A&P2 Chapter 15
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What pathways do the afferent division of the NS have?
Somatic Sensory Pathways and Visceral Sensory Pathways (Ascending Tracts)
What pathways do the efferent division of the NS have?
Somatic motor pathways (Descending Tracts)
What are our General senses?
Pain, temperature, pressure, vibration, touch, and proprioception
What are our special senses?
Olfaction, gestation, vision, equilibrium, and hearing
What are Tonic receptors?
They are always active. An increase or decrease in stimulation causes an increase or decrease in frequency of action potential.
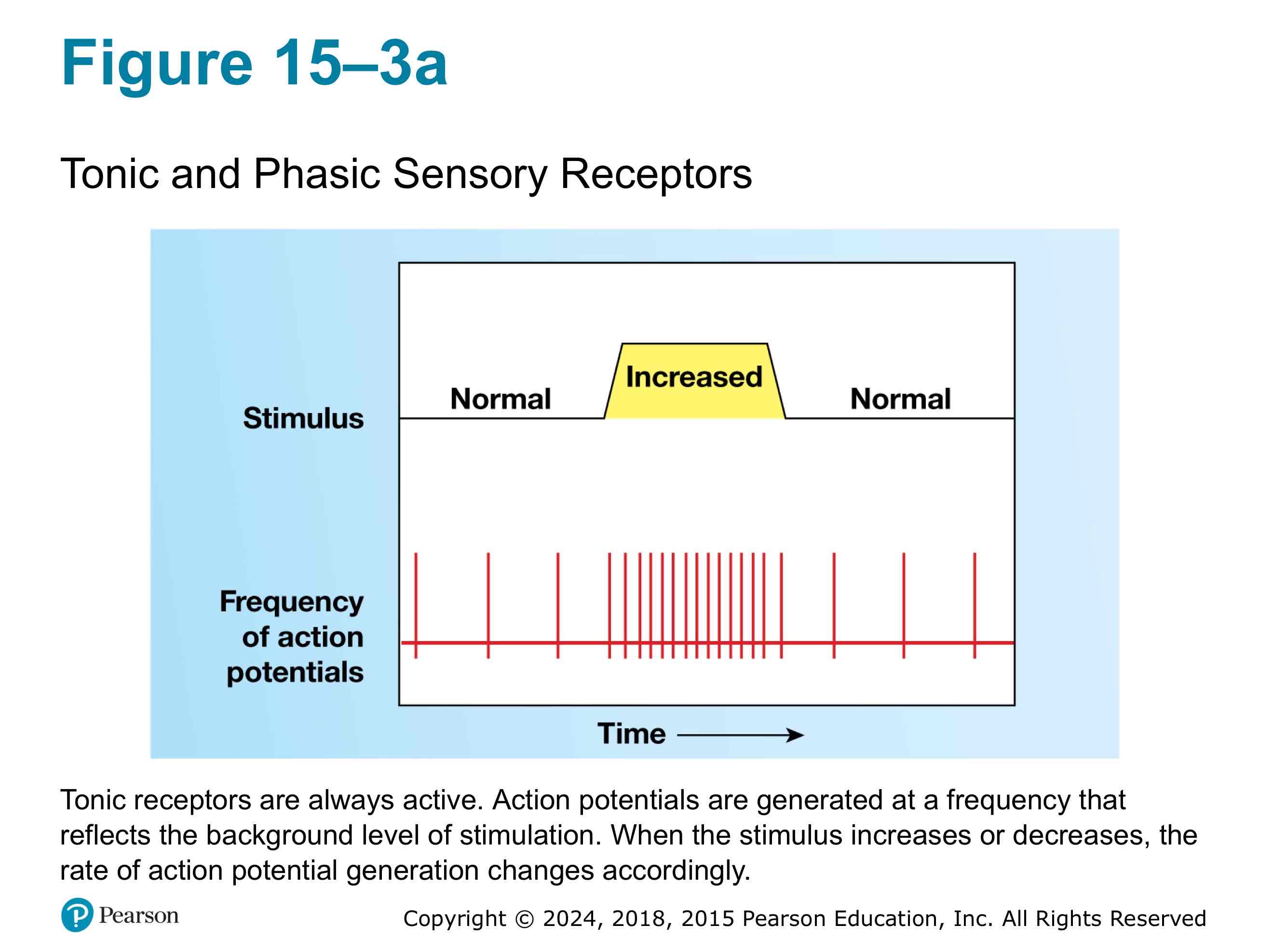
What are isotonic receptors?
refers to muscle contractions, where muscle length changes while tension stays the same
What are phasic receptors ?
They are inactive and only gets activated by large stimulus. Stimulation causes a burst of action potential that ends when stimulus stops.
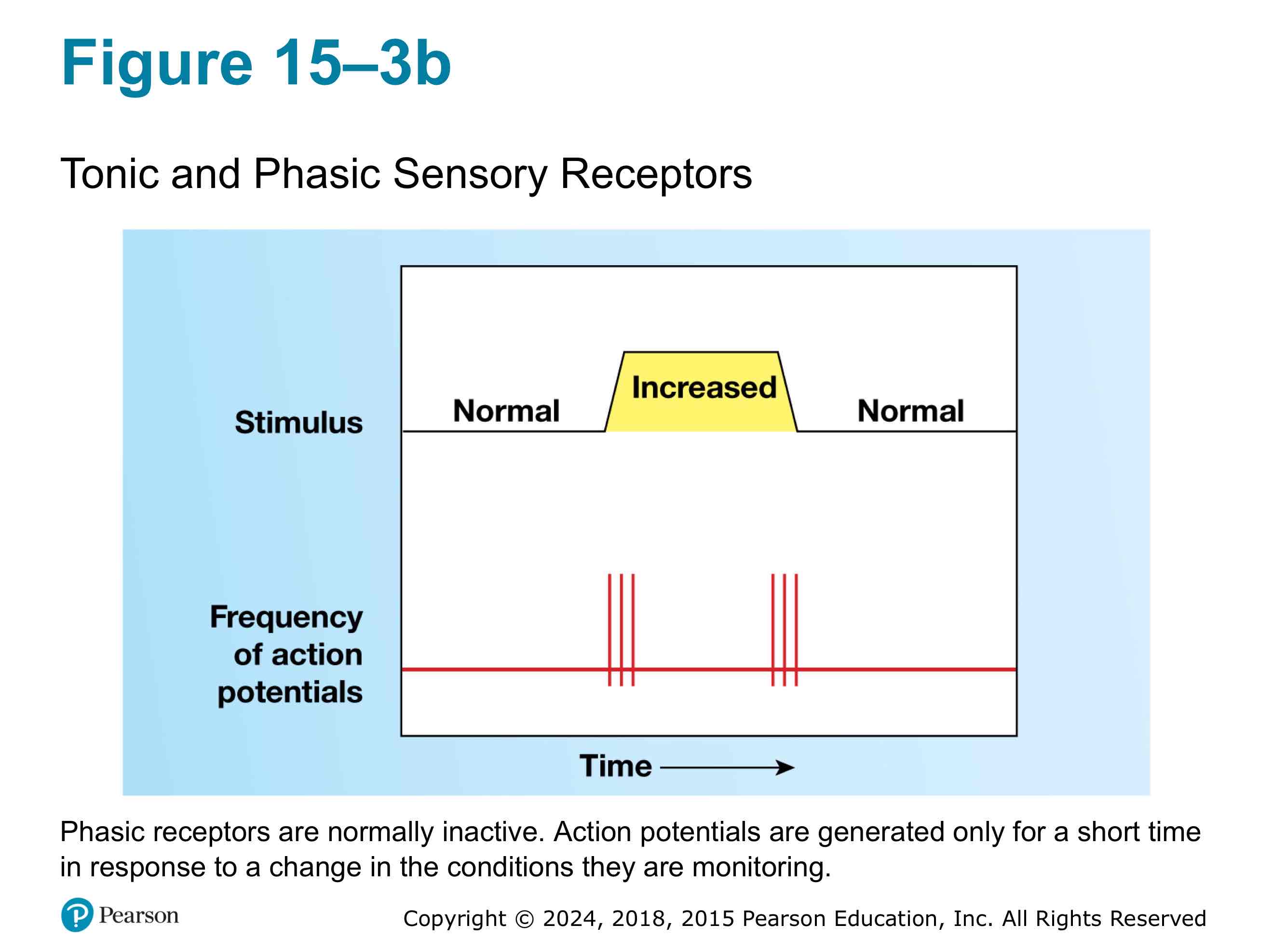
What is adaptation?
Reduction of sensitivity in the presence of constant painless stimuli
What are fast adapting receptors?
Respond strongly at first then activity decreases (phasic receptors) eg. temperature
What are slow adapting receptors?
Shows little peripheral adaptation (tonic receptors) eg. Pain
What are exteroceptors?
Provide info about external environment (eg.cold outside)
What are proprioceptors?
Provide information about the position of skeletal muscles and joints (eg.tells you what butt cheek you’re sitting on.)
What are interceptors?
Provide information about visceral organs (eg. let’s you know when to pee.)
Nociceptors
nerve endings that detect pain, tonic receptors (common in skin, joint capsules, bone caps and blood vessel walls)
What are the two types of pain?
Fast pain and slow pain
What is slow pain?
Burning and aching pain, carried by unmyelinated Type C fibers, aware of pain but only general idea of where it's at (e.g. Feeling sore after workout)
Thermorecptors
Nerve endings that detect temperatures, phasic receptors (located in the dermis, skeletal muscles, liver and hypothalamus
Mechanoreceptors
Sensitive to physical distortion
What are the classes of mechanoreceptors?
Tactile receptors, baroreceptors, proprioceptors
What are tactile receptors?
Detects touch, pressure and vibration
What is fine touch?
Provides detailed info on stimulus, extremely sensitive and has narrow receptive fields
What are the different types of tactile receptors in our skin?
Tactile Discs, Lamellar corpuscles, Tactile corpuscles
What are lamellar corpuscles?
fast adapting receptors sensitive to deep pressure, sensitive to pulsing and vibrations
What are tactile corpuscles?
large fast adapting receptors sensitive to fine touch, pressure and vibrations (located mostly in eyelids, lips, external genitalia, fingertips, and nipples) *most sensitive receptors we have*
what are barorecptors?
detects changes in pressure in our organs
Baroreceptors of carotid sinuses and aortic arch
Provides info on our blood pressure
Baroreceptors of lung
Provide information on our lung expansion for control on respiratory rate
What is proprioception?
only a somatic sensation, so no proprioceptors in visceral organs
What are the two locations of chemoreceptors ?
Carotid bodies: near the carotid arteries in the neck
Aortic bodies: in the aortic arch of heart
What neurons are in the sensory pathway?
First order neurons, second order neurons, third order neurons
First Order Neuron Function
Sensory neuron that delivers sensations from the PNS to CNS
Second Order Neuron function
interneurons in spinal cord, where decussation occurs
Third Order Neuron function
neuron in the thalamus that decides the importance before sending to the primary somatosensory cortex.
What are the 3 somatic sensory pathways?
Spinothalamic Pathways, Posterior column pathways, Spinocerebellar pathways
What are somatic sensory pathways?
Carries sensory info from body to CNS
What is the spinothalamic pathway function?
Carries sensations of crude touch, pressure, pain, temperature
What are the two tracts of the spinothalamic pathways?
Anterior spinothalamic tract and Lateral spinothalamic tract
What sensations do the anterior spinothalamic tract carry?
carries crude touch and pressure
("A" for All around) (because crude touch and pressure are general sensations that don’t need to be very precise)
What sensations do the lateral spinothalamic tract carry?
carries pain and temperature
"L" for Lava (because lava is hot, helping you remember temperature and pain sensations).
What is referred pain?
When visceral pain manifests as body surface pain because internal organs and body surface are innervated by the same spinal segment.
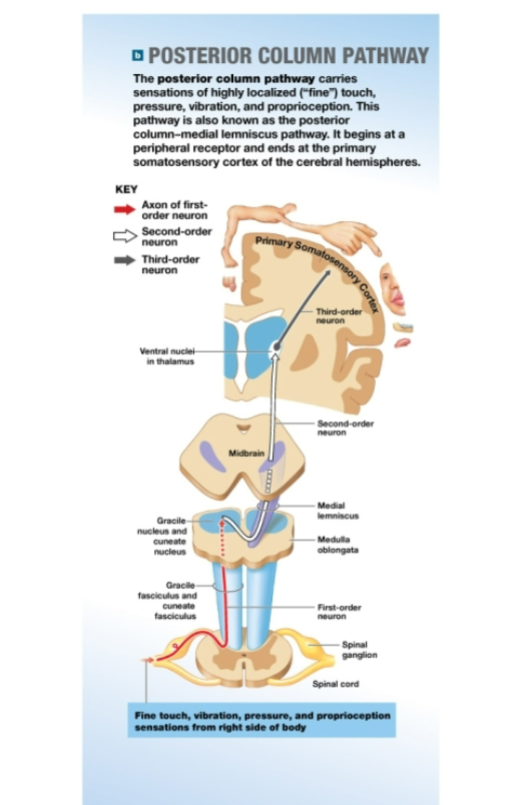
What is the Posterior Column pathway function?
carries fine touch, vibration, pressure and proprioception sensations
What are the tracts of the posterior column pathways?
Left&Right Gracile fasciculus, Left&Right Cuneate fasciculus, Medial Lemniscus
What sensations do the L&R gracicle fasciculus carry?
carries sensory info from the lower body
(think “G” for ground")
What sensations do the L&R cuneate fasciculus carry?
carries sensory info from the upper body
(think “C” for ceiling)
What is the medial lemniscus?
pathway where second order neurons send signals to the thalamus after decussation.
What is the sensory homunculus?
Shows which parts of the brain are responsible for sensations from different body parts.
*larger body parts on map are more sensitive, meaning more brain space and vice versa*
What is the spinocerebellar pathway function?
carries muscle positions to the cerebellum
*No third order neuron since info is going to the cerebellum, not thalamus*
What are the tracts of the spinocerebellar pathway?
Posterior spinocerebellar tract and Anterior spinocerebellar tract
What is the Posterior spinocerebellar pathway?
signals travel through inferior cerebellar peduncle (allowing cerebellum to receive info about the lower body w/o decussation)
What is the Anterior spinocerebellar pathway?
After decussation, signals travel through the superior cerebellar peduncle (allowing cerebellum to receive info about the upper body)
What are somatic motor pathways?
carries subconscious and conscious motor commands
What are the neurons are in the somatic motor pathways?
Upper motor neuron and lower motor neuron
Upper motor neuron
cell body lies in CNS (premotor/motor cortex)
Lower motor neuron
cell body lies in spinal cord
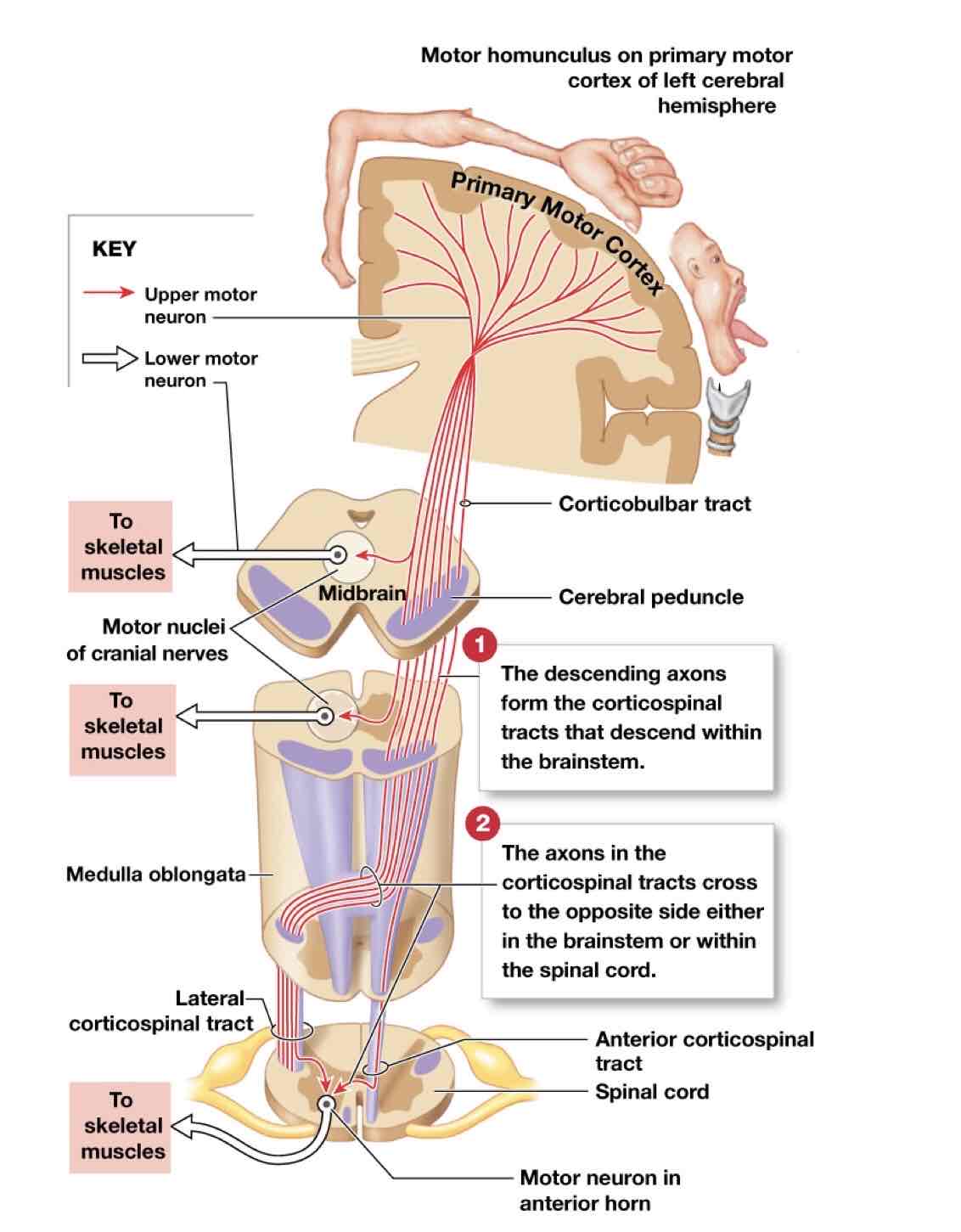
What is the corticospinal pathway?
provides voluntary control over skeletal muscles
What is the corticobulbar pathway?
provides conscious control of the movement of the eyes, jaw, face and neck
What is the motor homunculus?
functional map of the primary motor cortex, size of area corresponds to degree of fine motor control
What is the function of the cerebellum?
monitors body position, visual info and vestibular sensations to adjust movement as needed (Brains movement control center)
What is the function of Basal Nuclei?
provides automatic background movements that support your voluntary actions
(eg. when you walk you don’t need to think about swinging your arms due to basal nuclei)