IMMUNOLOGY & BLOOD BANKING
1/187
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ACTS REVIEW SYSTEM
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
188 Terms
IMMUNE SYSTEM
Integrated system of cells, substances, and organs responsible for destruction of foreign susbtances (antigens) and keep body safe from injury and infectious agents
IMMUNOLOGY
The study concerned with the processes by which all living organisms defend themselves against infection
ANTIGENS
Refers to the substances which are considered foreign to a host (the intruders)
CELLULAR IMMUNITY
HUMORAL IMMUNITY
2 Components of Immunity:
CELLULAR IMMUNITY
Cells that make up the immune system acts as protection example: WBCs
HUMORAL IMMUNITY
Non-cellular / soluble substance that promote immunity, proteins example: Antibody
INNATE IMMUNITY
ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
2 Categories of Immunity are:
INNATE IMMUNITY
Known as natural or non-specific immunity
ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
Known as the acquired or specific immunity
INNATE IMMUNITY
Does NOT have memory cells, the cannot target specific enemy
INNATE IMMUNITY
Functions in early stages of host defense in response to foreign agents
ANATOMICAL BARRIERS
RESIDENT FLORA
HEREDITARY OR GENETIC INFLUENCE
CELLULAR FACTOR
HUMORAL FACTOR
INFLAMMATION
6 Components of Innate Immunity:
ANATOMICAL BARRIER
This is the 1st line of defense, acts as “barrier” or “block of entry”
SKIN
CILLIA
MUCUS
SECRETIONS
EARWAX
GASTRIC ACID
TEARS
7 Components of Anatomical Barrier of Innate Immunity are:
SKIN
The largest barrier, and also known as the largest external organ in the human body
CILLIA
MUCUS
These (2) primarily protects the respiratory tract
CILLIA
Hair-like structures; to filter out the antigen (Ag)
MUCUS
Sticky substances; to trap the antigen (Ag) contained in sputum, which requires expectoration
SECRETIONS
Contains proteolytic enzymes; destroys proteins
EARWAX
Also a sticky substance; to trap antigen (Ag) causes ear infection such as Swimmer’s Ear
SWIMMER’S EAR
This infection is caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa
GASTRIC ACID
Protects the digestive tract because it contains Hydrochloric acid
1.0 - 3.0 pH
What is the pH of Hydrochloric acid (Hcl) in gastric acid?
Helicobacter pylori
Cysts form of Ameoba
What are some organisms that can survive in the acidity of a stomach?
Helicobacter pylori
This bacteria produces urease; causes peptic ulcer
Cysts form of Ameoba
These parasites have thick walled so they can survive in the acidity of the stomach
TEARS
Flushing mechanism; protects the eyes
TEARS
Which anatomical barrier can cause Soreyes / Conjunctivitis?
ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS (APCs)
cells that can connect Innate immunity with Adaptive immunity
RESIDENT FLORA
Also known as the normal microbiota / normal flora
RESIDENT FLORA
Organisms that reside in certain areas of the body
RESIDENT FLORA
Helps prevent the multiplication of the pathogen
ORAL CAVITY
INTESTINES
SKIN
VAGINA
What are the (4) Resident Flora:
ORAL CAVITY
This is where the most predominant flora resides?
Viridans Streptococci / Alpha-Hemolytic
Normal flora in Oral cavity?
Viridans streptococci
This bacteria causes Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis (SBE) which can be disrupted by prolonged antibiotic intake which promote antibiotic resistance
Gram-Negative anaerobic bacilli sp. Bacteroides
Normal flora in Intestines?
Lactobacillus casei
Lactobacillus paracasei
What bacteria can be seen in Probiotic drinks?
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Normal flora in Skin?
Staphylococcus epidermidis
This bacteria is known as the most common contaminant in blood culture.
Lactobacillus acidophilus
Normal flora in Vagina?
Lactobacillus acidophilus
This bacteria is known as the acid-loving bacteria
NORMAL DELIVERY VS. CESAREAN SECTION
BREAST FED BABIES VS. MILK FED BABIES
What are the (2) different normal flora fingerprints:
INTERSPECIES DIFFERENCES
RACIAL DIFFERENCES
BLOOD GROUP PHENOTYPES
INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCES
INHERITED HLA
What are (5) components of Hereditary or Genetic Influence?
DUFFY NULL PHENOTYPE
This blood group phenotype that can cause genetic influences is most commonly found in African population
DUFFY NULL PHENOTYPE
This blood group phenotype confers resistance to Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium knowlesi
DUFFY NULL PHENOTYPE
This blood group phenotype can produce anti-Fy3
P1 ANTIGEN
This blood group phenotype is susceptible to recurrent UTI
B27
Which inherited HLA can be a high risk of Ankylosing Spondylitis?
BASOPHILS
This the least predominant WBC in the blood; differential count is usually 0-1%
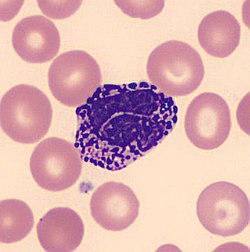
BASOPHILS
Deep bluish-purple granules that obscure the nucleus
BASOPHILS
This cell contains Heparin and Histamine
HISTAMINE
An inflammatory mediator promoting localized vasodilation
TO WIDEN THE ACCESS OF WBCs
Purpose of Histamine in Basophils?
WHEN LOCALIZED VASODILATION HAPPENS; CARDINAL SIGNS WILL APPEAR
What is the connection of histamine to inflammation?
BASOPHILS
This cell is involved in Type 1 Hypersensitivity reaction
EOSINOPHILS
1-3% of total WBC in the blood
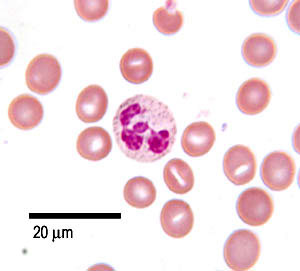
EOSINOPHILS
Large orange granules
EOSINOPHILS
This cell is the second least common WBC in blood
PARASITIC INFECTION
ALLERGIC REACTION
Eosinophils are INCREASED in:
HELMINTHIC INFECTIONS
Which parasitic infection that can cause increased eosinophils?
Ascaris lumbricoides
Strongyloides stercoralis
Hookworms
What are the Helminthic parasites (larva) that migrate to the heart and lungs that can cause increased eosinophils? (A-S-H)
IgE
Which Immunoglobulin is along with Eosinophils that is effective in engulfing and killing parasitic larva infections?
MAJOR BASIC PROTEIN (MBP)
What is called the granules of Eosinophils that are attached to kill parasitic larva infections?
EOSINOPHILS
This cell suppressed basophilic reaction?
PHAGOCYTES
This is the 2nd line of defense, acts as “soldier”
PHAGOCYTES
Responsible for phagocytosis, but can also present antigens
PHAGOCYTES
Includes neutrophils and monocytes
PHAGOCYTES
This is effective if the antigen (Ag) is extracellular
DIAPEDESIS
During phagocytosis; the squeezing movement of WBCs from the blood vessels to the tissues is known as?
NEUTROPHILS
Most predominant WBC in the blood
ACUTE INFECTION
BACTERIAL INFECTION
Neutrophils are INCREASED in:
MONOCYTES
Largest WBC in the peripheral blood
CHRONIC INFECTION
Monocytes are INCREASED in:
MONOCYTES
This is known as the “Scavenger cells”
MACROPHAGES
Tissue monocyte is known as the?
KUPPFER CELLS
Tissue macrophages that are located in the liver.
MICROGLIAL CELLS
Tissue macrophages that are found in central nervous system (CNS)
MESENGIAL CELLS
Tissue macrophages that are found in the kidney
HISTIOCYTES
Tissue macrophages that are found in connective tissue
OSTEOCLAST
Tissue macrophages that are found in bones
ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGE
Tissue macrophages that are located in the lungs.
SPLENIC MACROPHAGE
Tissue macrophages that are located in the spleen
DERMAL MACROPHAGE
Tissue macrophages that are located in the skin
HOFBAUER CELLS
Tissue macrophages that are found in placenta
CREOLA BODIES
CURSCHMANN SPIRAL
CHARCOT LEYDEN
What are the 3C’s found in patients with sputum of Bronchial asthma?
CHARCOT LEYDEN
This is the disintegration of eosinophils
NEUTROPHIL
LYMPHOCYTE
MONOCYTE
EOSINOPHIL
BASOPHIL
Arrangement of WBC Count: (Never Let Monkeys Eat Banana)
ELIE METCHNIKOFF
Phagocytosis is demonstrated by?
I - INITIATION
C - CHEMOTAXIS
E - ENGULFMENT
D - DIGESTION
Mnemonics for the Steps of Phagocytosis?
INITIATION
This step in phagocytosis triggers tissue damage?
CHEMOTAXIS
This step in phagocytosis is known as the movement of WBCs to a certain direction under the influence of chemical substances
WBCs MOVE WITH DIRECTION
What is the meaning of WITH chemotaxis?
WBCs MOVE RANDOMLY
What is the meaning of WITHOUT chemotaxis?
POSITIVE CHEMOTAXIS
NEGATIVE CHEMOTAXIS
2 Types of Chemotaxis?
POSITIVE CHEMOTAXIS
This type of chemotaxis defines as the movement towards the stimulus (infection)
NEGATIVE CHEMOTAXIS
This type of chemotaxis defines as the movement away from the stimulus
CHEMOTAXIN / CHEMOTACTIC AGENT / CHEMOKINES
This promotes chemotaxis (C3a, C5a)?
CHEMOTAXIS
This step in phagocytosis is defines that from blood, WBCs can move through the blood vessel wall
JOB’S SYNDROME
LAZY LEUKOCYTE SYNDROME
What are the (2) Disorders under the Phagocyte Movement: (J-L)