EXAM 3- AUSTIN
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
What is the essential pharmacophore of beta-lactam antibiotics? Describe each component.
LACTAM group with BETA cyclization
lactam group= cyclic amide functional group
beta position is 2nd carbon= refers to position of cyclization
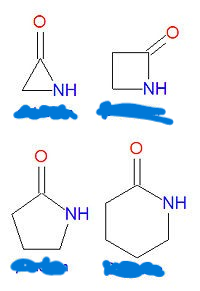
Which image picture is the pharmacophore of beta-lactams?
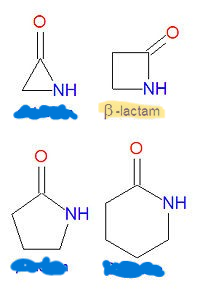
How does the reactivity of amides in vivo compare to b-lactams?
amides—> pretty stable
b-lactams—> aka non-cyclic amides—> more reactive
bc of angle/torsional strain
What are the 4 important derivatives of b-lactams?
penicillin
cephalosporin
carbapenem
monobactam
Which of the following describes b-lactams?
a. time-dependent
b. conc-dependent
c. AUC:MIC
a
Which of the following describes b-lactams?
a. bacteriostatic
b. bactericidal
b
What is the overall MOA of b-lactams?
how do they bind? (hydrogen bonds, intermolecular, covalent?)
reversible? irreversible?
why is the target of b-lactams ideal?
MOA: bind COVALENTLY to penicillin binding proteins (PBPs) also called transpeptidases (TPs)
IRREVERSIBLE inhibition
why are transpeptidases ideal? UNIQUE to bacteria, accessible, and essential for bacteria
What process of cell wall synthesis do b-lactams target?
a. NAG-NAM monomer synthesis
b. polymerization
c. cross-linking
c
Describe in detail, the mechanism of how beta-lactams inhibit the cell walls of bacteria. (idk how important, sorry lot of words)
SIMILARITY—>Beta-lactam abx have a shape that closely resembles a part of the bacterial cell wall (specifically, the D−ala−D−ala) during the process of building the cell wall.
“ENZYME MISTAKE”- the enzyme responsible for building the cell wall (TPs/PBPs) mistakes the B-lactam for the D-ala-D-ala part and so the TPs/PBPs bind to the b-lactam at its active site instead
“ENZYME ATTACK”- The enzyme's (TPs/PBPS) active site has a serine group that attacks and opens the beta-lactam ring, forming a strong covalent bond between the enzyme and the antibiotic.
“ENZYME INACTIVATION”- This bond creates a STERIC barrier that prevents the enzyme (TPs/PBPS) from functioning properly. result: the bacteria can't build a strong cell wall—> cell wall defects—> bacterial death
For the mechanism of beta-lactams, what acts as the electrophile and nucleophile?
electrophile- DRUG
nucleophile- enzyme (PBPs/TPs)
Which beta-lactam abx are active again all Gram + and - bacteria?
NONE
It’s easier for beta-lactams to target G+ bacteria… why?
in G- the abx has to get through porins
What enzyme breaks down b-lactams?
b-lactamase
There is 1 exception, but IN GENERAL… what bacteria are b-lactams inactive against?
MRSA/VRSA
atypicals
What are the most common ADRs of penicillins?
(NOTE: OVERALL considered generally safe class)
GI (n/v/d)
POTENTIALLY—> pseudomembranous colitis
bc incomplete oral absorption disrupts normal GI bacteria (broader spectrum= more GI)
hypersensitivity
hydrolysis by nucleophilic proteins
neurotoxicity (confusion, dizzy, seizures)
typically at high doses of lipophilic ones
renal
interstitial nephritis
electrolyte disturbances
What makes the β-lactam ring in penicillins highly reactive? Why is high reactivity a problem?
Angle and torsional strain
results in decreased resonance
HIGH REACTIVITY= DECREASES stability
easily cleaved/inactivated by nucleophiles like water
What is the pharmacophore of PENICILLINS?
THINK: PENICILLIN= PENT = 5 RING
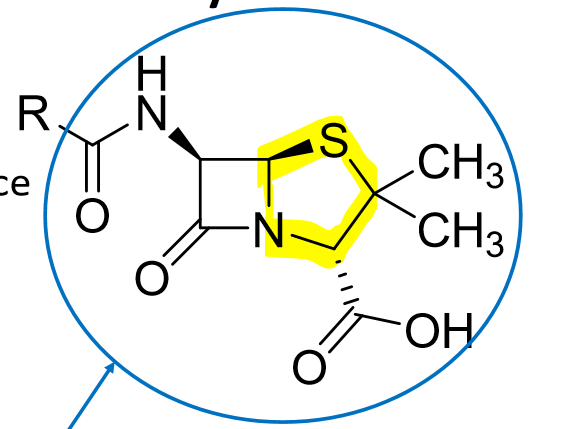
How can the challenges of penicillins be addressed? What are the 4 ways?
MODIFY THE R GROUPPPPPPP!!!!!
add an electroneg to R group
add an amine to R group
add a large, bulky R group
add a hydrophilic/ionizable R group
What’s the result of adding an electronegative atom to the R group of a penicillin?
e- withdrawing effect by induction = increases acid stability= able to give oral
What’s the result of adding an amine to the R group of penicillins? Example?
ENHANCES SPECTRUM= BROAD SPECTRUM (G-)
how? ENHANCES PORIN PENETRATION!!!
ex: AMINOPENICILLINS
Addition of an amine to the R group of penicillins also fixes what other challenge/problem with penicillins?
acid stability/oral admin—> bc amine group is also electroneg
IN GENERAL: How do lipophilic and hydrophilic groups affect penicillin activity?
lipophilic- shift towards G+ activity
hydrophilic- shift towards G- activity
What’s the result of adding a large, bulky R group to penicillins? Why must we be careful with the type of group we add?
helps protect from b-lactamase enzyme degradation
balance—> too large of a group and the drug loses ability to bind to PBPs
we also might lose acid stability and might not be able to give oral
What is considered a “large” R group on a penicillin?
PAY ATTENTION
≥ 1 ortho-poly-substituted aromatic ring (either ≥2 substituents or attached to a second ring)
basically that means the R group has the 2 groups in the ortho position (like the pic shown)
or would have 2 rings
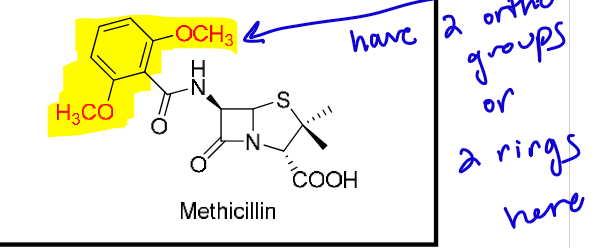
What’s the result of adding hydrophilic/ionizable R groups to penicillins?
EXTENDS THE SPECTRUM!!!!!
NOW WE COVER PSEUDOMONAS
hydrophilic groups, with peptide like characteristics facilitate PORIN penetration and decrease efflux pump affinity
kind of like adding an amine, but even more porin penetration= extended spectrum
A problem to consider with adding a hydrophilic/ionizable R group to penicillins is what?
not resistant to b-lactamases (remember bulky R groups that are lipophilic vs. hydrophilic)
What are 2 examples of hydrophilic/ionizable R groups added to penecillins?
urea derivatives—> “ureidopenicillins”
carboxylate derivatives—> “carboxypenicillins”
What penicillins are “natural penicillins”?
(austin said to know the bolded ones)
penicillin G
penicillin V
What penicillins are “amino-penicillins”?
(austin said to know the bolded ones)
ampicillin
amoxicillin
What penicillins are “anti-staphylococcal”?
(austin said to know the bolded ones)
methicillinoxacillin
nafcillin
dicloxacillin
What penicillins are “anti-pseudomonal”?
(austin said to know the bolded ones)
carbenicillin
piperacillin
ticarcillin
What penicillins have a narrow, broad, and extended spectrum?
narrow- natural and anti-staph penicillins
broad- aminopenicillins
extended- anti-pseudomonal pencillins
Why are B-lactamase inhibitors highly effective?
Is the binding reversible/irreversible?
What are some examples?
Why do we co-administer these with some penicillins?
effective bc LOW Koff values (aka means that these inhibitors bind to b-lactamase and don’t let go)
IRREVERSIBLE binding—> suicide inhibitors
examples: clavulanate, sulbactam, tazobactam
co-administer with some penicillins that are susceptible to b-lactamase
DO NOT GIVE ALONE!!
What are 3 resistance mechanisms for penicillins?
G- bacteria in general
have porins and pumps/enzymes
few penicillins are effective towards these bacteria despite modifications
modified PBPs
bacteria modify the PBP so penicillins can’t bind
penicillinases/b-lactamases
these enzymes cleave/break the lactam ring of penicillins= loss of activity
DOES THIS BY HYDROLYSIS
Why with MRSA does a penicillin + b-lactamase combination still not work?
bc the issue with MRSA is binding to the active site (modified PBP), not b-lactamase breaking the abx down…
why would we add a b-lactamase inhibitor when that’s not our issue here
What are some examples of penicillin + b-lactamase inhibitor combinations? (I don’t think that important)
aminopenicillins + b-lactamase inhibitor
amoxicillin + clavulanate (Augmentin)
ampicillin + sulbactam (Unasyn)
extended spectrum + b-lactamase inhibitor
piperacillin + tazobactam (Zosyn)
ticarcillin + clavulanate (Timentin)
What are the general pharmacokinetic properties of all penicillins?
short t ½
mostly renal elimination
hydrophobic penicillin are highly protein bound
Anti-staph penicillins are inducers of ______________.
CYP3A4
It varies by disease state, but in general natural penicillins have what PK considerations?
incomplete absorption—> best on empty stomach
variable BBB penetration
What drug combo can be employed to clinically increase b-lactam levels? How does this work?
PROBENACID + b-lactams
probenacid works by inhibiting OAT transporters and b-lactams use this transporter to get out the body
What happens when warfarin is combined with antibiotics? Why is this so?
INCREASED BLEEDING RISK!!!!!!!!
why?
warfarin antagonizes the action of vit K
antibiotics destroy normal gut flora that produce vitamin K
together= both decrease vit K = increase bleeding risk
What is the only antibiotic proven to decrease oral contraceptive efficacy?
rifampin (use backup method)
What is the interaction between antibiotics and oral contraceptives? results?
OC is metabolized by CYP3A4 and conjugation
abx induce 3A4
results: decrease concentrations of estrogens
PRACTICE:
True or false: no penicillins are active against MRSA.
TRUE
In general, as you increase cephalosporin generation you increase what?
G- activity
Be able to identify the pharmacophore of cephalosporins. What is the name of the 6 membered ring in its pharmacophore?
dihydrothiazine
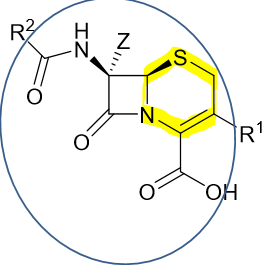
How does the chemistry of cephalosporins compared to penicillins?
cephalosporins—> less angle/torsional strain and an ADDITIONAL reaction (has 2 R groups we can modify)
What’s the result of adding an electronegative atom to the R2 group of cephalosporins?
similar to penicillins
e- withdrawing effect by induction = increases acid stability= able to give oral
What’s the result of have a more reactive group at the R1 of cephalosporins?
decreases stability—> parenteral admin only
What’s the result of adding an oxime to the R2 group of cephalosporins?
enhances stability to b-lactamase
RECOGNIZE AN OXIME
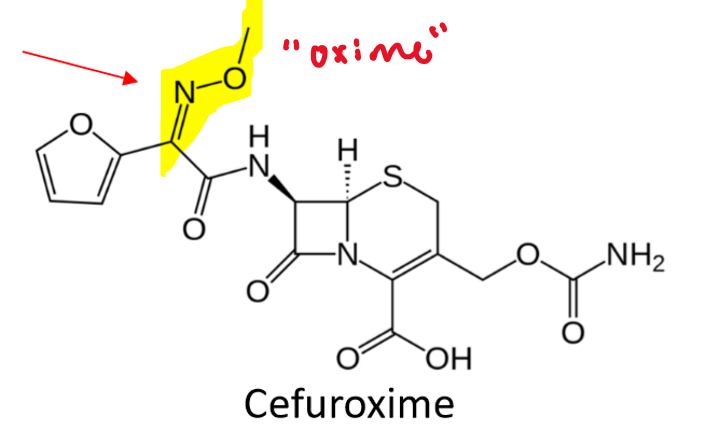
Even with an oxime to enhance stability to b-lactamases, cephalosporins are still all inactivated by…
ESBL (extended-spectrum B-lactamase)
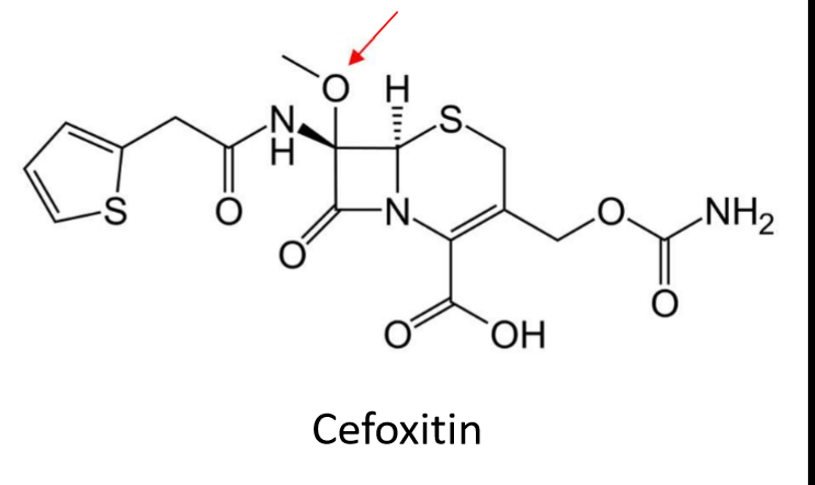
What’s the result of adding a methoxy group on position Z/carbon of the pharmacophore of cephalosporins? What are these drugs referred to as?
enhances spectrum—> includes ANAEROBES
also increase b-lactamase stability
CALLED CEPHAMYCINS
RECOGNIZE A METHOXY GROUP ON A CEPHALOSPORIN
What’s the result of adding a large, aminothiazole to the R2 group of cephalosporins?
enhances G- activity
What are the ONLY 2 cephalosporins with pseudomonas activity?
SAID TEST QUESTION!!!!!
ceftazidime
cefepime
List the names of the cephalosporins in each class:
1st gen
2nd gen
3rd gen
4th gen
5th gen/ newer abx
(these are the ones austin wants us to know)
1st gen- cefazolin, cephalexin
2nd gen- cefuroxime, cefotetan
3rd gen- ceftriaxone, cefdinir, ceftaxidime
4th gen- cefepime
5th gen/ newer abx- ceftaroline, caftolozane
What is the coverage of each of the following cephalosporins:
1st gen
2nd gen
3rd gen
which agent has anti-pseudomonal coverage?
(remember the generalization as you increase gens)
1st gen- aerobic G+, few G-
MSSA, streptococci, limited Enterobacteriaceae
2nd gen- less G+ than 1st gen, more G-
true cephalosporins
G- like Haemophilus, Neisseria, limited Enterobacteriaceae
cephamycins
ANAEROBES!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
3rd gen- low G+, BROAD G- coverage
ceftazidime—> ONLY 3rd GEN ANTI-PSEUDOMONAL
What is the coverage of each of the following cephalosporins:
4th gen
5th gen/ newer cephalosporins
4th gen—> broadest spectrum of G+ and G-
MSSA, strep, enteric G-, P. aeruginosa
5th gen
Ceftaroline—> ACTIVATE AGAINST MRSA/VRSA
Ceftolozane—> ACTIVE AGAINST PSEUDOMONAS
Avycaz is a combination of what 2 antibiotics? What does this combination protect against that is unique?
Avycaz= ceftazidime + Avibactam
AVIBACTAM IS A NON B-LACTAM CONTAINING B-LACTAMASE INHIBITOR
protects ceftazidime against ESBL’s, KPCs, and AmpC
Which cephalosporin is one of the few beta-lactams with no renal adjustments?
Ceftriaxone (3rd gen)
Why does Cefotetan react with alcohol?
Cefotetan has an MTT side chain
when co-administered with alcohol this can form a dimer that inhibits the enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase.
This enzyme is responsible for breaking down acetaldehyde (a metabolite of alcohol)
if we can’t break down the acetaldehyde—> it builds up and causes disulfiram like reaction!!!
Cefepime (a 4th gen ceph) is a combo of what two cephalosporins?
cefazolin + ceftazidime
Common ADRs of cephalosporins?
like penicillins
GI
hypersensitivity
renal
Resistance mechanisms of cephalosporins?
like pencillins
G- porins/efflux pumps
modified PBPs
b-lactamases
What is the name of the 1 abx in the monobactam class?
Aztreonam
How does the pharmacophore of monobactams/aztreonam compare to other beta-lactams? What unique groups does it have?
(be able to recognize the pharmacophore)
MONOBACTAM= mono= 1 ring
has a SULFAMIC ACID GROUP—> strong electron-withdrawing
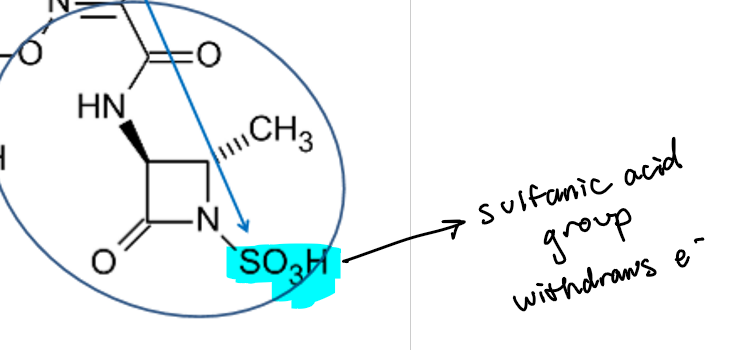
What’s the coverage of monobactams/Aztreonam?
significant G-
INCLUDING PSEUDOMONAS
no anaerobes
no G+
What groups on Aztreonam protect from b-lactamases and help with porin penetration?
methyl group= helps protect from b-lactamase
ring= porin penetration
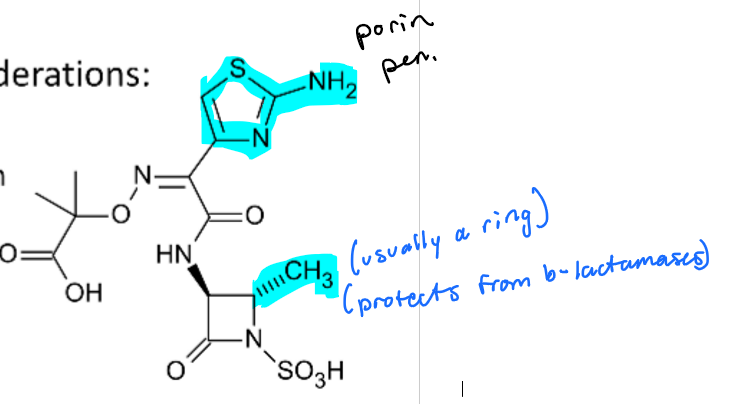
Aztreonam is safe to use in what kind of allergy? What is the exception?
IMPORTANT
safe to use in penicillin/cephalosporin allergy
no cross reactivity
1 EXCEPTION—> CEFTAZIDIME
Why can’t Ceftazidime and Aztreonam be given together if a patient has a penicillin/cephalosporin allergy?
both SHARE a side chain
List some examples of Carbapenems:
Doripenem
Ertapenem
Imipenem
What’s the coverage/spectrum of Carbapenems?
“ULTRA BROAD SPECTRUM”
G+ and -
anaerobes
pseudomonas
except ertapenem
Because of it’s ultra broad spectrum, carbapenems have an increased risk of…
C. diff/ CDI
ADRs of carbapenems?
like other b-lactams
GI
hypersensitivity
neurotoxic—> highest seizure rates
MOAs of resistance to carbapenems?
like other b-lactams but less
modified PBPs (like PBP2a, PBP5)
G- and porins (like OprD)
MDR—> efflux pumps
Are any carbapenems active against MRSA?
no
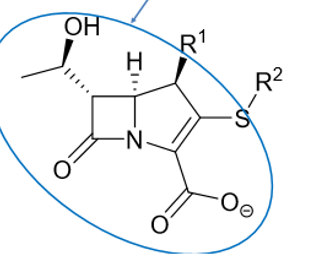
recognize the pharmacophore of carbapenems.
What’s unique compared to other b-lactams?
unique
TRANS stereochemistry
severe angle/torsional strain
most reactive lactam
What might carbapenems be co-administered with do reduce hydrolysis?
cilastatin
What R1 group can be added to carbapenems to reduce hydrolysis?
methyl group on C4
For carbapenems with anti-pseudomonal activity what is the most potent group that can be placed on the structure?
sulfamide
What drug interaction exists with carbapenems?
What does that do to the seizure threshold?
carbapenems + valproic acid
AVOID COMBO
lowers seizure threshold
Answer the following about Vancomycin:
MOA
oral route is only for what?
what happens in renal impairment?
_________ dependent
bactericidal/static?
ADRs
doesn’t cover what kind of bacteria?
MOA—> cell wall inhibitor (binds to D-ala-D-ala) blocks elongation and cross linking
oral route only for C.diff
half-life is prolonged in renal impairment
AUC:MIC dependent
bacteriacidal
ADRs- nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, red man syndrome
no G- coverage
Answer the following about Telavancin:
what type of peptide?
bactericidal/static?
_________ dependent
MOA?
ADRs
BBW
glycopeptide
bactericidal
concentration dependent
MOA like vanco—> cell wall inhibitor (binds to D-ala-D-ala) blocks elongation and cross linking
ADRs: nephrotoxicity, QT prolongation
BBW—> MODERATE to severe renal impairment
Answer the following about Dalbavancin:
what type of peptide?
MOA
half-life
lipoglycopeptide
MOA like vanco—> cell wall inhibitor (binds to D-ala-D-ala) blocks elongation and cross linking
LONG HALF LIFE
Answer the following about Oritavancin:
what kind of peptide?
MOA
lipoglycopeptide
MOA like vanco cell wall inhibitor (binds to D-ala-D-ala) blocks elongation and cross linking
PLUS RNA SYNTHESIS INHIBITION
Answer the following about Bacitracin:
what kind of peptide?
MOA
bactericidal/static?
route of admin
cyclic peptide mixture
cell wall inhibitor
bactericidal
TOPICAL ONLY
Answer the following about Fosfomycin:
MOA
bactericidal/static?
coverage?
MOA
Inhibits enzyme UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-3-enolpyruvytransferase (MurA)
Binds to cysteine residue of active site and blocks addition of phosphoenolpyruvate to UDP-N-acetylglucosamine
BASICALLY BLOCKS NAG/NAM MONOMER SYNTHESIS!!!!
bactericidal
mostly G-
Answer the following about Daptomycin:
what kind of peptide?
bactericidal/static?
MOA
depends on what?
___________ dependent
administration
cyclic lipopeptide
bactericidal
MOA
binds to inner membrane of bacteria, cause depolarization, membrane potential is lost= cell death
CALCIUM DEPENDENT
concentration dependent
ONLY IV
Answer the following about Polymyxin:
what kind of peptide?
bactericidal/static?
ADRS
cyclic polypeptide
bactericidal
ADRs—> nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity