S1.4 Counting particles by mass: The mole
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Mole (mol)
Definition:The SI unit for amount of substance.One mole contains exactly 6.02 × 10²³ elementary entities (particles).
Analogy:Just like a dozen = 12 items,1 mole = 6.02 × 10²³ items.
Question:Q: What does 1 mole of water molecules represent?A: 6.02 × 10²³ H₂O molecules
Avogadro's Constant (Nₐ)
Definition:The number of particles in 1 mole of a substance.Nₐ = 6.02 × 10²³ mol⁻¹
Unit: mol⁻¹
Question:Q: What does the unit mol⁻¹ mean?A: "Per mole" — used to convert moles to number of particles
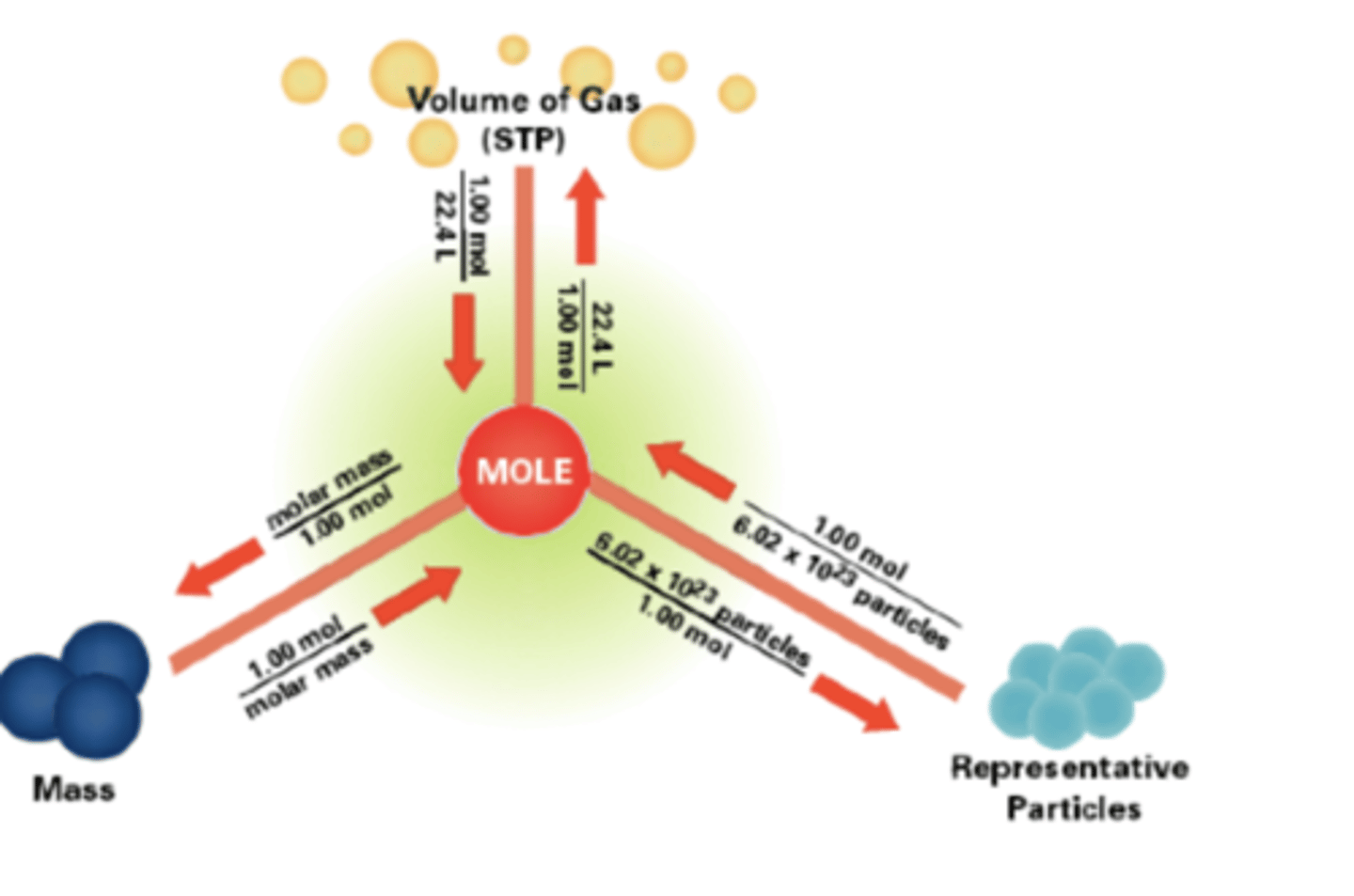
Mole-Particle Conversion
Formula:
No. of particles=n×N_A
Where:
n = amount in moles
N_A = Avogadro’s constant (6.02 × 10²³ mol⁻¹)
Electrons as Particles
Definition:Electrons can be counted in moles too.
Example:1 mol e⁻ = 6.02 × 10²³ electrons
Application:Useful in redox and electrolysis calculations.
Relative Atomic Mass Ar
Definition:The weighted average mass of a naturally occurring isotope of an element compared to 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
Key fact:
It is a relative value.
No units are used.
Carbon-12 as a Standard
Carbon-12 (¹²C) is the reference isotope used for defining Ar and Mr.
Value:Carbon-12 is assigned a mass of exactly 12.00.
Molar Mass (M)
Definition: The mass of one mole of a substance.It is numerically equal to the relative atomic or formula mass, but its units are g mol⁻¹.Example:
M of Na = 22.99 g mol⁻¹
M of H₂O = 18.02 g mol⁻¹
Formula (from Data Booklet):
n=m/M
where:
n = amount in moles (mol)
m = mass in grams (g)
M = molar mass (g mol⁻¹)
Units for Mass, Moles, and Molar Mass
Mass (m) → grams (g)
Moles (n) → mol
Molar mass (M) → g mol⁻¹
Empirical Formula
Definition:The empirical formula shows the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
Example:Glucose:
Molecular formula = C₆H₁₂O₆
Empirical formula = CH₂O
Molecular Formula
Definition:The molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule.
Formula:
Molecular formula=n×Empirical formula
Empirical Formula from % Composition
Assume 100 g sample → % becomes mass in grams
Convert mass → moles using:
moles=mass (g)/Ar
Divide all mole values by the smallest number of moles
Adjust to whole numbers (×2, ×3, etc. if needed)
Concentration
Definition:Concentration is the amount of solute dissolved in a certain volume of solution.
It can be expressed in:
g dm⁻³ (grams per cubic decimetre)
mol dm⁻³ (moles per cubic decimetre or molarity)
Formula for Molar Concentration
Formula (from data booklet):
n=C×V
n = amount of solute in mol
C = molar concentration (mol dm⁻³)
V = volume of solution in dm
Converting Units for Concentration
From g dm⁻³ to mol dm⁻³:
C(mol dm−3)=C(g dm−3)/M
Where:
M = molar mass of solute (g mol⁻¹)
From mol dm⁻³ to g dm⁻³:
C(g dm−3)=C(mol dm−3)×M
Avogadro's Law
Definition:At constant temperature and pressure, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of molecules (or moles).
V∝n (at constant T and P)
Implication of Avogadro's Law
Key Concept:1 mole of any gas occupies the same volume at the same T and P.
At standard temperature and pressure (STP):
Volume = 22.7 dm³ mol⁻¹
At room temperature and pressure (RTP):
Volume = 24.0 dm³ mol⁻¹ (if specified in question)
Factors Affecting Number of Gas Particles
The number of gas particles in a container depends on:
Volume of container – more volume, more particles
Temperature – higher temperature, faster particles, more space needed
Pressure – higher pressure, more particles in same space
↑ T⇒↑ KE⇒↓ particle density
Using Mole Ratios with Gas Volumes
For a balanced equation:
2H2(g)+O2(g)→2H2O(g)
You can treat mole ratios as volume ratios:
2 mol H₂ : 1 mol O₂ → 2 mol H₂O
So,2 dm³ H₂ + 1 dm³ O₂ → 2 dm³ H₂O(at same T & P)
Gases and Molar Volume at STP
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP):
T = 273 K
P = 100 kPa
At STP,
1 mol of any gas=22.7 dm³
Use this for converting between moles and volume.
Solving Volume-Mole Problems
Formula:
n=V/V_m
Where:
n = number of moles
V = volume of gas (dm³)
V_m = molar volume (22.7 or 24.0 dm³ mol⁻¹)
1⃣ – What Counts as an “Elementary Entity”
Definition: An elementary entity can be an atom, molecule, ion, electron, or any specified group of particles.
Example: 1 mol Na+ = 6.02 x 10^23 sodium ions.
Relationship Between Ar, Mr, and M
Ar = relative atomic mass (no units)
Mr = relative formula mass (no units)
M = molar mass (g mol^-1)
Note: M has the same number as Mr, but with units (g mol^-1).
Empirical and Molecular Formula Relationship
Formula: Molecular formula = n × Empirical formula
Where: n = molar mass ÷ empirical formula mass
Volume Unit Conversion for Concentration
1 dm^3 = 1000 cm^3 = 1 L
If volume is given in cm^3, divide by 1000 before using n = C × V.
Gas Volume Ratio Example
Question: What volume of O2 is needed to react with 4.0 dm^3 of H2
Equation: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Ratio H2:O2 = 2:1
So O2 volume = 4.0 ÷ 2 = 2.0 dm^3.
Relative molecular mass
Definition: The weighted average mass of one molecule compared to one-twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. It is calculated by adding together the relative atomic masses (Ar) of all the atoms in the molecular formula.
Used for: Covalent (molecular) substances.
No units.
Relative formula mass
Definition: The weighted average mass of a formula unit of a substance compared to one-twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. It is calculated by adding together the relative atomic masses (Ar) of all the atoms shown in its formula.
Used for: Ionic compounds and giant structures.
No units.
formula for concentration
c(g dm³) = mass of solute (g) / volume of solution
c(mol dm ³) = amount of solute ( mol) / volume of solution (dm³)
ppm = mass of solute (g) / mass of solution (g)
solution
a homogenous mixture of two or more substances in relative amounts
solvent
a substance that dissolves a solute to form a homogeneous mixture called a solution
in a salt solution, water is the solvent and the salt (sodium chloride) is the solut
solute
solute is the substance that gets dissolved in another substance (the solvent) to form a solutio
dilution formula and is used to calculate the unknown quantity (concentration or volume) when diluting a solution.
The equation C₁V₁ = C₂V₂ (or M₁V₁ = M₂V₂