End game
1/389
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
390 Terms
Drug which binds B7-1 and B7-2 on APCs
Abatacept
CI does not cross zero, so effect is
significant
P < 0.001 indicates
strong statistical significance.
MAS Tx refractory to mtx and TNFi
cycloosporine/ CNI
CI is narrow, indicating
precision.
coombs +
warm AHA tx steroids
HLH Tx
high-dose steroids and etoposide
if The 95% CI includes 1, indicating the RR is
not statistically significant at α = 0.05
p-value > 0.05
does not prove the null is true; it indicates insufficient evidence to reject it
bars physicians from referring Medicare/Medicaid patients to entities with which they have a financial relationship for designated health services, unless an exception applies
stark law
The ADA prohibits
discrimination against qualified individuals with disabilities and mandates reasonable accommodations to perform essential job functions
. Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FDCA) — FDA REMS provisions
high-risk drugs. Thalidomide and isotretinoin require prescriber certification, patient registration, and pregnancy prevention documentation.
teardrop cells
myelofibrosis
IgM monoclonal protein associated with a demyelinating neuropathy
Monoclonal gammopathy of clinical significance (MGCS) with anti-myelin IgM — treat with rituximab.
Hypocellular marrow + pancytopenia in autoimmune patients and tx
aplastic anemia, start high-dose corticosteroids and cyclosporine.
decreased GPI-anchored proteins CD55 and CD59
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) — consider complement inhibition with eculizumab.
Mixed cryoglobulinemia: treat underlying HCV when possible; if immunologic disease persists, tx
ritux
PAH first line Tx
Endothelial receptor antagonists (bosenten) and PDE5 antagonists (sidenafil)
Paraneoplastic Ab
Anti Hu
LIP Tx
Steroids, then cellcept, imuran, ritux
Positive trendelembergif sagging is on the left side what nerve is it
Right L5
Only ILD associated Ab that doesn’t have to have +ANA
Ro52
septic arthritis always must be
drained
Hepatosplenomegaly and bone pain
Gauchers
Stress fracture (small line on lateral side)
acute kidney injury + severe hypertension + microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA) ± thrombocytopenia.
scleroderma renal crisis
rheum condition with highest rate of ILD
scleroderma
Radial sagittal band rupture
extensor tendon subluxes ulnarly.
Findings: can’t actively extend MCP, but can hold extension once passively placed (no complete rupture).
young lady with provoked DVT and 1 prior miscarriage, labs neg
treat as provoked- warfarin x3 months
non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis.
X-ray is normal but the MRI shows clear sacroiliitis
recurrent painful lesions with fever
panniculitis- which can be from lupus profundus or weber christian
wilsons disease treatment
d penacillamine or zinc
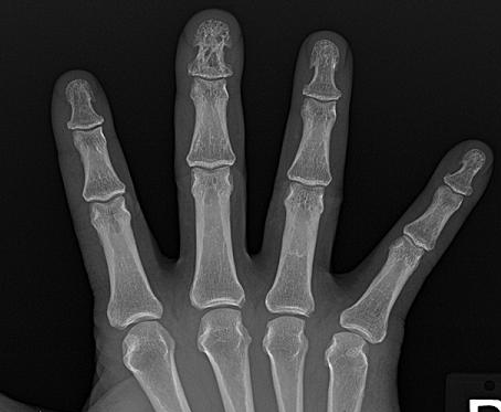
lace like sarcoid lesions
aneursyms and hep b
PAN
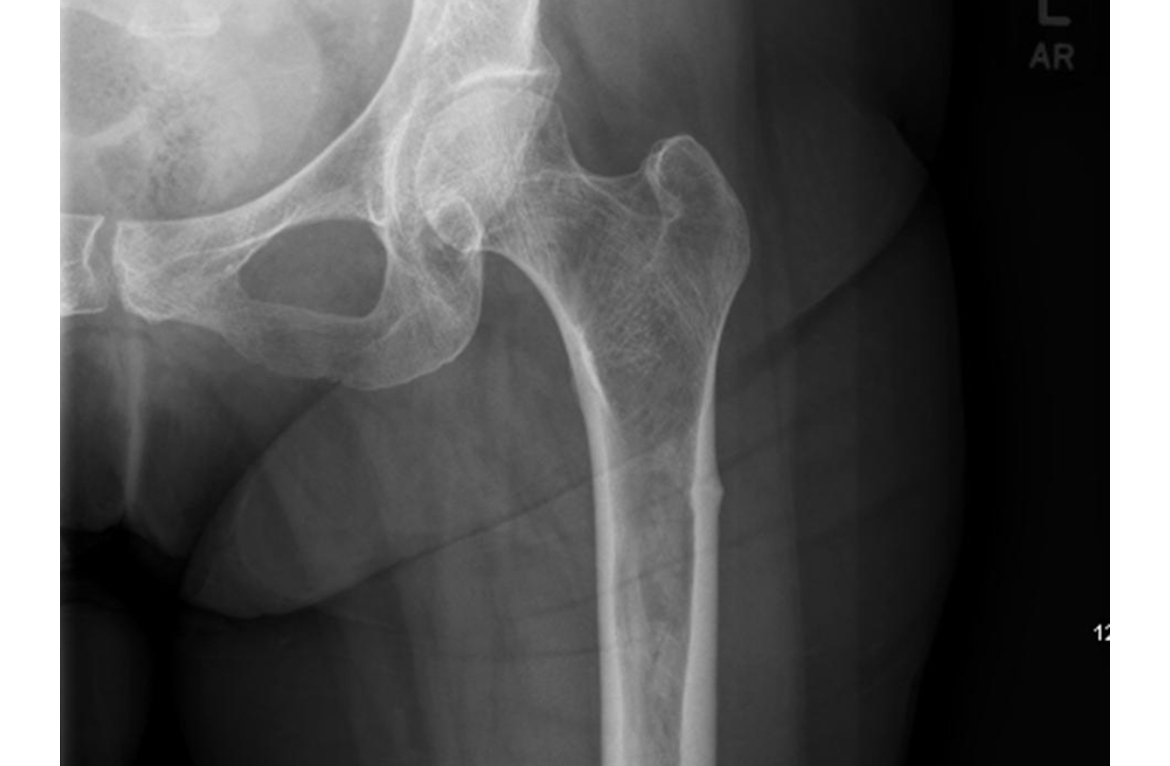
hetertopic ossification- happens after hip surgery esp if they have ank spond, tx ibuprofen
looks like its ankylosed
Pathologic formation of lamellar bone in soft tissues (muscle, periarticular tissue).
Common complication after hip arthroplasty, acetabular fracture fixation, or spinal cord/head injury.
best treatment for hip OA
weight loss (as opposed to knee which is both weight loss and PT)
Tx for RA with any history of melanoma or lymphoproliferative malignancy.
Rituxan
late onset neutropenia happens with what medication
rituximab
can be safely added to hydroxychloroquine in patients with cutaneous lupus not controlled by HCQ alone.
Quinacrine
US showing bilateral glenohumeral synovitis, subacromial bursitis, and biceps tenosynovitis.
PMR
drugs which cause SCLE
thiazide diuretics, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2 receptor antagonists.
Terbinafine (an antifungal).
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Certain cancer treatments, such as checkpoint inhibitors.
TNFi
drugs which cause SLE
Hydralazine (antihypertensive)
Procainamide (antiarrhythmic)
Isoniazid (antibiotic)
Minocycline (antibiotic)
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors (e.g., adalimumab, infliximab)
Diltiazem (calcium channel blocker)
A palmar plantar rash (a rough, red, or reddish-brown rash on the palms and soles of the feet)
oral ulcers
syphillis “the great mimicer”, dont confuse with reactive
SI capsular bridging has been described in patients with
DISH, which on the pelvic anteroposterior radiograph may give the false appearance of obliteration of the SI joint space
TB testing in someone on pred who had BCG
Pred lowers quant accuracy and BCG lower skin test, do both for more accuracy
Ab with highest predicative value of pregnancy loss
LAC
When to restart TNFi when being treated for latent TB
4 weeks after starting Tx
Flexor tenosynovitis boxing gloves appearance
RS3PE
PIN
Causes finger and thumb extension weakness, possibly radial deviation
“PIN syndrome paralyzes fingers but barely hurts.
radial tunnel syn
Causes dull, aching pain 3–5 cm distal to lateral epicondyle, pain with resisted supination or long finger extension, no motor deficits initially
“Radial tunnel is a tunnel 3–5 cm below the epicondyle.”
how does diabetic cheiroarthropathy present
bilateral prayer sing but no cords palpable, and affects more than just a few digits
ACR EULAR SSc criteria
Feature | Score |
|---|---|
Skin thickening of fingers extending proximal to MCPs | 9 (sufficient alone for classification) |
Fingertip lesions (ulcers/pitting) | 2 |
Telangiectasia | 2 |
Abnormal nailfold capillaries | 2 |
Pulmonary arterial hypertension / ILD | 2 |
Raynaud phenomenon | 3 |
SSc-related autoantibodies (anticentromere, anti-topoisomerase I, anti-RNA pol III) | 3 |
note no calcinosis or esophageal issues
child with history of leg pain and bowed legs
ricketts
warm, swollen, erythematous foot with good pulses and little pain
charcot, may flare after trauma
how to diagnose non vascular thoracic outlet syn
clinical, no imaging
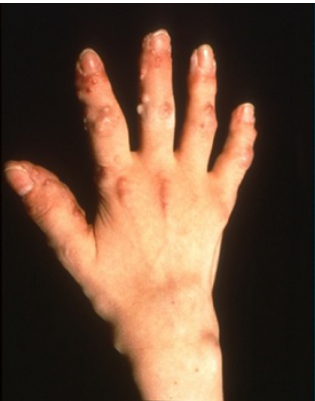
MRH
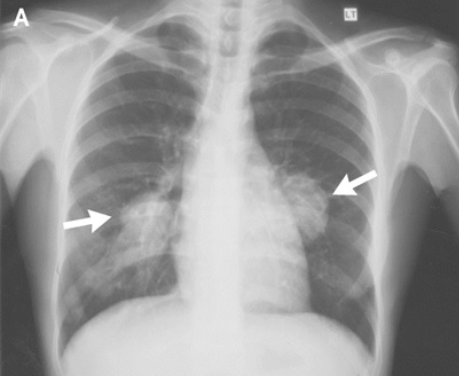
Pulm art aneurysms in bechets, need to do CT
Infiltration of histiocytes with finely-granular eosinophilic cytoplasm, multinucleated giant cells, and fibrosis in nodules
MRH
Lace-like cystic lesions in the phalanges of the hands
sarcoid
painful red eye, common in RA.
Scleritis
red eye but no loss of vision.
Episcleritis
most likely autoimmune disease associated with retinitis
bechets
where does enbrel bind
TNF alpha and Beta
Do you need skin Bx for psoriasis
Not if typical presentation
Alk p in hyperthyroidism
Increased
U1 RNP is associated with
MCTD
where does non enbrel TNFi bind
TNF alpha
FIP1L1/PDGFRa associated with
primary hypereosinophillic syndrome
indicates worse prognosis in eGPA
cardiac involvment
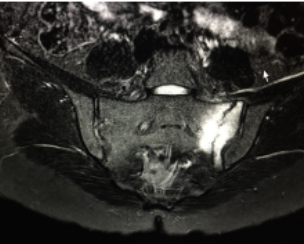
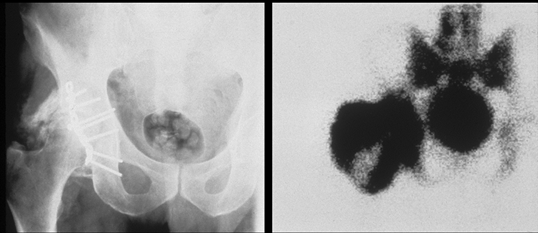
sacral Fx with bone marrow edema, avoid exercise
HCV cryo
Polyclonal B-cell activation leading to IgM anti-IgG Fc
age around 20 with high CPK and proximal muscle weakness, all refractory to immunosuppression
muscular dystrophy, check dysferlin
: exercise-induced episodes (rhabdomyolysis, myoglobinuria), often normal exam between flares
CPT II
patient with joint pain and likely lung cancer, +Tx
Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (HOA) is a syndrome characterized by digital clubbing, periostitis of long bones, and joint pain and swelling
can be primary or secondary (like this)
biopsy shows hypercellularity and vascular thickening
skin changes mimic acromegally
Tx celecoxib, then bisphosphonates
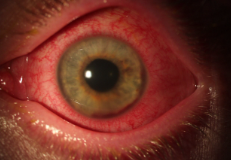
anterior uveitis
limited in active and passive especially external but not as much internal rotation and is most often age 40-60.
highly associated with diabetes
adhesive capsulitis
shoulder OA
can also be limited in active and passive ROM, often older and limited in all planes of motion
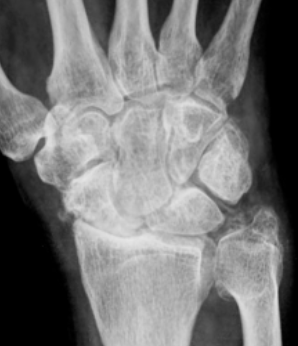
SLAC- can be caused by OA, RA, trauma
Kienboeck’s disease
lunate bone in the wrist loses its blood supply, leading to bone death (avascular necrosis)
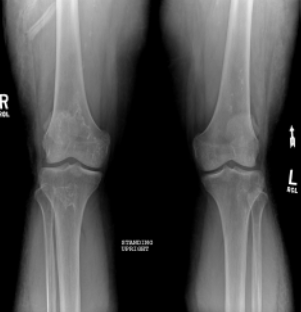
Right knee AVN
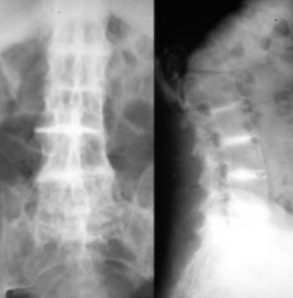
Accumulation of homogentisic acid in connective tissue
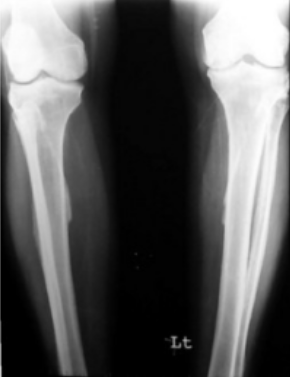
of skeletal fluorosis with interosseous membrane calcifications- has been described as endemic in areas with high concentrations of fluoride in the drinking water, excessive tea consumption (100-150 tea bags daily) and consumption of toothpaste
seronegative inflammatory arthritis + myositis + Raynaud’s + ILD symptoms + Gottron’s papules/mechanic’s hands, biopsy shows perifascicular necrosis (not atrophy), less inflammation, often called an “intermediate” or “overlap” pattern
Anti-synthetase syndrome (classically anti–Jo-1 positive)
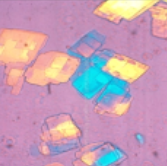
cholesterol which is indicative of chronic inflammation, rule out infection
drugs which cause seratonin syn
SSRI + MAOI (most dangerous)
SSRI/SNRI + linezolid
SSRI + tramadol or meperidine
SSRI + triptan
Antidepressants
SSRIs: fluoxetine, sertraline, paroxetine, citalopram, escitalopram
SNRIs: venlafaxine, duloxetine, desvenlafaxine
TCAs: clomipramine, imipramine, amitriptyline (some more serotonergic than others)
MAOIs: phenelzine, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, selegiline
2. Other Psychiatric Drugs
Atypical antidepressants: trazodone, vilazodone, vortioxetine
Buspirone (5-HT1A agonist)
Lithium (rare, but potentiates serotonin)
3. Analgesics
Tramadol
Meperidine (pethidine)
Methadone
Fentanyl
Tapentadol
Dextromethorphan (cough syrup, especially in abuse/OD)
4. Migraine Drugs
Triptans: sumatriptan, rizatriptan, zolmitriptan (5-HT1B/1D agonists)
5. Antiemetics
Ondansetron, metoclopramide, granisetron (weaker, but possible in combos)
6. Antibiotics / Other
Linezolid (acts like an MAOI!)
Chlorpheniramine (OTC antihistamine with serotonergic activity)
St. John’s Wort (herbal supplement, induces serotonin release)
MDMA (ecstasy), LSD, cocaine, amphetamines → recreational causes
macroglossia seen in
amyloidosis
amyloidosis prolonged PTT due to
binding of factor X, Tx chemo or spleenectomy
undetectable complement component is due to
complete deficiency
Belimumab MOA
inhibits a B cell survival factor
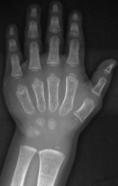
Pseudoachondroplasia
to Mutation in the COMP gene –which can also cause multiple epiphyseal dysplasia.
Scleromyxedema
primary cutaneous mucinosis characterized by a generalized, papular and sclerodermoid, cutaneous
eruption that usually occurs in association with monoclonal gammopathy. Skin bx: acid mucopolysaccharide deposition in upper reticular dermis
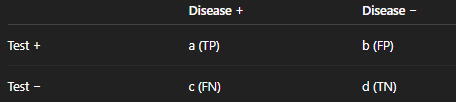
senstivity
a / (a + c)
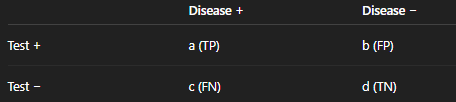
Specificity
d / (b + d)
PPV
Sensitivity / (1 − Specificity)
“SpPin” → High Sp → Positive rules in → LR+ ↑
NPV
(1 − Sensitivity) / Specificity
SnNout” → High Sn → Negative rules out → LR− ↓
HBsAg
Current infection (acute or chronic)
HBsAb
Immunity (from vaccination or past infection)
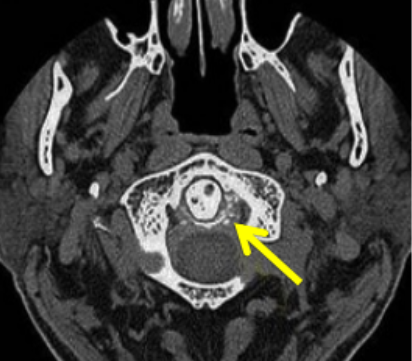
Calcification of C1-C2 ligament- crowned dens, improves with NSAIDs
Apreimlast MOA
inihibits PDE4 which would normally break down cAMP thereby decreasing IL 17 and 23 and TNFa and increasing IL 10
TTP labs
elevated LDH and plt <50