AQA A-Level Physics Particles
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
What is a nucleon
a proton or neutron in a nucleus
Why does the electron orbit the nucleus
This is because the electron has negative charge and the nucleus is positively charged because of protons, so electrons attracted by electrostatic forces of attraction.
charge of electron
-1.6 x 10^-19 C
charge of proton
1.6 x 10^-19 C
mass of electron
9.11 x 10^-31 kg
mass of proton and neutron
1.67 x 10^-27 kg
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
Nuclide
a general term for a specific isotope of an element
Specific charge
The charge per unit mass of a particle
Example of specific charge calculation on sodium ion
A sodium ion has a mass of 23 proton masses (mp).
This is 3.85 × 10-26kg.
It also has a charge of +1 electron charges (e).
This means its charge is 1.60 × 10-19C.
So:
Specific charge = (1.60 × 10-19C) ÷ (3.85 × 10-26kg)
Specific charge = 4.16 × 106C/kg
strong nuclear force
a powerful force of attraction that acts only on the neutrons and protons in the nucleus, holding them together
What force does the strong nuclear force overcome
Overcomes the electrostatic forces of repulsion between protons in the nucleus
Range of strong nuclear force
0.5-3fm. Repulsion below 0.5fm
Is the effect of strong nuclear force the same between 2 protons as it is between a proton and a neutron or 2 neutrons
Yes
What happens below 0.5 fm
The strong nuclear force becomes a resistive force acting to prevent neutrons and protons being pushed into each other
What makes a nucleus unstable
too many or too few neutrons relative to the number of protons
How do nuclei with too many nucleons decay
Alpha decay (emission of a helium nucleus formed of 2 protons and 2 neutrons).
How do nuclei with too many neutrons decay
Beta minus decay in which a neutron decays to a proton by the weak interaction (quark character has changed from udd to uud)
Beta minus decay equation
neutron -> proton + beta - particle + antineutrino
Beta plus decay equation
proton -> neutron + positron + neutrino
How was existence of neutrino hypothesised
The energy of particles after beta decay was lower than before, a particle with 0 charge (to conserve charge) and negligible mass must carry away this excess energy, this particle is the neutrino.
What is a photon
a particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy
How does a photon behave
It can behave as a particle or a wave
_____ of a photon is directly proportional to _________
Energy of a photon is directly proporional to frequency
Equation of energy
E=hf where h = Planck's constant
Value for Planck's Constant
6.63 x 10^-34 Js
In what planes does an electromagnetic wave oscillate
They oscillate in multiple planes.
When are electromagnetic waves emitted from charged particles?
When they lose energy
Give 2 examples of this occurring
fast-moving electron is stopped, changes direction, slows down
Electron in shell of an atom moves to different shell of lower energy
How are EM waves emitted
Electromagnetic waves are emitted as short bursts of waves, each burst leaving the source in a different direction. Each burst is a packet of electromagnetic waves and is referred to as a photon.
A laser beam contains ______ of the same _________
A laser beam contains photons of the same frequency
Power of a Beam Equation
p=nhf for n number of photons
Important equations
W=QV E=hf f=c/wavelength
electron volt
An energy unit, particularly for atomic and nuclear processes, is the energy given to an electron by accelerating it through 1 volt of electric potential difference.
Electron volt to Joules conversion
1.6 x 10-19 joules.
What is an antiparticle
For each particle there is an antiparticle with the same rest energy and mass but all other properties are the opposite of its respective particle. Have equal but opposite charge.
Does every particle have an antiparticle
Yes
Do untable particles and antiparticles have same lifetime
Yes
What occurs when a particle and antiparticle meet
Annihilation:
The mass of the particle and antiparticle is converted back to energy in the form of 2 gamma ray photons which go in opposite directions to conserve momentum.
What is pair production
This is where energy is converted into mass and you get equal amounts of matter and antimatter. This only happens if there is enough energy to produce the total rest masses of the particles. It must always produced a particle and corresponding antiparticle as certain quantities have to be conserved.
Minimum energy of photon needed=
hf(min)=2E(0)
where f(min) is minimum photon frequency required. E(0) is rest mass energy of particles
4 fundamental forces
electromagnetic, strong nuclear force, weak nuclear force, gravitational force
4 fundamental forces ranked by strength
1) strong nuclear force
2) electromagnetic force
3) weak nuclear force
4) gravitational force
what are exchange particles
virtual particles which are responsible for how forces act between two particles
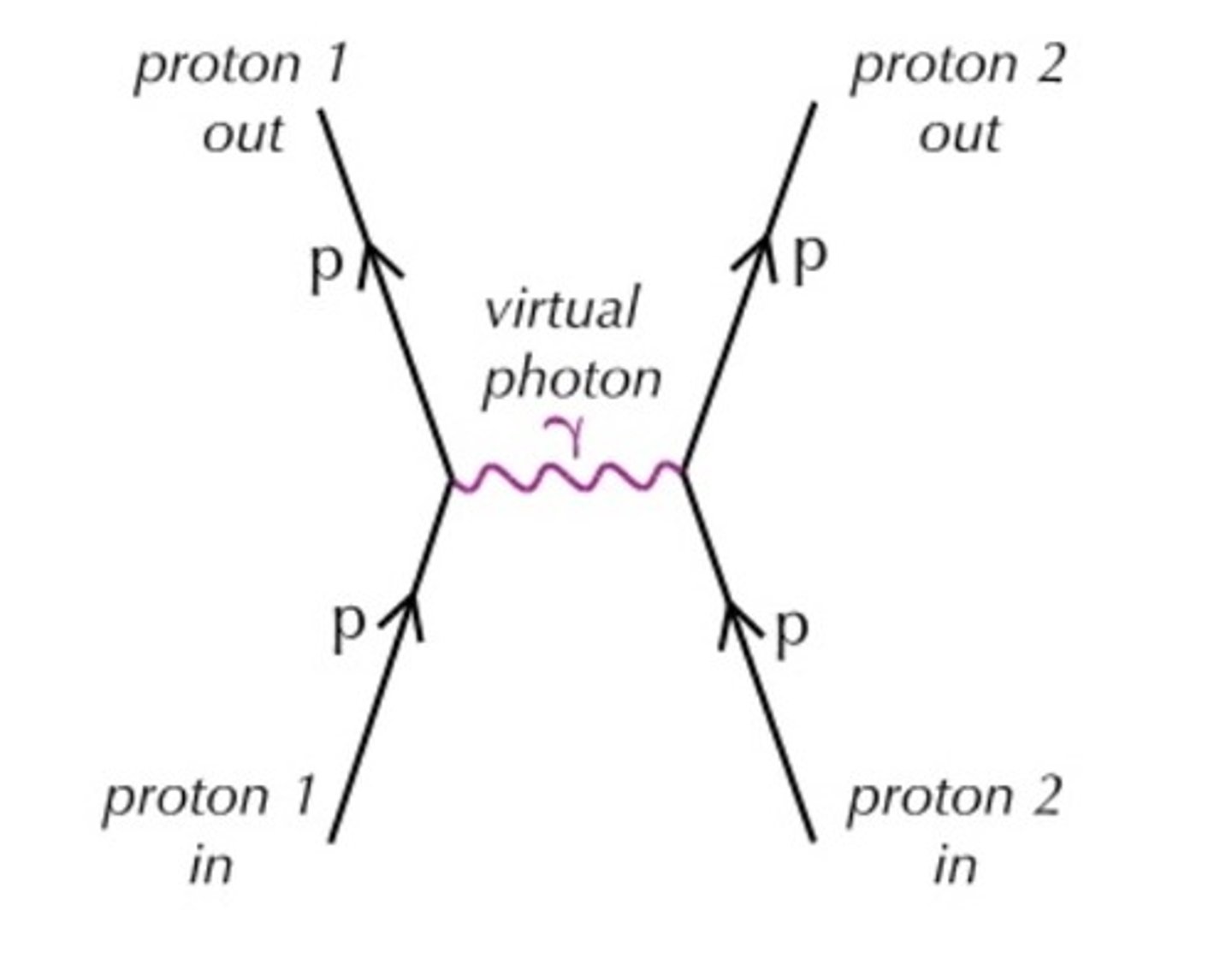
Exchange particle for electromagnetic force
Virtual photon
Exchage particle for strong nuclear force
Gluon (inside nucleons) and meson (between nucleons)
Exchange particle for weak nuclear force
W + and - bosons
Exchange particle for gravitational force
graviton
Why are exchange particles virtual?
Because they cannot be detected directly
fennyman diagram
What does the electromagnetic force act on
All charged particles
Feyman diagram for electromagnetic force
Why is the weak nuclear force weaker than strong nuclear force
As it does not affect stable nuclei and only affects unstable nuclei
What fundamental force is involved in beta decay
weak nuclear force in beta + and - decay
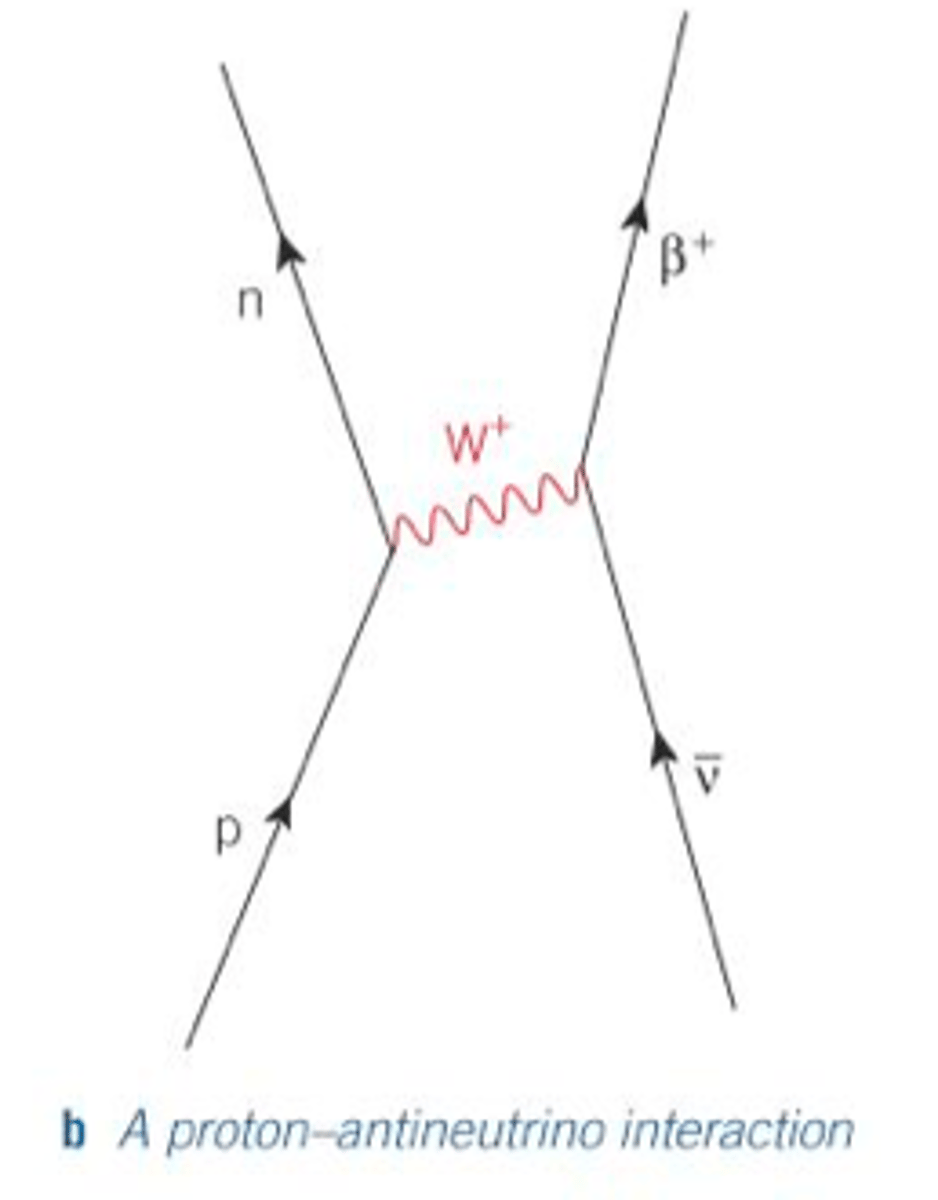
What exchange particle is used in beta + and - decay
W+ bosons for beta + decay
W- bosons for beta- decay
Neutron neutrino interaction

Proton antineutrino interaction
W-bosons and photons differences
W-bosons have non-zero rest mass
W-bosons have very short range of no more than 0.001 fm
W-bosons are positively charged or negatively charged.
Beta - decay
W- boson decays into beta - particle and antineutrino
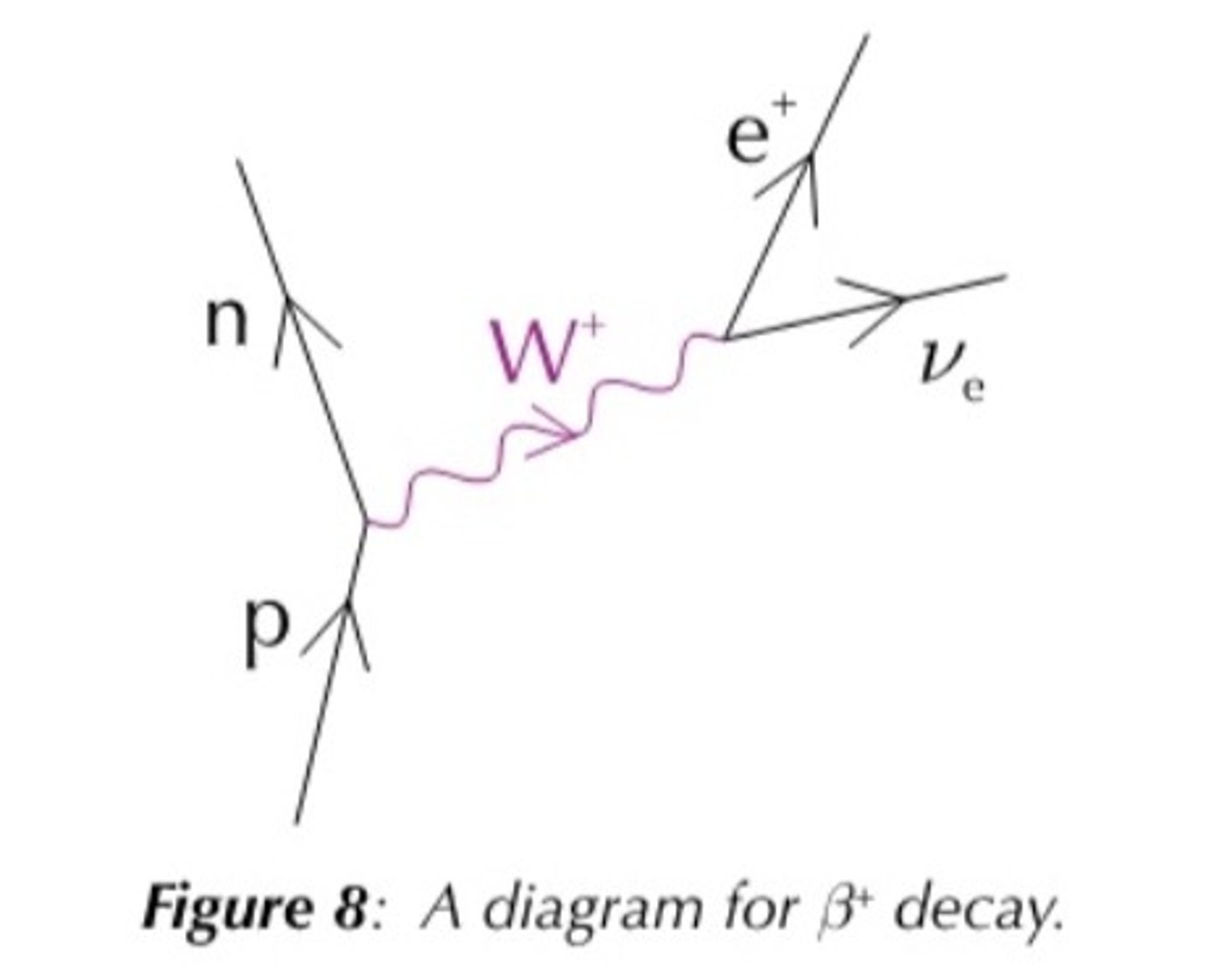
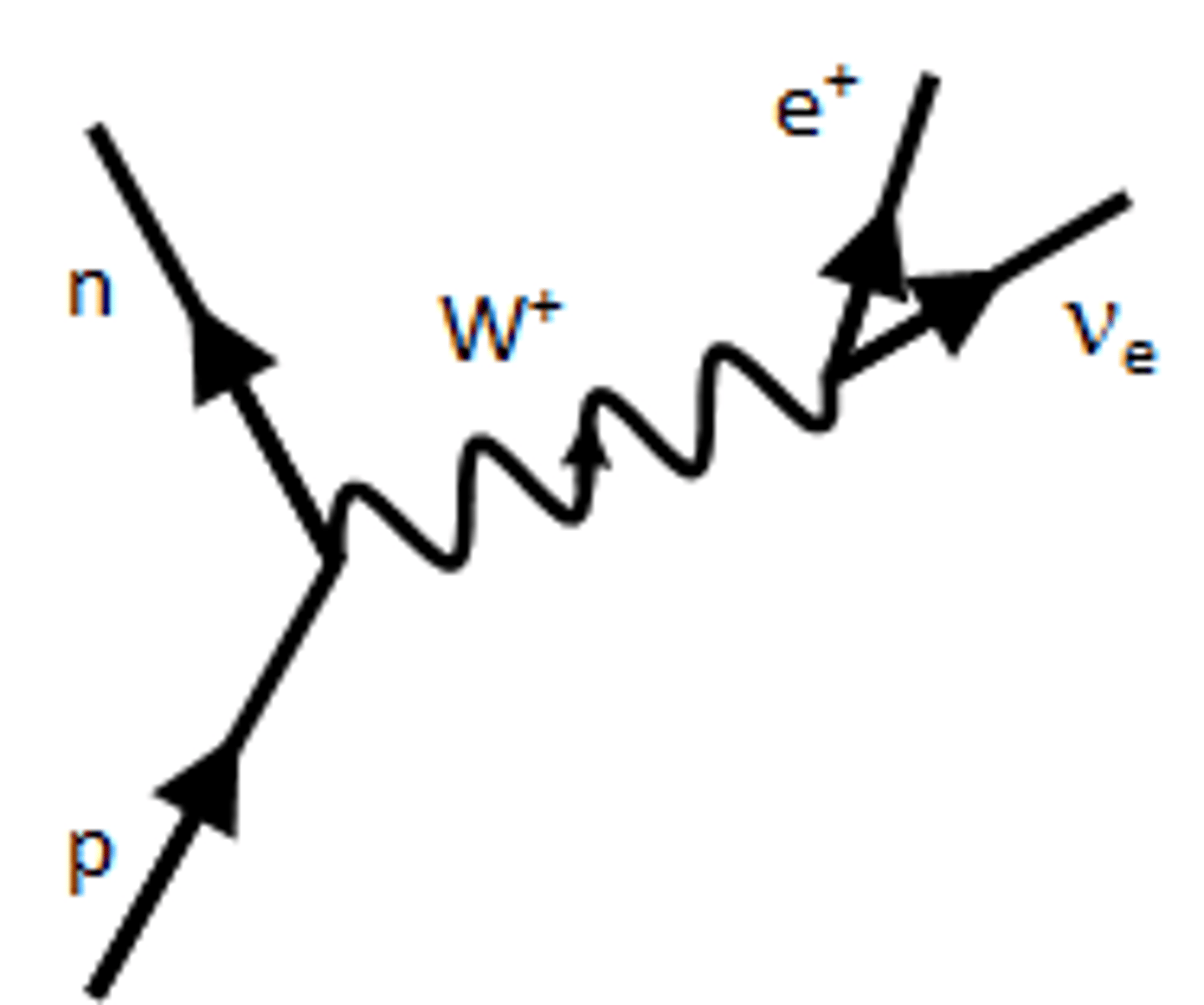
Beta + decay
W+ boson decays into beta + particle and neutrino
electron capture
Proton in proton-rich nucleus turns into neutron as result of interacting through weak interaction with inner shell electron.
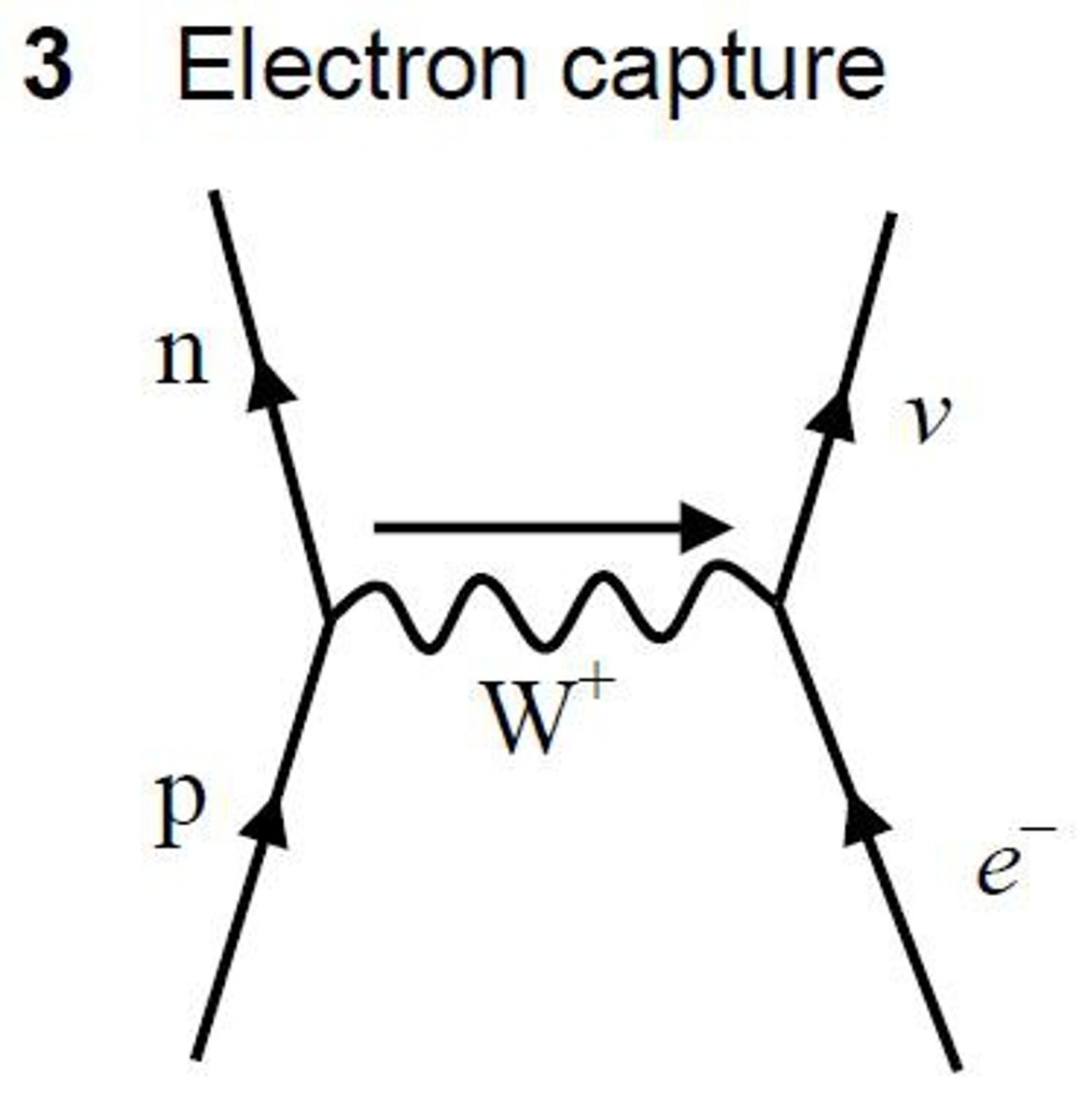
What does W+ boson do in electron capture
Turns electron into neutrino
What types of particles are affected by strong nuclear force
Hadrons
the antiparticle to the proton is the
antiproton
charge of antiproton
-1
interactions the proton undergoes
strong, weak, electromagnetic
antiparticle of neutron
Antineutron
interactions neutron undergoes
strong, weak
why does neutron not undergo electromagnetic force
Because it is not charged
Interactions neutron undergoes
strong, weak forces
antiparticle of electron and it's charge
positron, +1
interactions electron undergoes
weak, electromagnetic
neutrino charge and antiparticle
0, anti-neutrino
muon charge and antiparticle
-1, anti-muon (charge +1)
What charge can pions have?
They can be positive, negative, or neutral.
What do pions decay into?
Muons, antimuons and neutrinos.
What forces do pions interact via?
Strong, weak and electromagnetic forces
What types of charge can kaons have?
They can be positive, negative, neutral, or anti-neutral.
What do kaons decay into?
Pions.
What types of forces do kaons undergo?
Strong and electromagnetic forces.
What do muons decay into
Muons decay into electrons, neutrinos and anti-neutrinos.
Hadrons
Particles that are affected by strong nuclear force, and contain quarks
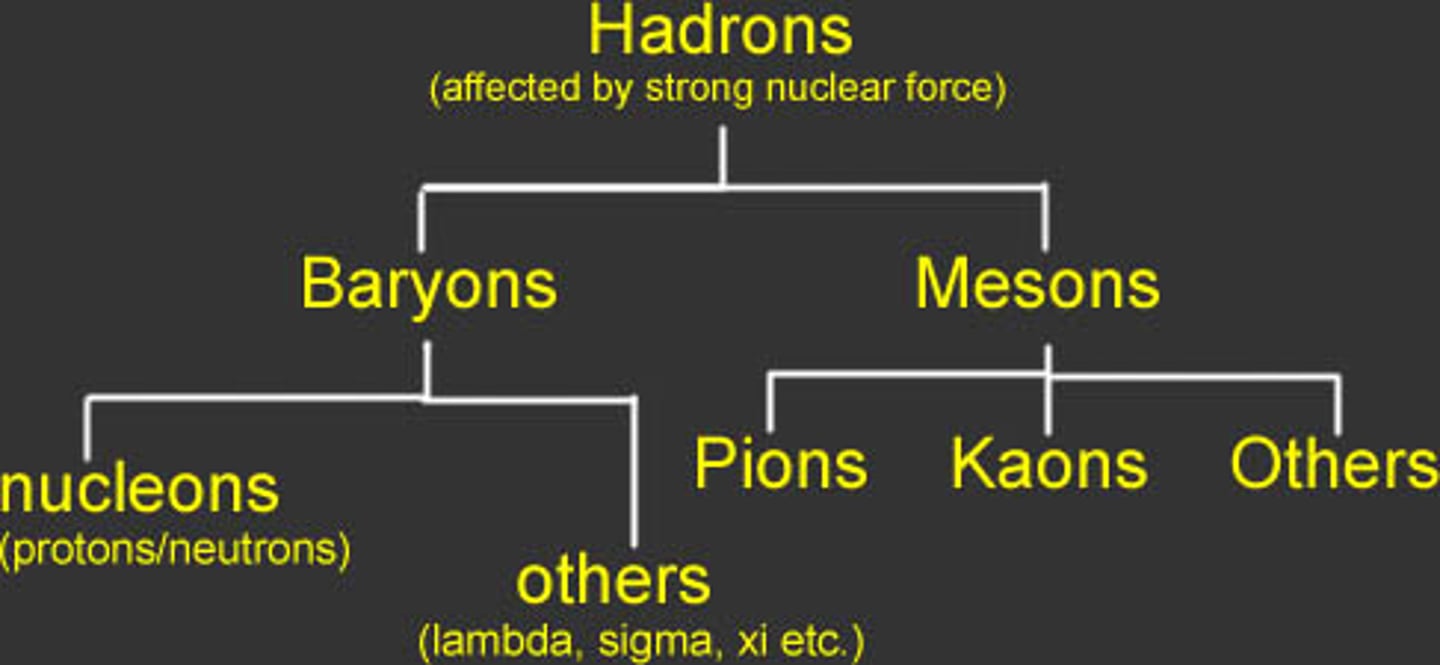
How do hadrons tend to decay
through weak interaction
What are leptons?
Leptons are one of the classes of fundamental particles.
Can leptons be broken down into smaller particles?
No, leptons cannot be broken down into smaller particles.
Name four types of leptons.
Electrons, muons, tauons, and neutrinos.
How do leptons interact
Via the weak interaction
Energy of particles before collision
Total energy of particles and antiparticles before= rest energy + kinetic energy
Energy of particles after collision
rest energy+ kinetic energy
Baryons
Hadrons which contain 3 quarks, including protons and neutrons
Mesons
Subatomic particles made of quark-antiquark pairs
What happens when lepton and antilepton collide
Produce quark and antiquark
What happens in an interaction between lepton and hadron
neutrino/antineutrino can change into or from a corresponding charged lepton
Lepton number of leptons and antileptons
+1 for all leptons
-1 for all antileptons
What happens in muon decay
-Muon changes into a muon neutrino. An electron is created to conserve charge and a corresponding anti neutrino is created to conserve lepton number.
quark properties
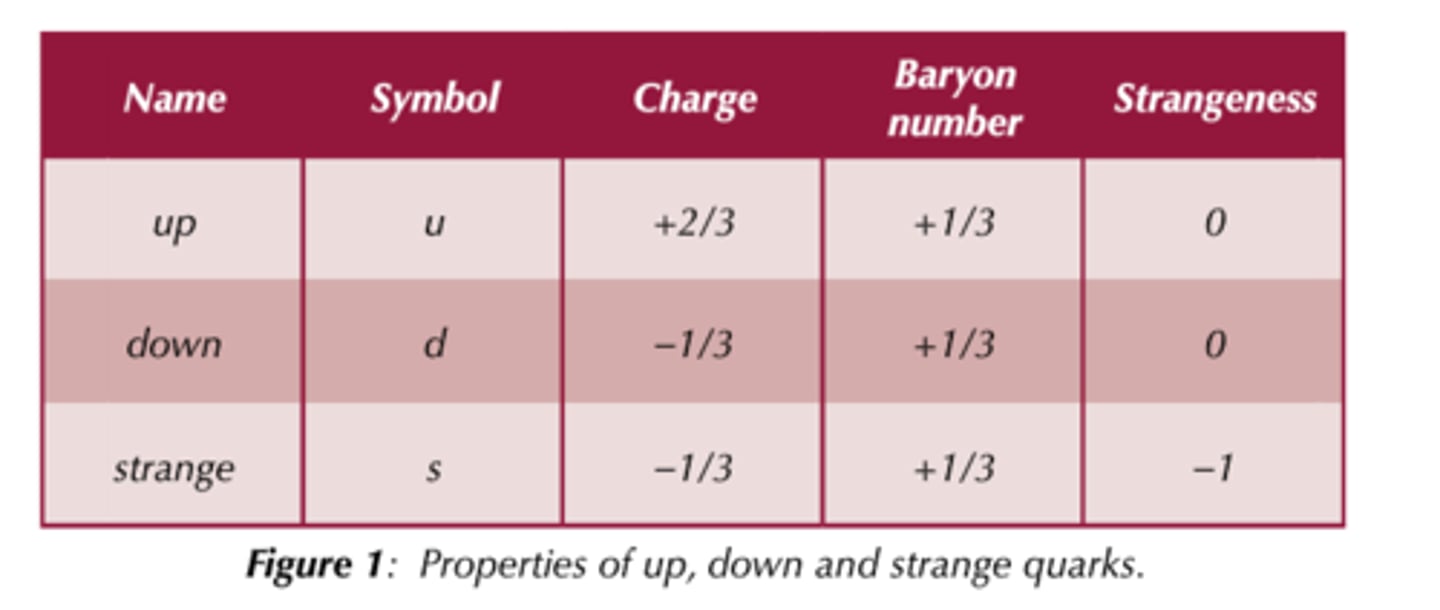
In what number are strange particles created
In twos
What does a kaon decay into?
2 pions