20s and 30s history test
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
Two things Hitler did to help Germany's economy
Authorizing the production of the Volkswagen, and building the military back up
2
New cards
What is Facism?
Fascism is a system of government led by a dictator who typically rules by forcefully and often violently suppressing opposition and criticism, controlling all industry and commerce, and promoting extreme nationalism and often racism. Blaming miniority groups for unrelated issues (scapegoats), using propoganda, restricting rights.
3
New cards
Propoganda used by Hitler
He didn't show his face at first, took photos that put him in a good light (made him seem like 'everyone's favourite uncle', wrote a book, orders a famous director/actor to make a movie about his events
4
New cards
John Maynard Keyne's solution to the Great Depression
Governments should borrow loads of $, go into debt, create many jobs with loaned money, pay decent wages to workers to get money moving again, and create product demand, those businesses with more product demand now need more workers, so they hire more workers, good times! The government can now tax people more, and they use that tax to pay off their debts. (Prosperity cycle) POTUS supported it, but Canada's PM did not at first, and our situation became direr
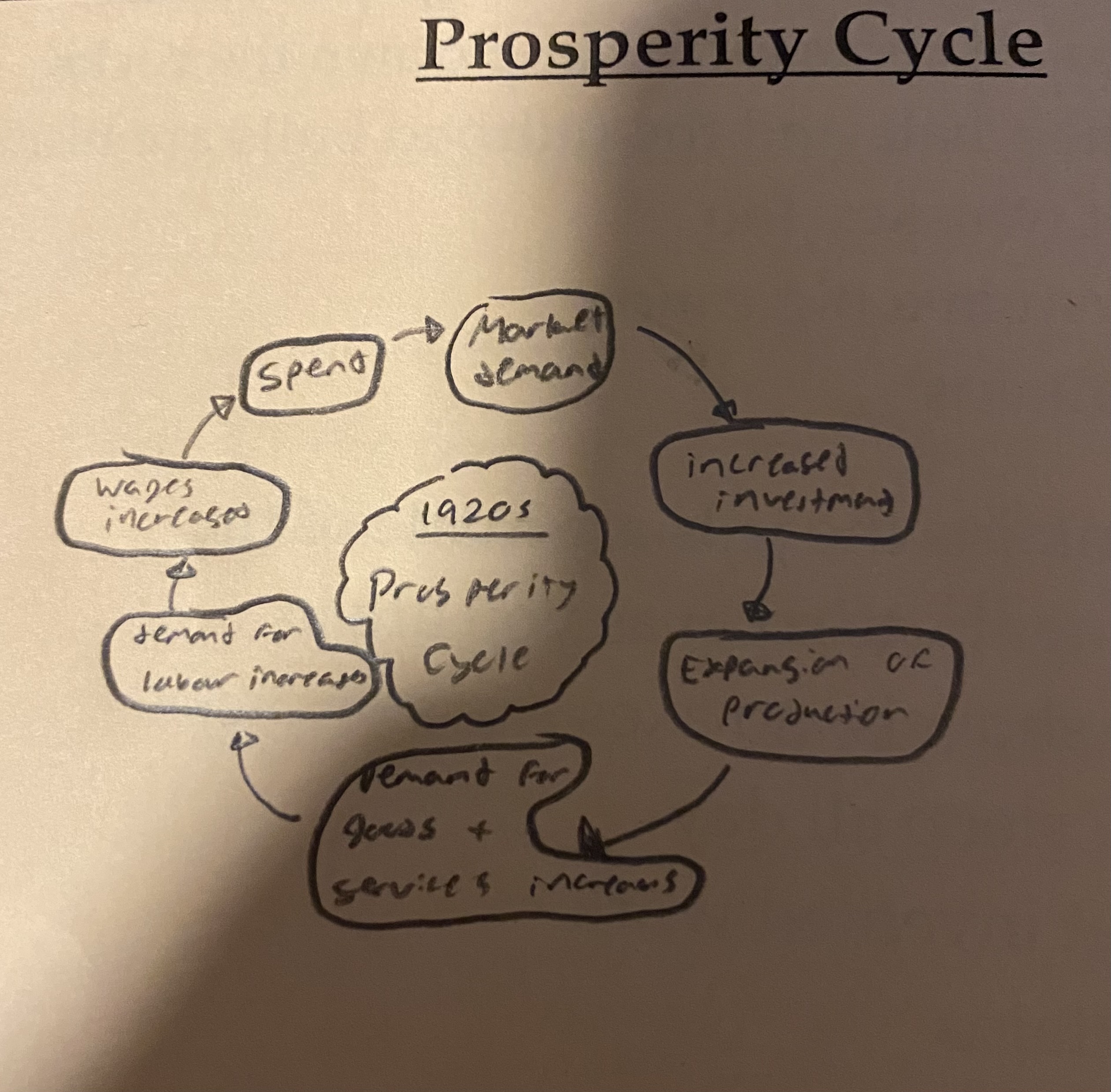
5
New cards
Two immigration laws Canada passed
Empire settlement act (1922, gov wanted immigrants from Britain and other white countries), Chinese immigration act (1923, stopped nearly all Chinese immigration, also made it hard for other Asians, South Asians, and Africans)
6
New cards
What is prejudice?
Pre-judging someone or something when you don't know anything about them or it
7
New cards
What is discrimination?
unfair and unkind treatment of those different than you, especially on the grounds of race, age, or sex
8
New cards
Discrimination against women
women were losing their jobs to men, those that were lucky enough to stay in their jobs were facing pay cuts
9
New cards
What do bad times induce?
Discrimination
10
New cards
Discrimination + racism
Many Jewish, Italians, Poles, and Asians faced discrimination + racism in the workforce (last hired, first fired)
11
New cards
Deportation
The government deported over 30 000 new immigrants back to their countries because people were so upset, before the depression started many people were more than happy to give immigrants all the hard physical labour jobs, but now they wanted them back
12
New cards
St Louis
boat, one of the last ships to leave Germany before the total outbreak of WW2, 937 Jewish people (men, women, and children), headed for Havana, Cuba, but were denied entry. Denied again by the US, Canada, Argentina, and Uruguay. Looked like they'd have to head back to Hamburg. As they came close to Europe, Belgium, France, Holland, and Britain, said they would take the passengers. Many of them died in concentration camps later on when three out of the four countries were under Nazi rule. Only the ones in Britain stayed safe.
13
New cards
What was life like during the Great Depression?
wages decrease, cost of goods decrease. unemployment skyrockets. many forced to be put on relief, 'the dole'. came in the form of vouchers/coupons to eat at free soup kitchens
14
New cards
Farmers in the Great Depression
they were hit hardest, crop prices decrease due to bumper (really good) crops, Alberta and Saskatchewan were hit by bad drought. Crops failed and the soil turned into concrete + dust. In areas without drought, locusts ate thousands of hectares of crops, 13 000+ farms go bankrupt
15
New cards
Hobos
single jobless men, 'riding the rails' or 'rods' in search of work, relief camps were created for them to give them a job. 8hr/day, 6 days/week, paid 20 cents a day, very strict, some grew tired of the treatment and their situation in general. some thought communism was starting to look good.
16
New cards
Mackenzie King
(Liberal) saw the stock market crash and the rising unemployment rates as inconvenient, and a minor short-term setback
17
New cards
RB Bennett
(Conservative) defeats King and is now the prime minister, promises relief and gives 20m to each of the provinces, lowers income taxes, places tariffs on imported goods. his actions didn't work that well
18
New cards
Democratic Socialism
Believed in democracy and free elections, blamed big business and capitalism for the great depression, rejected revolution as a solution, now known as NDP
19
New cards
Communism
Wanted to use violent revolution to overthrow the government, believes capitalism should be replaced with a society run for and by workers, everyone is paid equally and treated equal no matter what
20
New cards
Canadian Economy at the time
Canadian economy relied almost solely on the exports of natural resources, business was booming, and Canadians believed times would be this good for a long time. Farmers borrowed money to expand farms, businesses expanded factories and hired more workers, and banks lent money more freely. Cdns ignored signs of economic weakness, businesses ended up making too much product, and things were stockpiling
21
New cards
Credit
people used credit very often to buy large items that were popular at the time (cars, appliances, etc.), people also used credit to buy stocks
22
New cards
What makes stock markets crash?
People have less money to spend -> people buy even fewer things, factories lay off workers, and some even close -> unemployment rises, more people have even less money to spend -> people buy even fewer things, unemployment rises even more (circles around and around)
23
New cards
What is Collateral?
people put up things (houses, cars, businesses) for the bank to take over if they somehow can't pay back their loans, when the stock market crashed and many people lost tons of money, many lost big items as well
24
New cards
Consumerism
the theory that an increasing consumption of goods is economically beneficial, many new things were popping up at this time, things such as natural gas or electric stoves, and cheap electricity changed the game for many (helped with the production of cars as well)
25
New cards
Insulin
Frederick Banting arrived at a formula to produce insulin, diabetes was life thratening at this time so it changed the world and saved many lives
26
New cards
Radio
a new form of entertainment for many, Canadians worried there weren't enough Canadian radio stations so they had to change that, CBC was created (Foster Hewitt's Hockey Night in Canada was also very popular at the time)
27
New cards
Automobile
changed the whole country, Henry Ford wanted to mass produce his car (Model T/Tin Lizzie) on a big scale to make it more affordable, the moving conveyor belt was invented, millions of jobs were created in the car factories, gas stations, road paving, and much more
28
New cards
Residential Schools in the 1920s
this was the peak of Residential Schools, children were being forcefully taken away to 'schools' where they were abused, assaulted, raped, and stripped of their culture and language. Canadians believed these schools were good for them because of government propoganda that was spread around
29
New cards
Canadian Women in the 1920s
women earned respect for their work during the war and earned the right to vote, still faced discrimination and were second to their male counterparts though
30
New cards
Famous Five
Emily Murphy (writer, politician, journalist, and first female magistrate in the British empire - pen name Janey Canuck)
Irene Parlby (first female provincial cabinet minister)
Nellie McClung (fighter for women's suffrage and prohibition, elected to Alberta Legislature in 1921)
Henrietta Edwards ( Author, and cofounder of the National Council of Women)
Louise McKinney (Organized Women's Christian Temperance Union, elected to Alberta legislature in 1917)
Irene Parlby (first female provincial cabinet minister)
Nellie McClung (fighter for women's suffrage and prohibition, elected to Alberta Legislature in 1921)
Henrietta Edwards ( Author, and cofounder of the National Council of Women)
Louise McKinney (Organized Women's Christian Temperance Union, elected to Alberta legislature in 1917)
31
New cards
Cairine Wilson
First woman to be appointed to Canadian Senate (1930)
32
New cards
What helped with the development of a Canadian Identity
a sense of pride in one's country, a sense of pride in one's nation, common background with fellow citizens (cultural homogenity)
33
New cards
Famous Artists
Group of Seven (JEH MacDonald, Lauren Harris, Franklin Carmichael, Arthur Lisner, FH Varley, AY Jackson, Franz Johnston), Emily Carr (aboriginal art)
34
New cards
Famous in Literature
Stephen Leacock (funny books), Lucy Maud Montgomery (Anne of Green Gables!!), Charles Leslie McFarlane (Franklin W. Dixon, Hardy Boys books)
35
New cards
Famous in Sports
Bluenose (racing schooner, on the dime, won every race it entered, Howie Morenz (Montreal Canadiens), Lionel Conacher (The Big Train, all-round athlete), Bobbie Rosenfeld (Russian-born immigrant, female Lionel Conacher, all-round athlete), Percy Williams (gold medals in 100m dash and 200m event, had a chocolate bar named 'our percy')
36
New cards
Chanak Affair
1922 - Turkey and Greece went to war, Britain called Canada in but King said parliament was to make that decision, Canada would no longer automatically agree to Britain's call
37
New cards
Halibut Treaty
1922 (later) - Canada and the US negotiate how many halibut fish they could both catch, the first treaty Canada signed independently
38
New cards
King-Byung Crisis
1926 - King decided to call an election, but he needed permission from the Governor General though (Julian Byung), Governor General refused and King believed Gov General was just Britain meddling in Canadian Politics, so King changed the position of Gov General to purely ceremonial
39
New cards
Balfor Report
1926 (later) - Countries of Europe come together in English for a conference, they created the Balfor Report, which stated that Britain and all its colonies were now equal, this made Canada no longer a part of the British Empire
40
New cards
The Statute of Westminster
The Statue of Westminster was the final thing needed to fully pass the Balfor Report, this solidified Canada's new independence