Acid and bases
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Arrhenius Acid
A substance that produces hydrogen ions when dissolved in water
Arrhenius Base
A substance that produces hydroxide ions(OH⁻¹) when dissolved in water
Bronsted-Lowry acid
a hydrogen (proton) donor. The substance that remains after the hydrogen has been donated is called the conjugate base
Bronsted-Lowry base
a hydrogen (proton) acceptor. The substance that forms after the hydrogen has been accepted is called the conjugate acid
Strong acids/bases
All of the molecules will separate into ions.ALL acid molecules separate (dissociate) into [H+] ions in water; only ions present
weak acids/bases
Mostly Molecules and few ions present. Most acid molecules stay together, only a FEW separate into [H+] ions when in water; few ions present, mostly molecules.
pH scale
a logarithmic scale used to determine if a solution is acidic or basic
Properties of acids
Produce H3O+1 (hydronium ion) when dissolved in water. tastes sour. React with metals to form hydrogen gas. Neutralizes a base to form a salt and water
Properties of Bases
Produce OH-1 (hydroxide ion) in when dissolved in water.Tastes Bitter.Feels slippery. Neutralizes an acid to form a salt and water
conducts electricity: They are called ELECTROLYTES
what do both properties of acids and bases have in common
Solve for pH or pOH

Solve for [H⁺] or [OH⁻]
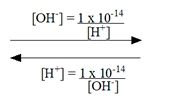
to relate pH and pOH
pH +pOH=14
Equilibrium constant of water
Kw = [H₃O⁺][OH⁻]=1.0 x 10⁻¹⁴
Titration Formula
MaMaVa=NbMbVb