Bio98 Lecture 11 (Fermentation & Gluconeogenesis)
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Fermentation (lactate or alcohol) • How does it work? • When would a cell choose to do this? • Gluconeogenesis: the reverse of glycolysis • Steps that are different • Idea of compartmentalization • Definition of a futile cycle
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Pyruvate in terms of Fermentation
Pyruvate → Reduction (lactate dehydrogenase) → lactate → transported from cell (fermentation for eukaryotes, bacteria)
Pyruvate → decarboxylation (pyruvate decarboxylase/ PDC) → acetaldehyde → alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH)→ ethanol (fermentation of yeast)
Pyruvate in terms of Gluconeogenesis (Anabolic)
Pyruvate → Carboxylation (pyruvate carboxylase) → oxaloacetate → glucose production
Explain Pyruvate Catabolism: Anaerobic (doesn’t need O2)
-Low energy yield per molecule of glucose
-Fermentation
-different modes in yeast and other organisms
-produces lactate or ethanol
Explain Pyruvate Catabolism: Aerobic (requires O2)
-high energy yield per molecule of glucose
-requires coupled use of the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) & oxidative phosphorylation via the electron transport chain
Anaerobic Metabolism = ___?
NAD+ Regeneration.
-generates ATP/NAD+ in muscle without needing O2.
Yeast fermentation
-Pyruvate converted to acetaldehyde via Pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC)
-Acetaldehyde converted to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH)
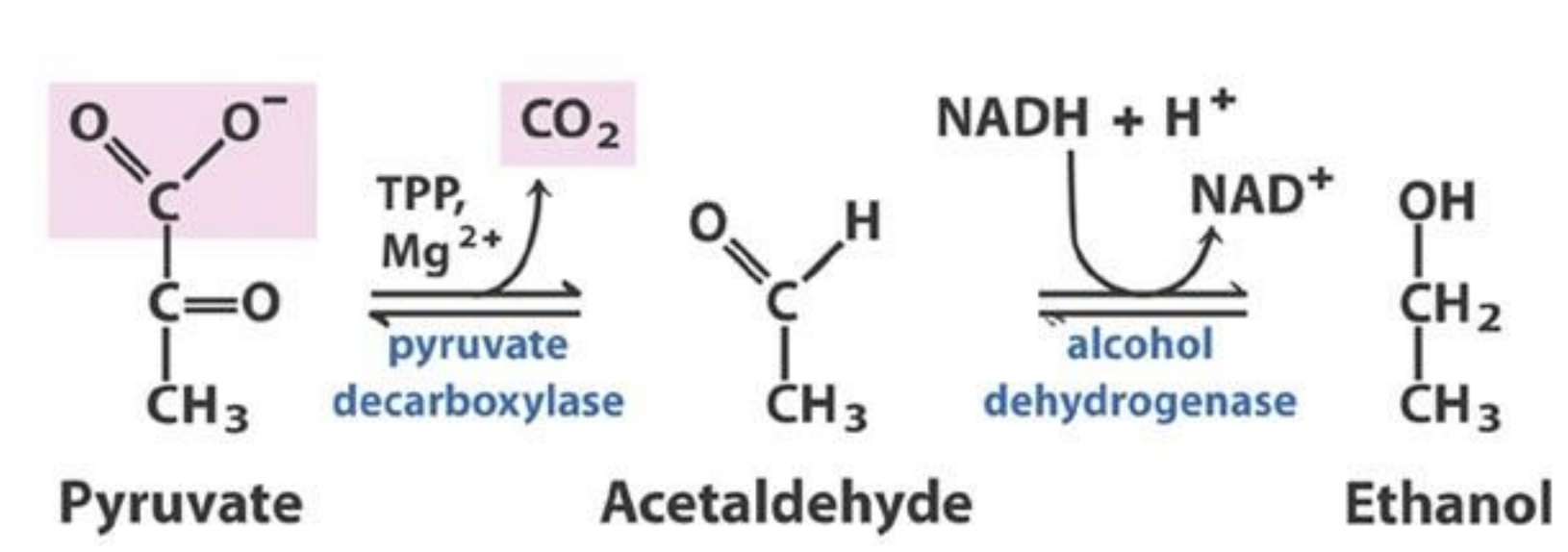
Explain what the image is showing.
Yeast fermentation:
-Pyruvate converted to acetaldehyde via Pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC)
-Acetaldehyde converted to ethanol by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH)
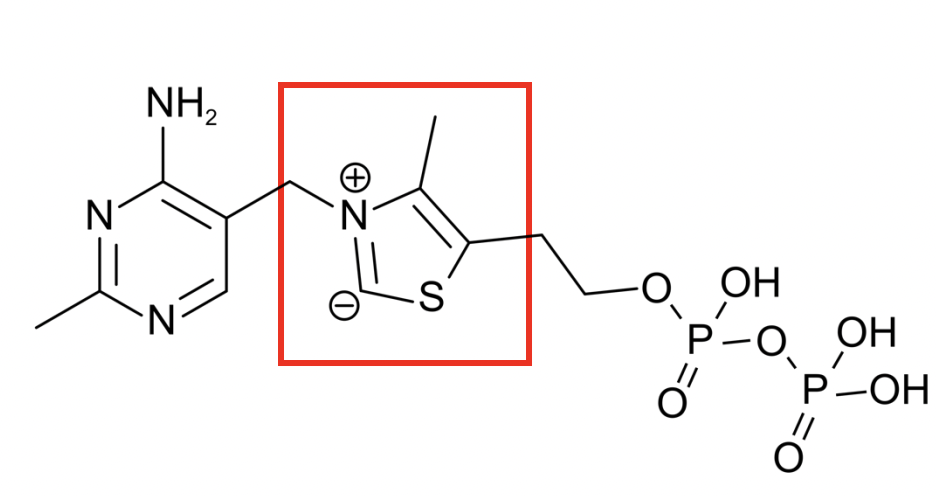
Pyruvate decarboxylase
-Thiamine disphosphate (TPP) cofactor
-Thiazole ring is important for catalysis (ylide)
-derived from vitamin B1 (essential)
-apart of yeast fermentation
Auto-Brewery Syndrome
-eat sugar, make alcohol → pt appears drunks
-caused by yeast infection
Ethanol detoxification is ___.
Yeast fermentation in reverse:
-ethanol converted to acetaldehyde (ethanal) by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) ; requires NAD+
-Acetaldehyde converted gto acetic acid by acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH)
Disfunction (mutation/genetic variation) of ADH or ALDH drives:
toxic buildup of acetaldehyde (hangover, flush)
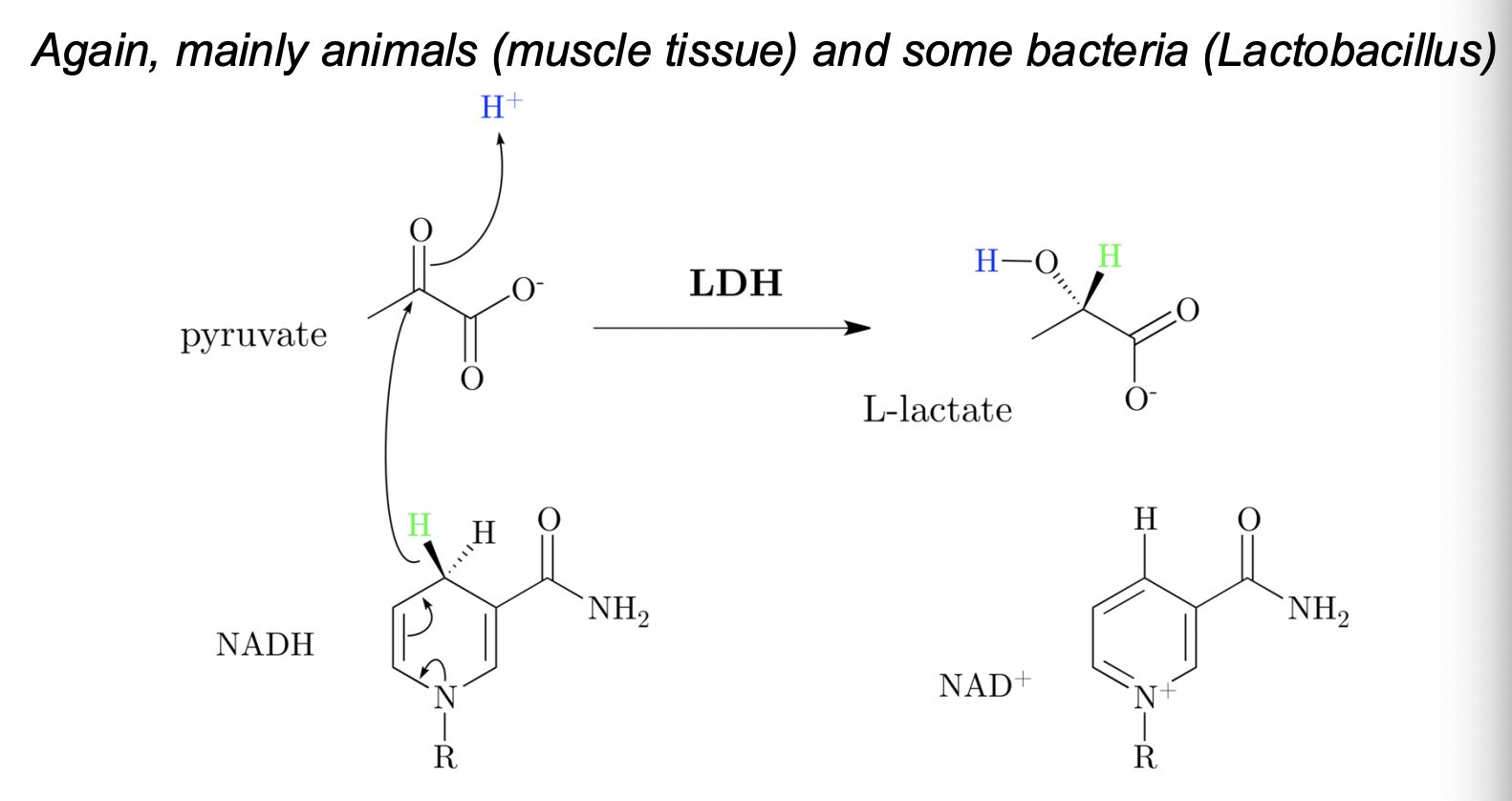
Lactic acid fermentation
pryuvate converted to lactate via lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
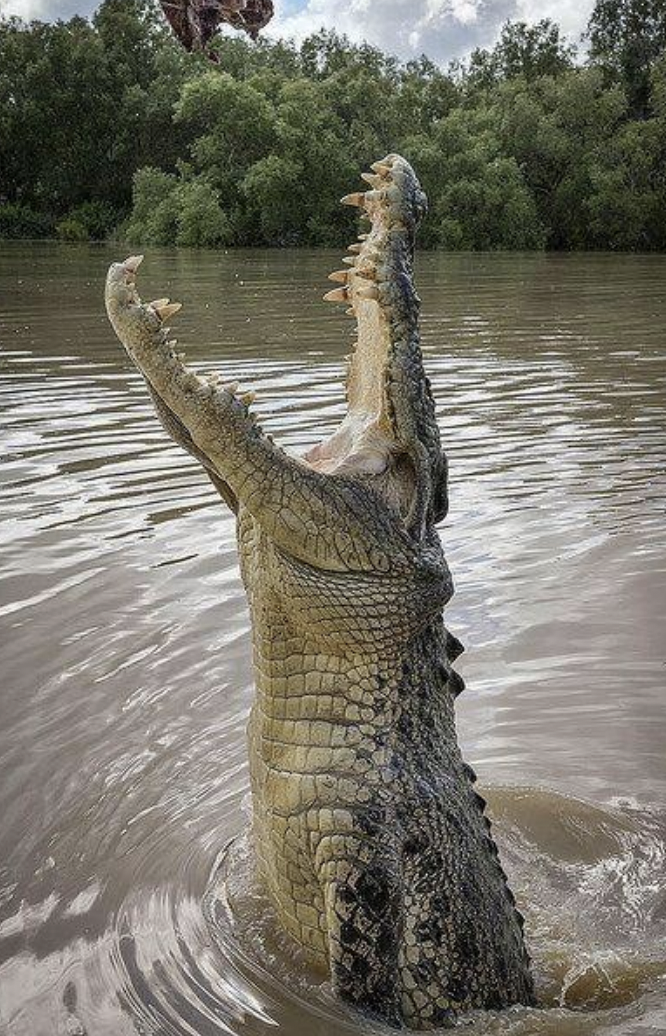

Example of anaerobic metabolism: alligator
-quick burst of energy by lactic acid fermentation
-generates ATP/NAD+ in muscle quickly w/o needing O2
-needs long recovery to clear excess lactate (source of sourness after exercise)
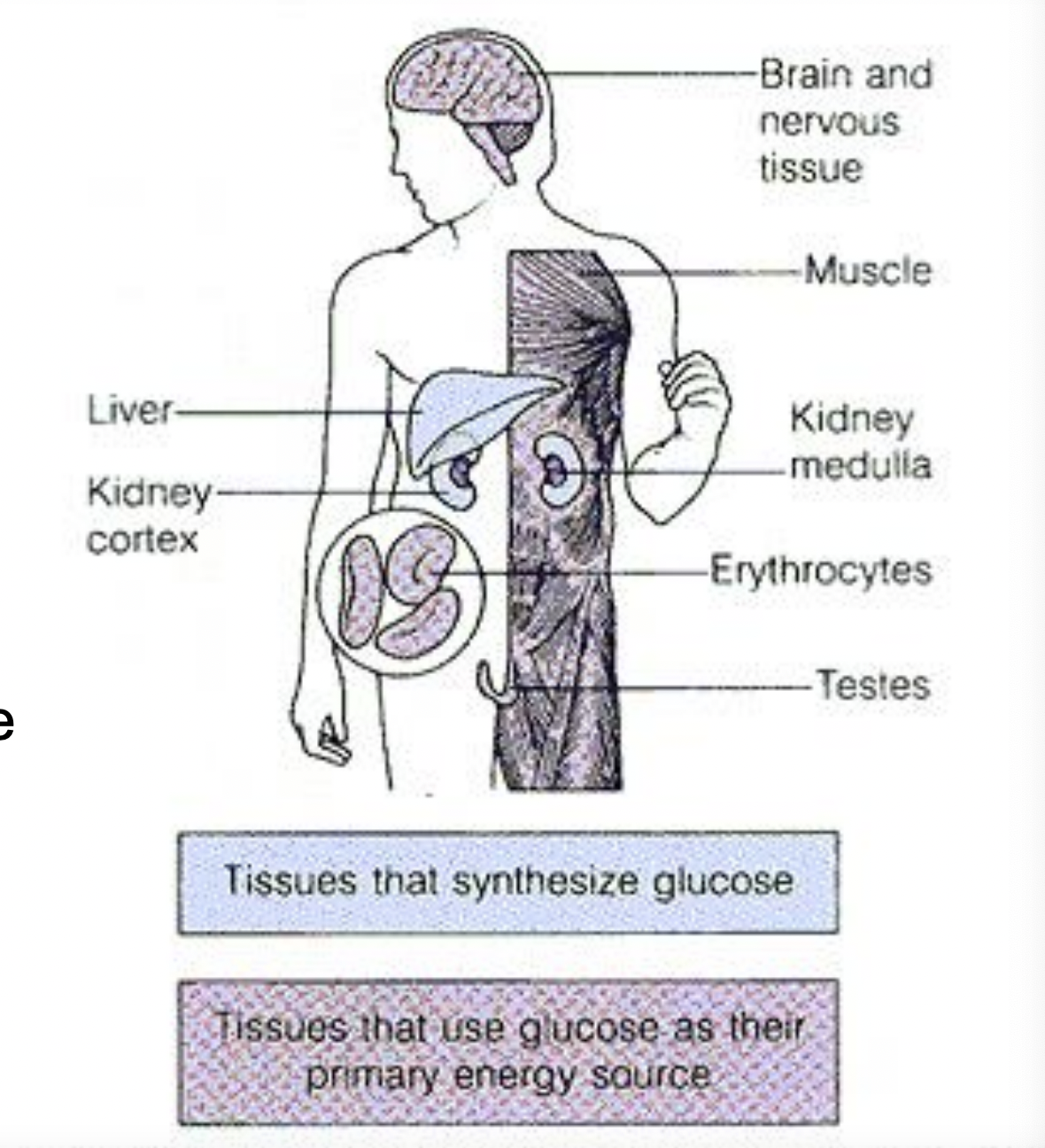
Gluconeogensis in terms of how much needed in body
-total need: ~160 g glucose/day
-brains and eyes alone: 120 g/day
-reserve: 190 g
When fasting or conducting extreme endurance exercise (marathon), need other source for glucose
Gluconeogenesis Definition
synthesis of 6 carbon glucose from 3-4 carbon precursors, normally non-carbohydrate sources
4 sources of precursors for gluconeogensis
Lactate: skeletal muscle, erythrocytes
Amino acids: dietary protein, muscle protein breakdown
Propionate: derived from fatty acids, amino acids
Glycerol and stored fats under starvation conditions
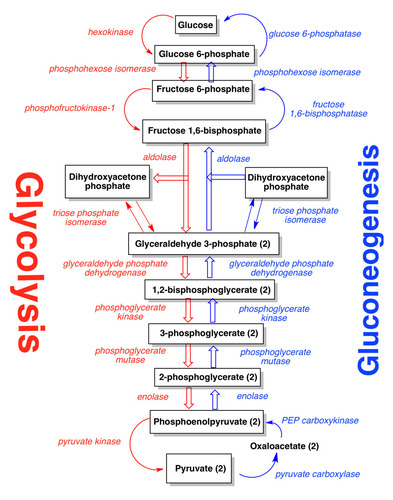
Gluconeogensis Purpose
- formation of glucose from NON-CARBOHYDRATE molecules
- mainly carried out in LIVER and KIDNEY
- another source for glucose
- similar to GLYCOLYSIS process except for 4 REACTIONS
Cori Cycle Purpose
turn lactate to glucose then transport it back to muscles
Cori Cycle After Exercise:
Lactate: transported from muscle to liver
Glucose: transported from liver to muscle
Anabolic Glucose Metabolism
-Glucose is made within most organisms
-Pathway is known as gluconeogenesis
-Process if strikingly simialr to glycolysis, with the exception of 4 reactions
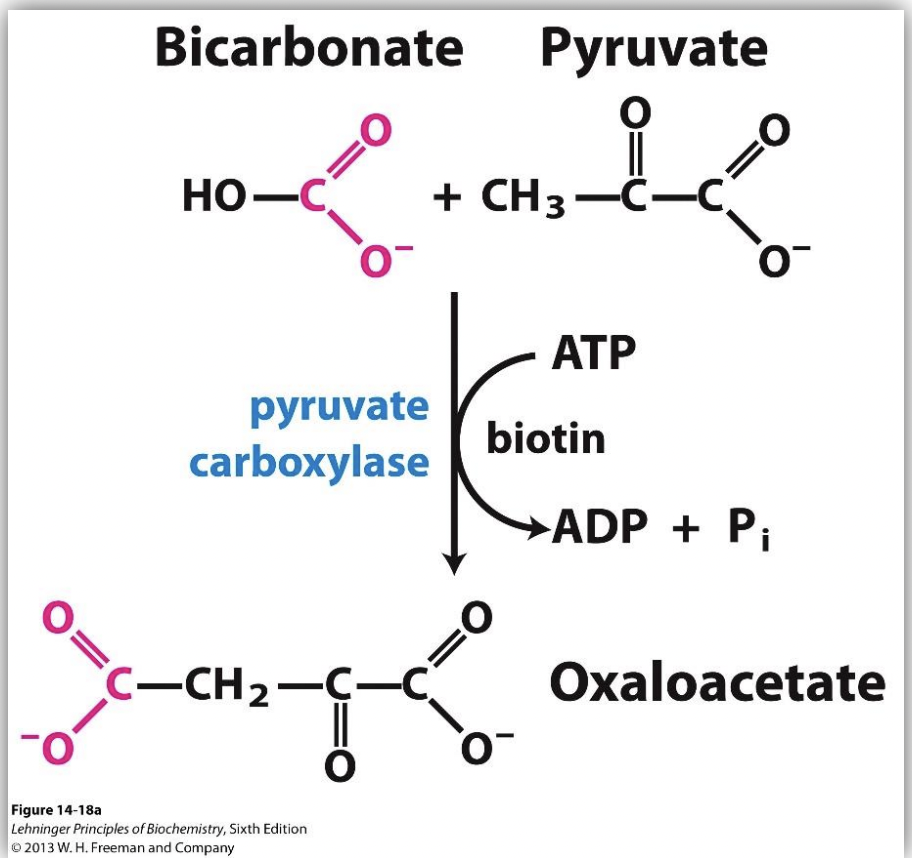
GLUCONEOGENESIS STEP 1: Pyruvate cannot be ___.
directly converted to PEP; requires ATP.
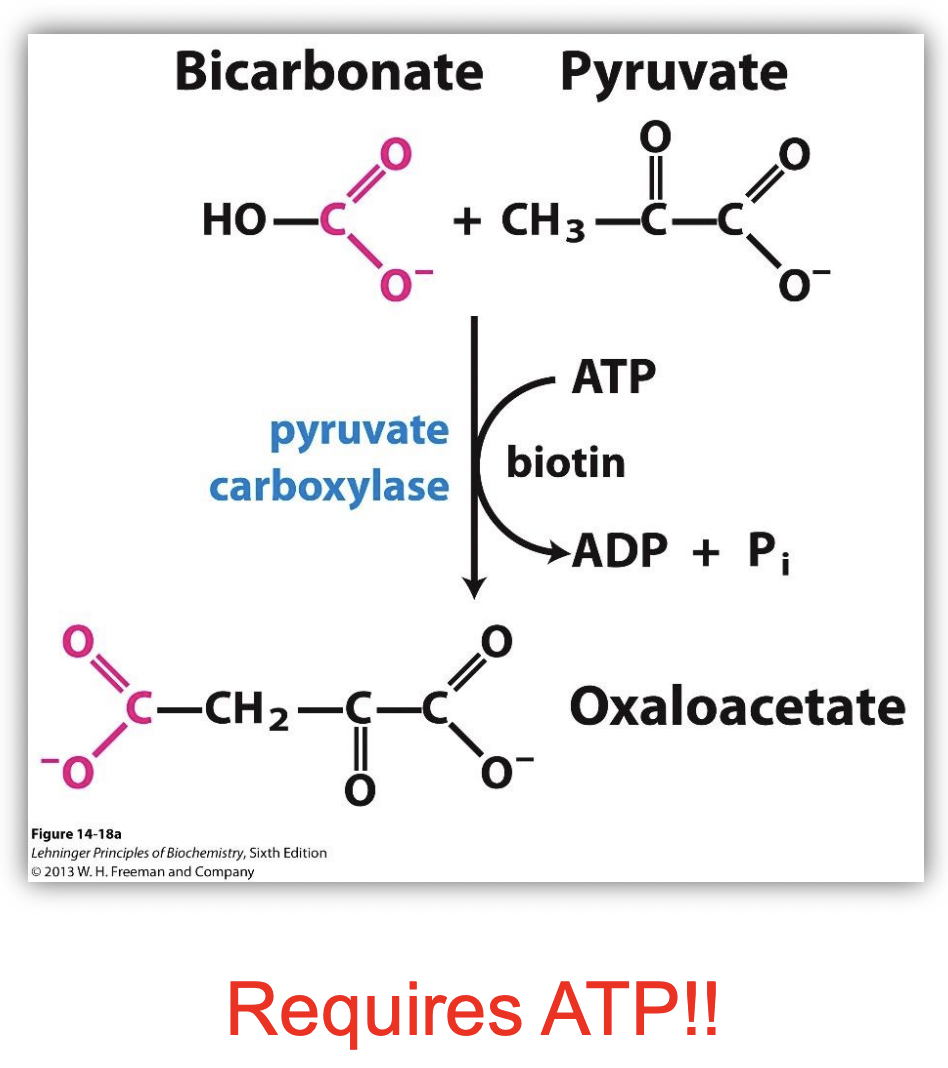
GLUCONEOGENESIS STEP 1: involves…
turning pyruvate to oxaloacetate
-how? take CO2 from molecule of bicarbonate and link it onto a molecule of pyruvate through the action of an enzyme (pyruvate carboxylase), ATP (putting energy to remake glucose), a cofactor (biotin), and magnesium (Mg2+) = oxaloacetate
Glycolyis happens in the ___ while pyruvate carboxylase is in the ___ for glucogenesis (step 1).
cytosol, mitochondria
GLUCONEOGENESIS STEP 1: compartmentalization is an issue why?
Pyruvate is funneled into mitochondria, meaning it’s compartmentalized or sequestered away; the enzyme pyruvate carboxylase is also in the mitochondria, which is an added issue.
GLUCONEOGENESIS STEP 1 & 2: COMPARTMENTALIZATION (pathway)
1) -Pyruvate carboxylase @ mitochondria.
-pyruvate transported to mitochondria → turned into oxaloacetate (OAA), an important precursor
-OAA can’t cross mitochondrial membrane → converted to malate
-Malate transported to cytosol, then converted back to OAA
2) -Cytosolic OAA is converted to PEP by PEP carboxykinase (PEPCK)
-Uses GTP - another energy currency
-Purpose: to get pyruvate out of mitochondria and back in cytoplasm for gluconeogenesis.
REMIND: 2 DIFFERENCES FROM GLYCOLYSIS
Gluconeogenesis uses how many ATP, GTP, and NADH total?
6 ATP (4 ATP + 2 GTP, which are equivalent) and 2 NADH ( 2 pyruvate → 1 molecule of glucose conversion)
remind: breaking down a molecule of glucose = 2 ATP
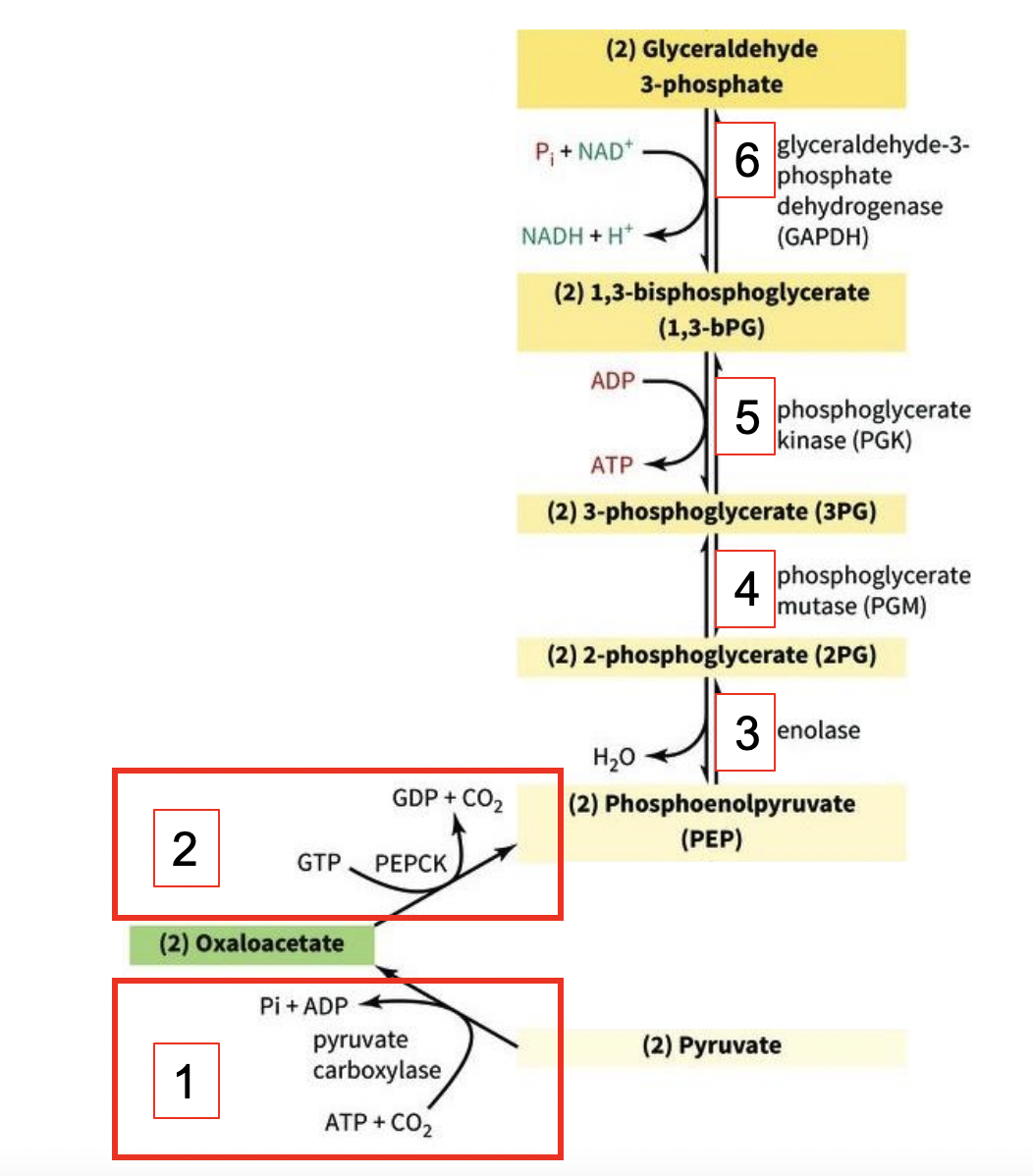
GLUCONEOGENESIS: 1st 6 Steps
1) Pyruvate (in mitochondria) → use pyruvate carboxylase + ATP (and etc.) = oxaloacetate (OAA)
2) (Cytosolic) OAA → PEPCK (PEP carboxykinase) + GTP = Phophoenolpyruvate (PEP)
3) PEP → enolase = 2-phosphoglycerate (2PG) + loss of H2O
4) 2PG → phosphoglycerate mutase (PGM) = 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG)
5) 3PG → phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) + ATP = 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-bPG)
6) 1,3-bPG → glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GADPH) & regenerates NAD+ = Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
REMIND: done 2Xs so 2 of everything (excluding the enzymes)
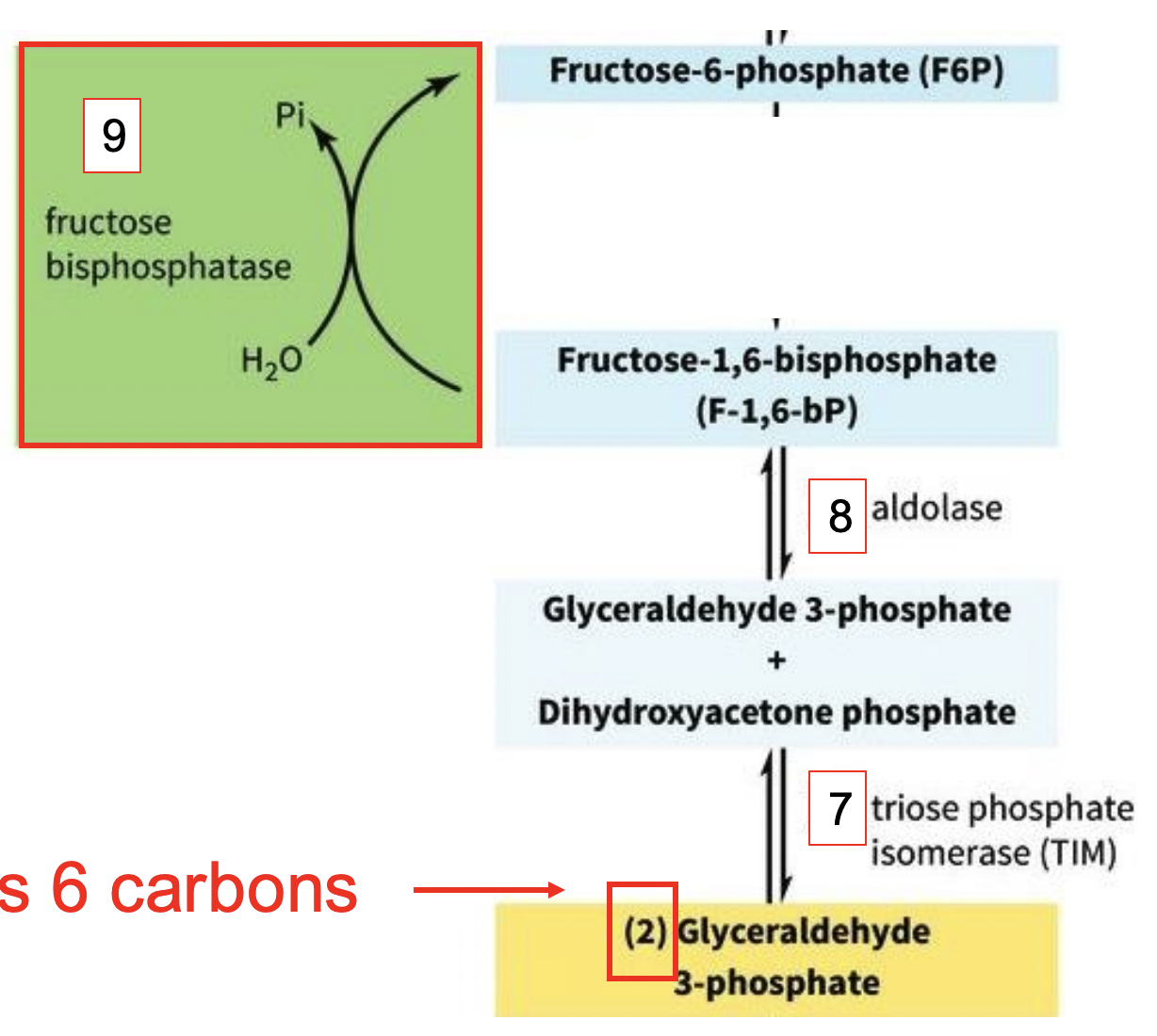
GLUCONEOGENSIS: FRUCTOSE BISPHOSPHATASE (Step 9)
-removes one of the phosphates on F-1,6-bP
-removes 1 x Pi while using H2O
REMIND: GLUCOSE HAS 6 CARBONS
-3rd difference
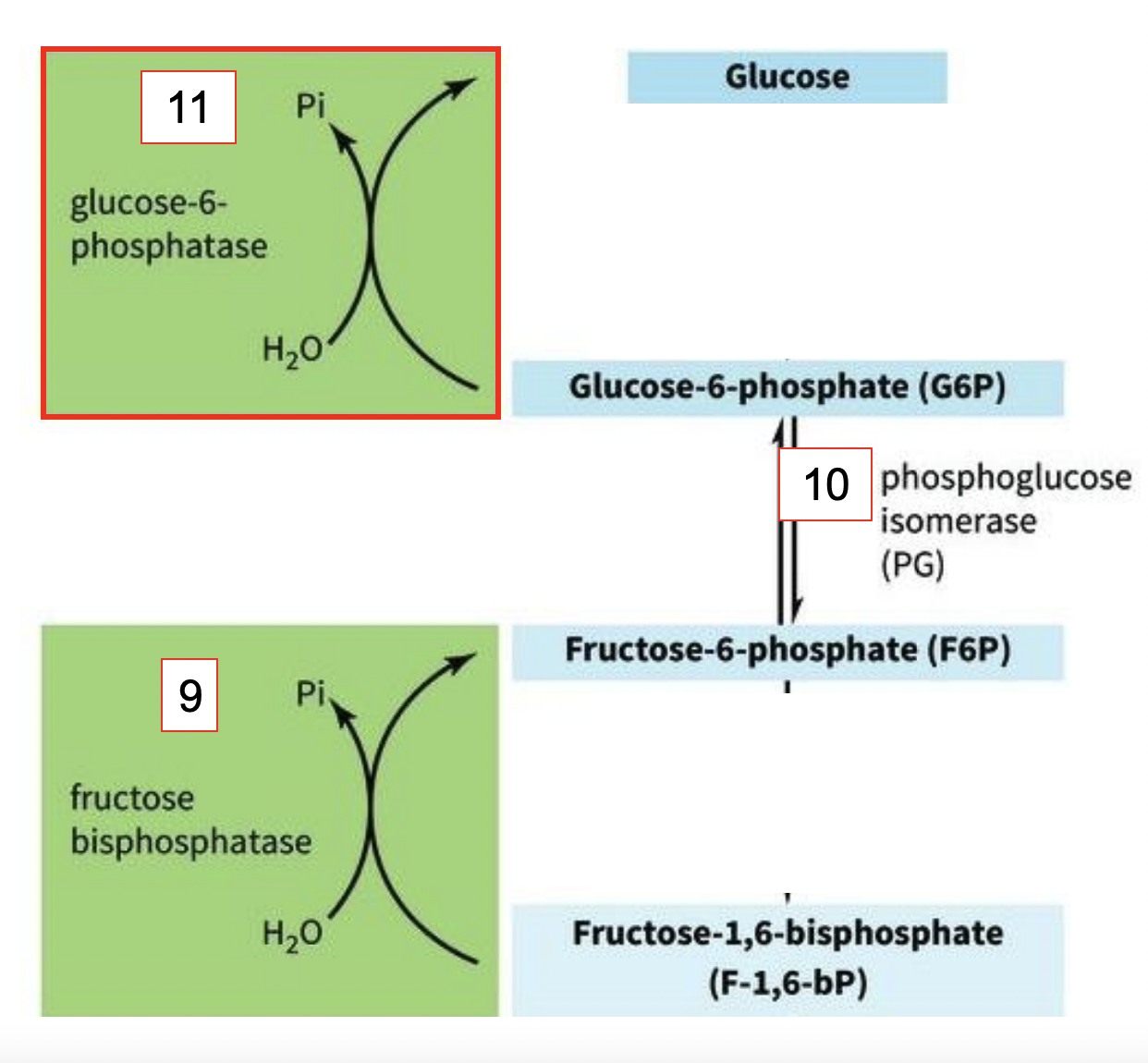
GLUCONEOGENSIS: GLUCOSE 6-PHOSPHATASE (final step 11)
-removes the last Pi
-allows glucose to leave the cell
GLUCONEOGENESIS: STEPS 7-11
7) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate → triose phosphate isomerase (TMI) = 2 products. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate & Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
8) 2 products → aldolase = Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (F-1,6-bP)
9) F-1,6-bP → fructose bisphosphatase removes one of the phosphates on F-1,6-bP & 1 x Pi = Fructose-6-phosphate (F6P)
10) F6P → phosphoglucose isomerase (PG) = Glucose-6-phosphate (G6P)
11) G6P → glucose-6-phosphatase removes the last Pi using H2O & allows glucose to leave the cell (GLUCOSE IS MADE!)
How do we keep cells from spending all the energy they make from glycolysis doing gluconeogensis?
Futile cycle: pathways running in opposite directions resulting in loss of energy.
COMPARTMENTALIZATION (extra)
-Not just about organellar separation of pathways, tissue too!
-Not all the organs have the same metabolic needs
-Gene expression in different tissues, or different cells within different tissues allows for the use of one pathway or another
Other cells can feed cancer cells what?
alanine and glucose