Biochemistry Additional Practice Chapter 4
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
Passage
On every medical drama, the first procedure ordered in an emergency is, “hang two units of O negative, type and cross.” This is probably a good idea for a serious injury, because this sentence translates to “give the patient some blood that won't hurt him, but find out exactly what kind he needs. The letters, A, B, AB, and O,refer to the blood type, and the letters A and B refer to the blood group antigens.
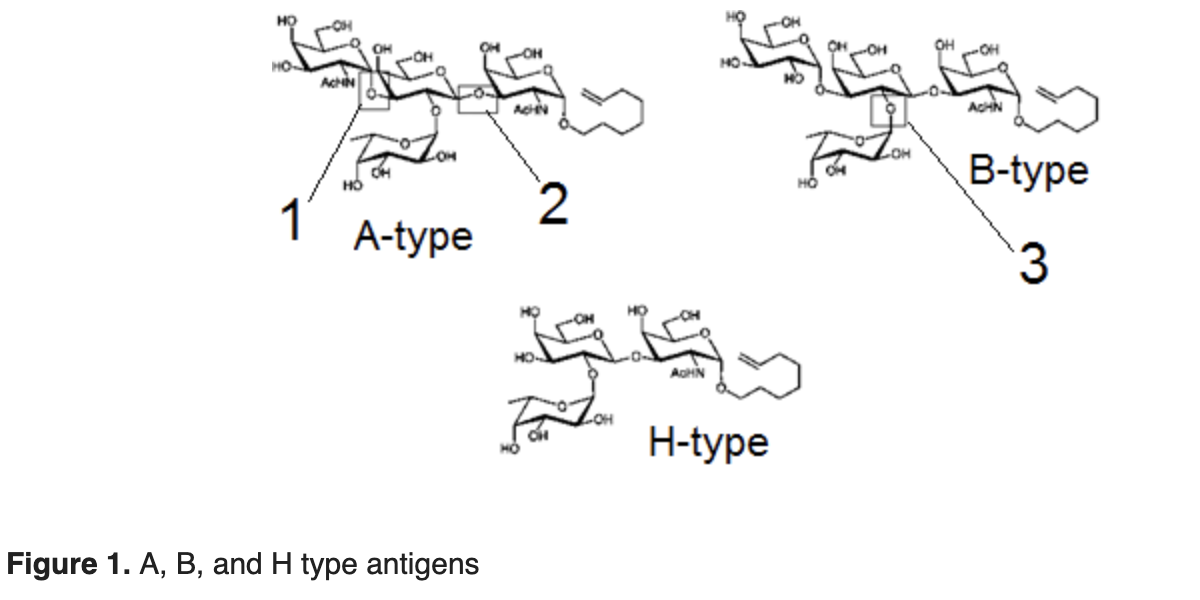
Individuals begin by producing antigen H, a precursor molecule, that is modified with different carbohydrates to form either of the antigens A or B, or which remains as antigen H in individuals with type O blood. In a rare phenotype, individuals from Mumbai may not produce the H antigen. Since this condition is so rare outside of Mumbai, a reaction to an O negative blood transfusion may be the first indication that the physician receives. Figure 1 shows the structures of the blood group antigens.
To isolate the blood group antigens from a group of whole cells, extraction was first attempted with ethanol, which had very poor yields. It was later discovered that the antigens are closely associated with lipid molecules in the cell membrane, and that the membrane had to be dissolved first with a detergent. Unfortunately, some of the harsh reactions also severed the carbohydrate chains from the single associated lipid or protein. Finally, a dichloromethane wash of the resulting solution was performed, leaving behind the peptides and simple sugars.
In order to quickly determine blood type in the hospital, a different method is used. Several drops of blood are placed on opaque slides, before antibodies are added. If the cells agglutinate (clump) in response to anti-A antibodies, then the individual has A antigens, likewise for B. The types of antigens on the erythrocytes determine the ABO blood type. Rh groups, which designate positive or negative, are tested similarly.
Contrast the connection defined by the box labeled 1 and the connection defined by the box labeled 2.
A. Box 1 represents a 1,3-alpha linkage while Box 2 represents a 1,3-beta linkage.
B. Box 1 represents a 1,3-beta linkage while Box 3 represents a 1,3-alpha linkage.
C. Box 1 and Box 2 both represent 1,3-alpha linkages.
D. Box 1 and Box 2 both represent 1,3-beta linkages.
A. Box 1 represents a 1,3-alpha linkage while Box 2 represents a 1,3-beta linkage.
Explanation: Anomeric carbons in sugars are labeled as alpha or beta. In bonding, the orientation is determined by the position of this anomeric carbon, which in almost always 1 because it is either an aldehyde or a ketone.Alpha/beta configuration is determined by the anomeric carbon and a reference carbon- carbon 4 in the sugars above. If they have opposite stereochemistry-axial and equatorial-the compound is alpha; if they have the same stereochemistry then the compound is beta. Box 1 indicates an alpha linkage, while Box 2 shows a beta linkage. This matches (A).
The branched connection defined by the box labeled three is most analogous to a structure in which of the following compounds?
A. mRNA
B. Glycogen
C.Sucrose
D. Oligopeptides
B. Glycogen
Explanation: The best approach to this question is to quickly determine the characteristics seen in Box 3 and then ask which answer choice shares as many similarities with these characteristics as possible.The connection illustrated in Box 3 is a branch point in a chain of carbohydrates. Oligopeptides (D), which do not contain sugars and are not branched, can thus be eliminated immediately. Of the three remaining choices, only glycogen is branched; hence (B) is correct.
BLANK
BLANK