Gen Chem 2: Lecture 3
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Define what molar enthalpy of vaporization is:
The amount of energy needed to turn one mole of a liquid into a gas at a constant temperature.
Define what molar enthalpy of condensation is:
Molar enthalpy of condensation is how much heat a gas gives off when it turns back into a liquid. (the opposite of molar enthalpy of vaporization)
Define what Equilibrium vapor pressure is:
How much a liquid tries to turn into a gas in a closed container (the pressure applied by a vapor over a liquid in a closed container)
What happens in the equilibrium?
Rate of evaporation equals rate of condensation.
What is volatility?
Volatility is how easily a liquid turns into a gas.
What is the relationship between equilibrium vapor pressure and volatility?
- Higher equilibrium vapor pressure → Higher volatility (the liquid evaporates easily).
- Lower equilibrium vapor pressure → Lower volatility (the liquid evaporates slowly).
Draw and describe A graph of how vapor pressure of a substance changes with the temperature:
The left of the graph the compounds exist as liquids for temperature and pressures. To the right are gasses under higher conditions.
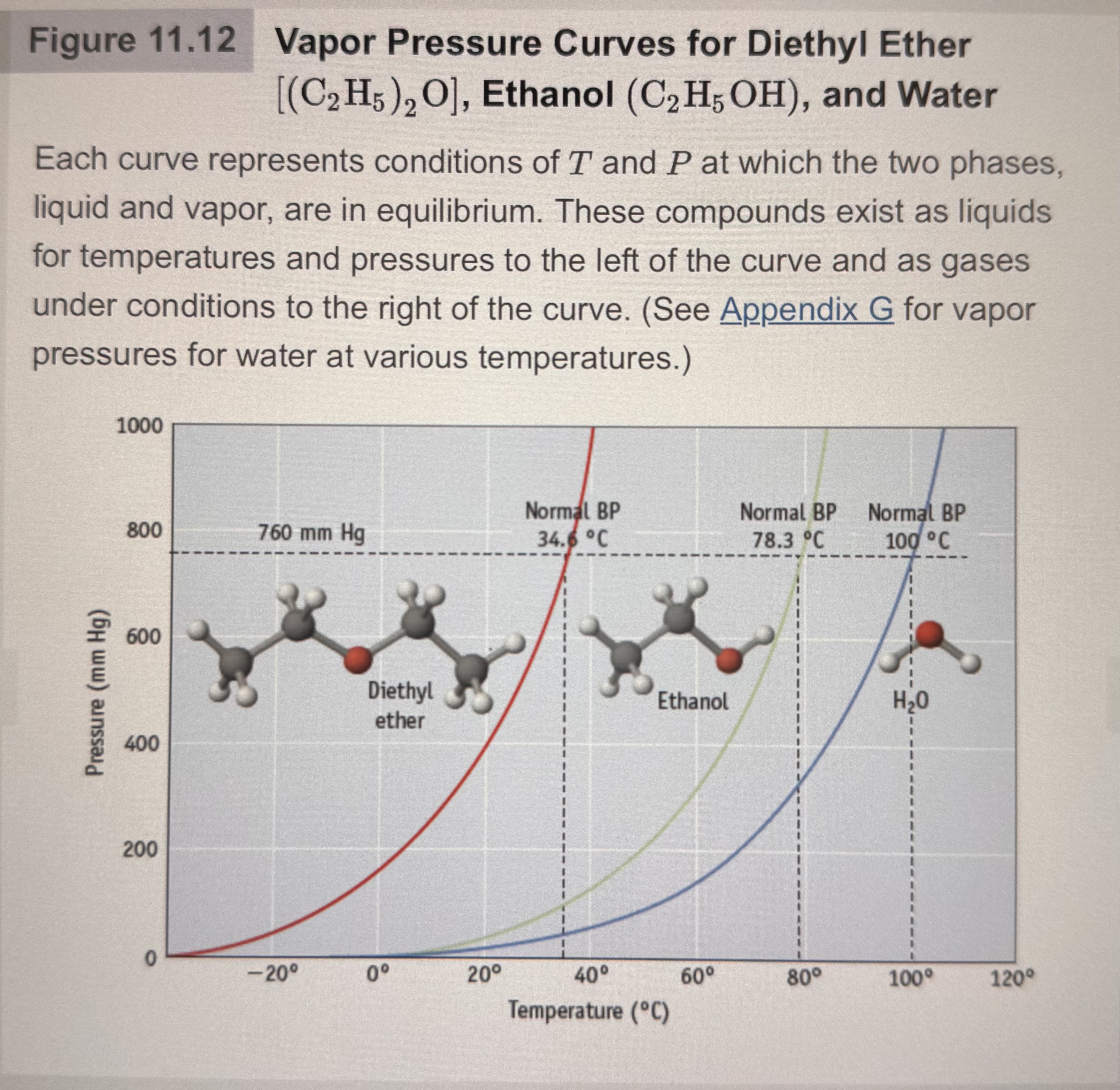
What is boiling point?
Temperature where the vapor pressure equals external atmospheric pressure.
Be able to draw the boiling point sketch:
image should’ve been:
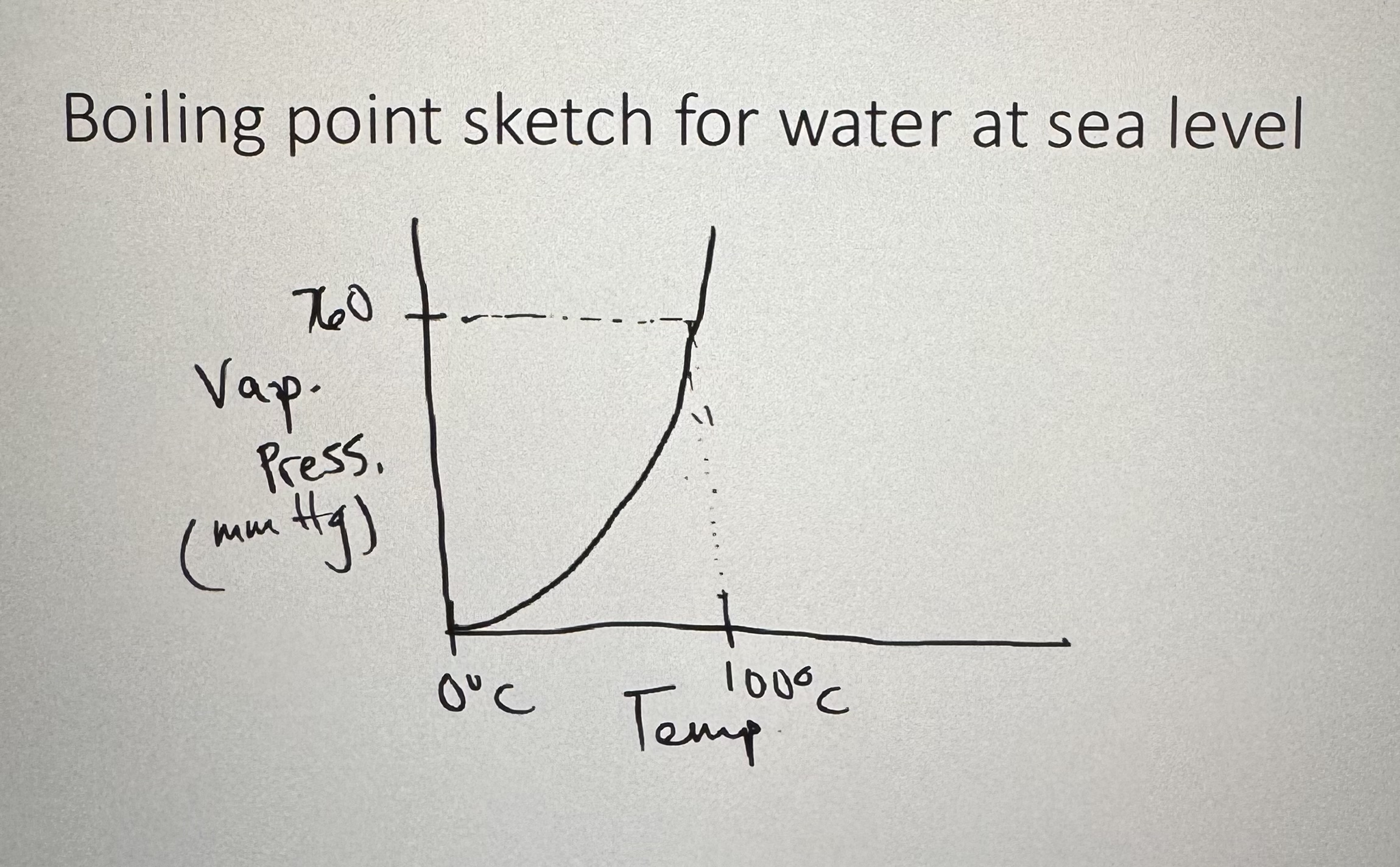
What is the normal boiling point?
Each substance happens at 760 mm Hg (or 1 atm) of atmospheric pressure.
What is viscosity?
The resistance of liquids to flow. (sticky when high; unable to move around much & slides when low; move freely)
What is one way to measure viscosity?
To compare the rate at which a heavy object drops in a liquid.
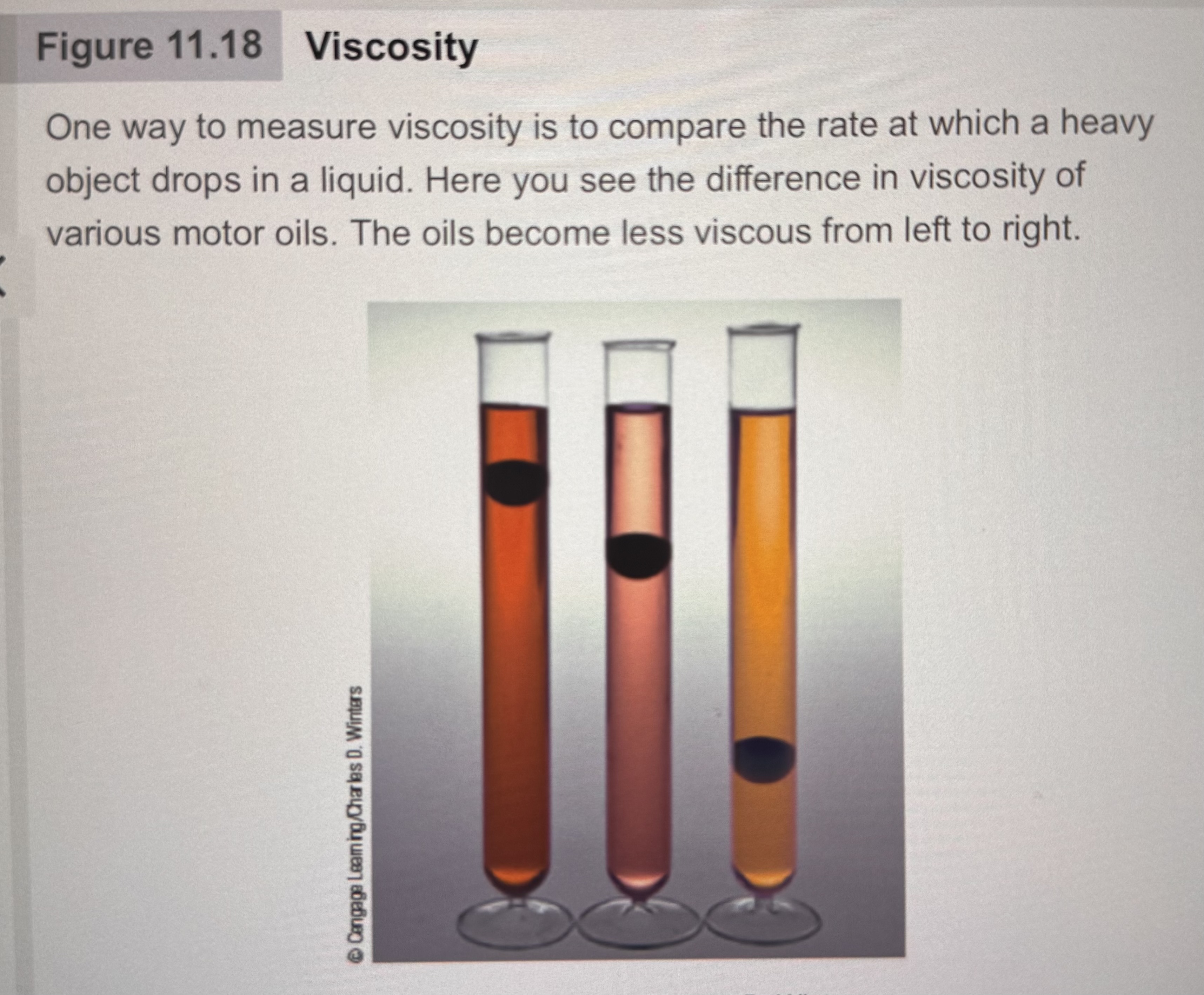
What The relationship between intermolecular forces and viscosity?
Strong Intermolecular Forces: higher viscosity
Weak Intermolecular Forces: lower viscosity
What is surface tension?
Is the physical property of a liquids surface to resist an external force. The stronger the intermolecular forces in a liquid are, the higher the surface tension is.
What is surface tension’s relationship with intermolecular forces?
Stronger intermolecular forces mean higher surface tension, weaker intermolecular forces mean lower surface tension.