Lecture 11-Stem cells and more
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is transfection ?
It is the process of introducing DNA into eukaryotic cells.
What are the physical methods for transfection ?
Microinjection : Direct injection of DNA into the nucleus or cytoplasm.
Electroporation : Cells are exposed to brief electric pulses that create temporary pores in the membrane, allowing DNA to enter.
Biolistic method : DNA-coated microscopic particles are shot into cells using high pressure.
What are the chemical methods for transfection ?
Calcium phosphate precipitation : DNA forms a precipitate with calcium phosphate, which is taken up by endocytosis.
Liposome-Mediated transfection : DNA is enclosed in lipid vesicles that fuse with the cell membrane to deliver genetic material.
Polymer-Based Transfection : Uses cationic polymers to form complexes with negatively charged DNA.
What are the biological methods for transfection ?
Retrovirus/Lentivirus : RNA viruses that integrate into the genome.
Adenovirus : DNA virus which doesn’t integrate into the genome.
Adeno-Associated Virus : Small DNA virus with low immunogenicity.
Herpes Simplex Virus : Large DNA virus which targets neurons.
What are a couple of gene editing technologies ?
CRISPR-Cas9 System : Uses a guide RNA to target a specific DNA sequence so that Cas9 cuts the DNA enabling insertion, deletion or correction.
RNA interference : Uses small interfering RNAs to silence gene expression.
What are a couple of plant-specific methods for gene editing ?
Agrobacterium tumefaciens-Mediated Transformation : Uses a soil bacterium to naturally transfer parts of its DNA into the plant cells.
Protoplast Transformation : DNA is introduced into plants through electroporation.
What is a transgenic organism ? What is a transgene ?
It’s an organism that has been genetically modified and a transgene is the foreign DNA that has been added.
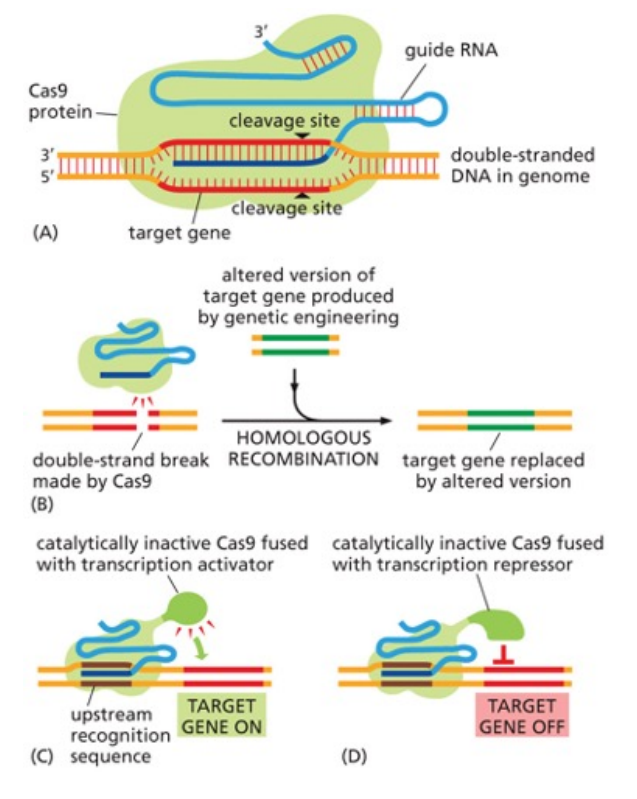
Explain how the CRISPR-Cas9 system works.
Cas9 and guide RNA associate and mediate double-strand break of the chosen DNA region.
It is repaired by non-homologous repair system and it either leads to gene deletion or gene addition if an altered target gene is provided.
Can also be used to turn genes on and off.
What are stem cells ?
They are unspecialized cells which reproduce indefinitely and differentiate into specialized cells upon signals.
What are embryonic stem cells (ES)?
Stem cells from early embryos.
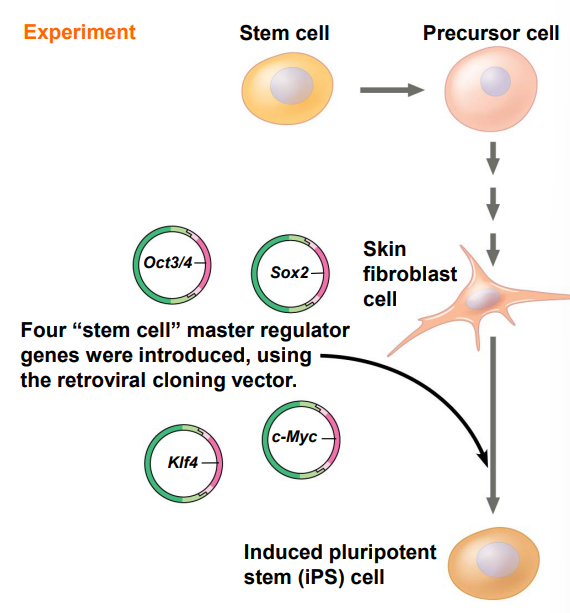
What are induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) ?
They are differentiated cells reprogrammed to act as ES.
What methods can be used to study gene expression ?
Looking at mRNAs in situ.
Using Northern blotting.
Using Reverse transcriptase-PCR/RT-PCR.
Using quantitative RT-PCR/qRT-PCR.
Using microarrays.
Using reporter genes.
Using RNA sequencing (RNA-seq).
Using Genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChiP).
Using ribosome profiling.
How does looking in situ work ?
It’s based on nucleic acid hybridization, where tissues are fixed and probes are added.
Nothing is engineered
Not good for quantification.
How does qRT-PCR work ?
The RT-PCR is monitored using chemical fluorescent dyes to visualize the number of copies made per cycle.

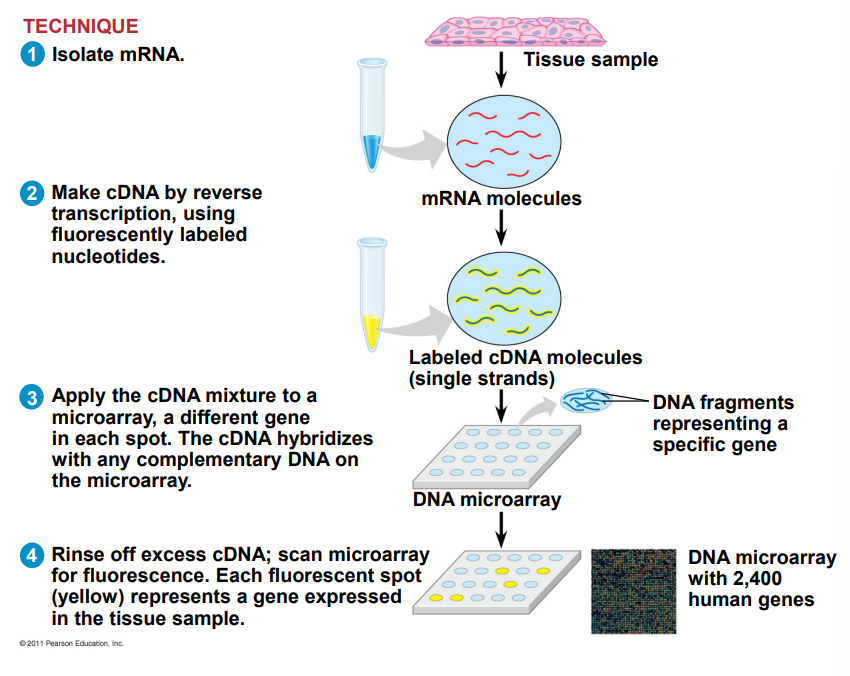
How do you use microarrays for studying gene expression ?
The goal is to isolate tissue mRNA and reverse transcribe it into cDNA using fluorescently labeled nucleotides. Then, the solution is applied to a microarray, each well containing a different gene. When the cDNA hybridizes with the complementary DNA, it activates the fluorescence.
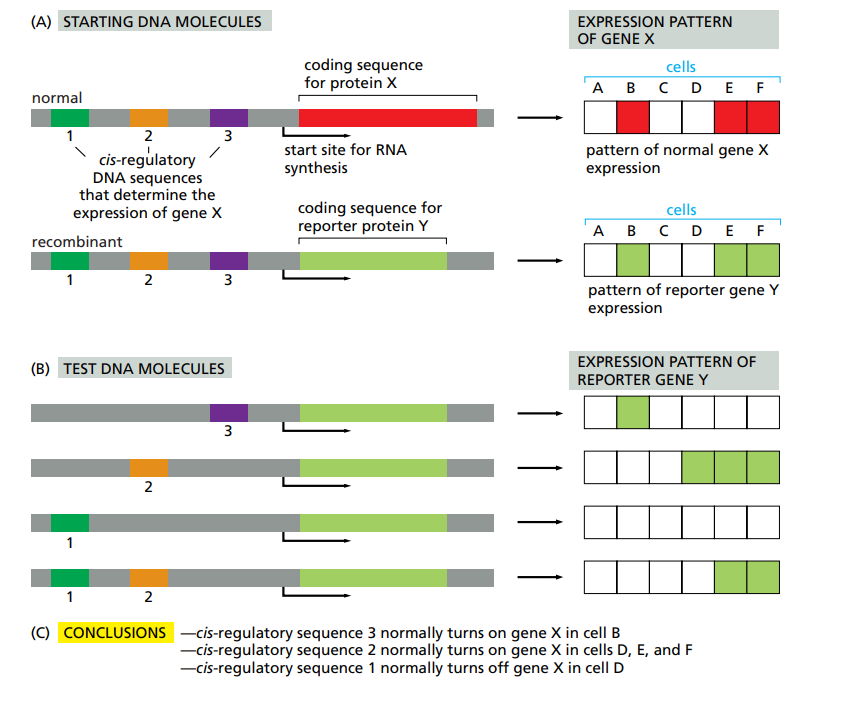
How would you use reporter genes to study gene expression ?
You use different reporter genes to figure out which regulatory sequences allow expression of which gene.
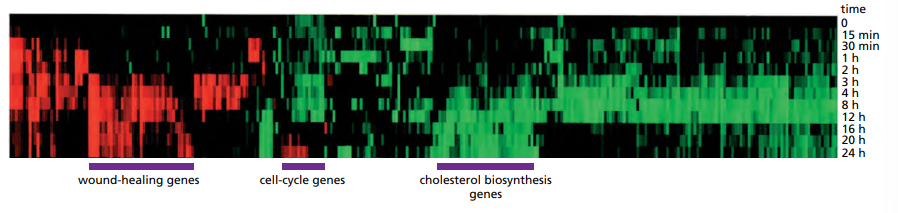
How would you use RNA sequencing for studying gene expression ?
Measures which genes are being transcribed at a given time. Uses RT to copy all RNAs into cDNAs and then they are sequenced. The more abundant RNAs lead to a larger amount of cDNA copies.
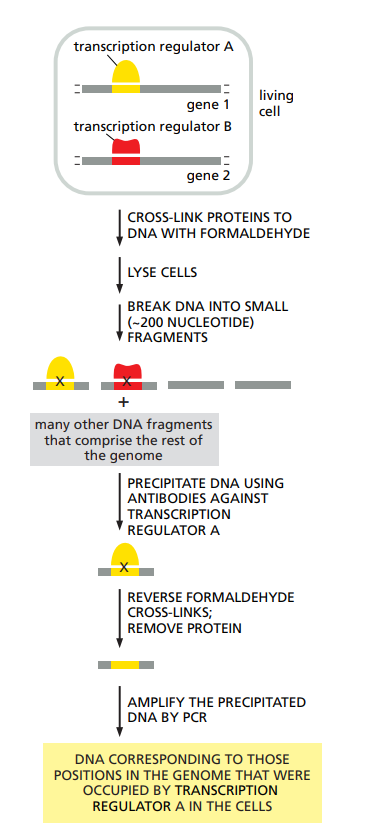
How does ChiP work for studying gene expression ?
Proteins are cross-linked to DNA.
Cells are open.
DNA is fragmented.
Antibodies that recognize a transcription regulator precipitate them and their bound DNA.
DNA is sequenced.
Allows us to see which regulation sites are occupied.
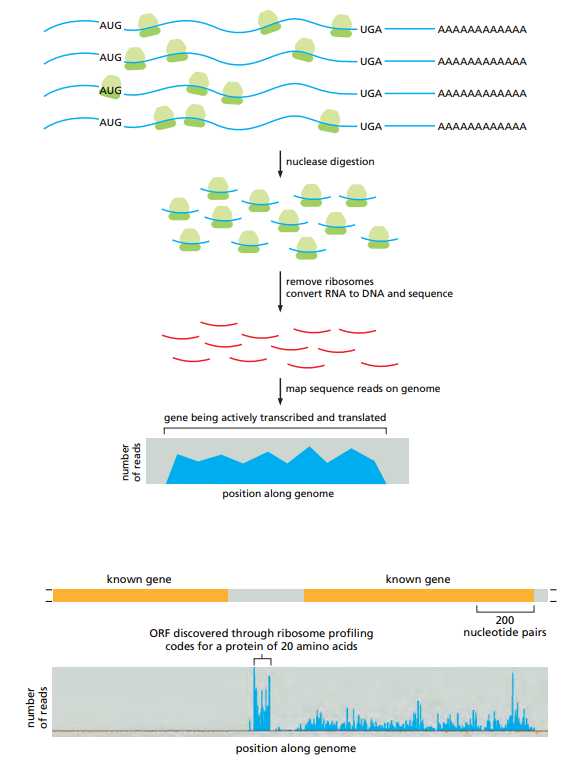
How does ribosome profiling work for studying gene expression ?
Used to identify RNAs being transcribed at a given moment in time.
RNA with ribosomes is exposed to a ribonuclease.
RNA sequences covered in ribosomes are spared by the ribonuclease.
Protected RNA is converted to DNA and sequenced.
What are dominant and recessive mutations ?
Dominant mutations cause the mutation when only present in one copy while recessive causes it only when mutant is in both copies.
What is epistasis analysis ?
It is the analysis of the relationship between different genes.
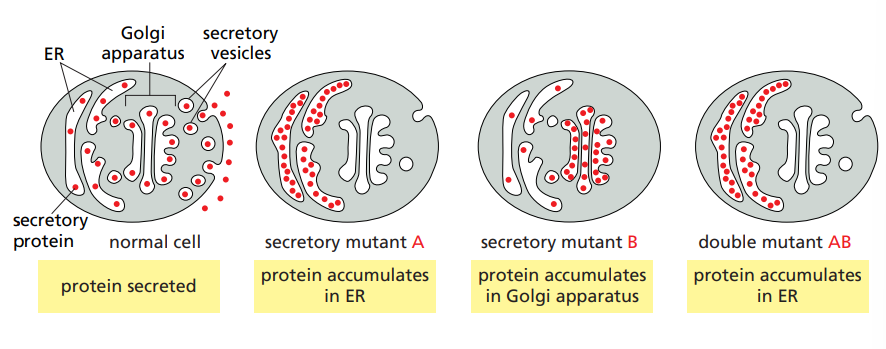
What are the two situations for double mutants in epistasis analysis ?
Synthetic phenotype : The phenotype of a double mutant is more severe than each of the single mutants.
Synthetic lethality : The phenotype of a double mutant is death , whereas each of the single mutants survive.