CHEM121 - CH 8 VOCAB
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
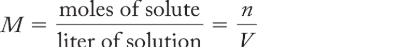
molarity (M)
the number of moles of solute in a volume of solution; n/V
standard solution
a solution of accurately known concentration used in chemical analysis
dilution
the process of reducing solute concentration by adding more solvent to a solution
absorbance (A)
a measure of the quantity of light a solution absorbs
Beer’s law
relates absorbance to three quantities: concentration, the path length that the light travels through the solution, and molar absorptivity (ε)
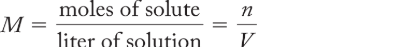
molar absorptivity (ε)
a measure of how well a compound or ion absorbs light
calibration curve
a graph showing how a measurable property varies for a set of standard samples that can later be used to identify an unknown concentration from a measured absorbance
electrode
a solid electrical conductor used to make contact with a solution or other nonmetallic component of an electrical circuit
electrolyte
a solute that produces ions in solution, enabling its solutions to conduct electricity
strong electrolyte
a substance that dissociates completely when it dissolves in water
nonelctrolyte
a molecular substance that does not ionize when it dissolves in water
hydronium ions (H3O+)
an H+ ion plus a water molecule, H2O; the form in which the hydrogen ion is found in aqueous solution
weak electrolyte
a substance that only partly ionizes when it dissolves in water
Brønsted–Lowry acid
proton donor
Brønsted–Lowry base
proton acceptor
neutralization reaction
a reaction that takes place when an acid reacts with a base and produces a solution of a salt in water
salt
the product of a neutralization reaction, made up of the cation of the base in the reaction plus the anion of the acid
molecular equation
a balanced equation describing a reaction in solution in which the reactants and products are written as neutral compounds
overall ionic equation
a balanced equation that shows all the species, both ionic and molecular, present in a reaction occurring in an aqueous solution
net ionic equation
a balanced equation that describes the actual reaction taking place in aqueous solution; it is obtained by eliminating the spectator ions from the overall ionic equation
spectator ion
an ion present in a reaction vessel when a chemical reaction takes place but is unchanged by the reaction; they appear in an overall ionic equation but not in a net ionic equation
strong acid
an acid that completely ionizes in aqueous solution
weak acid
a weak electrolyte that only partially ionizes in aqueous solution
carboxylic acid
a compound containing the -COOH functional group
strong base
a base that completely dissociates into ions in aqueous solution
weak base
a base that is a weak electrolyte and has a limited capacity to accept protons
amphirotic
describes a substance that can behave as either a proton acceptor or a proton donor
titration
an analytical method of determining the concentration of a solute in a sample by reacting the solute with a solution of known concentration
titrant
the standard solution added to the sample in a titration
analyte
the substance whose concentration is to determined in a chemical analysis
equivalence point
the point in a titration at which just enough titrant has been added to react with all the analyte in the sample
end point
the point in a titration at which a color change or other signal indicates that enough titrant has been added to react with all the analyte in the sample
precipitate
a solid product formed from a reaction in solution
precipitation reaction
a reaction in which soluble reactants form a product that has limited solubility
saturated solution
a solution that contains the maximum concentration of a solute possible at a given temperature
unsaturated solution
a solution that contains less than the maximum quantity of solute predicted to be soluble in a given volume of solution at a given temperature
supersaturated solution
a solution that contains more than the maximum quantity of solute predicted to be soluble in a given volume of solution at a given temperature
oxidation
a chemical change in which an element loses electrons; the oxidation number of the element increases
reduction
a chemical change in which an element gains electrons; the oxidation number of the element decreases
oxidation number (O.N) or oxidation state
a numerical value (+,0,-) based on the number of electrons than an atom gains or loses when it forms an ion or that it shares when it forms a covalent bond with an atom of another element
oxidizing agents
a reactant that accepts electrons from another in a redox reaction, thereby oxidizing the other reactant; the oxidizing agent is reduced in the reaction
reducing agent
a reactant that donates electrons to another in a redox reaction, thereby reducing the other reactant; the reducing agent is oxidized in the reaction
half-reaction
one of the halves of an oxidation-reduction reaction; one half-reaction is the oxidation component, and the other is the reduction component
activity series
a high-to-low ranking of metals on the basis of their strengths as reducing agents