Neurology
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Hand nerves motor functions?
· Median – rock – ape hand - wrist and finger flexion, moves thumb away from palm
· Radial – paper - extension of elbow, wrist, fingers, forearm supination
· Ulnar – scissors – claw hand - finger spreading and power grip
Reflexes?
· Biceps – C5-C6
· Triceps – C7-C8
· Knee – L3-L4
· Ankle – S1-S2
Dermatomes and myotomes?
C1 = no dermatome. Head and neck movements.
C2 = upper part of head.
C3 = side of face and back of head. (C3,4,5 diaphragm)
C4 = upwards shoulder movements.
C5 = deltoids and biceps, forearm rotation
C6 = elbow flexion, wrist extension
C7 = elbow extension and triceps
C8 = hands, finger flexion
L1 = sensation groin + genitals. Hip muscles.
L2,3,4 = sensation anterior thigh and medial lower leg. Hip and knee movements.
L5 = outside leg, upper foot, 1st webspace. Dorsiflexion, inversion, eversion.
S1 = lateral malleolus sensation. Plantar flexion.
Leg nerves? Sciatic nerve lesion? Common peroneal nerve lesion?
· Femoral nerve = hip flexion, knee extension, patella reflex
· Sciatic nerve lesion = knee flexion. lesion = paralysis of knee flexion and all movements below knee, sensory loss below knee, ankle and plantar reflexes lost, knee jerk intact
· Common peroneal nerve = neck of fibula injury, main sx is foot drop, can have weak dorsiflexion and eversion.
· Tibial nerve = Dorsiflexion, inversion, eversion, plantar flexion.
What nerve is affected in olecranon fracture, humeral neck/proximal humerus fracture and humeral shaft fracture?
· Olecranon fracture = ulnar nerve
· Humeral neck/proximal humerus = axillary nerve → reduced shoulder abduction
· Humeral shaft = radial nerve
Ascending tracts?
- DCML – vibration, proprioception, fine touch
- Anterior spinothalamic – crude touch and pressure
- Lateral spinothalamic – pain and temperature
- Spinocerebellar – info about muscle stretch
Descending tracts?
- Pyramidal
Ø Corticospinal – lateral and anterior
Ø Corticobulbar – head and neck
- Extrapyramidal
Ø Reticulospinal – muscle tone and voluntary movements
Ø Vestibulospinal – posture and tone adjustments
Ø Rubrospinal – upper limb flexion = disinhibition / upper limb extension = inhibition
Ø Tectospinal – superior colliculi = visual stimuli / inferior colliculi = auditory stimuli
Stroke arteries affected? PICA? AICA? Weber’s syndrome?
· ACA – leg
· MCA – arm and leg, hemianopia, dysphasia, facial droop
· PCA – contralateral homonymous hemianopia, headache
· Posterior inferior cerebellar artery / lateral medullary syndrome
- Ipsilateral face pain and temperature loss and contralateral body pain and temperature loss
- Ipsilateral Horner’s and contralateral weakness
- No face motor loss
- Vertigo, etc.
· Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- Similar to above but ipsilateral facial paralysis, deafness, vertigo, vomiting
· Weber’s syndrome = ipsilateral CN3 palsy and contralateral weakness
Medical management of stroke and TIA?
· Aspirin 300mg STAT 3 weeks along with clopidogrel then continue clopidogrel lifelong
· If clopidogrel CI, aspirin and dipyridamole lifelong
· AF – anticoagulated after 14 days
· Start statin 48 hours after
· TIA – aspirin 300mg initial dose then 75mg for 21 days + clopidogrel lifelong
Thrombolysis in stroke timeframe? Contraindications?
Thrombolysis within 4.5 hours,
Contraindications to thrombolysis – Seizure, SAH sx, stroke/head injury last 3 months, major surgery/trauma within 2 weeks, previous intracranial haemorrhage, intracranial neoplasm, LP within past week, current anticoagulation INR >1.7
Thrombectomy in stroke guidelines?
Thrombectomy within 6 hours of symptom onset + thrombolysis (if within 4.5 hours) if confirmed proximal anterior circulation occlusion
Offer thrombectomy ASAP to people who were last known to be well between 6 and 24 hours previously if confirmed proximal anterior circulation occlusion and potential to salvage brain tissue as seen by imaging
Consider thrombectomy with thrombolysis (if within 4.5 hours) ASAP for people last known to be well up to 24 hours previously with proximal posterior circulation occlusion if there is potential to salvage brain tissue
When is carotid endarterectomy done?
If carotid stenosis >50%
NICE suggest starting anti-epileptics after first seizure if? What are the rules on valproate and topiramate?
Any of following:
- Pt has neuro deficit
- Brain imaging shows structural abnormality
- EEG shows unequivocal epileptic activity
- Patient/family consider further seizure risk unacceptable
· Valproate must not be started for first time in male or female under 55 unless 2 specialists independently feel there is no other effective or tolerated treatment or there are compelling reasons that reproductive risks do not apply.
· Topiramate should not be used in women/girls of childbearing age unless conditions of Pregnancy Prevention Programme are fulfilled.
Anti-epileptics for gen ton-clon, focal, tonic/atonic, myoclonic and absence seizures?
· Gen ton clon – lamotrigine or levetiracetam
· Focal – lamotrigine or levetiracetam → 2nd line carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, zonisamide
· Tonic/atonic – lamotrigine → 2nd line clobazam, rufinamide, topiramate
· Myoclonic – levetiracetam → lamotrigine
· Absence – ethosuximide → 2nd line lamotrigine or levetiracetam (carbamazepine may exacerbate)
Management of status epilepticus?
· Status epilepticus = benzo → 5-10 mins later benzo again → IV phenytoin or levetiracetam or valproate. If no response after 45 mins from onset, GA or phenobarbital
Timeframe for CT head in head injury 1 hour vs 8 hours?
CT head within 1 hour of injury
- GCS <13 on initial assessment
- GCS <15 at 2 hours post injury
- Suspected open or depressed skull fracture
- Any sign of basal skull fracture
- Post-traumatic seizure
- Focal neuro deficit
- More than 1x vomiting
CT head within 8 hours of injury – following risk factors + some LOC or amnesia since injury
- >65, hx of bleeding/clotting disorders, anticoagulants, dangerous mechanism of injury, more than 30mins retrograde amnesia of events immediately before injury
- If on warfarin and head injury with no other indications for CT
SAH - when would you do LP?
CT head done within 6 hours and normal – guidelines suggest not doing LP
If CT head after 6 hours and normal – LP
LP should be 12 hours after symptom onset to allow xanthochromia to develop to distinguish SAH from traumatic tap
MND most common presentation? What isn’t affected? Is ALS UMN or LMN? Is PBP UMN or LMN? Medication?
Most common presentation is asymmetric limb weakness
No sensory signs/symptoms, doesn’t affect ocular muscles, no cerebellar signs
Nerve conduction studies – normal
ALS – UMN + LMN
PBP – LMN – CN9,10,11,12
Riluzole – monitor LFTs
MS types? CSF finding? What is Lhermitte’s sign?
Relapsing-remitting – acute attacks followed by periods of remission
Secondary progressive – relapsing-remitting pts who have deteriorated and developed neuro signs and symptoms between relapses
Primary progressive – progressive deterioration from onset
CSF - oligoclonal bands
Lhermitte’s sign = electric shock down spine into limbs when neck flexed
MS management in acute relapse? Fatigue? Spasticity? Bladder dysfunction? Oscillopsia?
- Acute relapse – high-dose steroids
- Disease modifying drugs
- Fatigue – amantadine
- Spasticity – baclofen, gabapentin
- Bladder dysfunction – need USS first!! If significant residual volume, intermittent self-catheterisation. If no significant residual volume – anticholinergics.
- Oscillopsia – gabapentin
Autonomic neuropathy symptoms sympathetic vs parasympathetic?
· Sympathetic – postural hypotension, ejaculation failure, reduced sweating
· Parasympathetic – erectile dysfunction, constipation, urine retention
Degenerative cervical myelopathy symptoms? Sign? Gold standard test? Management?
Pain, loss of motor or sensory function, loss of autonomic function
Hoffman’s sign – gently flick one finger of patient’s hand – positive = reflex twitching of other fingers in same hand
MRI c-spine gold standard
Decompressive surgery
GBS main symptoms and signs? LP findings?
Ascending weakness, flaccid weakness and HYPOreflexia
LP – increased protein, normal WCC, normal RCC and slow EMG
Brighton criteria
Meningitis CSF analysis - bacterial? Viral? TB? Fungal?
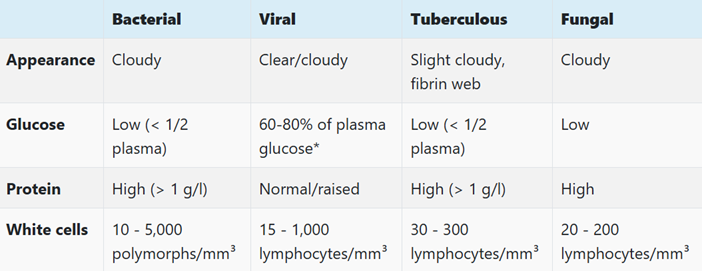
Signs in meningitis?
· Kernig’s sign – hips and knees at 90 – extend knee – pain
· Brudzinski’s sign – flexion of neck causes flexion of hips and knees
Meningitis management? Prophylaxis?
If LP cannot be done in 1st hour, start IV abx after taking blood cultures
3 months – 60 years – ceftriaxone
>60 – ceftriaxone + amoxicillin (covers listeria)
Add IV vanc if recent prolonged/multiple abx use or travel to areas with high resistance to pneumococci
IV dex no later than 12 hours after starting abx. Avoid in septic shock, meningococcal septicaemia, immunocompromised.
Prophylaxis – close contact within 7 days before onset. PO cipro or rifampicin. For pneumococcal no prophylaxis generally needed.
Giant cell arteritis symptoms? Investigations?
Scalp tenderness, jaw claudication, visual changes
Duplex USS – hypoechoic halo sign and stenosis of temporal artery
Temporal artery biopsy– multinucleated giant cells
Subacute combined degeneration of spinal cord - which tracts are involved - symptoms?
Due to vitamin B12 deficiency
Dorsal column involvement
Distal tingling/burning/ sensory loss – symmetrical and legs > arms
Impaired proprioception and vibration
Lateral corticospinal tract involvement
Muscle weakness, hyperreflexia
UMN signs
Spinocerebellar tract involvement
Sensory ataxia and Romberg’s sign
Parkinson’s disease management? What is on-off phenomenon? What is weaning off?
Motor sx affecting QoL – levodopa (always combined with decarboxylase inhibitor)
Motor sx not affecting QoL – dopamine agonist, levodopa or MAO-B inhibitor (rasagiline)
On levodopa and ongoing sx or developed dyskinesia – add dopamine agonist or MAO-B inhibitor or COMT inhibitor (entacapone)
Excessive daytime sleepiness – modafinil
Orthostatic hypotension – midodrine
On-off phenomenon – sudden changes in movement control
Weaning off – over time, symptoms a few hours after dose as medication wears off
Huntington’s disease inheritance pattern? Symptoms? What is anticipation?
Autosomal dominant. Chromosome 4 – CAG repeats in huntingtin gene
Personality change, dementia, agitation, rigidity, seizures, parkinsonism
Anticipation – disease presents at earlier age in successive generations.
Myasthenia gravis - what is it? Investigations? Treatment? Treatment for myasthenic crisis? What is Lambert-Eaton syndrome?
Antibodies against acetylcholine receptors and anti-MuSK antibodies
Ix – single fibre electromyography, CT thorax to exclude thymoma, CK normal, antibodies to acetylcholine receptors.
Treat with pyridostigmine
Myasthenic crisis – plasmapheresis, IVIG
Lambert-Eaton syndrome
LEMS – antibodies against voltage-gated calcium channels
Affects lower limbs first, hyporeflexia, autonomic sx
Unlike MG, ophthalmoplegia and ptosis not common features
Neurofibromatosis I and II features? Inheritance pattern? NF1 complications?
Autosomal dominant
NF1 - CRABING
Café au lait patches
Relative – FHx
Axillary/inguinal freckling
Bone dysplasia
Iris hamartomas
Neurofibromas (skin)
Glioma – optic
Complications - malignant peripheral nerve sheath and GI stromal tumour
NF2 - vestibular schwannomas, multiple intracranial schwannomas, meningiomas, ependymomas
Tuberous sclerosis - inheritance pattern? Features?
Autosomal dominant
Ash leaf spots, shagreen patches, angiofibroma, café au lait spots
Development problems, epilepsy, retinal hamartomas
Migraines management? Prophylaxis 1st line, 2nd line, menstrual migraines?
1st line – oral triptan + NSAID/paracetamol
12-17 – nasal triptan
2nd line – non-oral metoclopramide or prochlorperazine
Prophylaxis
- Propranolol, topiramate (teratogenic), amitriptyline
- If fails – up to 10 sessions acupuncture over 5-8 weeks
- Menstrual migraines – frovatriptan, zolmitriptan
What is normal pressure hydrocephalus? Triad? What does imaging show? Management?
Reversible cause of dementia due to reduced CSF resorption at arachnoid villi.
Triad – urinary incontinence, dementia, gait abnormality.
Imaging – hydrocephalus with ventriculomegaly in absence of or out of proportion to sulcal enlargement .
Management – VP shunt
CN3 palsy? CN4 palsy? CN6 palsy?
CN3 – oculomotor – palsy results in ptosis, ‘down and out’ eye, dilated, fixed pupil
CN4 – Trochlear – superior oblique – palsy results in defective downward gaze, vertical diplopia
CN6 – abducens – lateral rectus – palsy results in defective abduction
Quadrantanopia lobes inferior and superior? Causes of inferior and superior issues?
Quadrantanopia – PITS
Inferior = craniopharyngioma
Superior = pituitary tumour
What is parasellar syndrome?
CN5 damage – facial pain, paraesthesia
Pontine haemorrhage signs?
Reduced GCS, pinpoint pupils, paralysis
What is Charcot Marie Tooth disease? Motor or sensory? UMN or LMN?
Hereditary, mostly motor peripheral neuropathy, only LMN signs.
What is syringomyelia?
CSF in spinal cord. Spinothalamic sensory loss. Cape-like loss of sensation to temp.
Treatment of infantile spasms / West syndrome?
ACTH and vigabatrin
Gold standard investigation for venous sinus thrombosis?
MR venogram
What is Cushing’s reflex?
Hypertension, bradycardia, irregular breathing pattern
Bell’s palsy management?
Oral pred within 72hrs, can add antiviral if severe. If no improvement in paralysis after 3 weeks urgent ENT referral.
Cluster headaches investigation? Acute management? Prophylaxis?
MRI with gadolinium Ix of choice.
Acute – 100% O2, subcut triptan.
Verapamil for prophylaxis.
DMD inheritance pattern? What muscles are affected? Main sign?
X-linked recessive.
Progressive proximal muscle weakness from 5 years.
Gower’s sign.
30% have intellectual impairment.
Encephalitis main cause? What lobe is usually affected? CSF findings? Treatment?
HSV-1 in 95%.
Usually temporal lobe affected.
CSF – high lymphocytes, high protein, send for viral PCR.
IV acyclovir.
Essential tremor inheritance pattern? What usually helps? 1st line treatment?
Autosomal dominant
Improved by alcohol and rest.
1st line – propranolol.
Friedreich’s ataxia inheritance pattern? Age? Common features?
Autosomal recessive. Onset 1-15 years.
Common presenting features are gait ataxia and kyphoscoliosis.
Neuro features – absent ankle jerks, cerebellar ataxia, optic atrophy
Other features – HOCM, diabetes, high-arched palate
Myotonic dystrophy - inheritance pattern? Age? General features? DM1 vs DM2?
Inherited myopathy, autosomal dominant.
20-30 years old.
Skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle.
General features – myotonic facies, frontal balding, bilateral ptosis, cataracts, dysarthria
DM1 – distal weakness more prominent, DM2 – proximal weakness more prominent
Progressive supranuclear palsy symptoms?
Postural instability and falls, impairment of vertical gaze (down gaze worse), parkinsonism, cognitive impairment
IIH management? What meds can worsen IIH?
Weight loss, acetazolamide, topiramate.
Tetracyclines increase IIH risk.
Driving advice for TIA/stroke? Seizures? Withdrawing anti-epileptics? Fainting?
TIA/stroke – 1 month – unless ongoing symptoms
First unprovoked seizure and no structural issues on brain imaging – 6 months
Otherwise or established epilepsy – 12 months seizure free
Withdrawing anti-epilepsy meds – no driving whilst and for 6 months after last dose
Single faint episode – explained and treated – 4 weeks off.
Single unexplained faint – 6 months off. 2+ - 12 months off.
SEs of phenytoin? SEs of lamotrigine?
Phenytoin - peripheral neuropathy (glove and stocking), lymphadenopathy, bleeding gums (gingival hyperplasia), megaloblastic anaemia
Lamotrigine - skin rashes, SJS
Which CNs affected in vestibular schwannomas?
5, 7, 8