Overview of Anatomy of Thorax
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
what are the three main planes?
transverse/horizontal plane
coronal/frontal plane
sagittal plane
what does anterior or ventral mean?
towards the front or back
what is mean by superior or cranial?
towards head end of the body
what is meant by inferior or caudal?
towards the tail end
what is meant by medial and lateral (with respect to median plane)
In regards to the medium plane, medial is closet to the medium plane
what is abduction and adduction?
moving away/towards the medium plane
what is medial and lateral rotation?
medial - towards the medium plane
lateral - away from the medium plane
what is pronation and supination?
only in regard to the forelimb on the upper limb.
Supination - facing towards the front
Pronation - facing it backwards
What is inversion and eversion?
only in the lower limb - inversion the foot goes inwards
eversion - is foot going outward
What is elevation and depression?
lifting and dropping the shoulders
what is circumduction?
a complex of movement
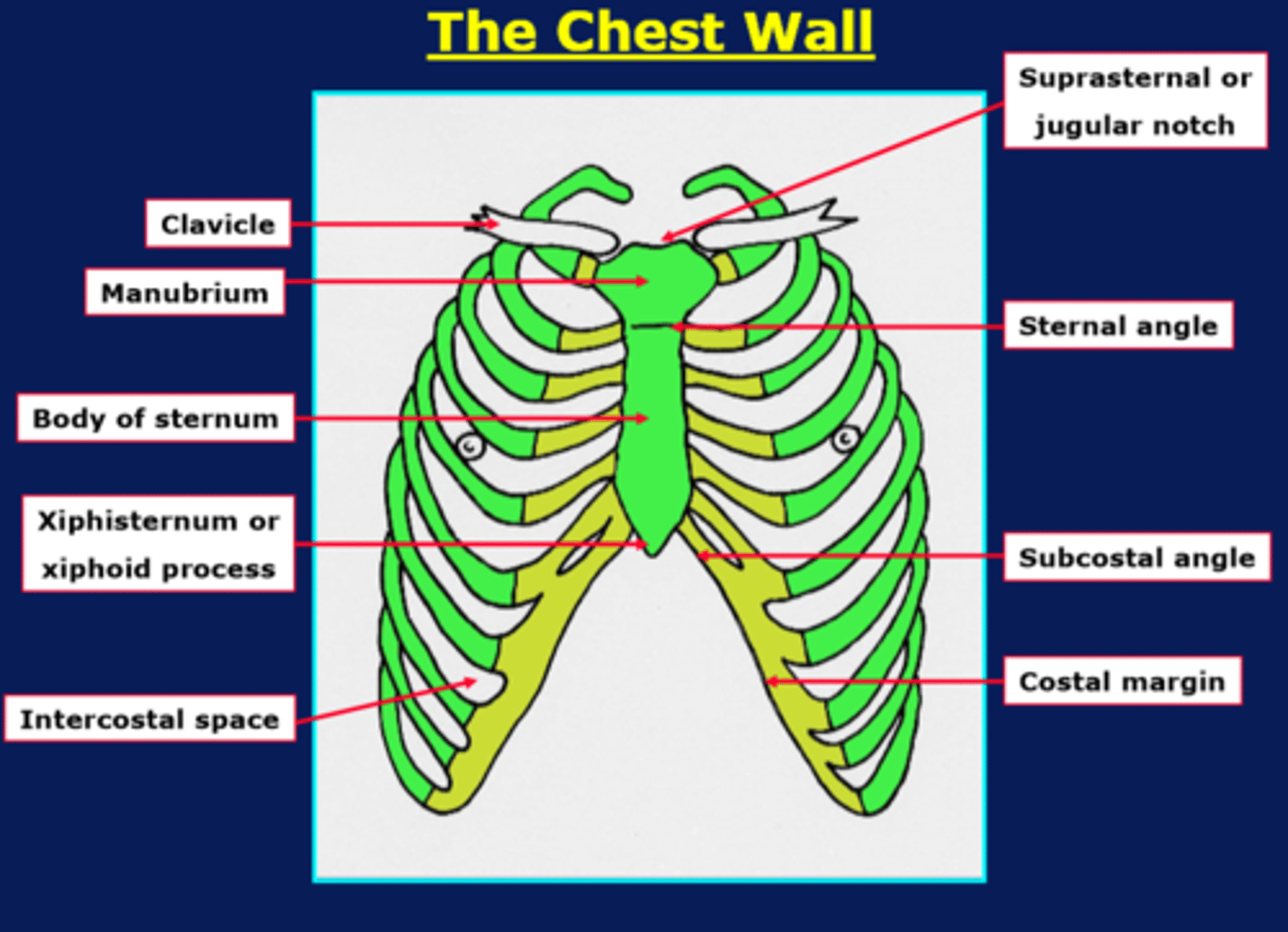
chest wall diagram (bones)
chest wall lines diagram
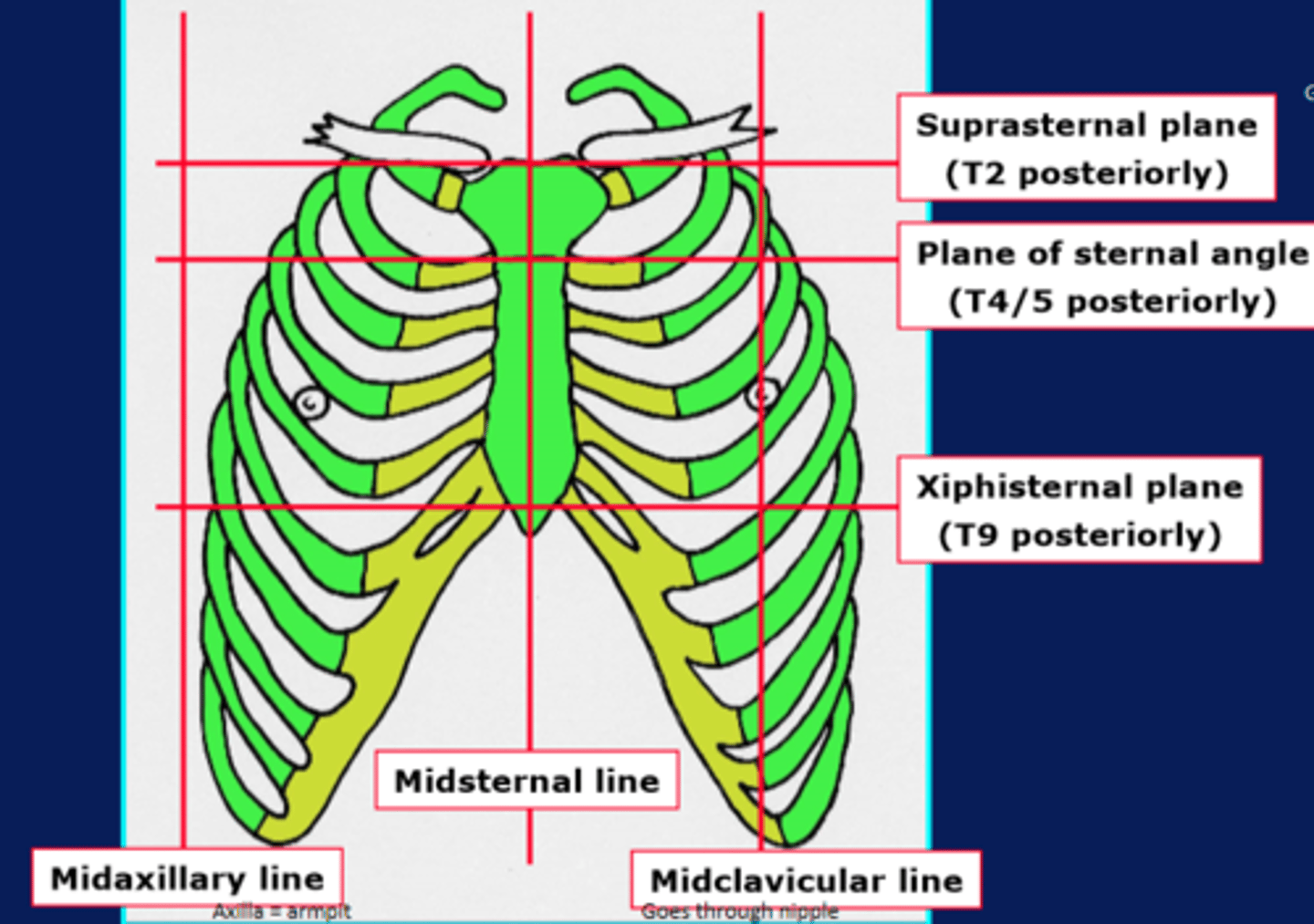
what does the suprasternal plane go through
the jugular notch
what are the 3 layers of intercostal muscles?
external, internal, innermost
what are the 2 pleural membranes?
visceral and parietal pleura
what does the visceral pleura do?
covers the lungs
what does the parietal pleura do?
lines the pulmonary cavities
chest wall diagram
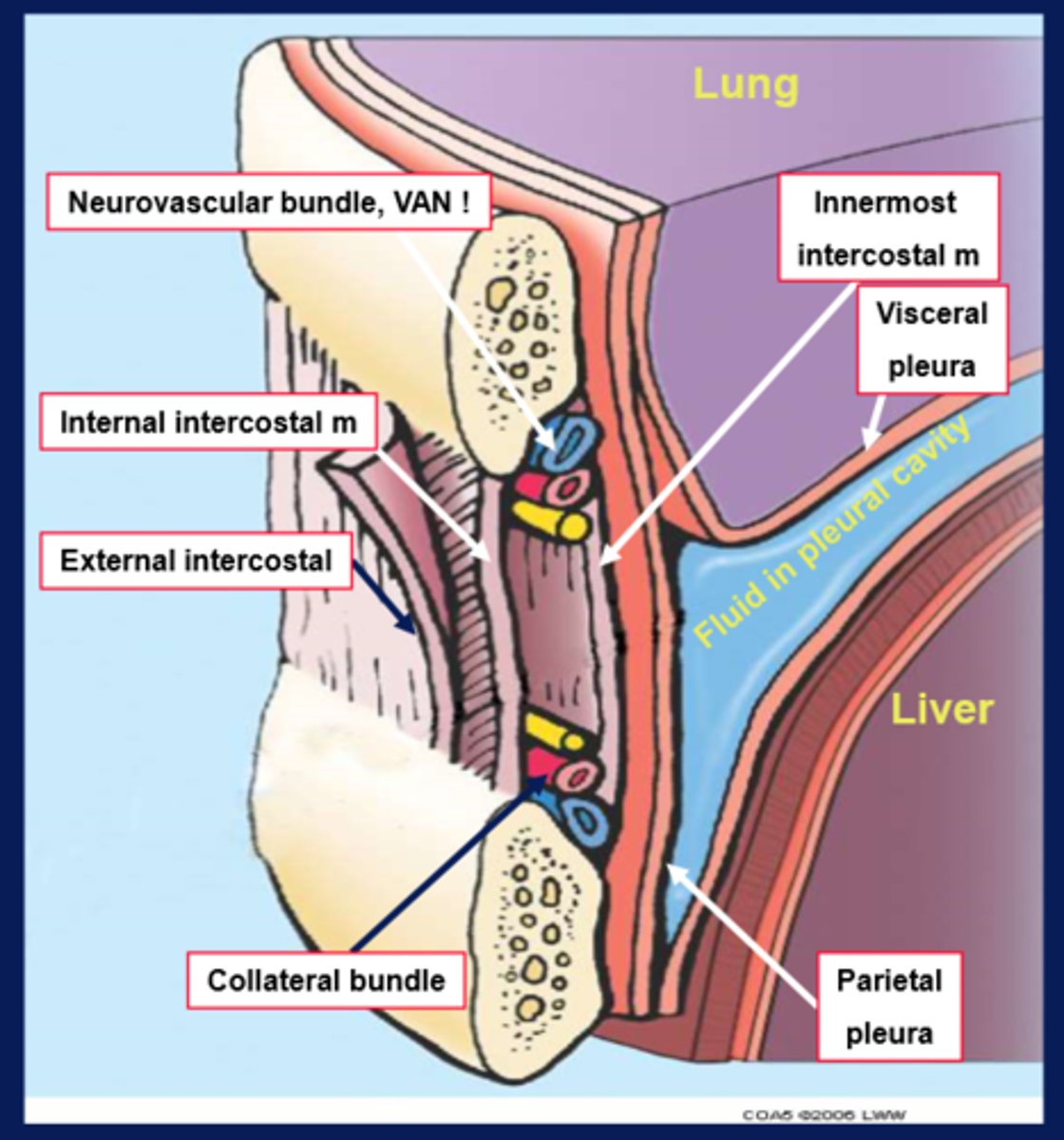
what is the name for a chest drain?
thoracocentesis
where is the supperior thoracic aperture?
opening at top of the ribs
what is the supperior thoracic aperture?
opening for structures to enter/leave neck/thorax
what and where is the inferior thoracic aperture?
opening at the lower part of the thoracic cavity that is closed by the diaphram
what is thoracic outlet syndrome?
Compression of one or more of the structures passing
out of the thoracic outlet. The subclavian artery or vein or lower portion of the brachial plexus is often involved.
diagram of the 1st rib (atypical)
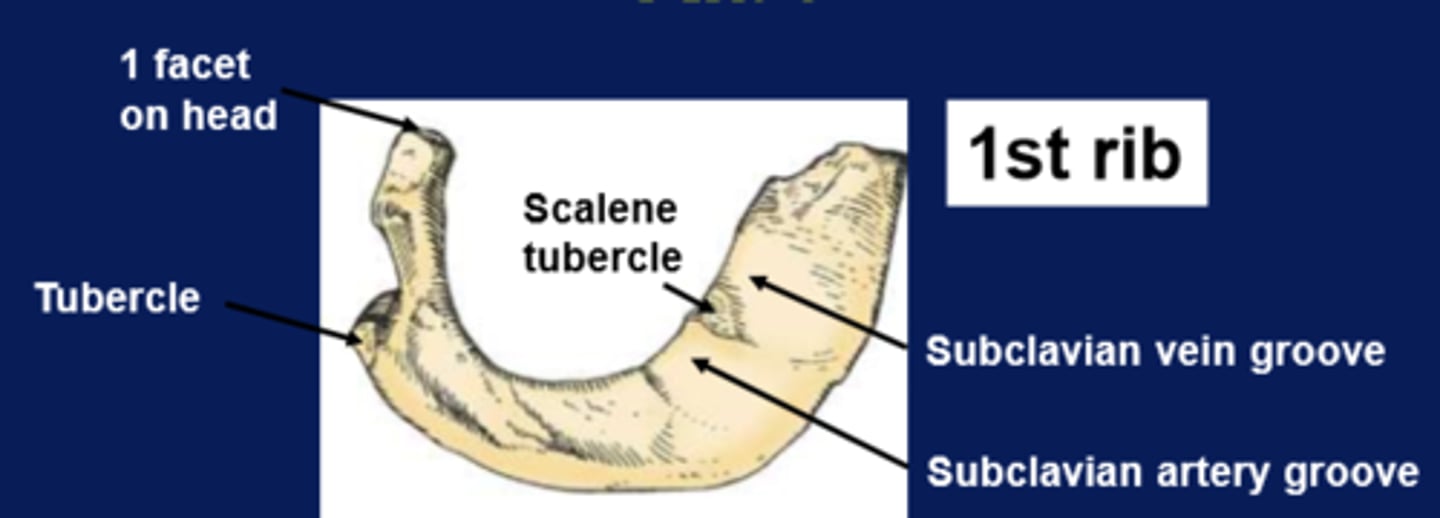
diagram of 8th rib (typical)
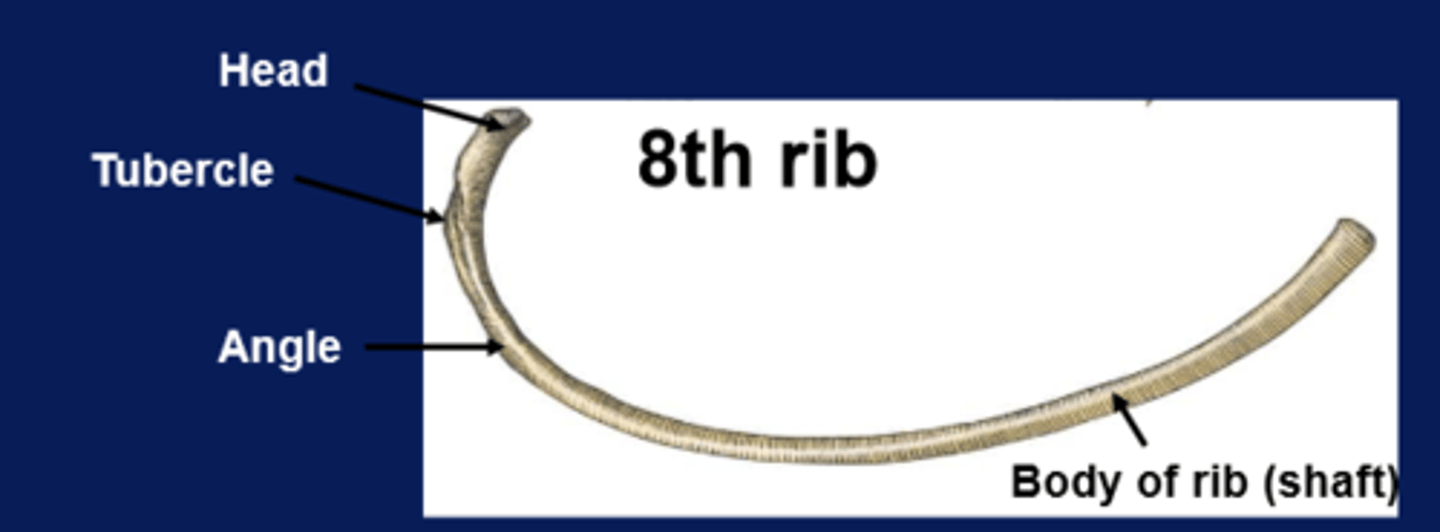
how many thoracic verterbrae are there?
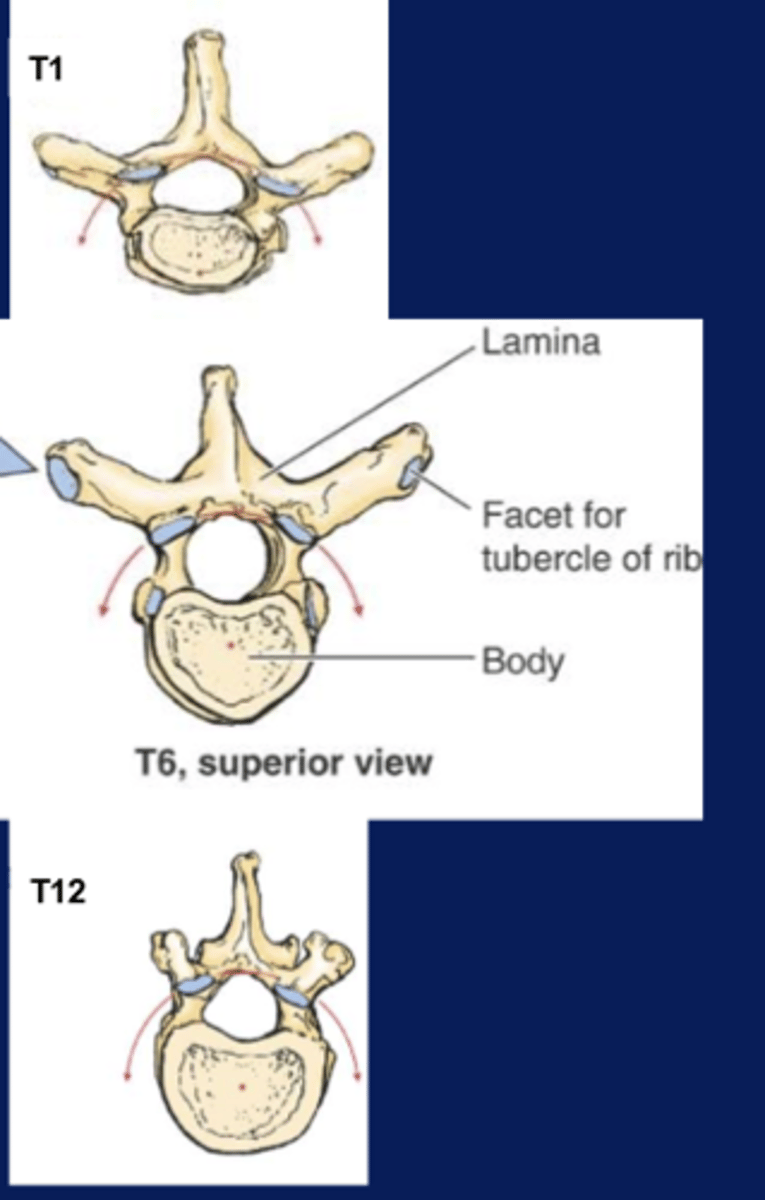
12
diagram of thoracic vertebrae
where does pectoralis major attach to the body?
clavicular head from medial half of clavicle.
sternocostal head from sternum and upper 6 costal cartilages.
All fibres converge on intratubular groove of humerus.
what are the actions of pectoralis major?
flexes, adducts and rotates humerus medially (extend humerus).
Pectoral girdle is fixed = accessory muscle of respiration.
what are the nerves that supply pectoralis major
medial and lateral pectoral nerves.
C5-8 T1.
where does pectoralis minor attach?
coracoid process of scapular.
Ribs 3-5 near their cartilages.
what actions is pectoralis minor associated with?
Depression of the scapular and protractor of the scapular.
If pectoral girdle is fixed = accessory to respiration.
what is the nerve supply for pectoralis minor?
medial pectoral nerve (mainly C8, T1)
where does the base of the breast extend from?
ribs 2-6 and the lateral margin of the sternum to the midaxillary line.
where does the auxiliary tail run in the breast?
superiorly and laterally towards the axilla
what is the breast?
a modified sebaceous gland
how many lobes does the breast have?
15-20 lobes
what do the lobes do in the breast?
send lactiferous ducts to the nipple
what do the lobes in the breast comprise of?
glands and adipose tissue separated by fibrous septa (suspensory ligaments)
how is the breast separated from the deeper pectoral muscle?
retromammary space
diagram of the breast
Don't need to know details, just good to be aware of the complexity
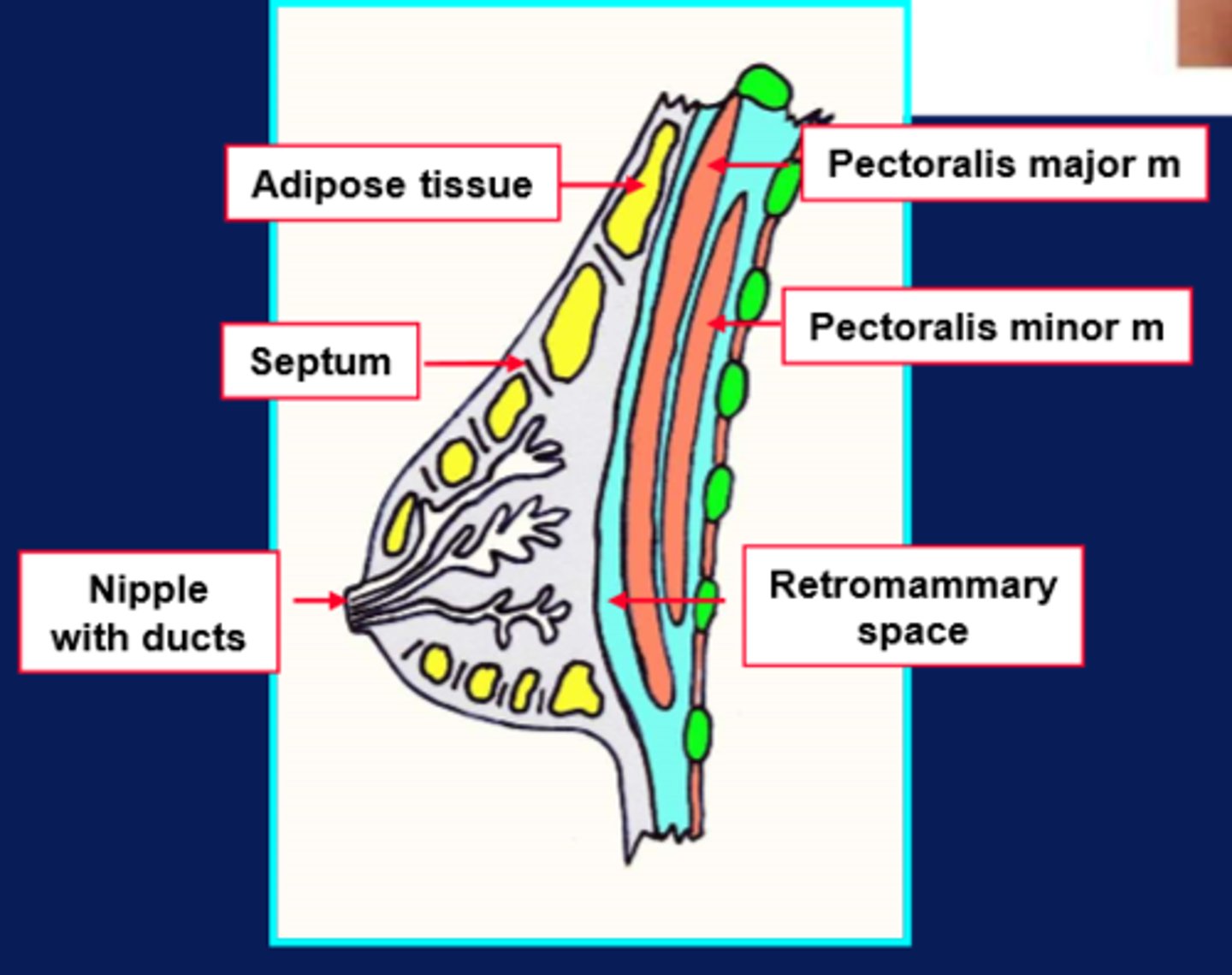
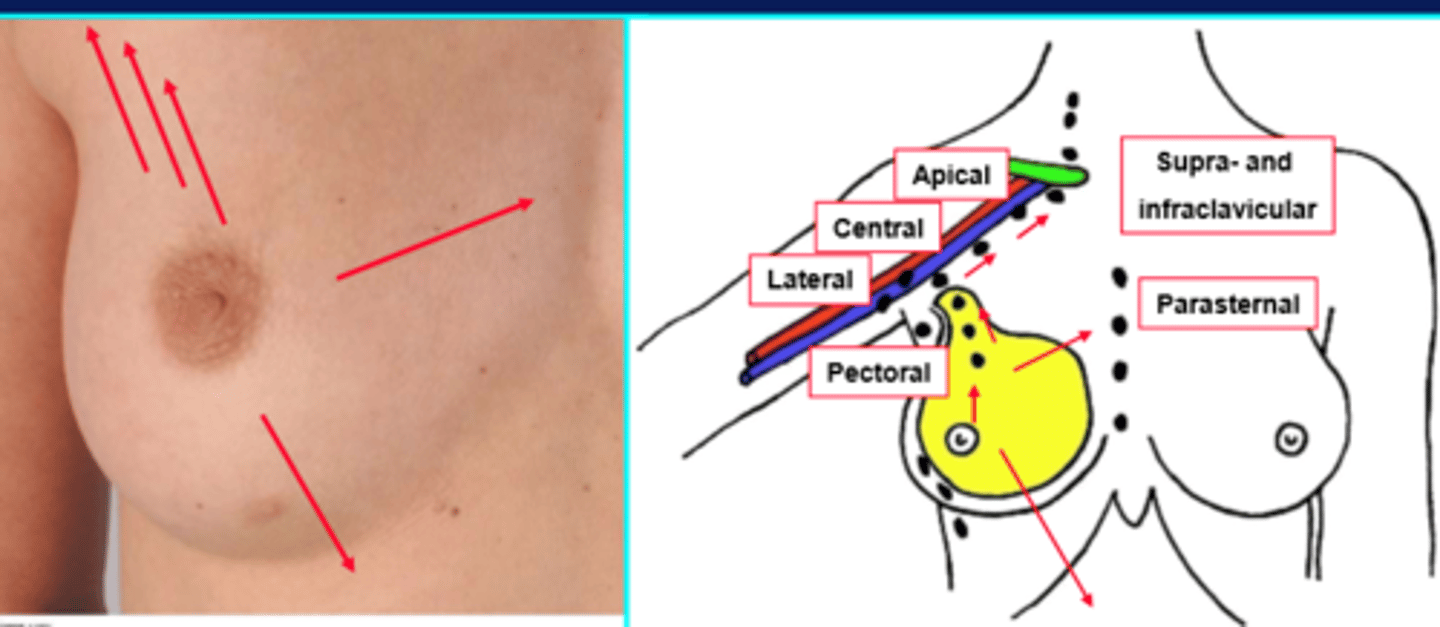
diagram of lymphatic draining in the breast
what is the mediastinum?
central part of the thoracic cavity that lies between the pleural cavities.
boundaries in the mediastinum?
anteriorly - sternum
posteriorly - thoracic vertebral column
superiorly - thoracic inlet and root of the neck
inferiorly - diaphragm
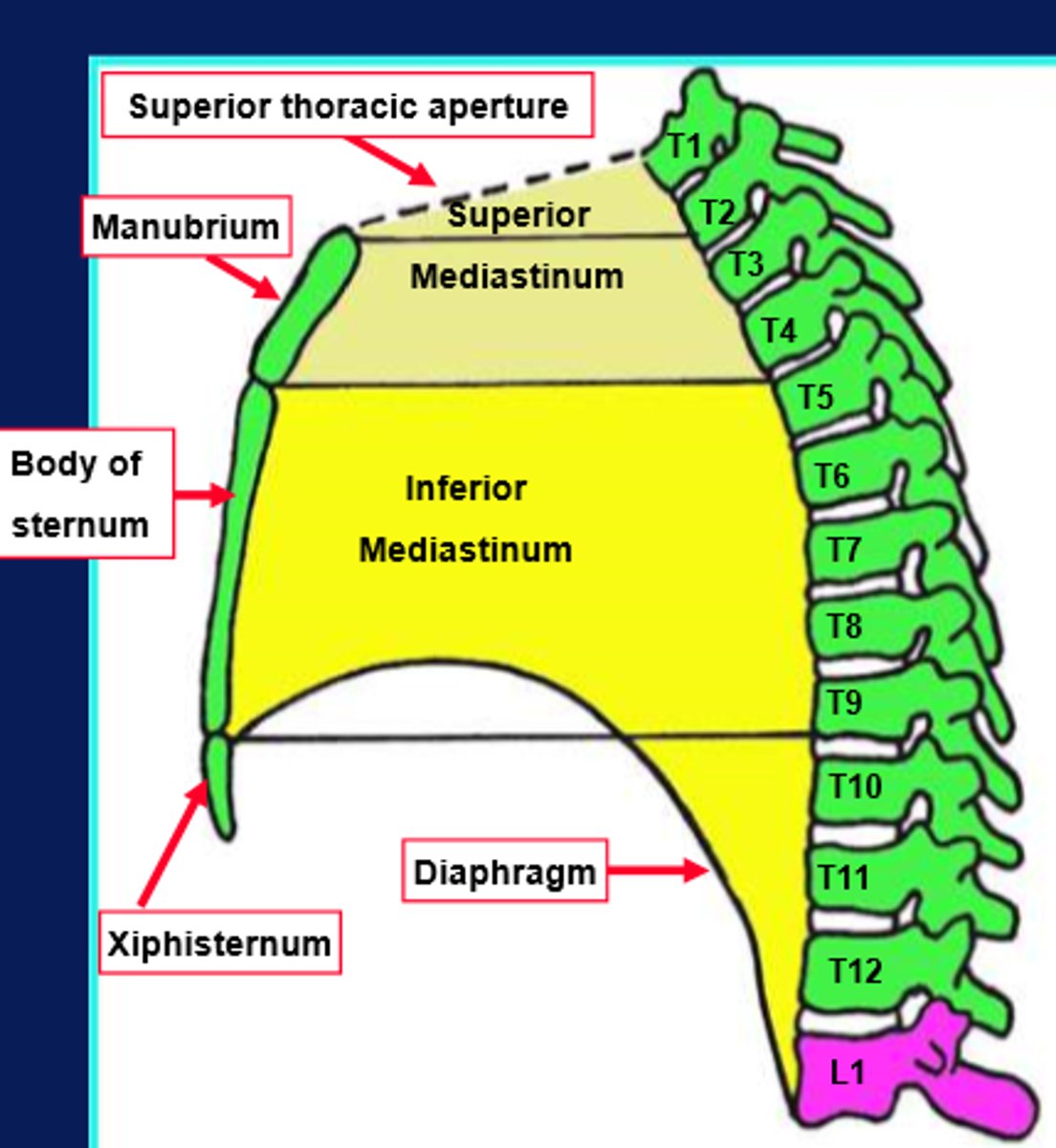
what parts is the mediastinum divided into?
superior and inferior
how is the mediastinum divided into two parts?
by the plane of the sternal angle (manubrial join to T4/5 disc)
where is the superior mediastinum?
lies behind the manubrium sterni
where does the inferior mediastinum lie?
behind the body and xiphoid process of the sternum (between the plane of the sternal angle and the diaphragm)
contents of the superior mediastinum?
SVC, arch of aorta, thoracic duct, trachea, esophagus, thymus, left recurrent laryngeal nerve
what sections is the inferior mediastinum divided into?
anterior, middle and posterior regions
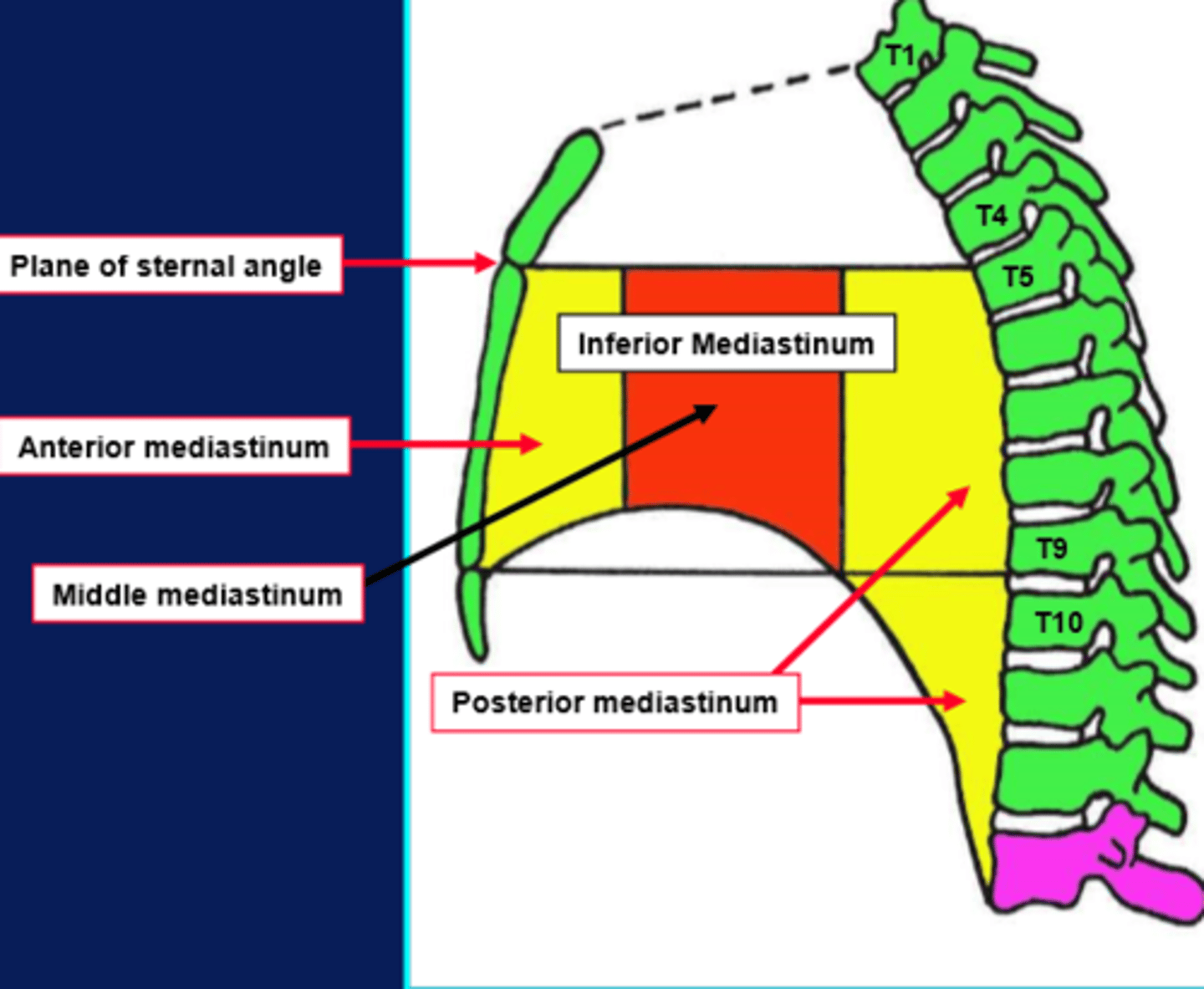
what is in the inferior anterior mediastinum?
internal thoracic aa and vv, thymus, sternopericardial ligaments.
what is in the inferior middle mediastinum?
heart and pericardium, phrenic nn and pericardiophrenic aa and vv, IVC.
what is in the inferior posterior mediastinum?
descending aorta, azygous vv, oesophagus, thoracic duct, sympathetic trunks.