area 51
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
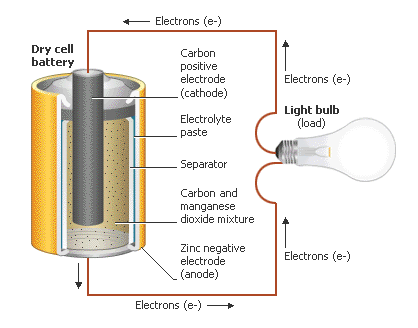
Zinc carbon dry cell anode half rxn
Zn(s) -> Zn²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻
Zinc carbon dry cell Cathode half rxn
2MnO₂(s) + 2NH₄⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ -> Mn₂O₃(s) + 2NH₃(aq) + H₂O(l)
Zinc carbon dry cell full rxn
Zn(s) + 2MnO₂(s) + 2NH₄Cl(aq) -> ZnCl₂(aq) + Mn₂O₃(s) + 2NH₃(aq) + H₂O(l)
Zinc carbon dry cell Primary or secondary
Primary
Zinc carbon dry cell voltage
1.5
Zinc carbon dry cell advantages
Low cost
Zinc carbon dry cell Weaknesses
Ammonia leaks, therefore limited shelf life
Zinc carbon dry cell
Single voltaic cell, AAA to D
Alkaline dry cell anode half rxn
Zn(s) + 2OH-(aq) → Zn(OH)2(s) + 2e-
Alkaline dry cell Cathode half rxn
2MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l) + 2e- → 2MnO2(s) + 2OH-(aq)
Alkaline dry cell full rxn
Zn(s) + 2MnO2(s) + H2O(l) -> ZnO(s) + 2MnO(OH)(s)
Alkaline dry cell Primary or secondary
primary
Alkaline dry cell weaknesses
primary, non rechargable
Alkaline dry cell advantages
no ammonium or ammonia, therefore no leakages
Zinc is powdered, more surface area and faster rxn
Alkaline dry cell voltage
1.5
Alkaline dry cell
alkaline pastee, zinc powdered
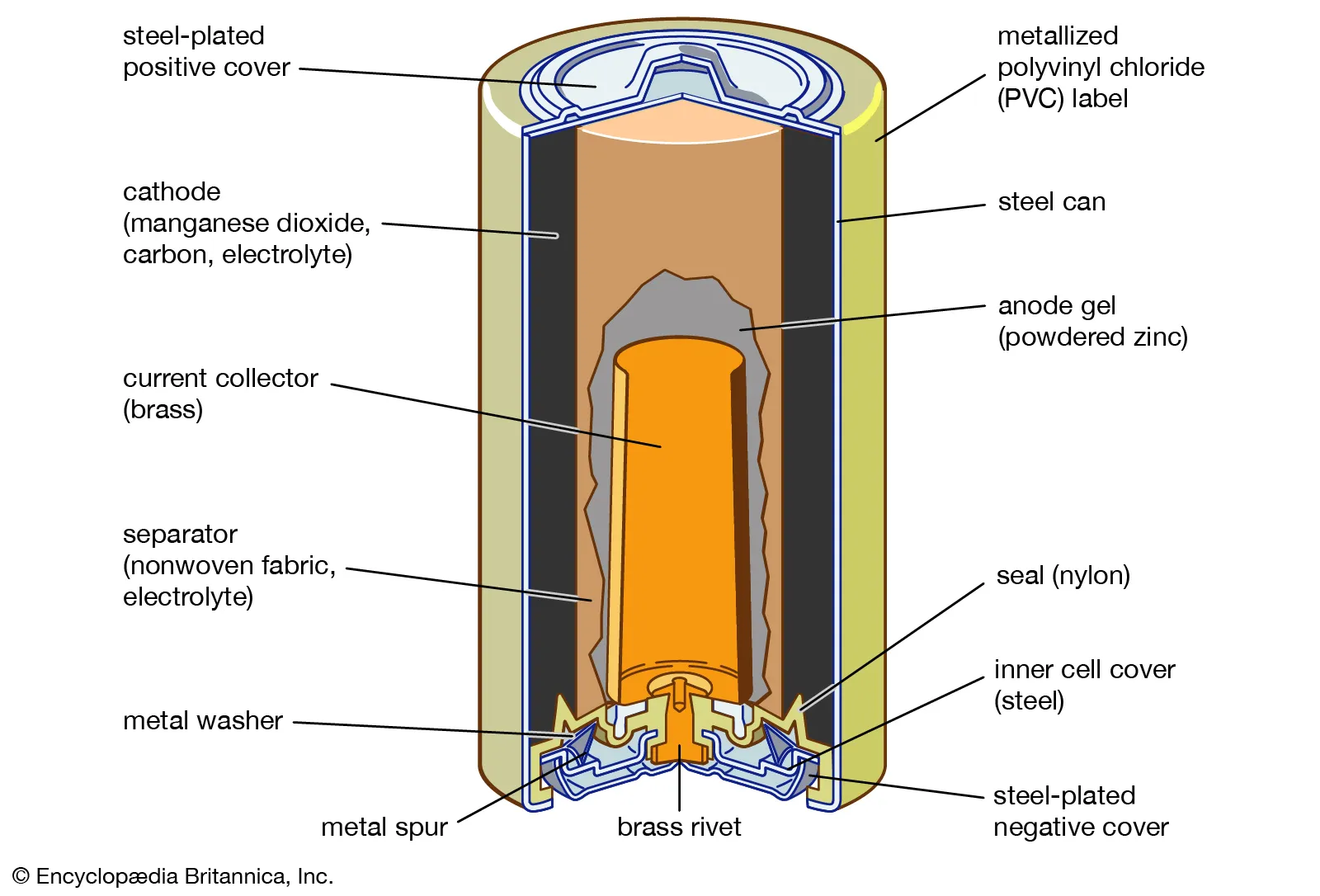
silver oxide anode rxn
Zn + 2OH- → Zn(OH)2 + 2e-
silver oxide cathode rxn
Ag2O(s) + H2O(l) + 2e- → 2Ag(s) + 2OH-(aq)
silver oxide full rxn
Ag₂O + H₂O + Zn → 2Ag + Zn(OH)₂
silver oxide primary or secondary
primary
silver oxide voltage
1.55
silver oxide advantages
longer shelf lifee, constant V at low current
silver oxide weaknesses
higher cost, limited energy capacity, primary
silver oxide
NaOH, constant V at low current, vs KOH, constant V at high current
lead acid anode half rxn
Pb + HSO4- → PbSO4 + H+ + 2e-
lead acid cathode half rxn
PbO2(s) + 3H+(aq) + HSO4-(aq) + 2e- → PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
lead acid net rxn
Pb(s) + PbO₂(s) + 2H₂SO₄(aq) → 2PbSO₄(s) + 2H₂O(l)
lead acid primary or secondary
secondary
lead acid advantages
large voltage, long shelf life, operates well at low temperature, energy transfer
lead acid voltage
6 cells, 2 V each, 12 in total
lead acid disadvantages
heavy weight, limited cycle life, toxic materials, low energy density (goes down over time)
lead acid
starting engines, spongy/poroud lead
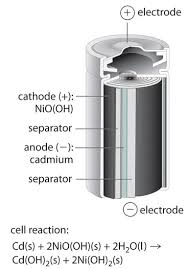
NiCd anode half rxn
Cd(s) + 2OH⁻(aq) → Cd(OH)₂(s) + 2e⁻
NiCd cathode half rxn
NiO(OH)(s) +H2O(l) + e- -> Ni(OH)2(s) + OH-(aq).
NiCd net rxn
Cd + 2NiO(OH) + 2H2O → 2Ni(OH)2 + Cd(OH)2 + 2e-
NiCd secondary or primary
secondart
NiCd volt
1.2
NiCd disadvantages
expensive
NiCd advantages
long shelf life, constant V, hard to damage
NiCd
ribbons of anode and cathode separated by material that allows ions too pass-through
Lithium advantages
lighter, higher capacity, lasts longer
Lithium metal
lightest metal, lowest standard reduction potential
Lithium primary or secondary
primary
Lithium volt
1.5-3.5
Lithium disadvantages
also farming ethicalities, primary
new fuel cell anode rxn
2H₂ → 4H⁺ + 4e⁻
new fuel cell cathode
O2 + 4H+ + 4e- → 2H2O
new fuel cell net rxn
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H2O
old fuel cell anode half rxn
2 H2 (g) + 4 OH- (aq) -> 4 H2O (l) + 4 e-
old fuel cell cathode
O2 (g) + 2 H2O (l) + 4 e- -> 4 OH- (aq)
old fuel cell net rxn
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H2O
new fuel cell advantages
no corrosive chemicals, lighter, smaller, same net (H2O)
old fuel cell disadvantages
corrosive materals
new fuel cell
proton exchange membrane between electroodes, acidic solutino replaces KOH salt bridge