C3 Attention and performance
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
goal-directed attention
e.g. looking for a certain object, attending to a certain sound in a sequence, where’s waldo?, dichotic listening task
stimulus-driven attention
e.g. unexpected change in sound, a colour that stands out
modes of attention
active and passive
active mode of attention
goal-directed
top-down processed
endogenous (sisäsyntyinen)
intentional
passive mode of attention
bottom-up
stimulus-driven
exogenous (ulkosyntyinen)
incidental
attention
cognitive process of selectively concentrating on one aspect of one’s environment while ignoring other aspects
= process by which certain information is selected for further processing and other info is discarded or (more likely) attenuated
“withdrawal from some things in order to deal effectively with others” - William James
attention might be needed to bind together the aspects of conscious perception, e.g. shape-colour, sound-vision
inattentional blindness
serial bottleneck
limit of attention; a point in the path from perception to action at which one cannot process all information in parallel
different types of information can be processed in parallel to some degree (different systems), but similar types of info cannot
attention studies
dichotic listening task
cocktail party effect
Treisman and Geffen’s experiment on attentional limitations (attenuation theory and Deutsch theory)
attending to part of vis field not focused
typical dichotic listening task
participants are presented with two streams of sound (story, message) in different ears and asked to shadow one
shadowing = repeating the words back from one message only
very little of the unattended message is processed (maybe just the sex of the voice or the language????tarkista)
goal-directed
auditory attention
cocktail party effect
situation of attending to one conversation and tuning out other noise and then hearing a meaningful sound (in this case one’s own name) and automatically shifting attention to that
Moray (1959)
auditory attention
filter theories
theories that try to answer the question: When do bottlenecks occur?
early selection theories (Broadbent, Treisman)
late-selection theories (Deutsch & Deutsch)
early selection theories
filter occurs before we perceive the entire stimulus (Broadbent)
attenuation theory (Treisman)
late-selection theories
filter occurs after we perceive the stimulus
Broadbent’s filter theory (1958)
Deutsch and Deutsch’s filter theory (1963)
Attenuation theory / Treisman’s filter theory 1964
modification of Broadbent’s model
auditory stimuli are never ______, but _____ and _____
auditory stimuli are never completely filtered out, but attenuated and enhanced
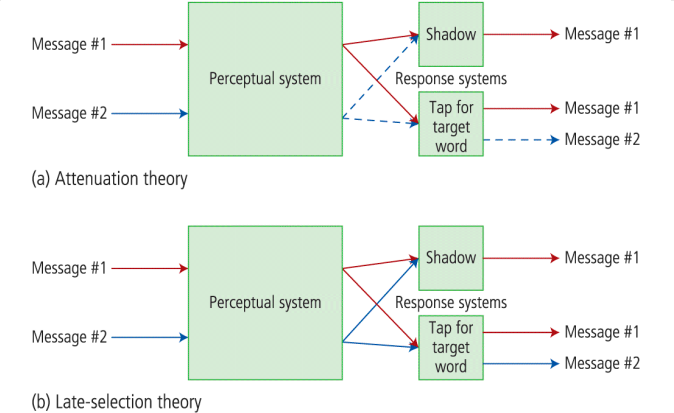
Treisman and Geffen’s experiment on attentional limitations
task:
two messages listened to simultaneously;
shadow message #1 while also trying to detect and respond with a tap to a target word, which can occur in either message
the photo shows predicted outcomes by the attenuation theory and Deutsch & Deutsch’s late-selection theory
support for the attenuation theory: 87% success rate in the shadowed ear and only 8% in the unshadowed ear
later experiments: there is not only attenuation of message #2, but also enhancement of msg #1
spotlight metaphor
attention can be moved to focus on different areas of the visual field
narrowing the spotlight allows maximal processing of the attended part of the visual field
attention can be focused on a part of the visual field that one is not focusing on (up to 24 degreed from the fovea)
experiment: fixation cross, stimulus 7 degrees to the L/R of point, cues of side, participants were faster when stim appeared in expected location
Neisser & Becklen (1975), visual attention study (shadowing a video)
O’Craven et al (1999): superimposed photos, brain activity
Visual attention: neural basis
similar to neural basis of auditory attention
Mangun, Hillyard and Luck (1993): enhanced neural processing in the portion of the visual cortex corresponding to the location of visual attention
Roelfsema et al (1998): directing visual attention takes more effort when it is done on the basis of content (ERP within 200ms) than on the basis of physical features (within 70-90 ms)
photo: brain areas involved in atttn and some of the perceptual and motor regions they control
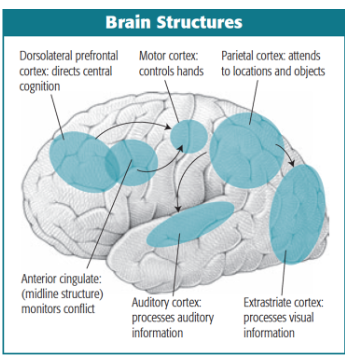
parietal regions and attention
particularly important in directing perception and allocating atttn
prefrontal regions and atttn
dorsolateral, prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate:
executive control
Visual search (atttn)
unique visual features = standing out
feature search/conjunction search: tasks that require recognizing a conjunction of features usually takes longer and gets harder with more distractors
The binding problem
how does the brain put various features in the visual field together?
illusionary conjunctions
Feature integration theory: ppl must focus attention on a stimulus before its features can be synthesized into a pattern
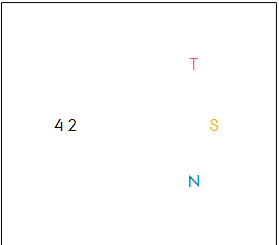
illusionary conjunction
Neglect
a disorder of visuospatial attention
lack of awareness of sttimuli when it is presented to the side of the visual field opposite to the side of the brain damage
(=typically impairment is in the contralesional visual field)
R/L parietal regions’ responsibilities (Robertson & Rofal (2008)
unilateral neglect
right parietal regions and neglect
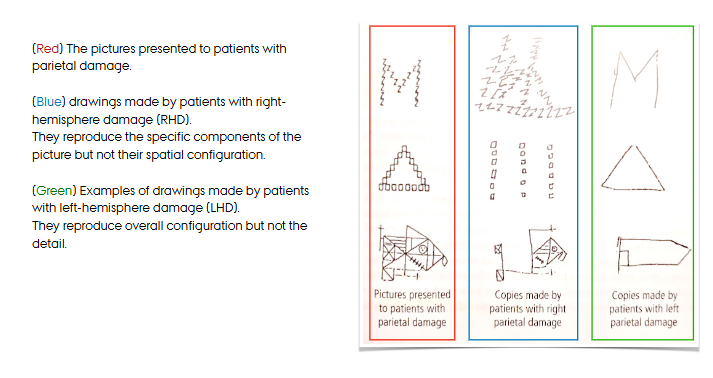
the right parietal region is responsible for attention to global features; spatial location (Robertson & Rofal (2008))
=overall configuration, but not details
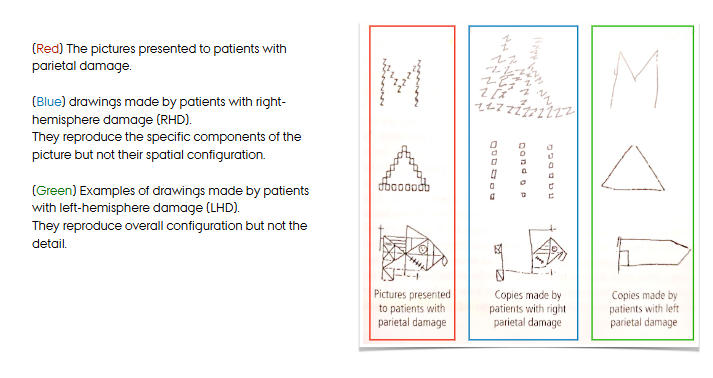
left parietal regions and neglect
the left parietal region is responsible for attention to local aspects of objects (Robertson & Rofal (2008))
=details, components, but not their spatial configuration
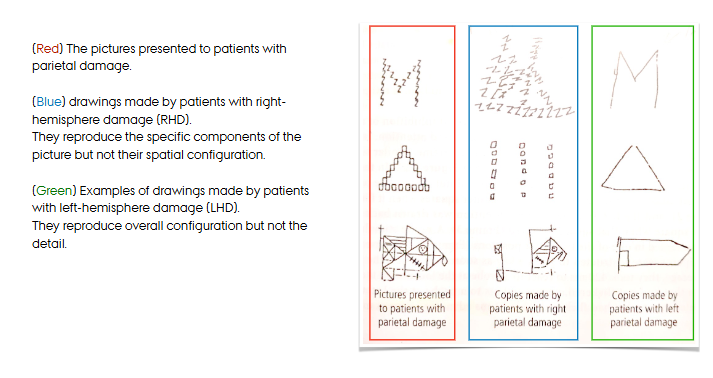
unilateral neglect
patients completely ignore one (contralesional) side of the visual field
typically damage is in the right hemisphere’s posterior parietal lobe
temporo-parietal junction
angular gyrus
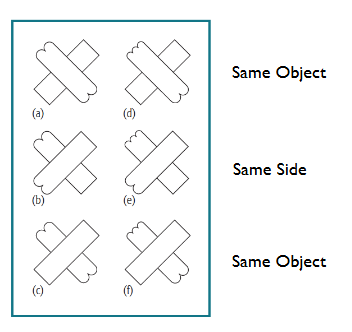
object-based atttn
people focus their attention on particular objects instead of regions in space
Behrmann et al (1998) photo
Chen & Cave (2008): effect found in the Behrmann study disappears with brief stimulus presentations (0.12s)
(inhibition of return)
inhibition of return
after looking at a region of space, it is harder to return attention back to that region
inhibition of return study that also provides evidence for object-based atttn: Tipper et al (1991)
Central attention
cognition after the stimuli are attended to and encoded; selecting lines of thought to pursue
multitasking and different attentional resources
perfect time sharing
central bottleneck: inability of central cognition to pursue multiple lines of thought simultaneously
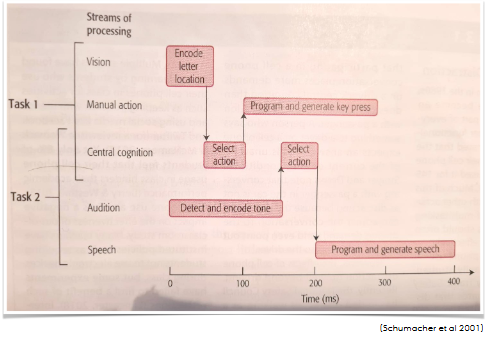
Byrne & Anderson (2001): simultaneous addition and multiplication is impossible
Schumacher et al (2001): simultaneous judgement of space and tone is possible
automaticity
when a skill has been practiced repeatedly, eventually it can be performed with little to no direct attention
hard to override aka inhibit (stroop)
procedural, implicit processes
DLPFC
Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
Executive control: setting intentions, controlling behavior (multitasking)
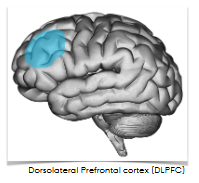
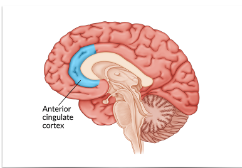
ACC
Anterior cingulate cortex
executive control: monitoring conflicts between tendencies (stroop task), cognitive control (simon says)
damage to prefrontal regions often results in …
deficits in executive control: increases stimulus driven behavior and failure to control behavior according to intentions