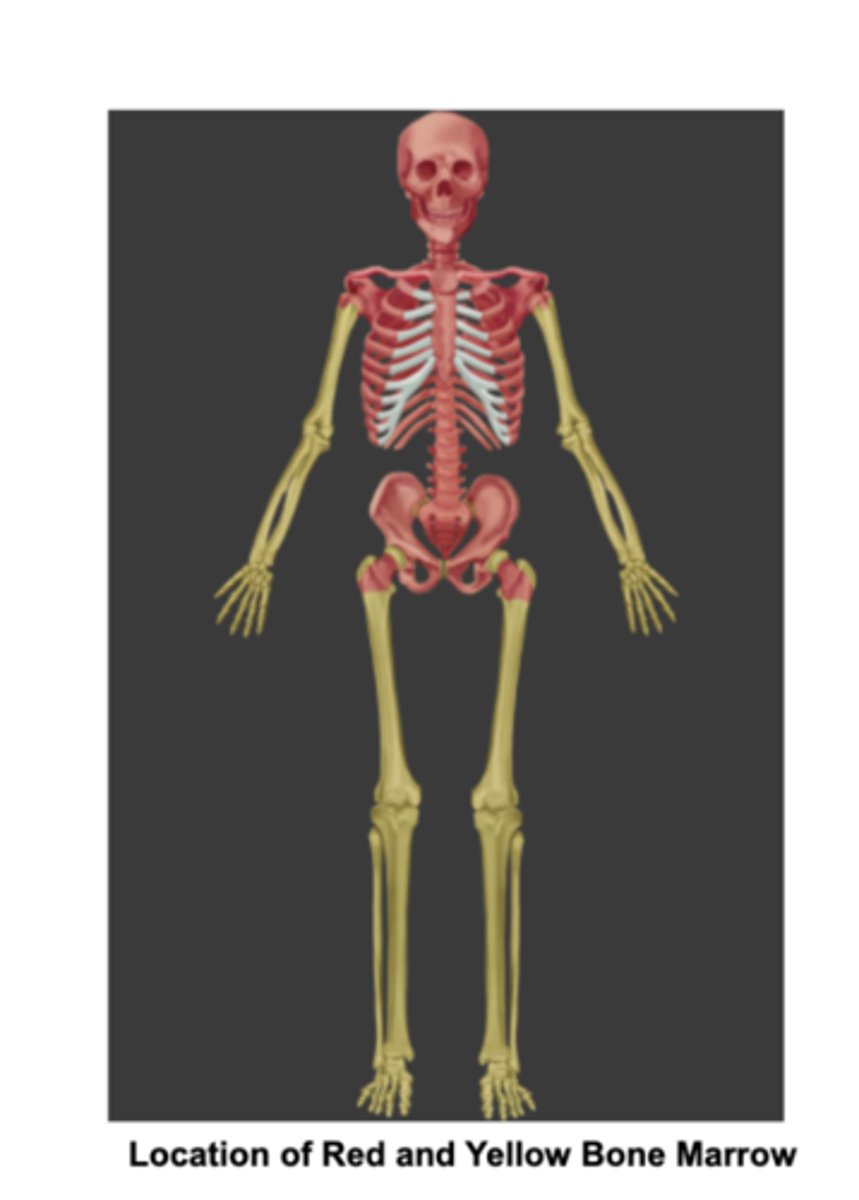
Which bones contain Red bone marrow in adults:
Flat bones and the ends of the femur and humerus.
(epiphyses = the end of long bones)
what does epiphyses mean?
the rounded ends of long bones, also containing the articular cartilage.
Where is yellow bone marrow in adults?
in the medullary cavity of long bones.
the limbs
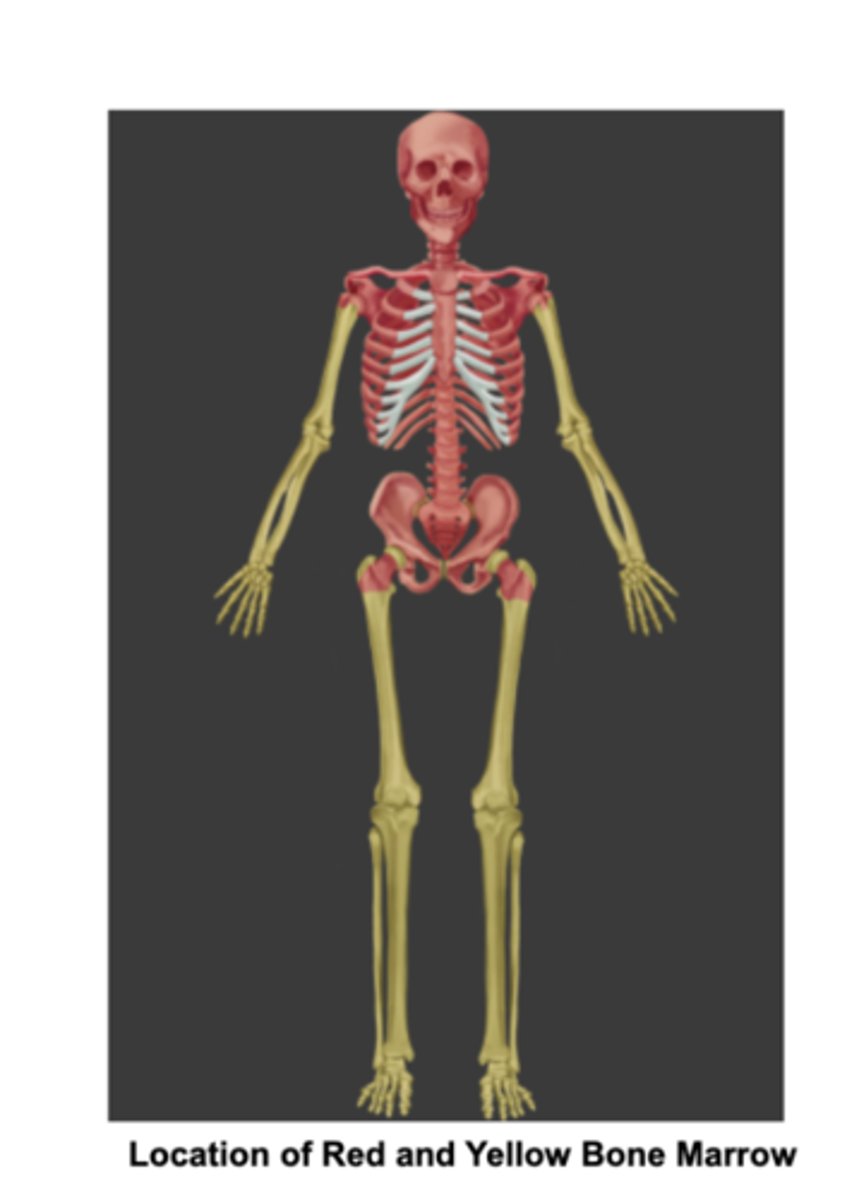
2 Bone marrows in adults
Red bone marrow- in Flat bones, the ends of the femur and humerus.
yellow bone marrow- found in the medullary cavity of long bones,
what is the medullary cavity?
The inner space of long bones.
Its filled with bone marrow
Whats the medullary cavity filled with?
Bone marrow
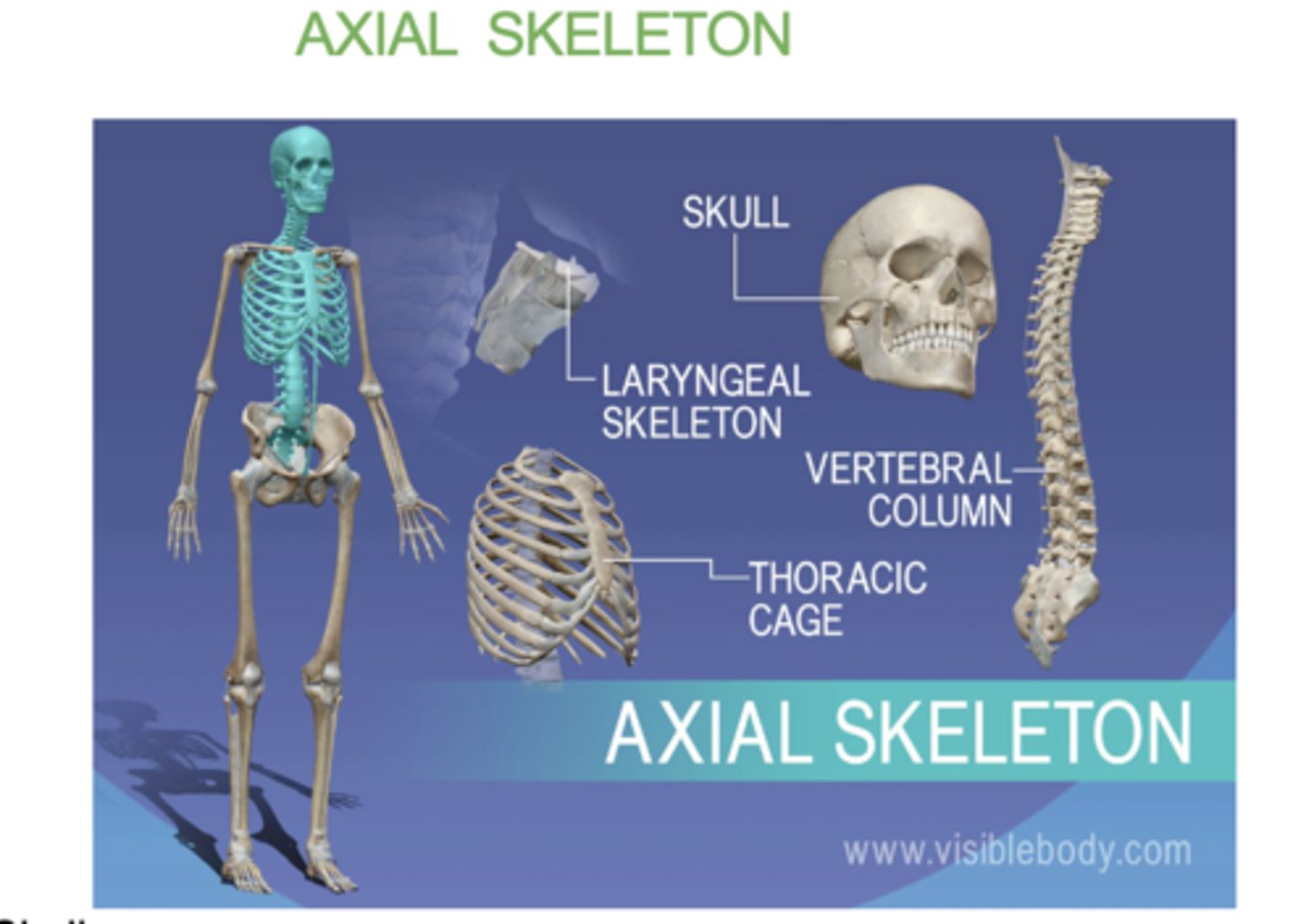
what does the axial skeleton consist of?
-skull
- verterbral column
- sternum
- ribs
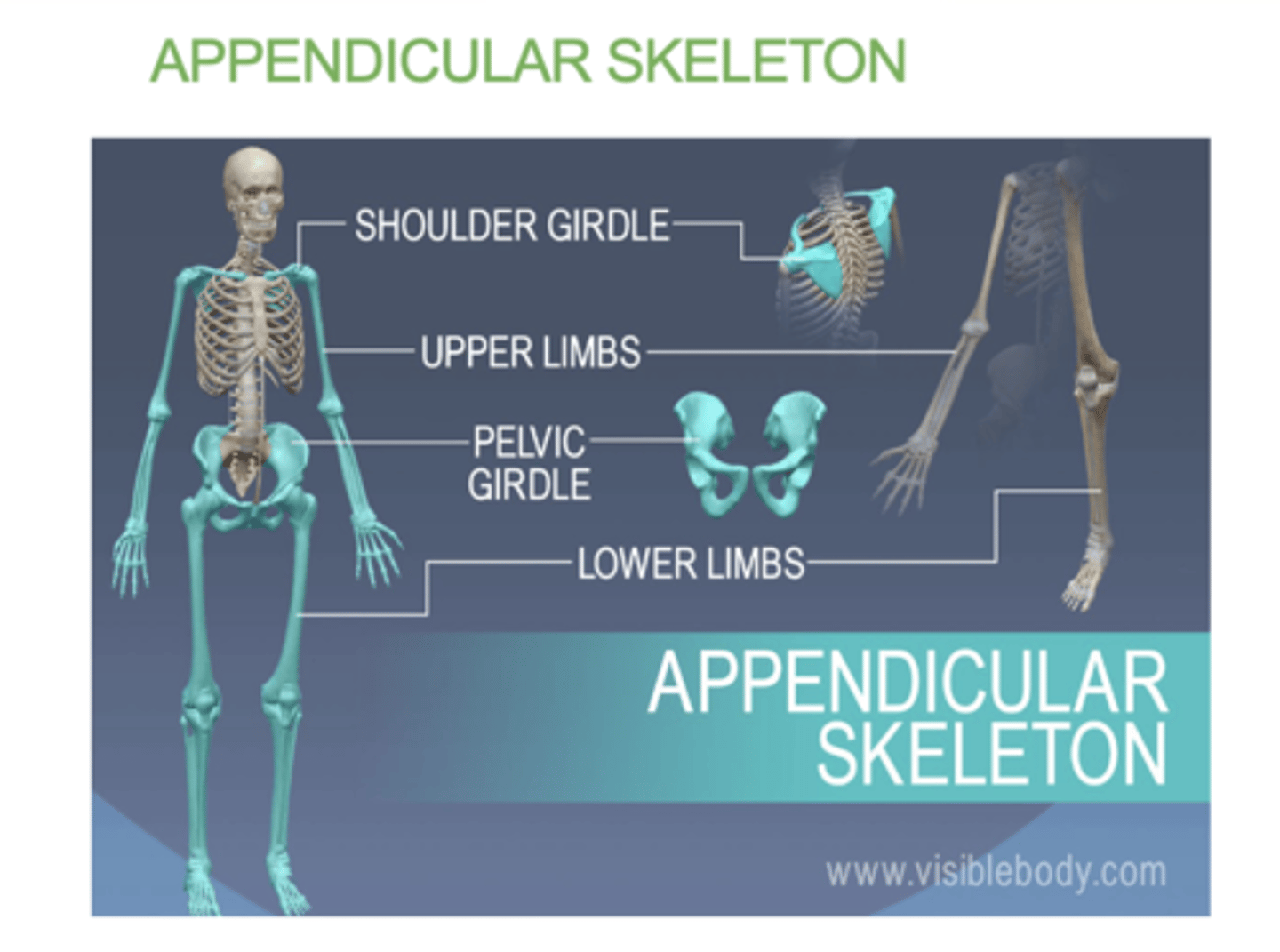
what does the appendicular skeleton consist of?
(Appendicular = Attachments)
• Shoulder girdle
• Upper limbs
• Pelvic girdle
• Lower limbs
4 bone cells within bones
a) Osteogenic cells: Stem cells that develop into osteoblasts.
b) Osteoblasts: Bone-forming cells. Lay down bone matrix and collagen fibers. They will mature into osteocytes.
c) Osteocytes: Mature bone cells .
d) Osteoclasts: Bone destroying cells. Break down bone for remodeling and release of calcium. Responsible for bone resorption. (completely seperate cell, does not have to do with the other)
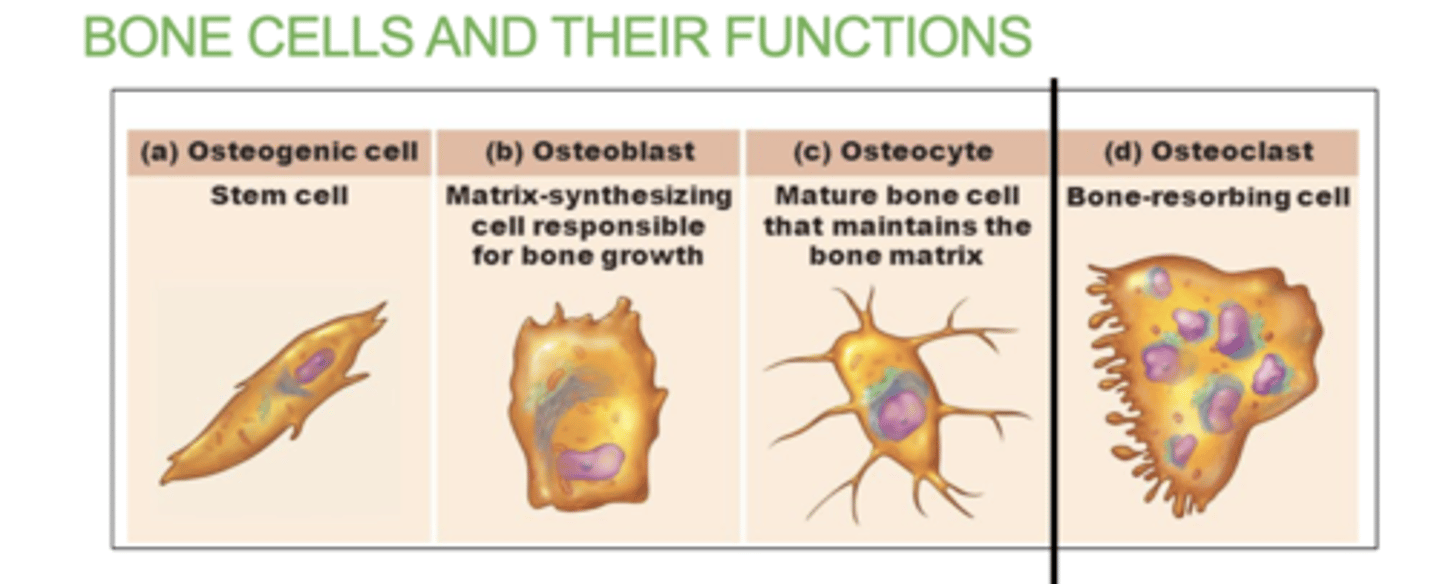
what does the Osteogenic cells do?
They contain stem cells that develop into osteoblasts.
What does the Osteoblasts cells do?
they are responsible for "building bone"
They Lay down bone matrix and collagen fibers. They will mature into osteocytes.
What are Osteocyte cells?
they are mature bone cells.
What do Osteoclast Cells do?
"claws bones"
Break down bone for remodeling and release of calcium.
Osteoclasts in diaphysis will break down bone forming the medullary cavity
Which bone cell will break down bone in the diaphysis and form the medullary cavity?
The Osteoclast cells
5 structures in the anatomy of long bone
- Epiphysis (spongy bone): end of long bone
- Diaphysis (compact bone): middle segment of bone
- Articular cartilage: cartilage that covers both ends of joins ( top and bottom epiphysis)
- Epiphyseal line: the line between epiphysis and diaphysis. An indication that growth in length is complete
-Medullary cavity - space filled with bone marrow
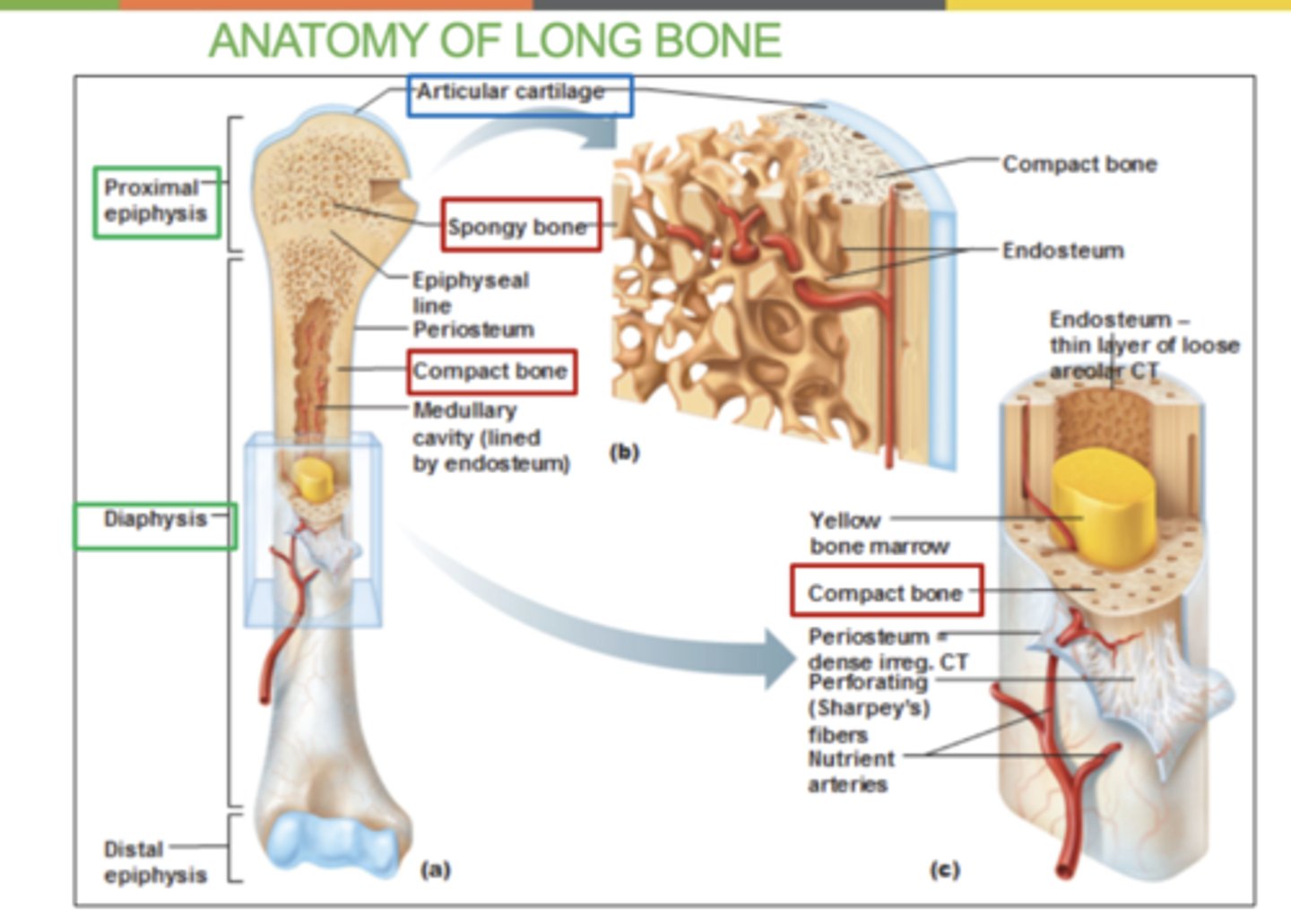
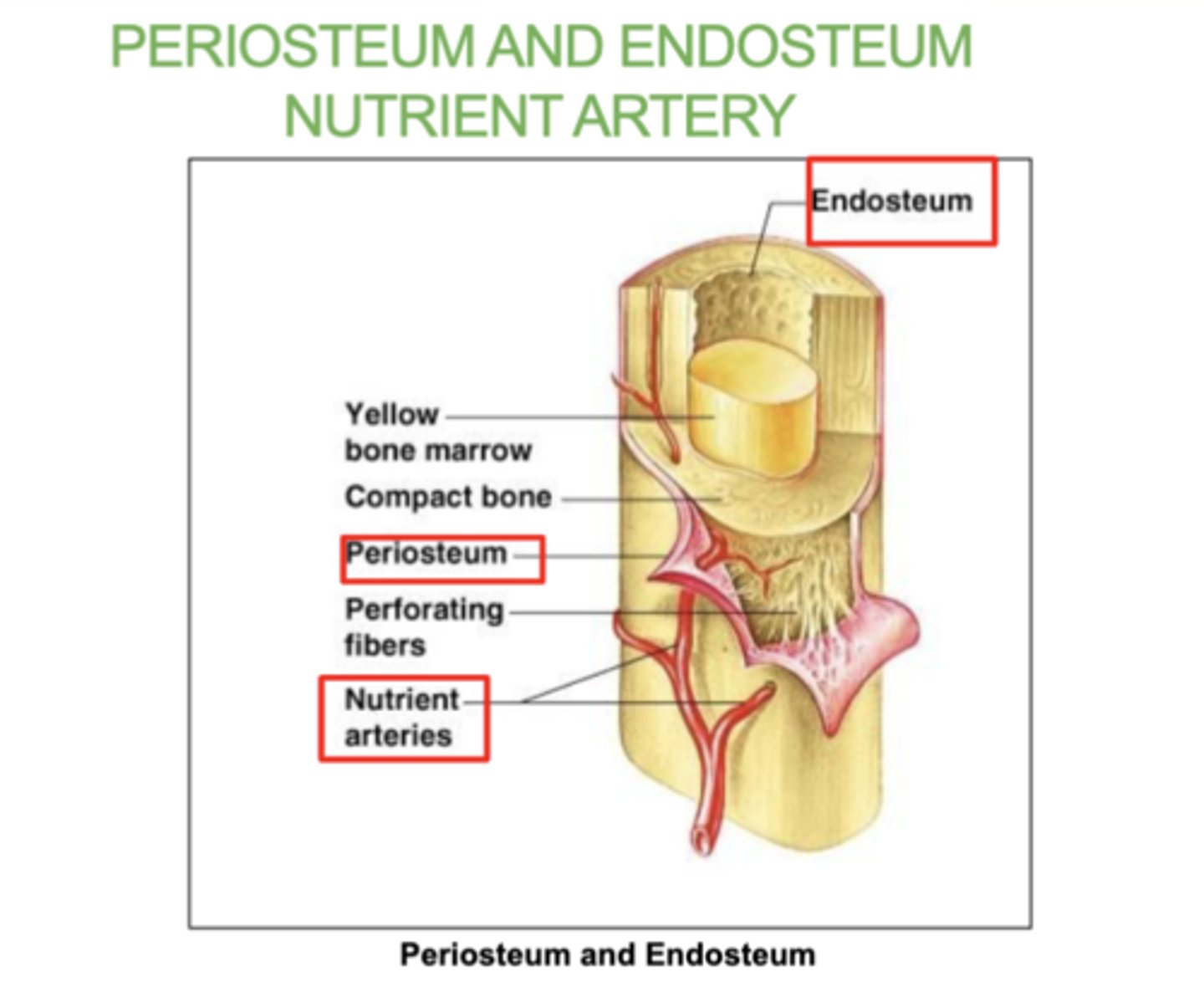
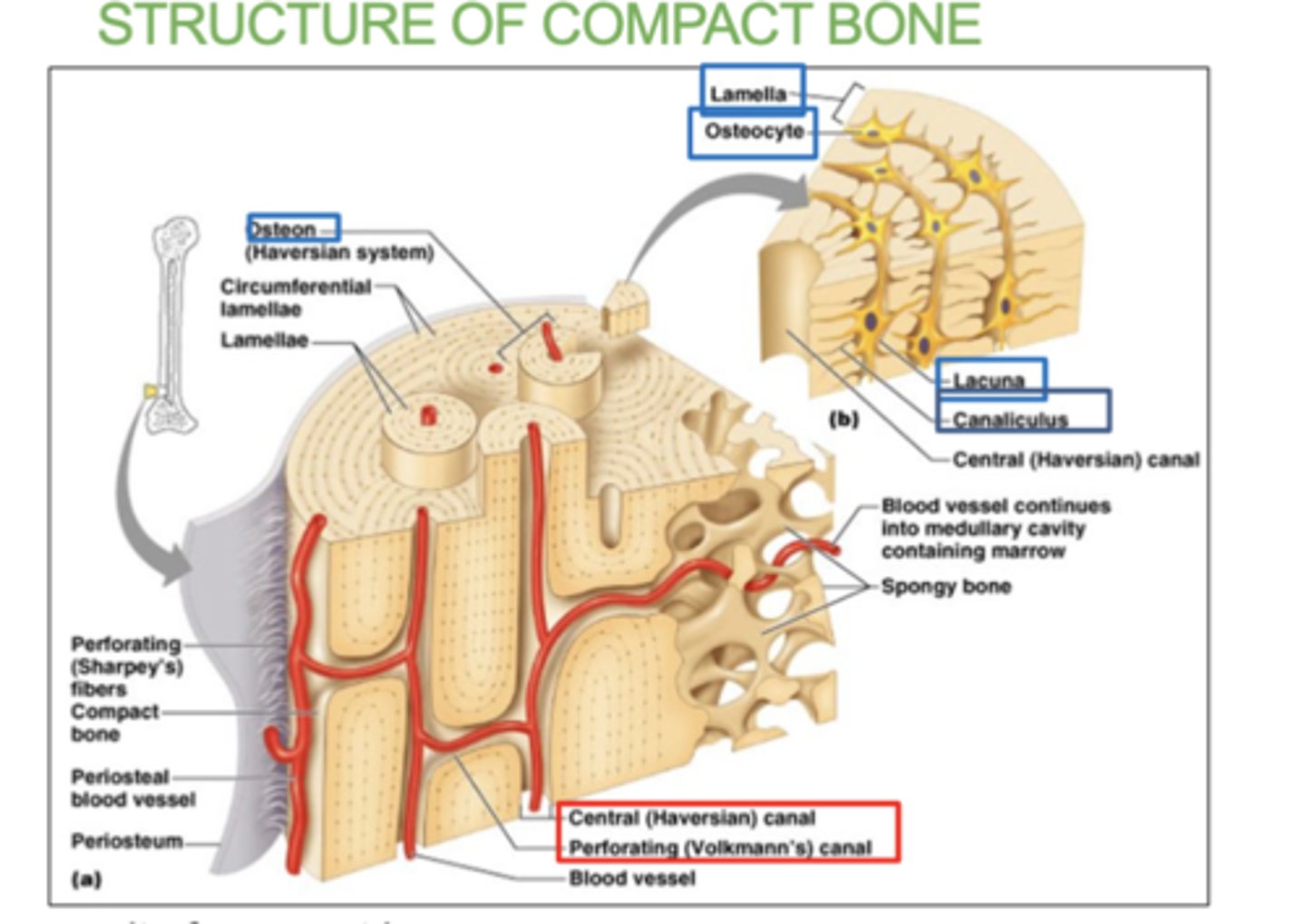
What is the periosteum?
A thin layer of tissue that covers the outside of bones
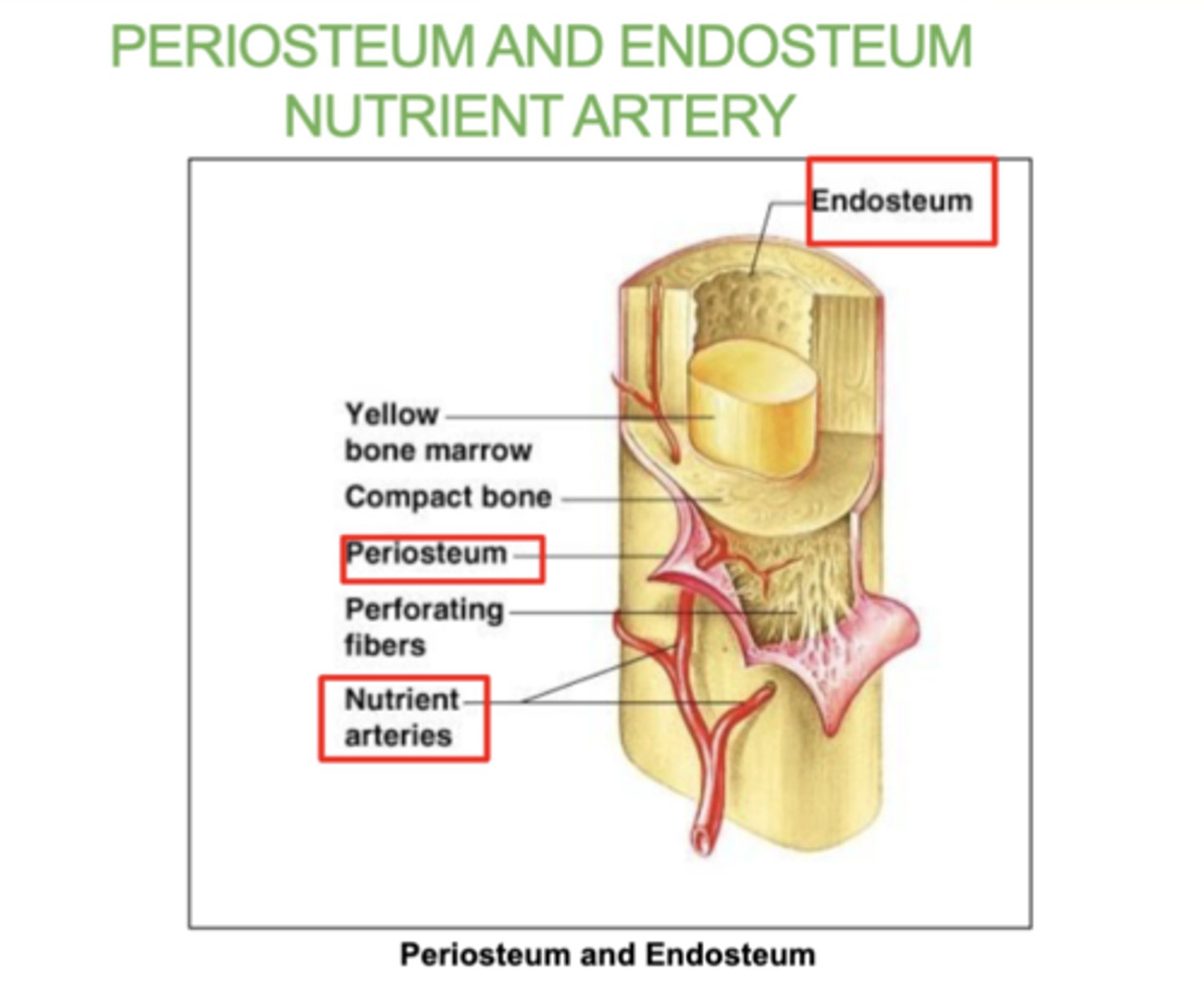
what is the Endosteum?
A thin tissue lining the inside of bones.
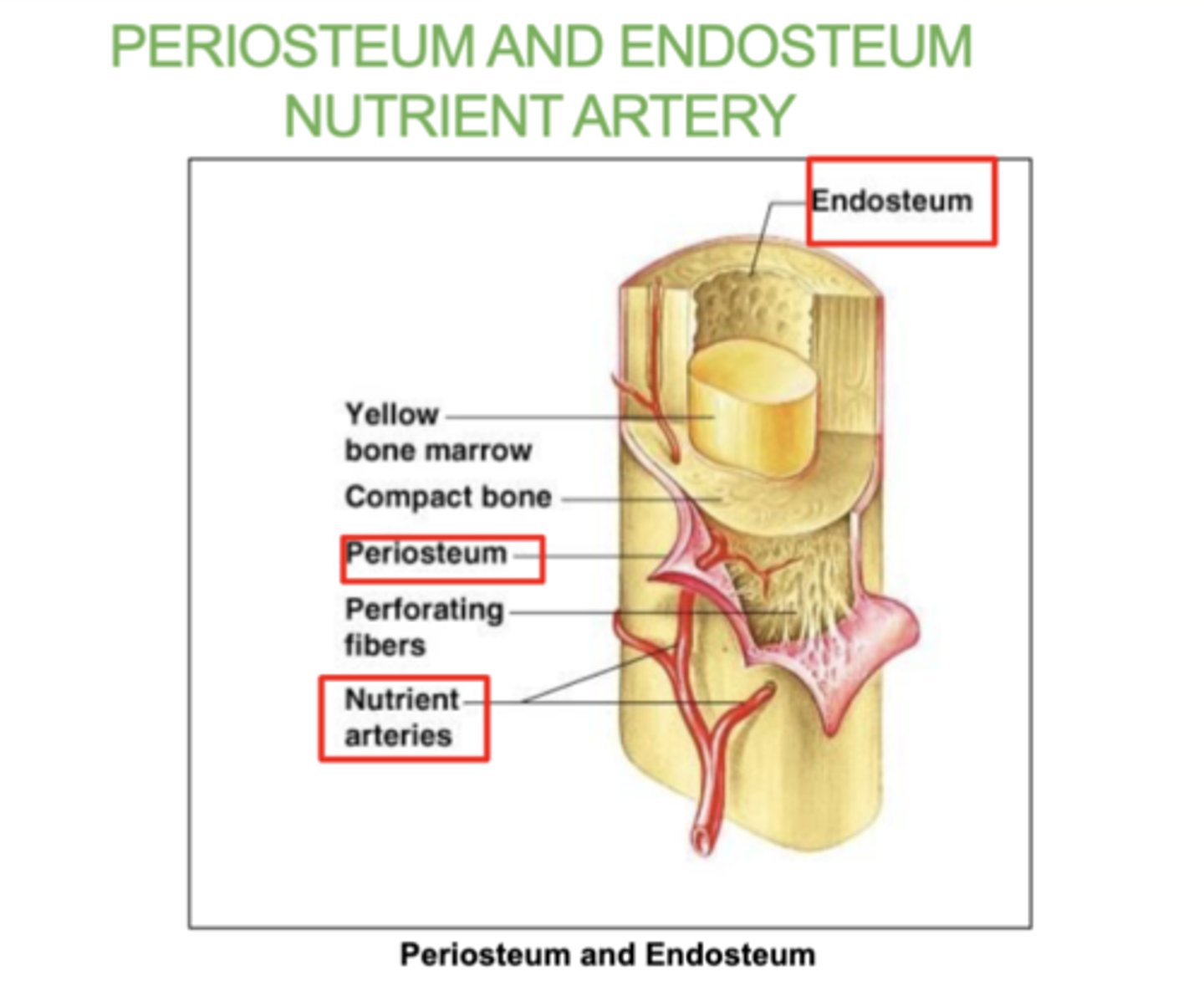
what is the Nutrient artery?
The blood vessel that supplies nutrients to the bone.
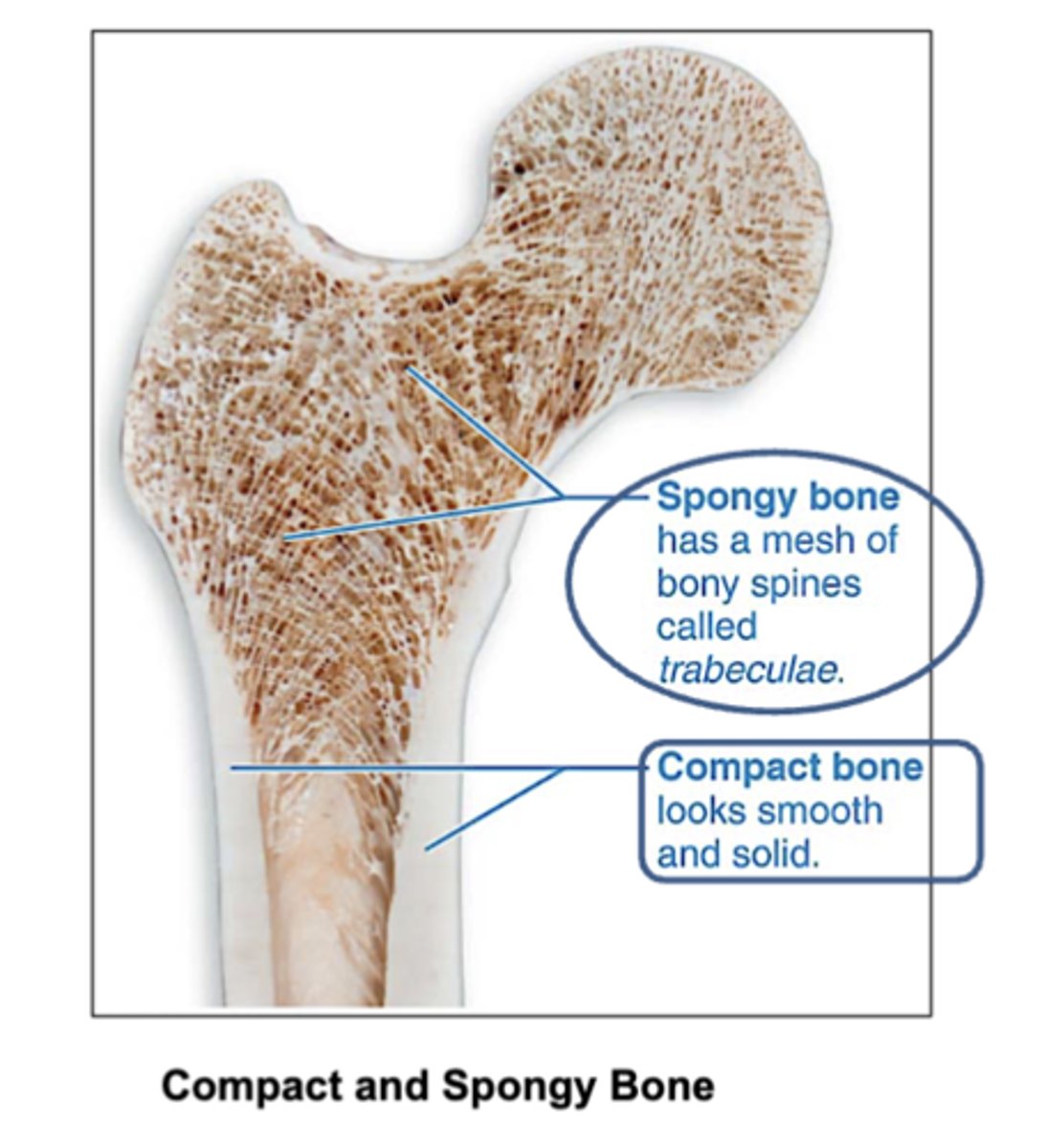
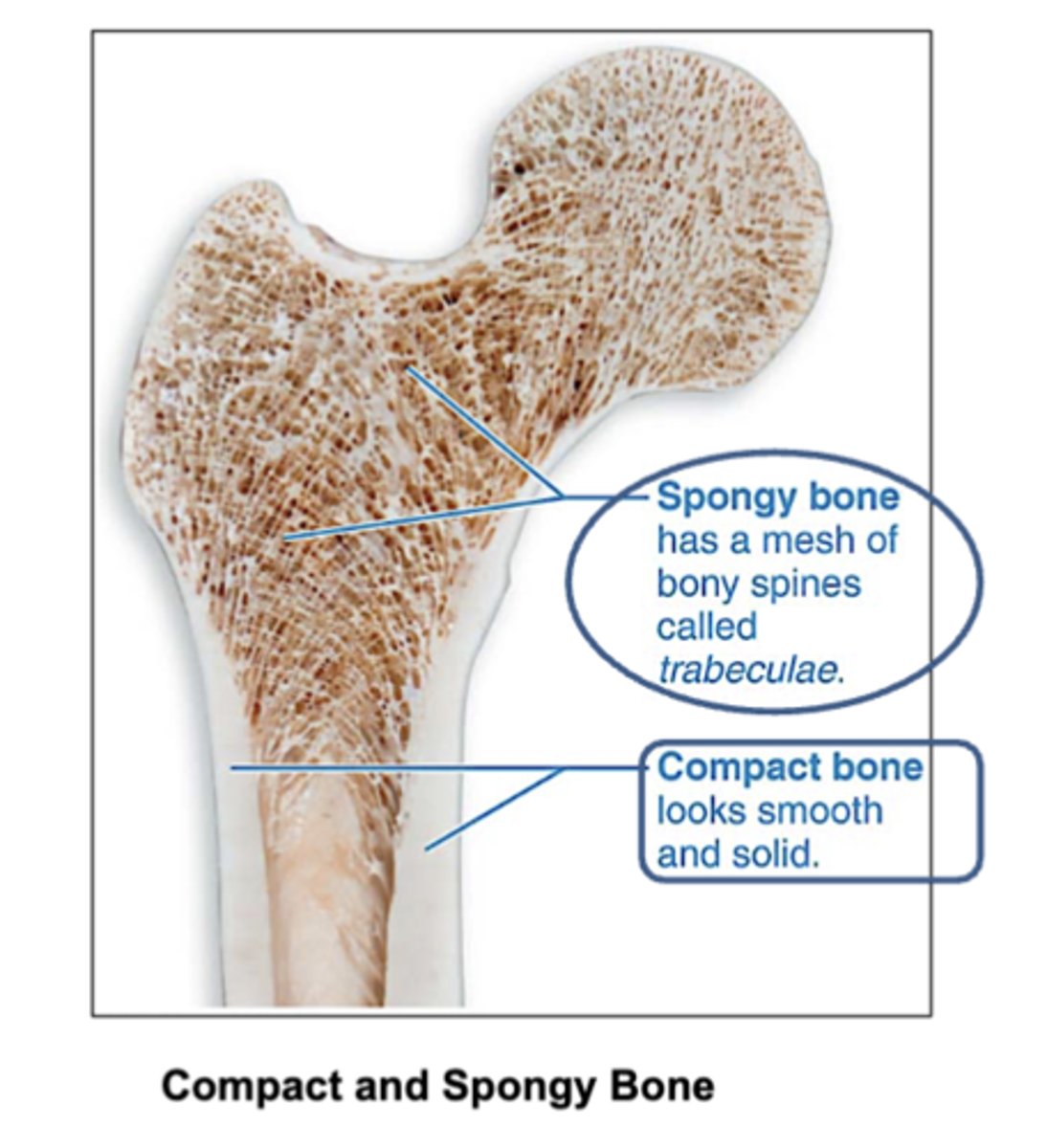
Location of compact and spongy bone?
Compact bone: Found on the outer layer of bones. (looks smooth and solid)
Spongy bone: Found inside bones, mainly at the ends of long bones.
And in flat bones like the ribs, vertebrae and skull bones.
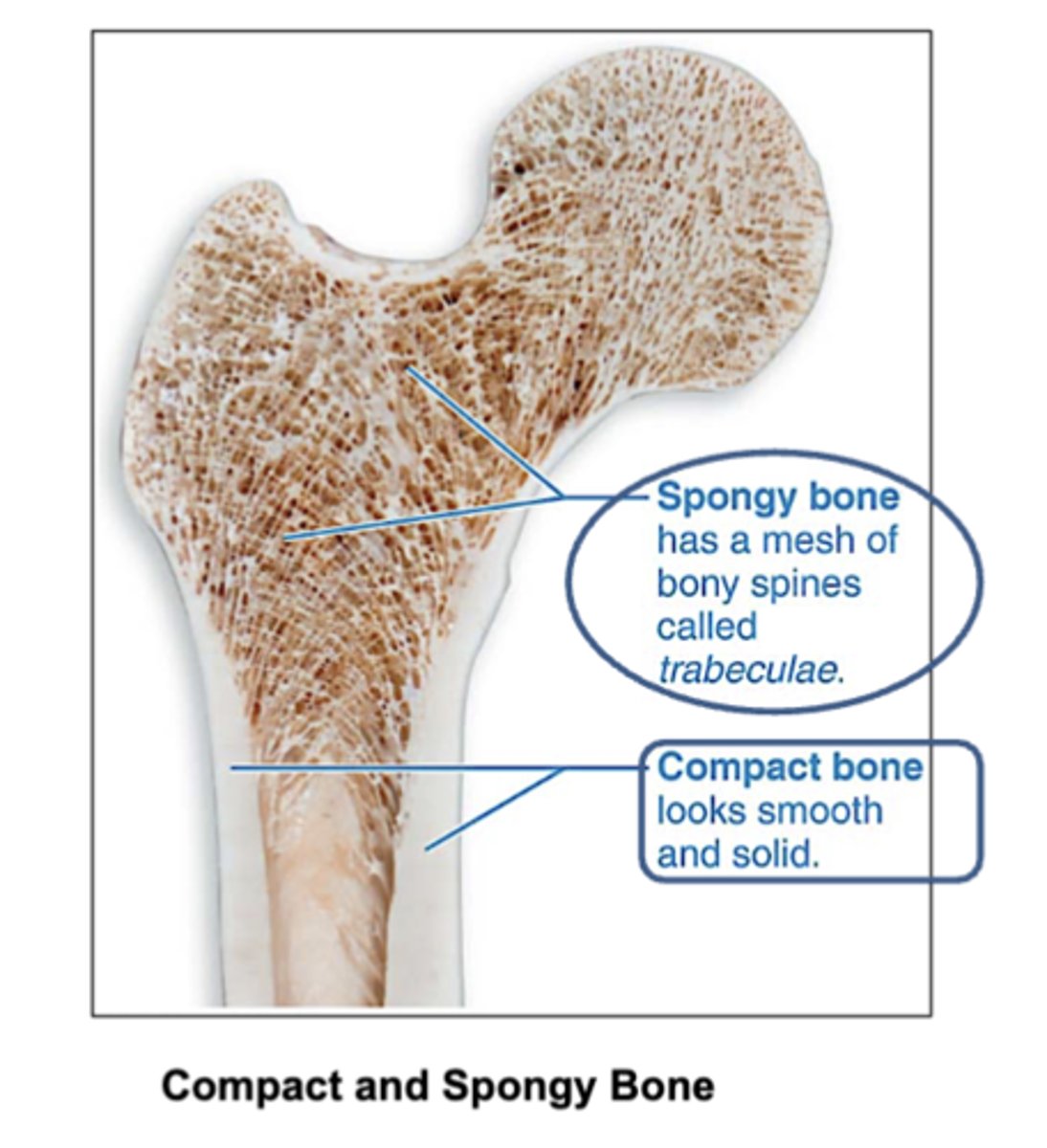
How does compact bone look?
smooth and solid
What are spongy bones made of?
trabeculae that contain the osteocytes.
Red marrow fills the spaces.
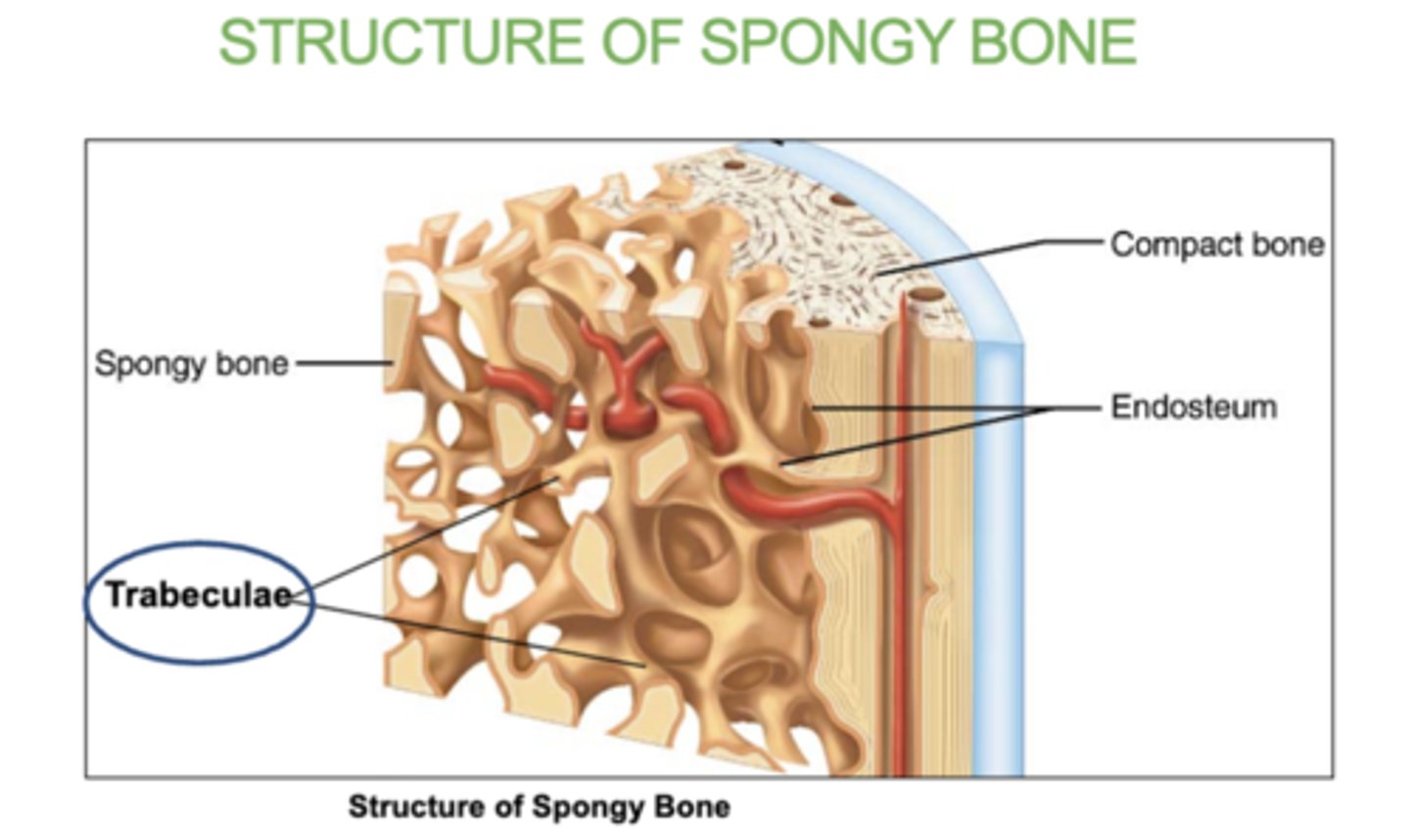
What fills in the inside of spongy bones?
red bone marrow
where is spongy bone found?
in epiphyses (ends )of long bones and in flat bones such as ribs, vertebrae and skull bones.
What is trabeculae?
the small, needle-like structures that form the network in spongy bone.
Inside of them is the red bone marrow.
3 Structure of compact bone:
- Osteon: basic unit of compact bone. there's a canal in between each osteon.
- Bone lamellae: basic structure of compact bone. concentric rings/layers of collagen fibers and bone matrix .
- Central canals and Perforating canals: contain blood vessels and nerves
4 Structures of an Osteon:
(all in the osteon)- osteocyte, lacuna, lamellae, & canaliculi
Each osteocytes sit inside hollow spaces called lacuna.
Very thin hair-like canals called canaliculi radiate from each lacuna and allow osteocytes to communicate.
They eventually connect to the central canals
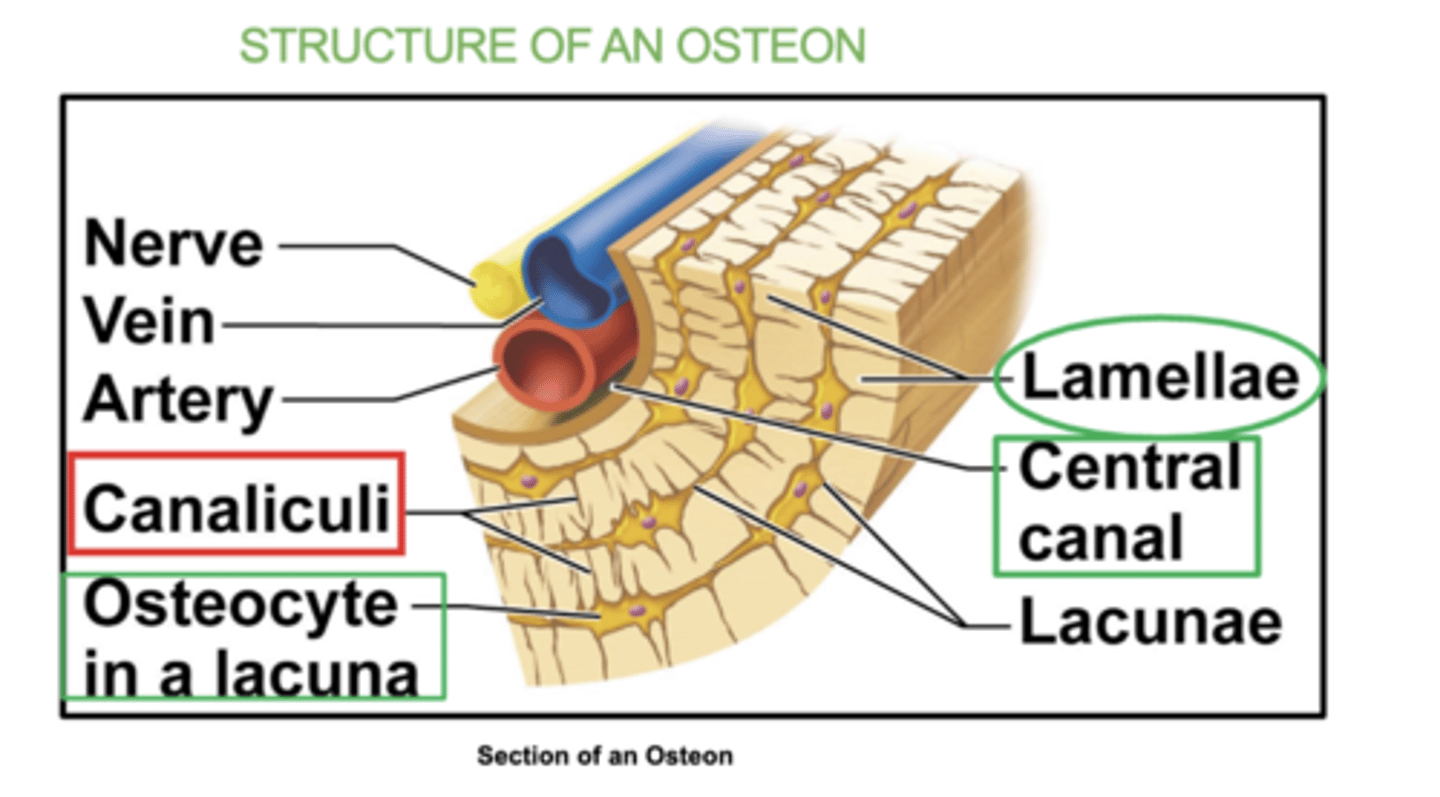
what is an osteocyte?
a mature bone cell that helps maintain bone tissue.
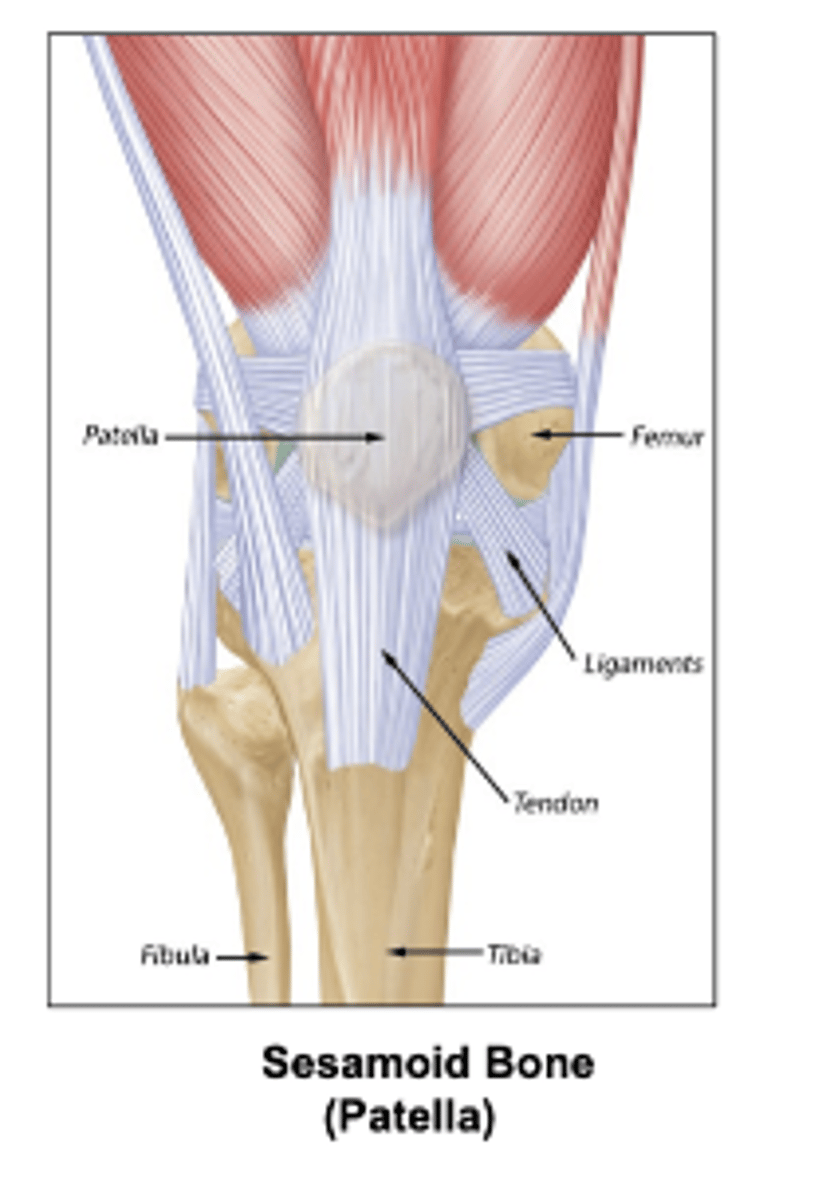
Some types of bones shapes are:
Long, short, flat irregular, irregular, and sesamoid (bone embedded within a tendon).
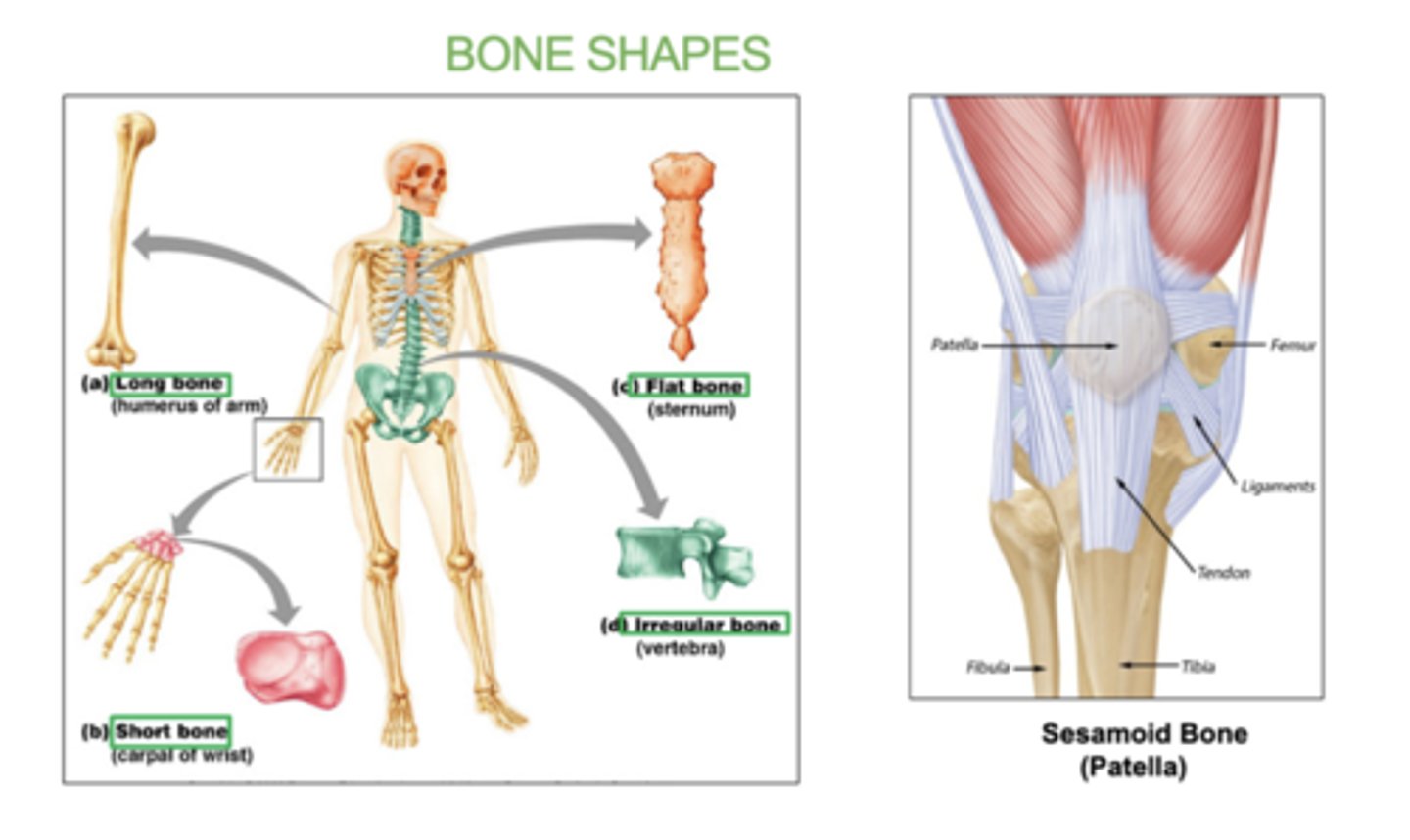
examples of long bones:
(all limbs)
femur, humerus, radius, ulna, tibia, fibula
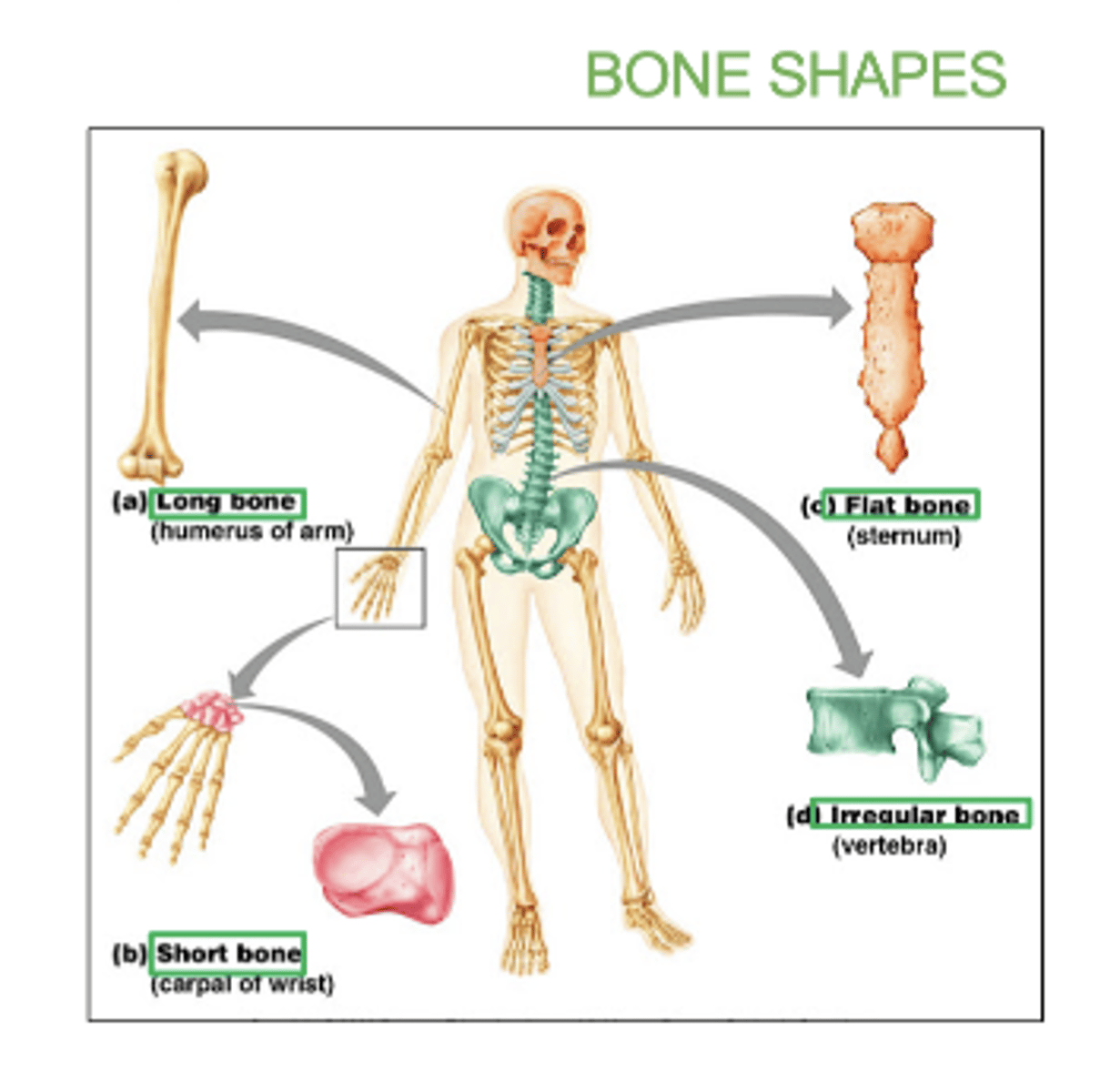
examples of flat bones:
skull, ribs, sternum, & scapula
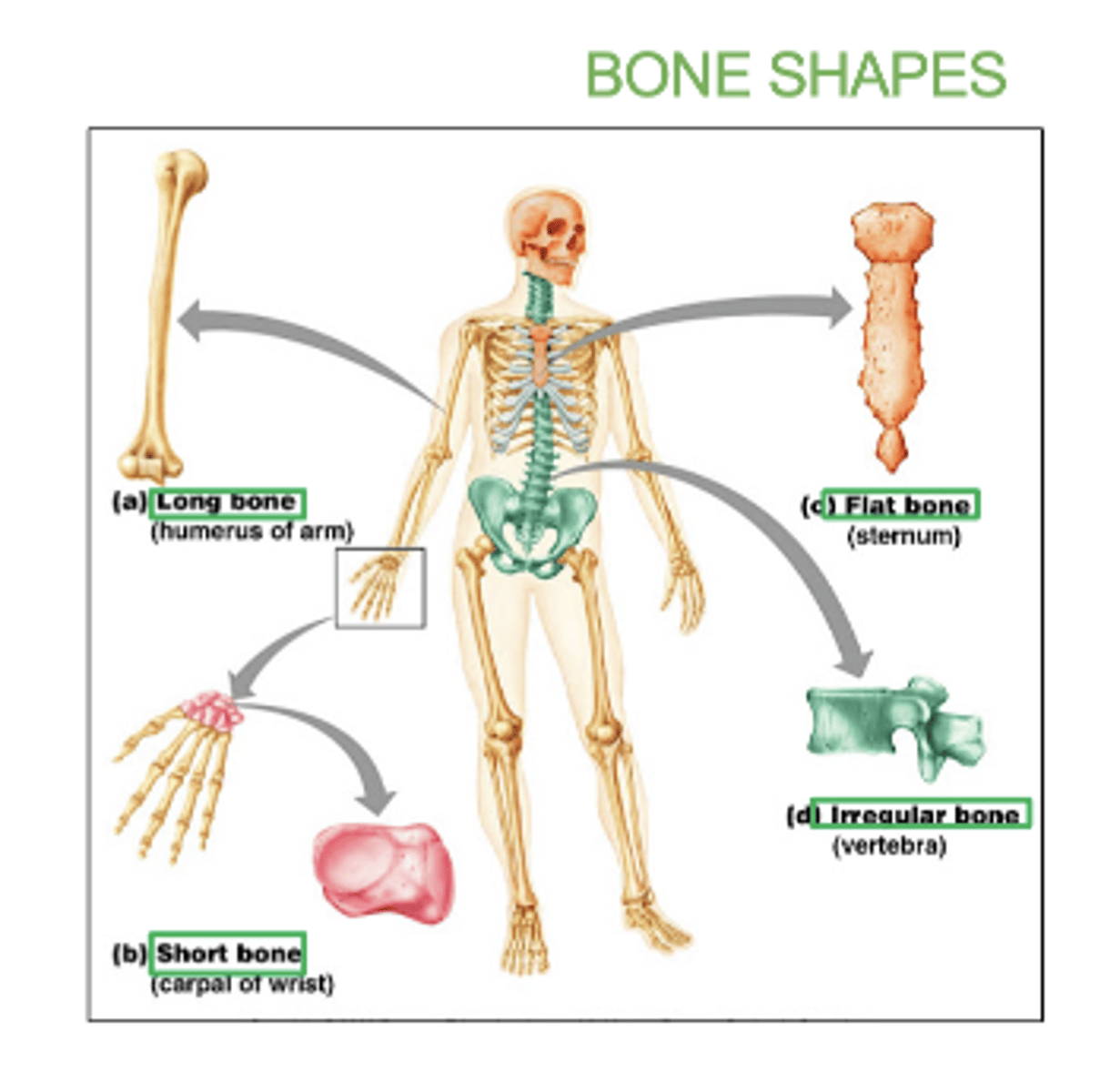
examples of short bones:
carpals and tarsals
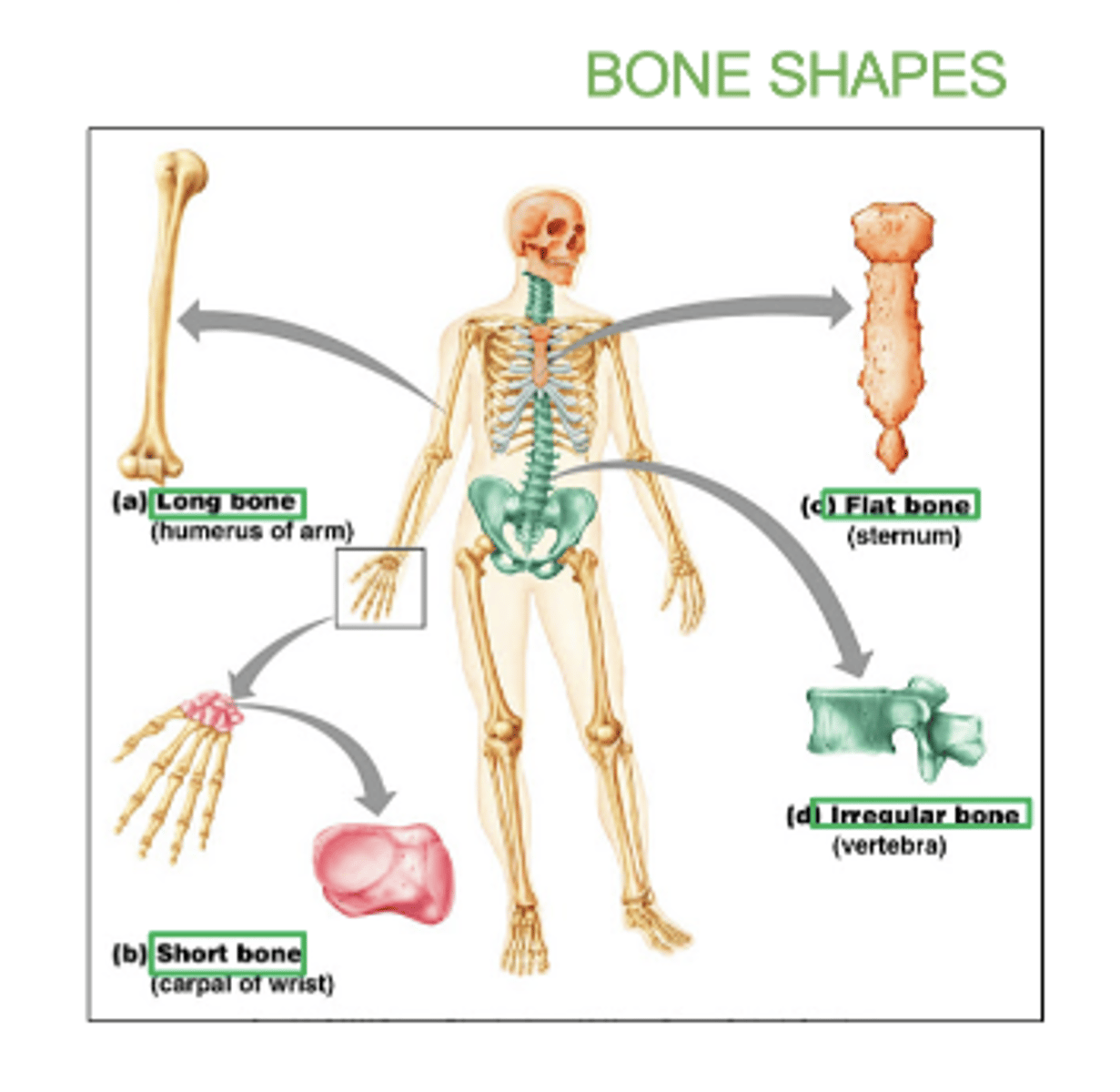
examples of irregular bones:
vertebrae and hip bones
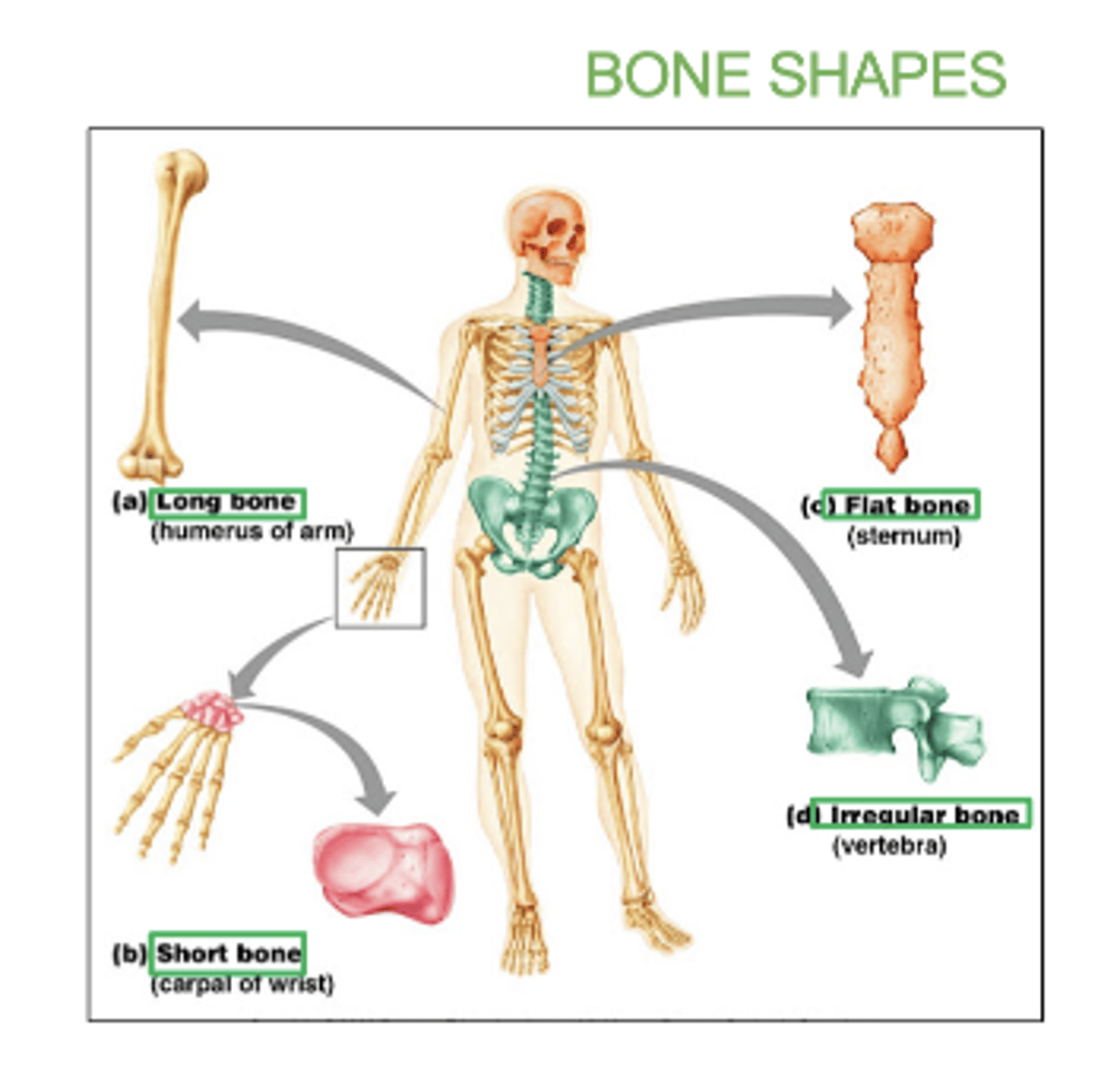
examples of sesamoid bone:
patella
All _____ bones contain spongy bones.
flat
What is bone ossification?
the process by which bone tissue is formed
- either by replacing cartilage or developing directly from connective tissue.
What is intramembranous ossification?
-Bone develops from mesenchyme (embryonic connective tissue)
-Forms flat bones (skull, clavicles) which are mainly spongy bone.
-Multiple ossification centers fuse
what's mesenchyme (embryonic connective tissue)?
the tissue found in embryos that develops into different types of connective tissue in the body, including bone, cartilage, and blood.
what does embryos have to do with bone ossification?
Embryos are where bone ossification begins.
-During early development, the bone starts forming from embryonic connective tissue (mesenchyme) or cartilage, leading to the creation of the skeletal structure.