NPB: Introduction to Skeletal Muscle Part 2
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Twitches, Motor Units and Contractile Strength
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Muscle Twitch Facts
A single AP can induce a twitch
small magnitude
short duration
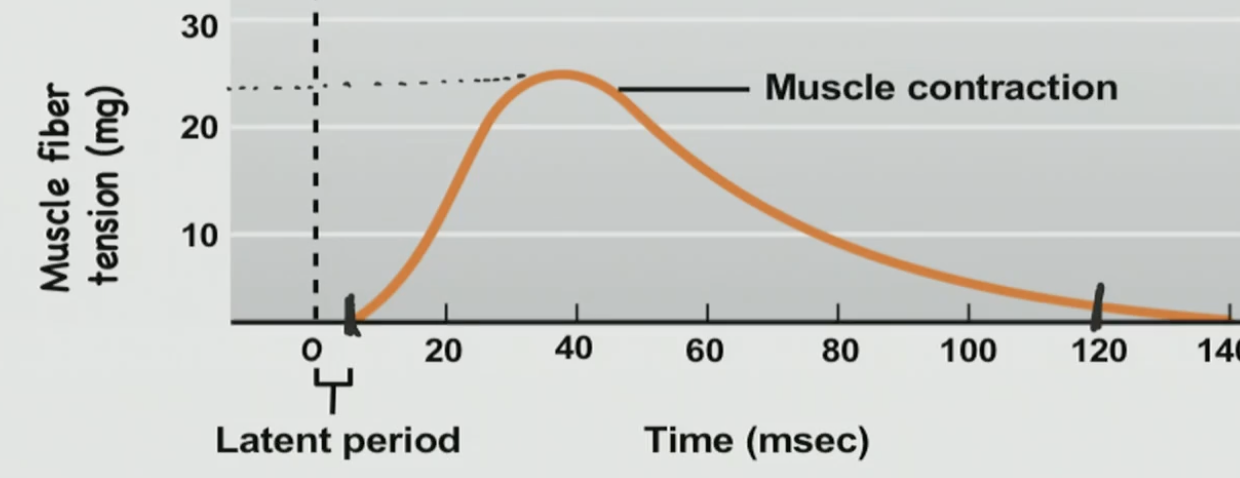
Muscle Twitch
doesn’t last very long
not a functionally full contraction
T/F: a single action potential causes a sustained muscle contraction
False, a single action potential does not cause a sustained muscle contraction. This is because this is only a brief twitch. And it would need to be a large enough action potential and constant to be sustained muscle contraction
Why is a muscle twitch not a functionally full contraction?
because they only last like 100 msec
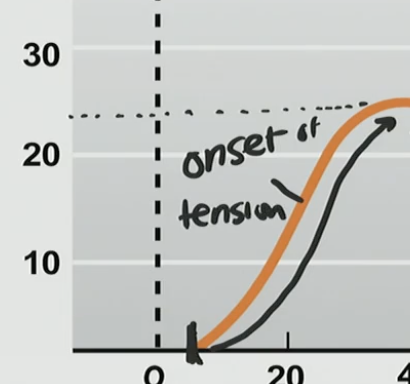
Onset of Tension
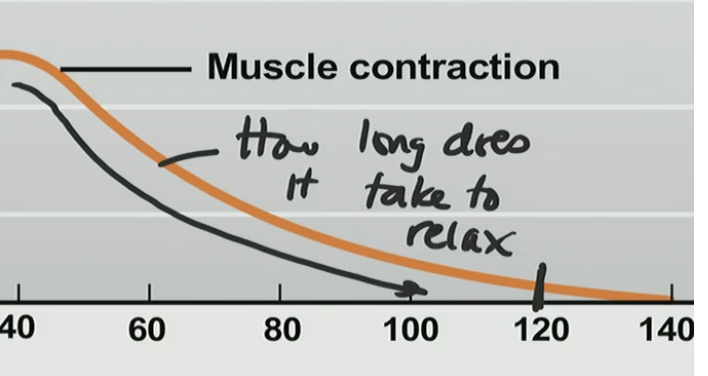
How long does it takes to relax
T/F: A single AP isn’t enough to induce a twitch
False, a single AP can induce a twitch, it will just be a short duration and small magnitude
Summation
twitches add up but still partly relax
Tetany
Allowing twitches to fuse together into a smooth sustained contraction and the overall sum of forces is larger than before
With twitches, summation refers to the summation of…
A) force
B) voltage
C) calcium release in the motor neuron
D) individual action potentials fusing together
E) acetylcholine levels in the synaptic cleft
A) force: this is force of like newtons or kg
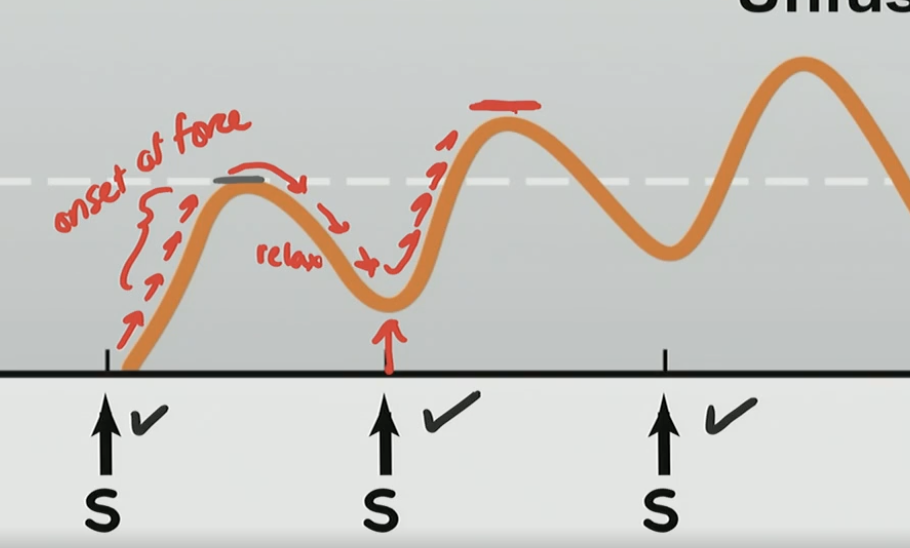
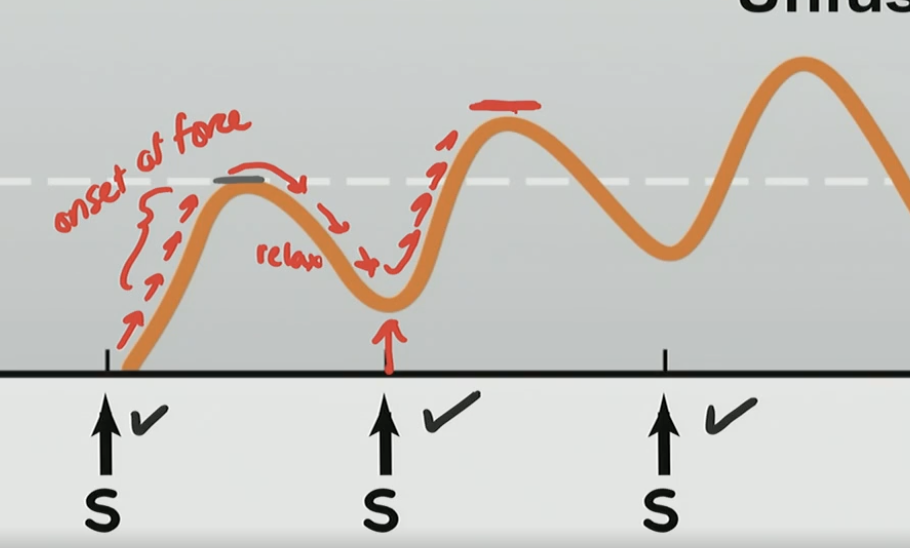
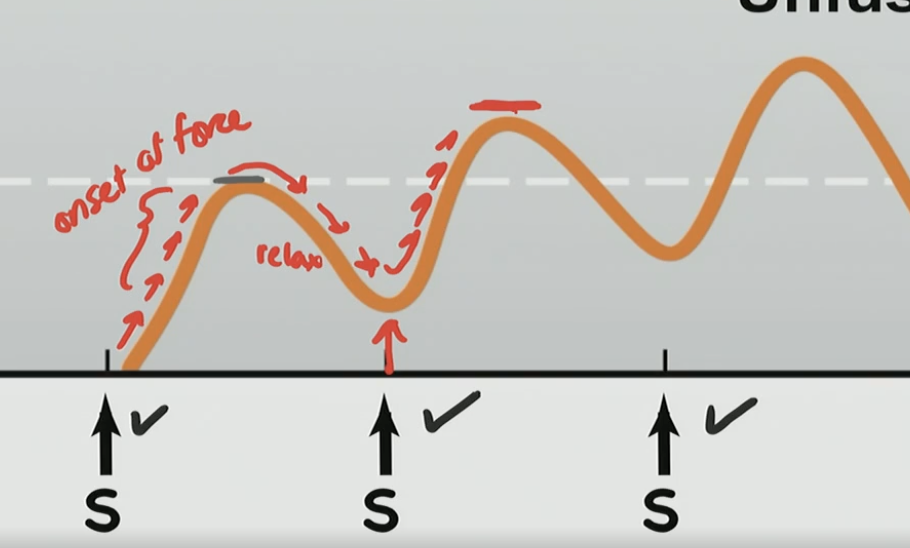
What is occurring here?
There is a onset force and relaxation, but its not fully relaxing, then another force and not full relax over and over again with a new peak higher than the one before
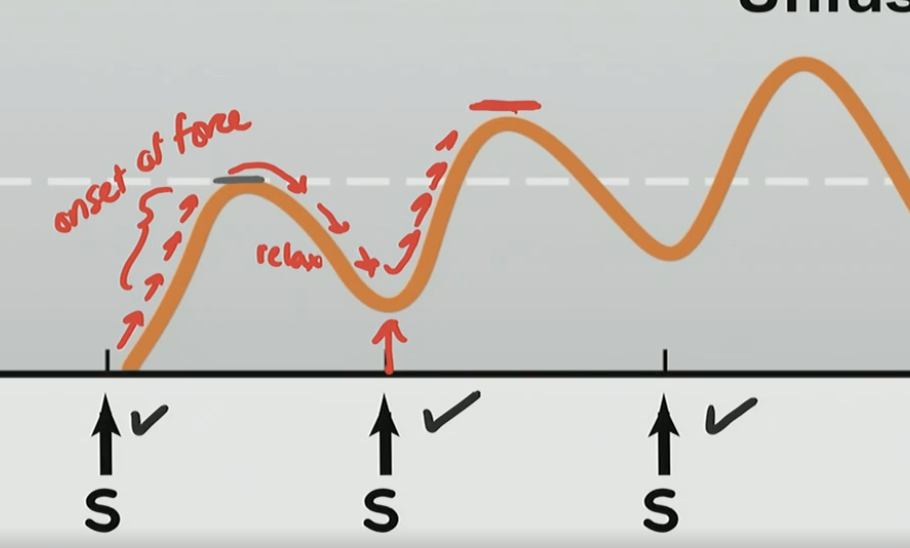
What is this phenomenon?
Unfused Tetany
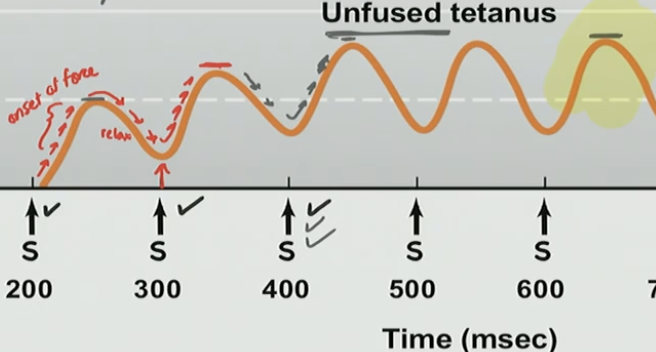
Unfused Tetany
Stimulus frequency is slow
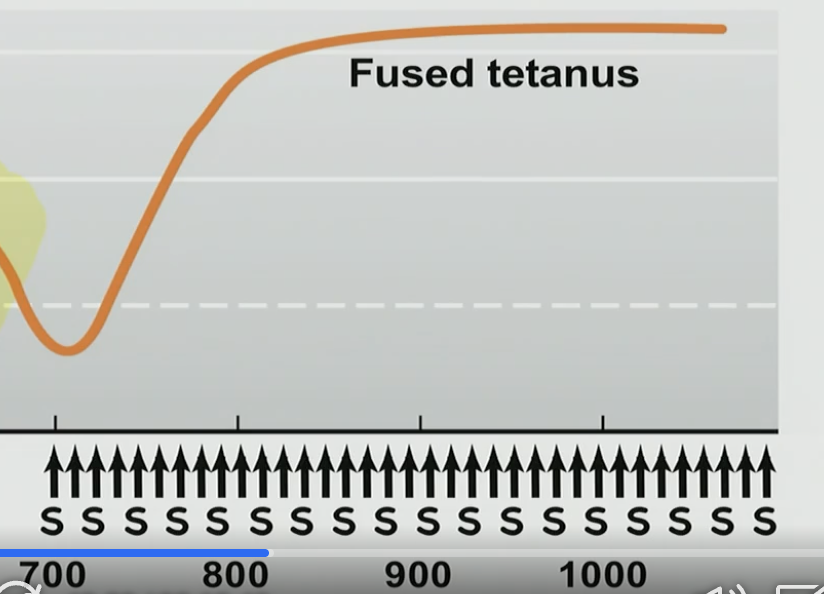
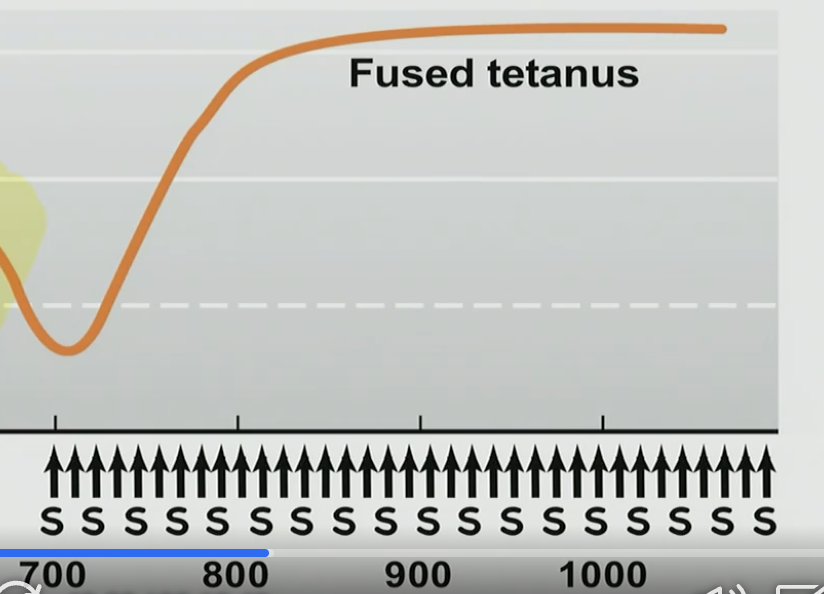
Fused Tetanus
Stimulating at higher frequency
Don’t give muscle time to relax
Long lasting, BUT only long lasting if there is a constant stimulus
T/F: Tetanus occurs when muscle twitches completely relax between action potentials
False, tetanus is the summation of twitches with no relaxing point because its constant stimulation
T/F: action potential frequency, controls the strength of muscle contraction
True, the actual potential frequency does control the muscle contraction because if there's a constant action potential, this would be fused tetanus with a higher frequency, and if there is spaced out action potential, this will have a lower frequency, and the twitches won't last very long as it will be short magnitude
T/F: Fused tetanus has lower frequency than unfused tetanus
False, fused tetanus has higher frequency because it is stimulating nonstop not giving the muscle time to relax
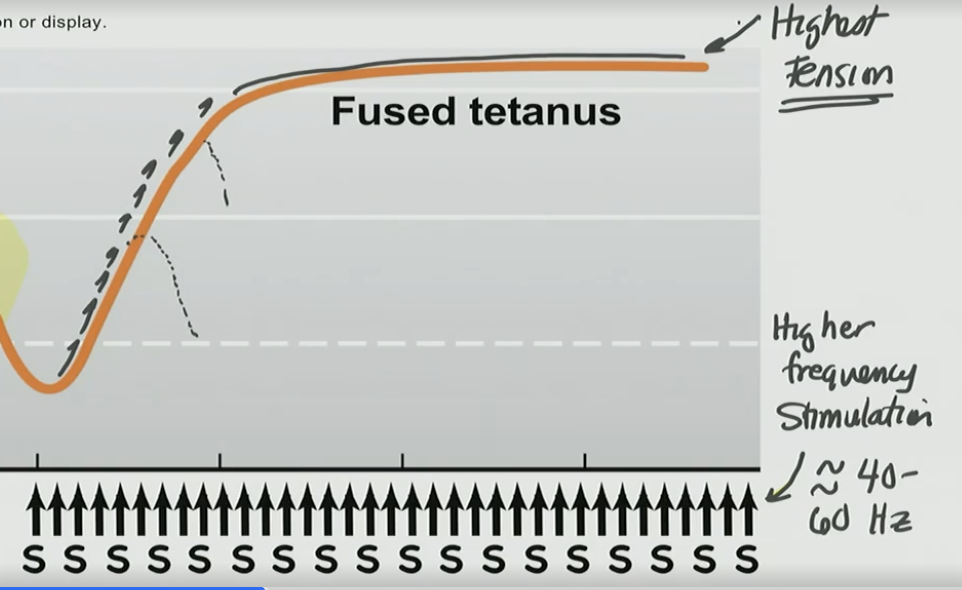
T/F: Relaxation occurs with fused/complete tetanus
False, no relaxation occurs because there is a nonstop stimulus
Fused tetanus have a ___(smaller/larger) contraction than unfused tetanus
larger
A __________ is the fusion of repeated muscle twitches that leads to a sustained contraction.
Tetany
During fused tetany...
A) the muscle is stimulated at low frequency
B) the latent period becomes longer in duration
C) twitches sum together to form a strong, smooth contraction
D) a weak, but smooth contraction occurs
C) twitches sum together to form a strong, smooth contraction
When more motor units are activated, this is called motor unit __________.
recruitment
The strength of a muscle contraction increases with more frequent __________.
action potentials
Why doesn’t one action potential create a strong contraction?
a single AP doesn't create a strong contraction because it causes only a brief twitch that ends quickly.
What’s the difference between summation and tetanus?
Summation = twitches add up but still partly relax
Tetanus = twitches fully fuse into a smooth, sustained contraction.
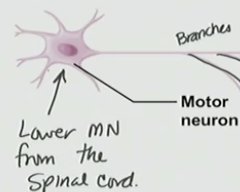
Motor neuron
control 5 muscle cells (in this example) = motor unit


Motor Unit
Arrangement of muscle cells & how it talks to the motor neuron and this overall arrangements is small
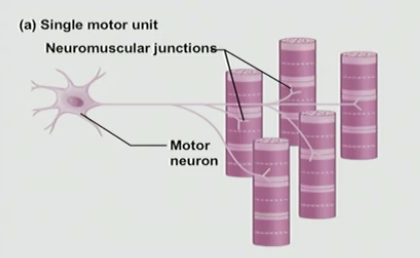
T/F: In all instances motor units will vary in size
True, in all instances motor units will vary in size
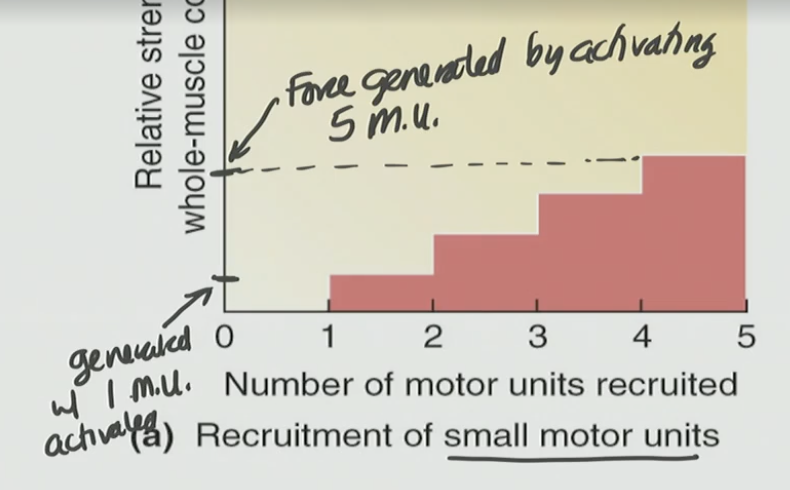
Small Motor Unit
Single motor neuron connected to ≈ 20-100 muscle cells
doesn’t generate as much force
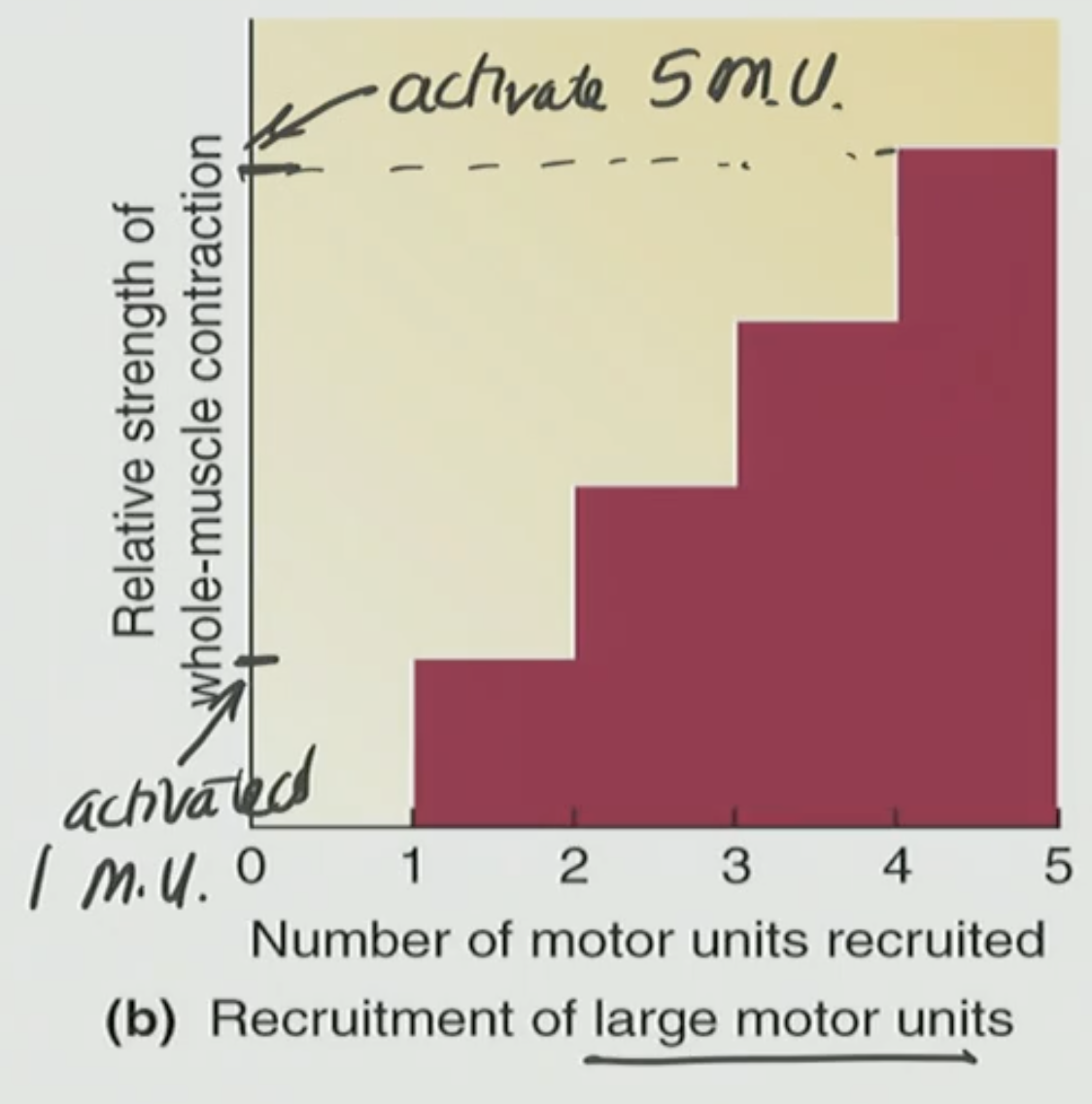
Large Motor Unit
Single motor neuron connected to ≈ 200-500 muscle cells
generates lots of force
Compared to large motor units, small motor units...
A) are only found in small muscles
B) are as strong as large motor units
C) contain smaller muscle cells
D) contain fewer muscle cells
D) contain fewer muscle cells
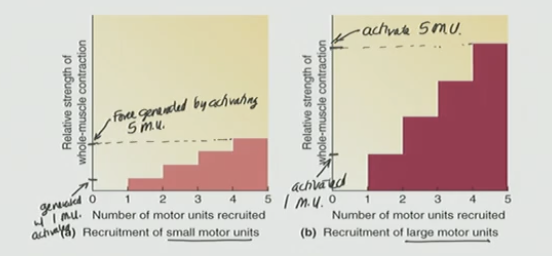
What is an advantage to small m.u.?
fine detection/ motor activities like for eyes
What is an advantage to large m.u.?
Having large buttocks for maintaining our posture when sitting
When would we have a mix of small and large motor units?
When we have muscles that do a mix of strong and weak forces
How do we increase our overall force generation (total amount of force a muscle produces when doing a task)?
We do this with a motor unit recruitment (the process of activating more motor units to increase the strength of a muscle contraction)
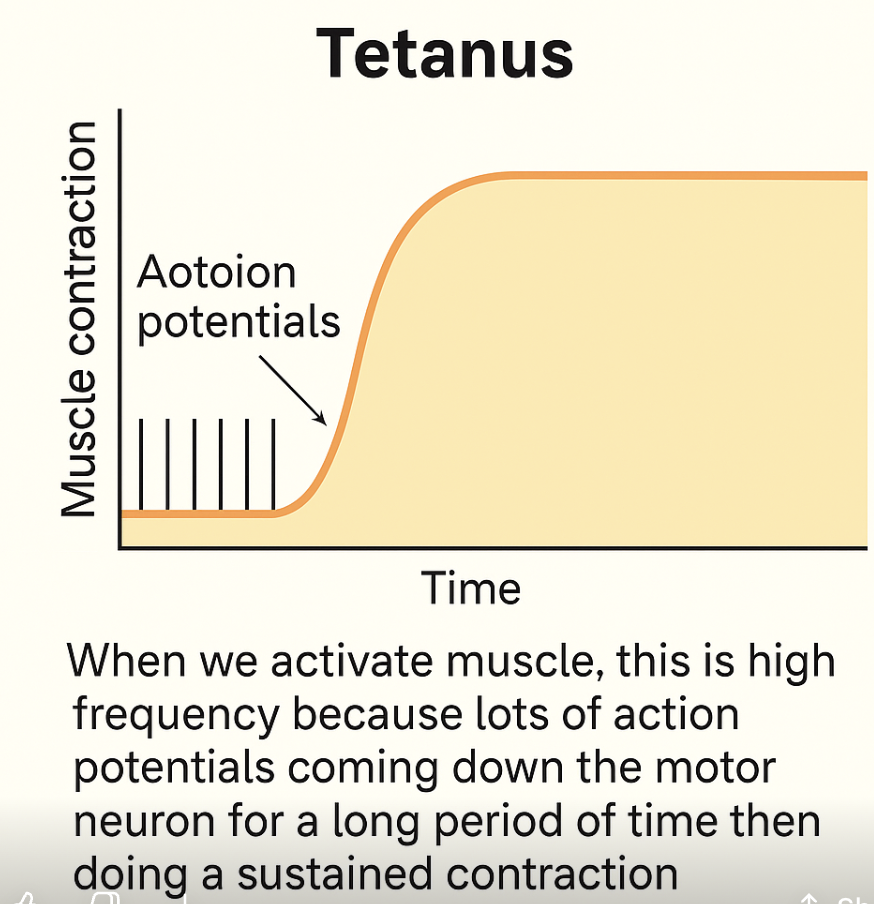
T/F: When we activate muscle, this is high frequency
True, when we activate muscle, this is high frequency because lots of action potentials coming down the motor neuron for a long period of time then doing a sustained contraction
if I pick up a pen in my activating small motor units or large motor units
If I pick up my pen, I'm activating small motor units because I don't need to activate every single motor unit for something super light
if I am picking up a TV and my activating large motor units or small motor unit?
I will be activating a large amount of motor units because this is something heavier so I need to activate more of the motor units