PNS
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
What are the two main divisions of the PNS
Somatic Nervous System
Autonomic nervous system
Autonomic Nervous System
consists of heart muscles, smooth muscles and glands
divides further into sympathetic and parasympathetic
Somatic Nervous System
consists of voluntary skeletal muscles, skin, fascia, connective tissue, bone, and cartilage
Segmental Innervation
Dermatomes and myotomes labelled with a letter and a number based on the spinal nerve innervating a specific segment
Peripheral innervation
Innervations carried by branches of a plexus, labelled with names of peripheral nerves
2 Types of Somatic Fibers
General Somatic Afferent (GSA)
General Somatic Efferent (GSE)
GSA
General Somatic Afferent fibers
Transmit FROM the body TO the CNS
Sensory information from body wall: skin, skeletal muscles, fascia, cartilage
Exteroceptive sensations - pain, temperature, touch, pressure
Proprioceptive sensations
GSE
General Somatic Efferent fibers
Transmit TO body FROM CNS
Transmit impulses to skeletal muscles
2 Types of Visceral Fibers
General Visceral Afferent (GVA)
General Visceral Efferent (GVE)
GVA
General Visceral Afferent fibers
Sensory information
Transmits pain or subconscious visceral reflex sensations FROM hollow organs and blood vessels TO the CNS
Ex. of sensory information: bloating, digestion, gas
GVE
General VIsceral Efferent fibers
Transmits TO smooth muscle, modified cardiac muscle, and glandular tissues FROM the CNS
Consists of presynaptic/preganglionic fibers and postsynaptic/postganglionic fibers
Where are the cell bodies of presynaptic/preganglionic fibers?
in the spinal cord
Where are the cell bodies of postsynaptic/postganglionic fibers?
in peripheral ganglia
GSE vs GVE
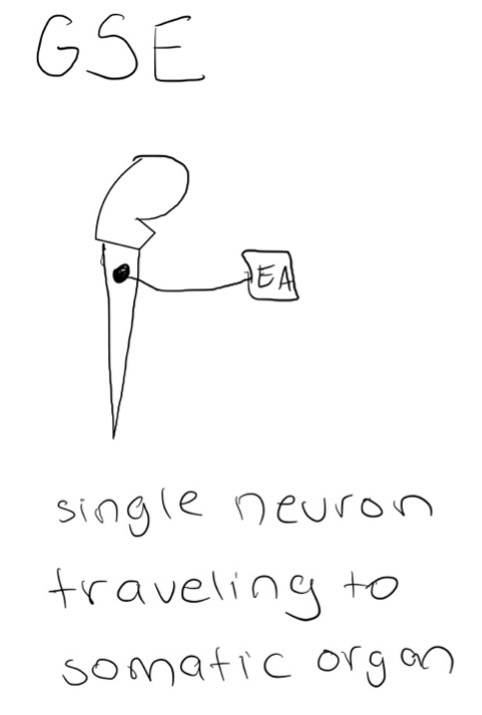
GSE transmits through a single neuron travelling to a somatic organ
GVE transmits through presynaptic fibers and postsynaptic fibers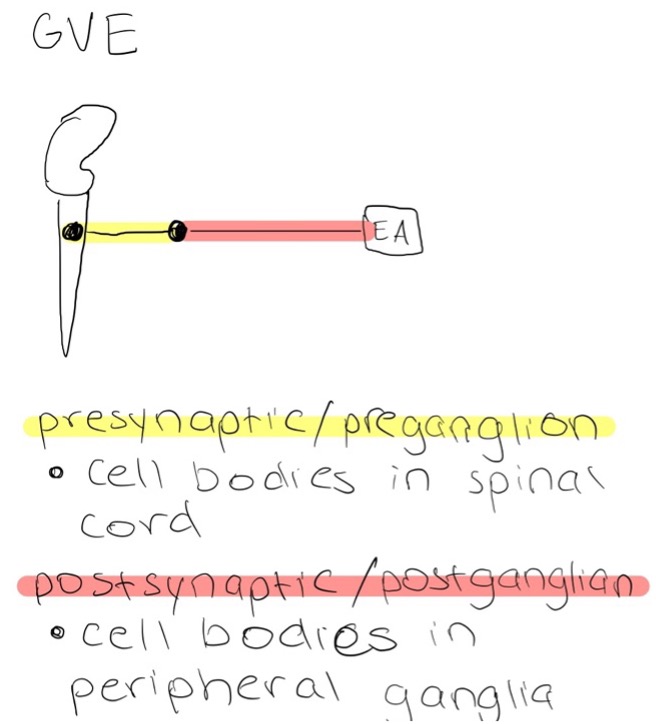
Somites
A bilteral row of biscuit-like structures which represent our primal spinal cord
Tissues will give rise to muscle, bone, and other connective tissue
Sclerotomes
Originate from medial sides of somites
Migrate ventrally to surround notochord and will make up body of vertebrae
Migrate dorsally to surround neural tube to create neural arch of vertebrae
Nerves and Somites
Develop in bilateral pairs that serve the dermis-forming and muscle forming tissue of some adjacent somites
Motor Neurons
Send processes peripherally into posterior and anterior dermatomyotome
Develop in the anterior neural tube
Sensory Neurons
Send peripheral processes into regions of dermatomyotome and central processes into posterior neural tube
Develop in neural crests
Somatic Sensory and Motor Nerve Fibers
Organized segmentally along neural tubes
Becomes part of all spinal nerves and some cranial nerves
Ganglia
Cluster of cell bodies
Derived from neural crest
Located OUTSIDE of the CNS
Myotome
Unilateral mass of muscle supplied by a single spinal nerve
Dermatomyotomes
Lateral aspect of somite
Give rise to skeletal muscles and dermis of the skin
Deep back muscles and overlying dermis originate from dermatomyotomes that migrate posteriorly
Hypaxial muscles of anterolateral trunk and limbs and associated dermis arise from dermatomyotomes that migrate anteriorly
Dermatomes
Unilateral area of skin supplied by a single pair of spinal nerves
Often there is overlapping of innervation zones
No C1 dermatome
Important Dermatomes
C2 - Innervates back of head (highest dermatome)
C4 - top of the shoulders
C6 - thumb
C7 - middle finger
C8 - little finger
T4 - level of nipples ;)
T10 - level of umbiculus
T12/L1 - skin along inguinal crease
L4 - big toe
S1 - little toe and sole of foot
What does C2 innervate?
Back of head
What does C4 innervate?
Top of shoulders
What does C6 innervate?
Thumb
What does C7 innervate?
Middle finger
What does C8 innervate?
Little finger
What does T4 innervate?
Level of nipples
What does T10 innervate?
Level of umbilicus
What does T12/L1 innervate?
Skin along inguinal crease
What does L4 innervate?
Big toe
What does S1 innervate?
Little toe and sole of foot
What does S4/S5/Cocc 1 innervate?
Skin around the anus ;)
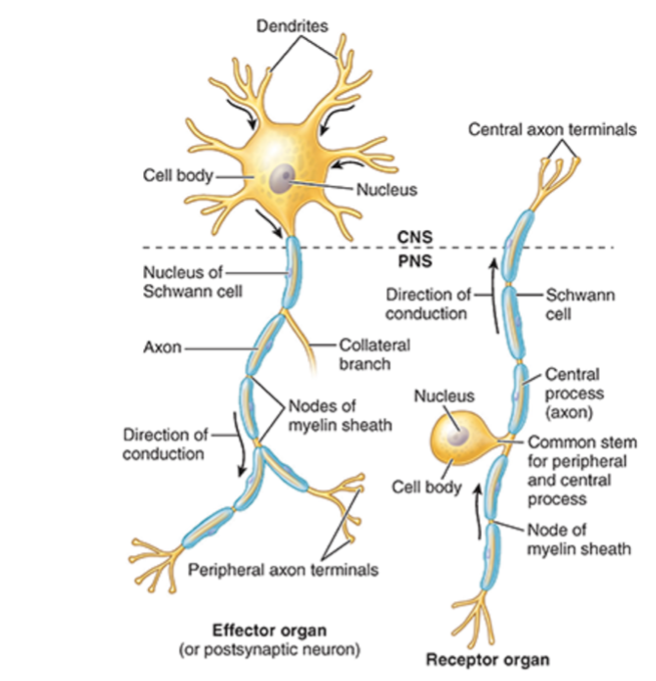
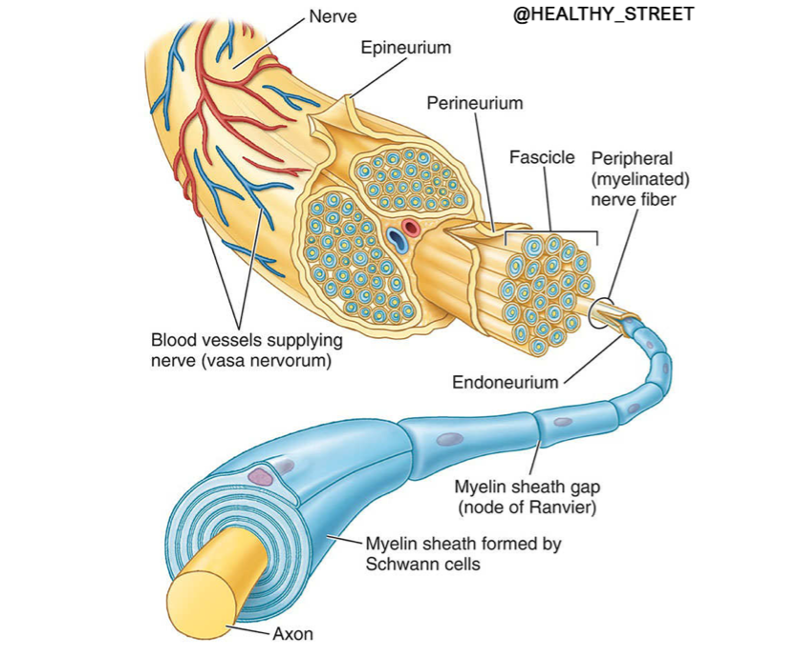
Nerve Fiber Components
Neurolemma
Dendrites
Axon
Soma
Neurolemma
Consists of cell membranes of Schwann cells surrounding the axon
Myelinate or unmelinated
Dendrites
Receive signals
Axon
Send signals
Soma
Cell body
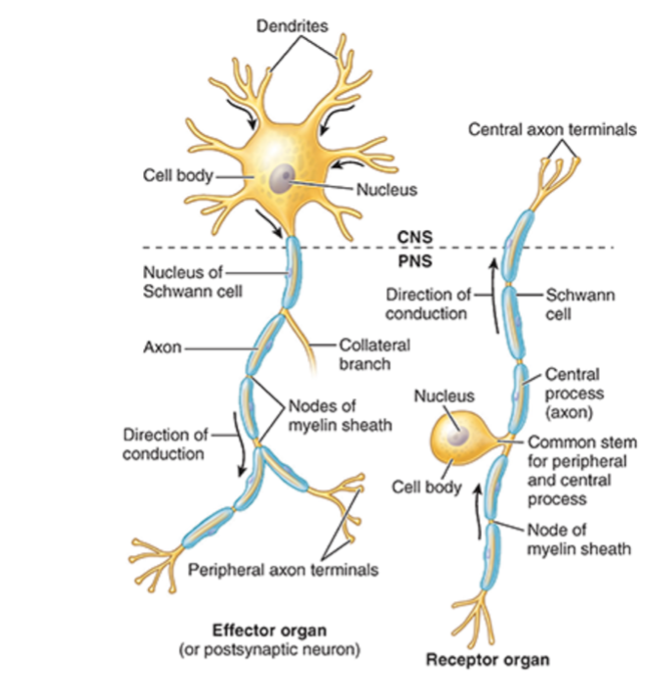
Label This Diagram
Connective Tissue Coverings of Nerves
Endoneurium
Perineurium
Epineurium

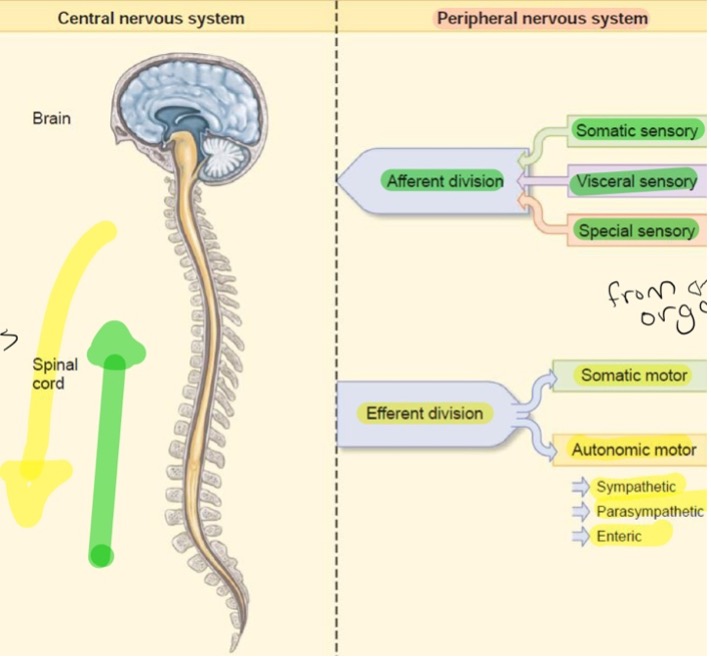
Afferent Division
Flows towards the brain
Somatic and visceral sensory
Special sensory
Efferent Divisions
Flows away from the brain
Somatic and autonomic motor
Autonomic motor divides into: parasympathetic, sympathetic, and enteric

Neuron
Bundle of axons
Ganglia
Bundle of soma
Ventral Root Ganglia
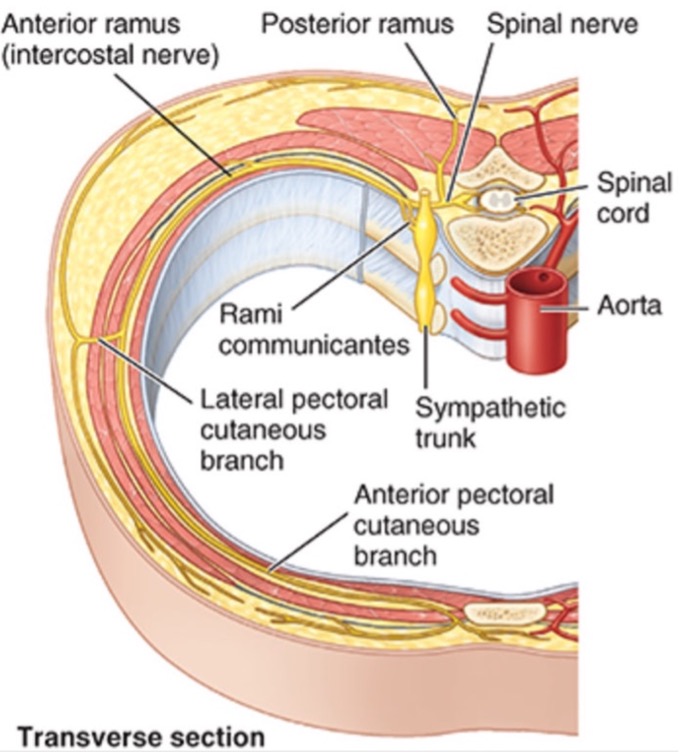
Sympathetic
Each spinal cord segment has two ventral roots that connect by a white ramus to a spinal sympathetic ganglion
Dorsal Root Ganglia
Spinal ganglia - close to the spinal cord
A collection of neuronal cell bodies of sensory neurons near the spinal cord
Most common type of sensory ganglia in the body
Autonomic Ganglia
Sympathetic Ganglia
Parasympathetic Ganglia
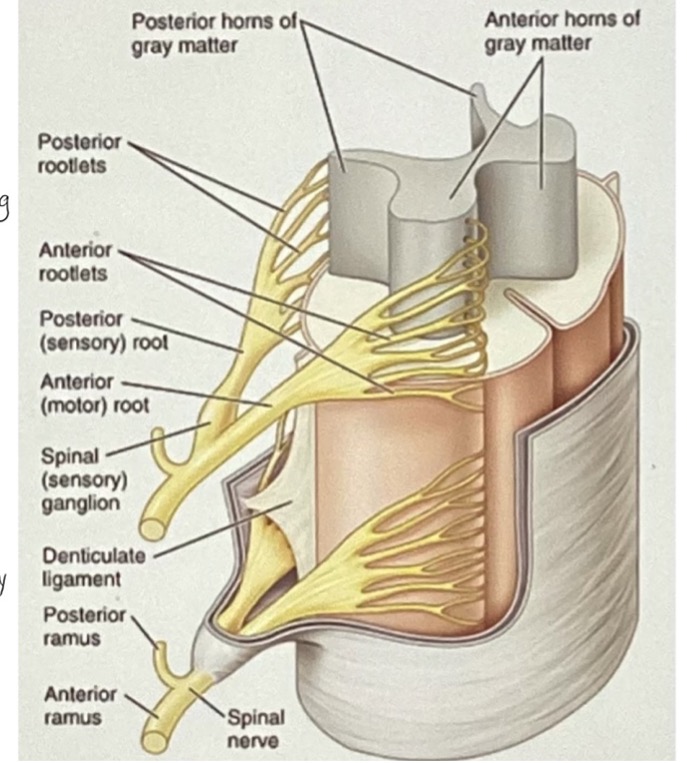
Spinal Nerves (definition and how many of each)
Exit the spinal cord through intervertebral foramina
Arise from spinal cord as rootlets and converge to form 2 nerve roots: anterior/ventral nerve root and posterior/dorsal nerve root
8 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral
1 coccygeal
Anterior/Ventral Nerve Root
Efferent fibers
Pass FROM nerve cell bodies in anterior and lateral horns of spinal cord gray matter TO effector organs located peripherally
Interwoven networks of nerves formed by ventral rami of adjacent spinal nerves
Plexuses of Ventral Nerve Root
Cranial plexus
Brachial plexus
Lumbar plexus
Sacral plexus
Coccygeal plexus
Cranial plexus made up of
C1-C4
Brachial plexus made up of
C5-T1
Lumbar plexus made up of
L1-L4
Sacral plexus made up of
L4-S4
Coccygeal plexus
S4-Co1
Posterior/Dorsal Nerve Root
Afferent fibers
Move FROM soma in sensory endings in dorsal root ganglia that extend peripherally to sensory endings and centrally to posterior horn
Dorsal and Ventral Root Labeled

Cranial Nerves
Exit the cranial cavity through foramina in cranium
Named from most anterior and superior to most inferior and posterior
Arise in bilateral pairs
Little overlap in innervations
Communicate only between cranial nerves and upper cervical nerves
Which two cranial nerves branch off the cerebrum instead of the brainstem?
CN I and CN II
List all the Optic Nerves
CN I = olfactory
CN II = optic
CN III = oculomotor
CN IV = trochlear
CN V = trigeminal
CN VI = abducens
CN VII = facial
CN VIII = vestibulocochlear
CN IX = glossopharyngeal
CN X = vagus
CN XI = spinal accessory
CN XII = hypoglossal
Visceral and Motor Nerve Fiber Pathways
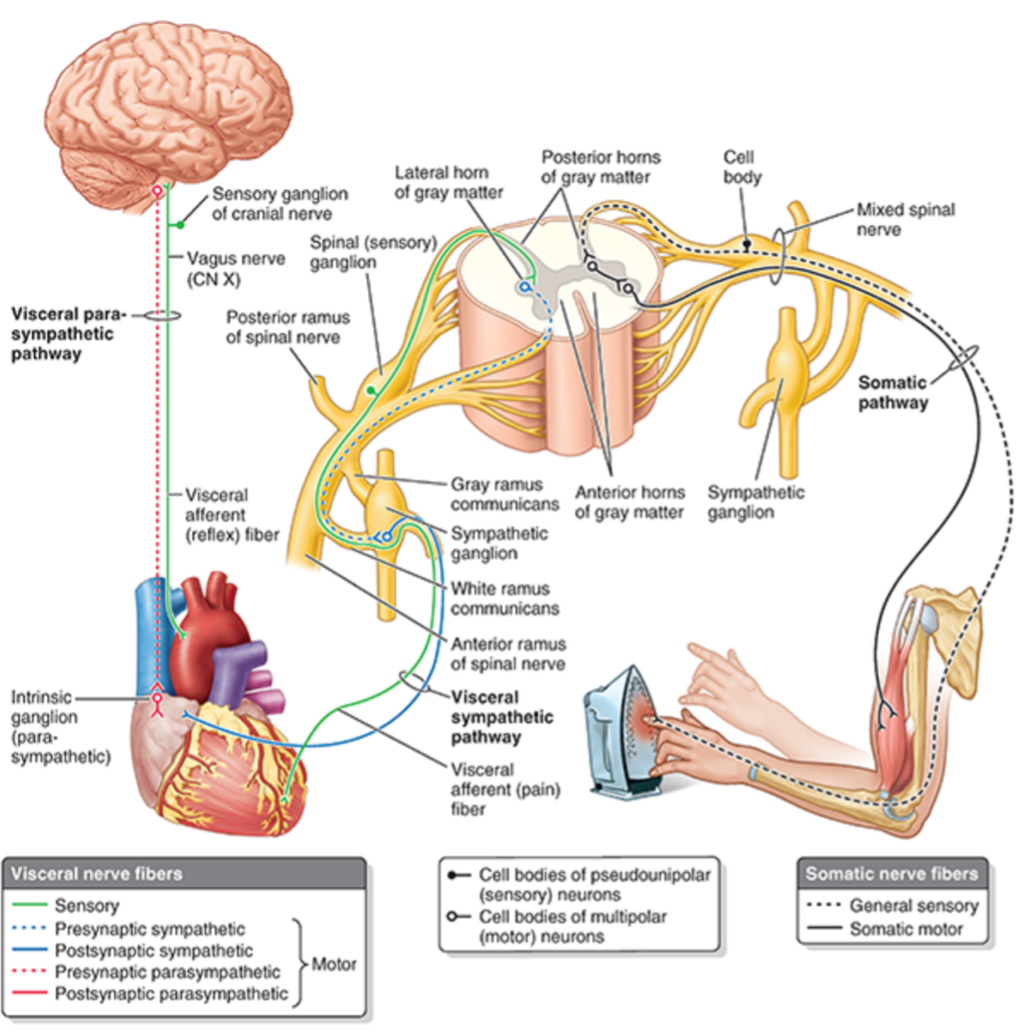

Cranial Nerves of GSA?
CN II and VIII
Cranial Nerves of SVE
Muscles of facial expression = CN VII
Muscles of mastication = CN V
Pharyngeal muscles (swallowing) = CN IX, X
Laryngeal muscles (speaking) = CN X
Trapexius and sternocleidomastoid = CN XI
Send and receive motor stimuli to all skeletal muscles derived from pharyngeal arches **
Cranial Nerves of SVA
CN I = olfactory
CN VII, IX, and X = gustation
receive olfactory stimuli and gustatory stimuli **
Nerves of GSE
Send motor stimuli to all skeletal muscles except those derived from pharyngeal arches
Nerves of GVE
Send motor stimuli to smooth muscles, cardiac muscle, and glandular tissues
Nerves of GSA
Receive sensory stimuli from somatic structures such as skin, superficial and deep fasciae, skeletal muscles, bones, joints, ligaments and tendons
Nerves of GVA
Receive sensory stimuli from visceral organs
Nerves of SSA
Receive visual and auditory stimuli through CN II and VIII
Gray Matter
Made up of soma of nerve fibers
Gray because of the high nucleus concentration
Deep to white fibers
Found in anterior/ventral horn and posterior/dorsal horn
Anterior/Ventral Horn
Lower motor neuron from the ventral horn
Somatic efferent signals
Send OUT signals
Posterior/Dorsal Horn
Somatic afferent signals
RECEIVES signals
White Matter
Outermost layer of spinal nerve
Primarily made up of myelinated axons
White because Schwann cells make up the myelination of the fibers
Where do the Ventral and Dorsal Nerve Roots Unite?
Within or proximal to intervertebral foramen as they emerge from the spinal column
What is formed by the uniting of the ventral and dorsal nerve roots?
Mixed spinal nerve —> both sensory and motor
Will immediately divide into 2 rami - dorsal and ventral ramus
Ventral Ramus (supply?) (location?) (merge?) (become?)
Supplies nerve fibers to: skin, hypaxial muscles of anterior and lateral regions of trunk, and upper and lower limbs
Remain in trunk
Merge in limbs with 1 or more other ventral ramus - form somatic nerve plexuses; fibers intermingle and multisegmented peripheral nerves emerge
Will become motor and cutaneous nerves
Neurons of the PNS
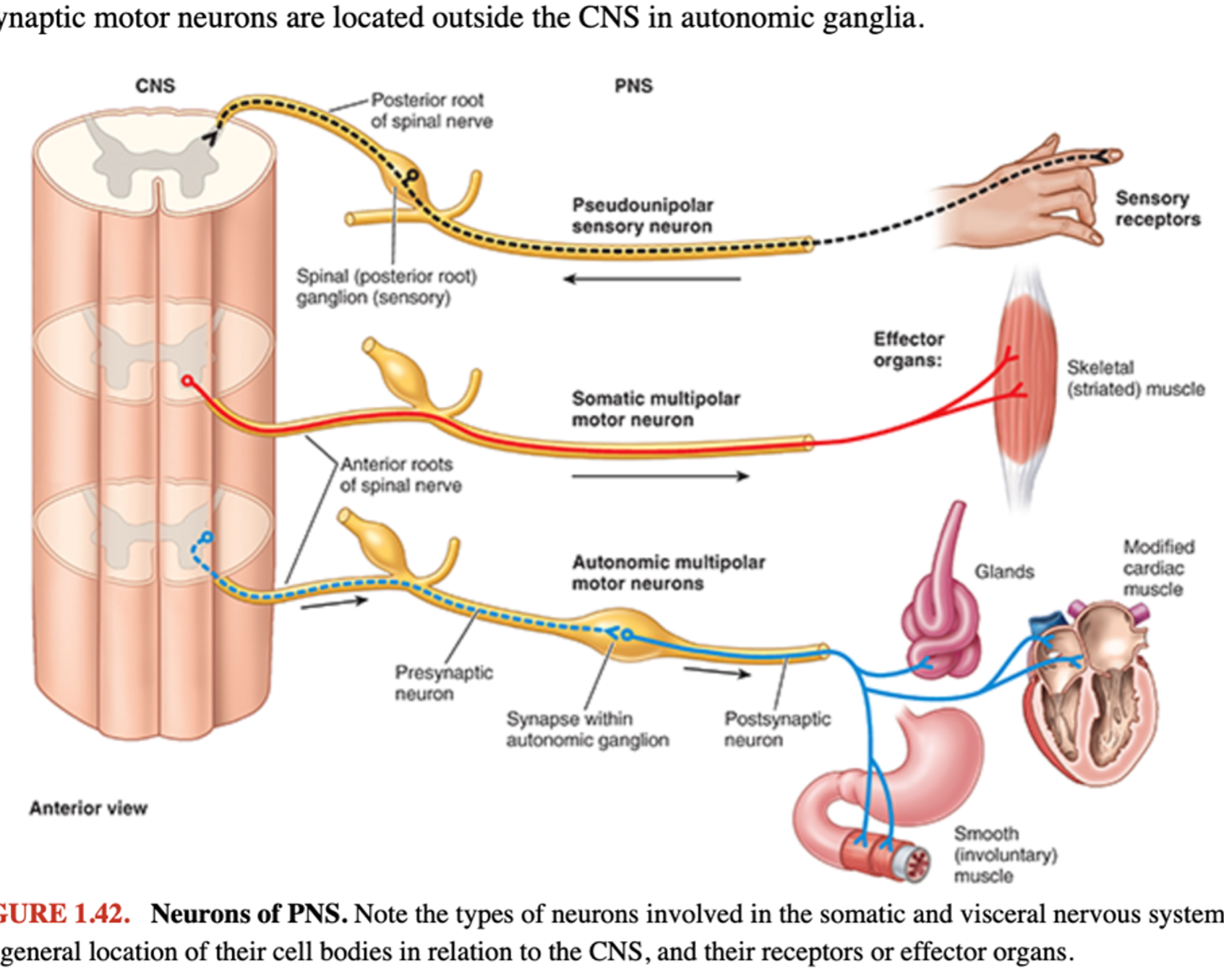

Sensory Neurons
Visceral and sensory are processes of pseudounipolar neurons with cell bodies OUTSIDE the CNS
In spinal or cranial sensory ganglia
Motor Neurons
Motor fibers of nerve are axons of multipolar neurons
Cell bodies of somatic motor and presynaptic visceral motor neuron are located IN the CNS in gray matter of spinal cord
Transverse Section Showing Rami
Referred Pain
Occurs when sensory information comes to the spinal cord but is interpreted as coming from another location innervated by the same spinal cord level
Viscero-Somatic Referred Pain
Stimulus acting on a visceral organ, sensation appearing in somatic structure
Somato-Somatic Referred Pain
Stimulus acting on a somatic structure, sensation appearing in a different somatic structure
Somatic Nervous System
Provides sensory and motor innervation to all parts of the body EXCEPT viscera
Transmits touch, pain, temperature, and position from sensory receptors
Most reach the conscious level
Innervate only skeletal muscle
Autonomic Nervous System
Visceral nervous system
Innervates smooth muscle, modified cardiac muscle and glandular cells
Efferent fibers accompanied by afferent fibers
Efferent autonomic regulation depends on feedback from sensory organs
Major Functions of Autonomic Nervous System
Regulate heartbeat
Smooth muscle contraction
Glandular secretions to maintain homeostasis
Efferent Fibers Divide Into:
Parasympathetic - BREAK PEDAL
Sympathetic - GAS PEDAL
Parasympathetic vs Sympathetic Anatomically
Location of presynaptic cell bodies
Which nerve conducts presynaptic fibers from CNS
Conduction of Impulses
Involves a series of 2 multipolar neurons: presynaptic/preganglionic neurons and postsynaptic/postganglionic neurons
Presynaptic/Preganglionic Neurons
Soma located in gray matter in CNS
Fibers (axons) synapse on soma of postsynaptic neuron
Postsynaptic/Postganglionic Neuron
Somas outside CNS in autonomic ganglia
Fibers (axons) terminate on effector organ
Reflex Arc
All neurons function in reflex arcs
Receptor picks up stimulus —> sends stimulus to afferent neuron —> brain/CNS —> efferent neuron (preganglionic and postganglionic) —> vector organ —> issues a response
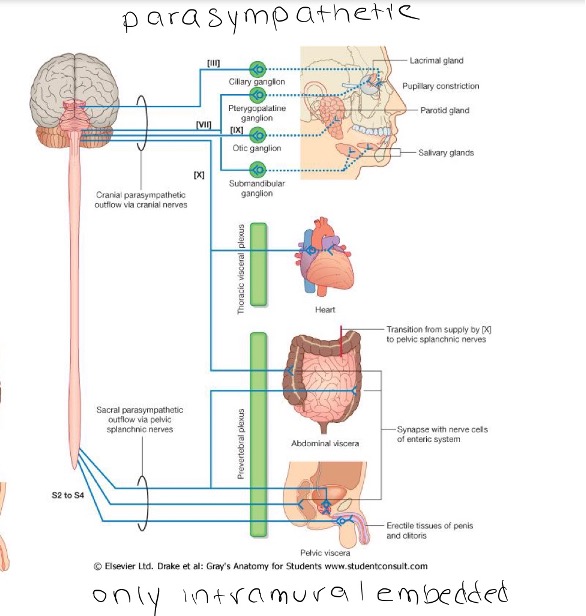
Parasympathetic System (origin) (types) (purpose)
Craniosacral origin = brainstem, S2-S4
Types: cranial and intramural (intramural is embedded in wall of vector organ)
Energy conserving - rest and digesr
LONG presynaptic neuron axons
SHORT postsynaptic neuron axons
Parasympathetic Pathways

Sympathetic (origin) (types) (purpose)
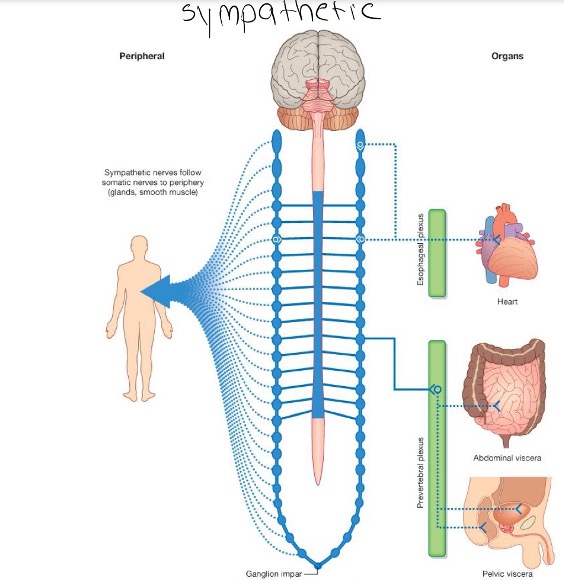
Thoracolumbar origin
Types: paravertebral and prevertebral/preaortic
Energy expending - fight or flight
SHORT preganglionic neuron axon
LONG postganglionic neuron axon
Sympathetic Pathways

Where are the cell bodies of the sympathetic division?
Cell bodies are in intermediolateral cell columns (IML) or in nuclei of spinal cord
Gray matter of T1-L2/3
IMLs are organized somatotopically