
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Health History
Headache
OLDCART
associated symptoms: visual changes? Coughing? Sneezing? Suddent movement of head
Associated with increased pressure
Dizziness or Vertigo
Has many meanings
need to elicit exactly what patient means
OLDCART
Weakness
Generalized or localized
inability to move
Proximal or distal
Loss of sensation
Fainting or blacking out
Seizures
Tremors
Syncope
Presyncope
Disequilibrium
Ataxia
Vertigo
Diplopia
Dysarthria
TIA
Seizures
Different types
Acute symptomatic seizure
Epilepsy, head trauma, withdrawal from alcohol/drugs, metabolic insults (glucose, calcium), stroke
May involve loss of consciousness
Abnormal feelings before seizure?
How long do they last?
How frequent? Any change in frequency?
Any history of head injury?
What are you doing to treat seizure?
Tremors
Involuntary movements
With or without other neurologic manifestations
Parkinson's
Restless Leg Syndrome- pregnancy, renal disease, meds
Uncontrollable body movements?
Bilateral?

CNS
Basal Ganglia
Movement
Thalamus
Sensory
Hypothalamus
Homeostasis and hormones
Spinal cord
Supplies entire body
Motor and sensory pathways
Motor fibers
Voluntary movement, muscle tone
Walking
Cerebellar system
sensory and motor equilibrium and posture
Peripheral Nervous system PNS
Cranial Nerves
Olfactory
Optic
Oculomotor
Trochlear
Trigeminal
Abducens
Facial
Vestubocochlear
Glossopharyngeal
Vagus
Accessory
Hypoglossal nerve
Sensory Fibers
Pain, Temperature, touch
Vibration, proprioception
Spinal Reflexes
The deep tendon response
Reflex: involuntary response
Briskly tap the tendon of partially stretched muscle
Tapping tendon activates special sensory fibers
For the reflex to work- sensory, spinal cord, motor, and muscular fibers must be intact
Each deep tendon involves specific spinal segments, can help locate a pathologic lesion
Physical examination equipment
Sensory examination
Objects to feel (coin, paper clip)
Tuning fork
Hot and cold water in test tubes/glass
Cotton swab
Reflexes
Reflex hammer
Tongue blade
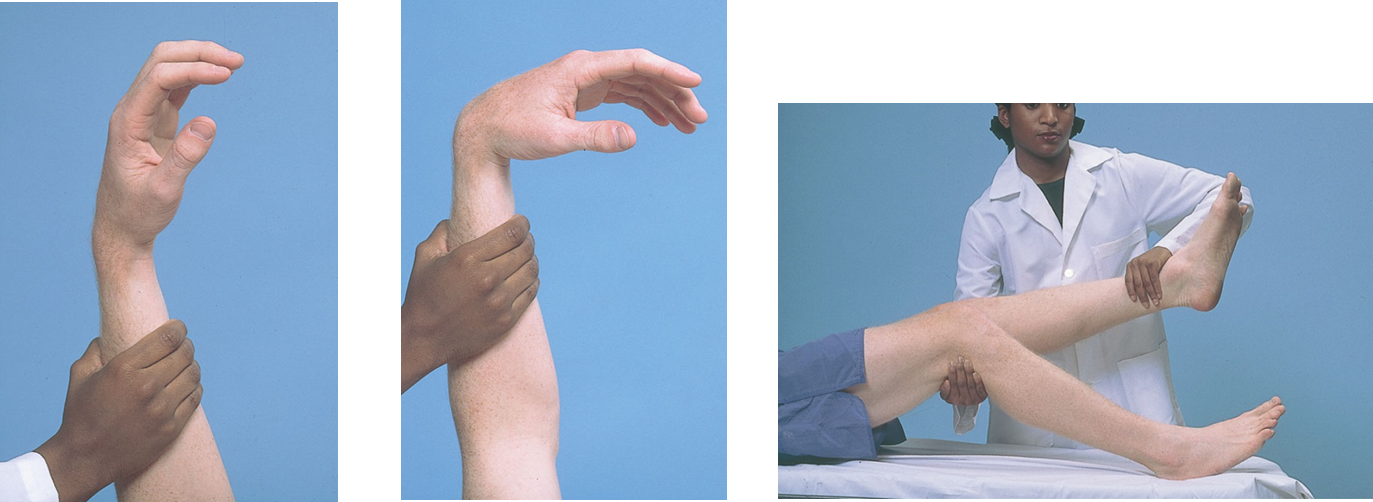
Physical examination of Motor system
Coordination
Requires four areas of the nervous system:
Motor system
Cerebellar system
Vestibular system
Sensory system
Observe performance
Rapid alternating movements
Point-to-point movements
Gait and other related body movements
Standing in specific ways
Rapid alternating movements
Arms
Legs
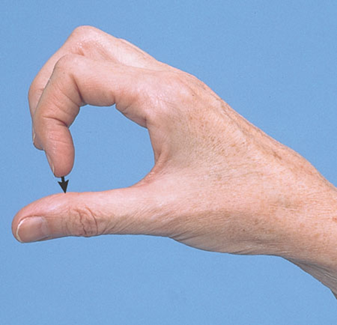

Point-point movements
Arms: fingers-to-nose-test
Legs: heels-to shin test


Gait physical examination
Ataxia- lacks coordination
Cerebellar Dfx
*Normal Gait
*Tandem Walk
Cerebellar Ataxia
Sensory Ataxia
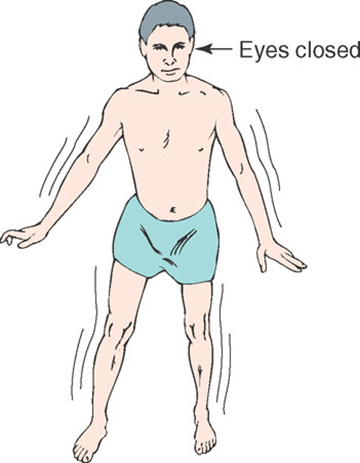
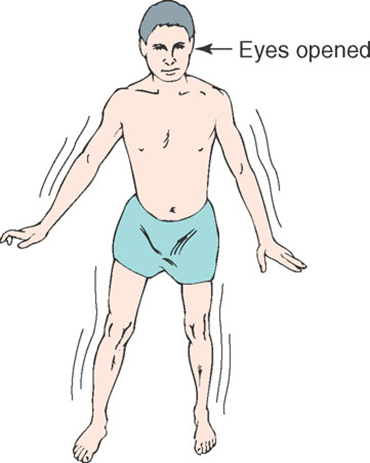
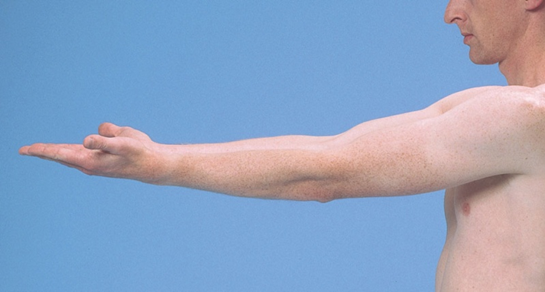
Stance physical examination
*The Romberg test
*Pronator drift
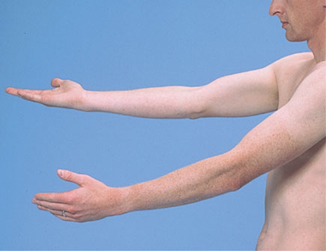
The sensory system (Physical Examination)
Test the following:
Pain and temperature
Position and vibration
**Light touch
Discriminative sensations
Correlate abnormal findings with motor and reflex activity
Underlying lesion central or peripheral?
Sensory loss bilateral or unilateral?
Pattern suggest dermatomal distribution, a polyneuropathy, spinal cord syndrome?
Loss of pain and temperature sensation?
Patterns of testing
Can fatigue patient, causing produce unreliable results
Pay special attention to:
Where there are symptoms such as numbness or pain
Where there are motor or reflex abnormalities
Where there are abnormal findings
Compare symmetric areas
Compare distal with proximal areas
Test fingers and toes first for vibration and position
Vary the pace of your testing
Map out boundaries if sensory loss or hypersensitivity is detected
Discriminative sensations
*Stereognosis
*Graphesthesia
**Two-point discrimination
Point localization
Extinction
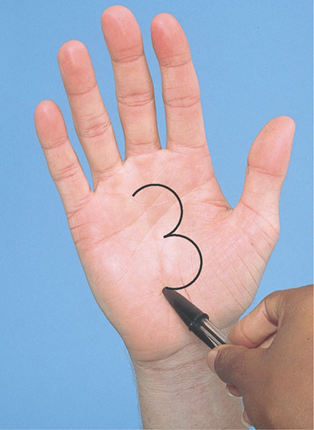
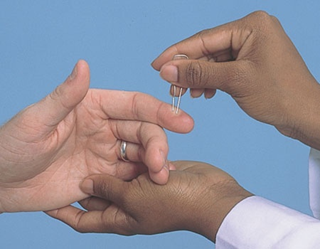
Pattern of testing physical examination
Pain
Use broken tongue blade/cotton swab.
Sharp and dull
Apply lightest pressure needed for stimulus to feel sharp; do not draw blood.
Temperature
Water, tuning fork
*Light touch
Cotton, avoid pressure
Vibration
Tuning fork
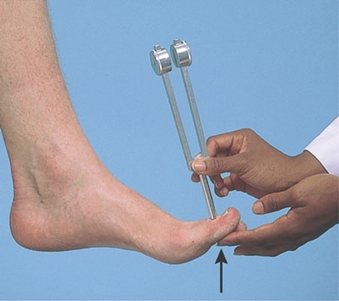
Pattern of testing (cont’d)
Proprioception (position)
Moving big toe up and down***
Deep tendon reflexes
*Deep tendon reflexes
Equipment: properly weighted reflex hammer
Encourage patient to relax.
Hold reflex hammer loosely between thumb and finger.
With wrist relaxed, strike tendon briskly .
Note the speed, force, and amplitude of reflex response.
Reflexes include:
biceps reflex
triceps reflex
supinator or brachioradialis reflex
knee reflex (patellar reflex)
ankle reflex (achilles reflex) (primarily S1)
Clonus
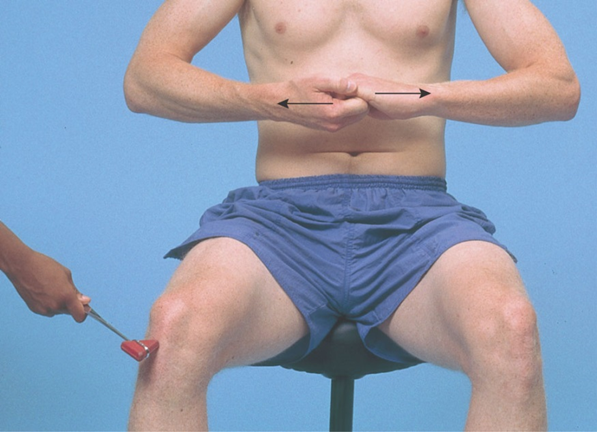
Deep tendon reflexes Reinforcement
Uses isometric contraction of other muscles
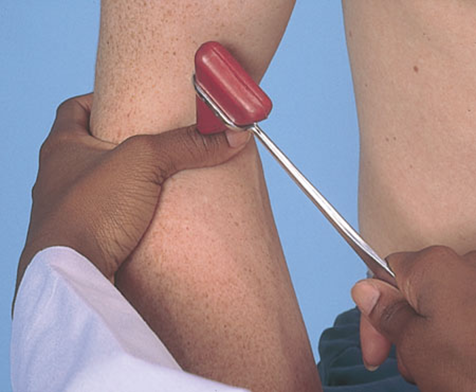
Deep tendon reflexes Bicep reflex
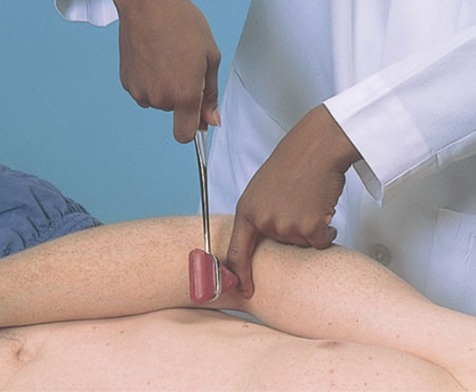
Deep tendon reflexes Triceps reflex
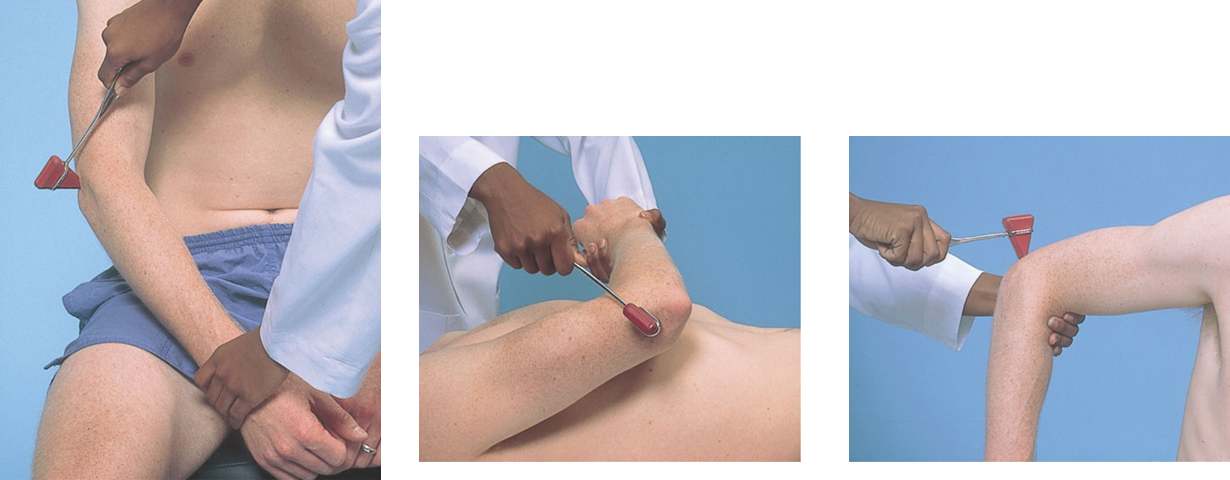
Deep tendon reflexes Supinator or brachioradialis reflex
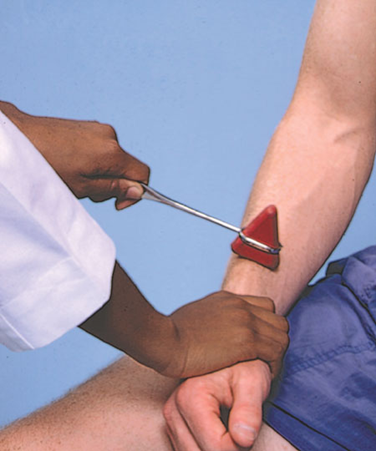
Deep tendon reflex The knee reflex
AKA patellar relex
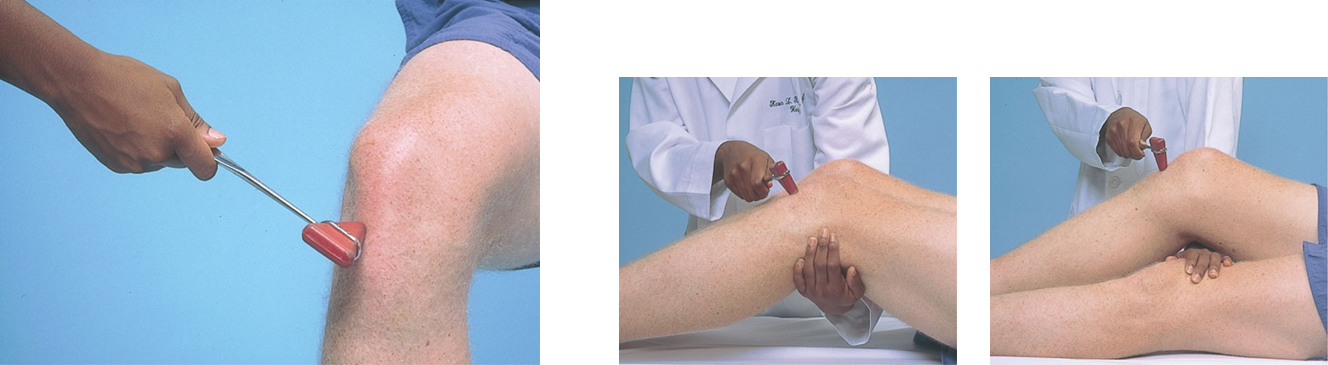
Deep tendon reflexes Ankle reflex
Achilles reflex
Primarily S1
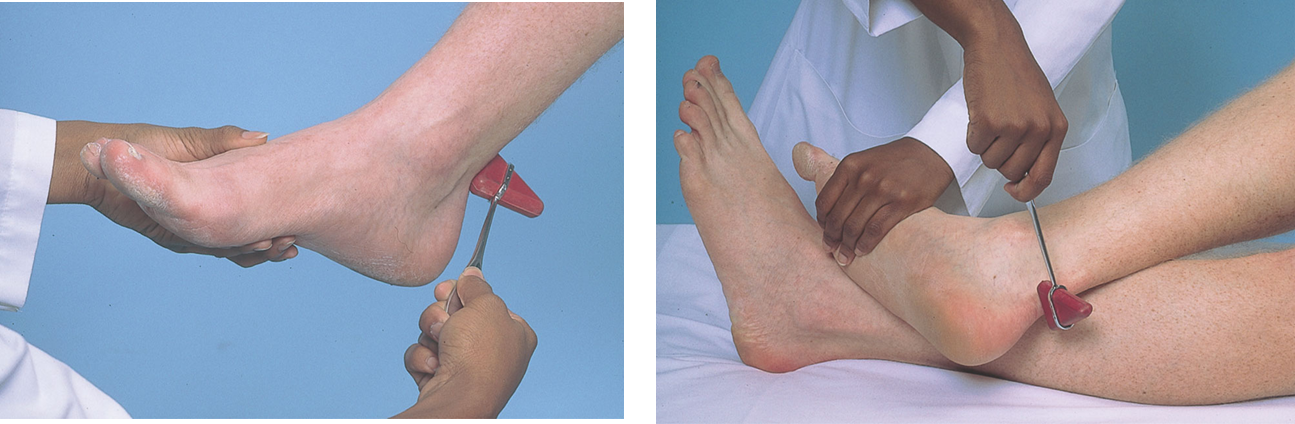
Deep tendon reflex Clonus
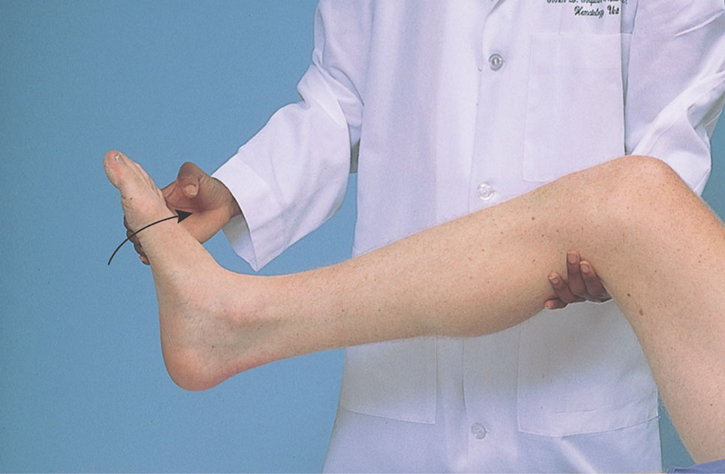
Cutaneous stimulation reflexes
Superficial reflexes
Plantar response (L5, S1)
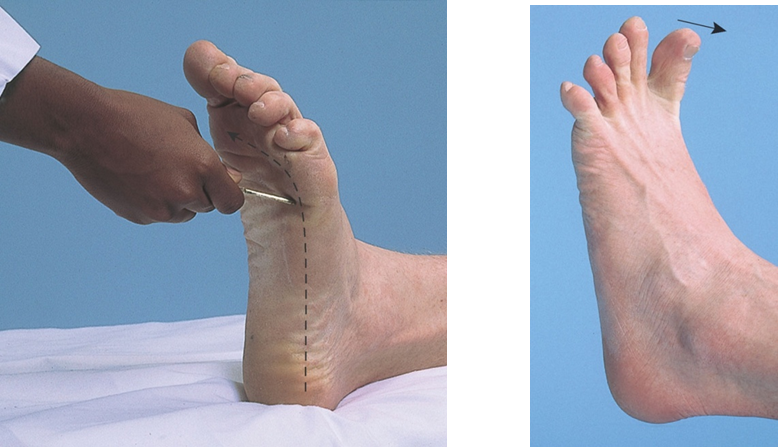
Abbreviated Neurological assessment For comatose patient
Assessment for comatose patient
ABCs
Level of consciousness
Metabolic or structural cause for LOC?
Interview relatives, friends, witnesses
“Don’ts” when assessing the comatose patient
Don’t dilate the pupils.
Don’t flex the neck if any question of trauma to the head or neck.
Pupils in Comatose Patients

Small or pinpoint pupils Misposition Fixed Pupils

Large pupils One large pupil
Level of consciousness for comatose patient
Alertness: Alert patient opens eyes, looks at you, and responds fully and appropriately.
Lethargy: Patient appears drowsy but opens eyes, looks at you, responds to questions, and falls asleep.
Obtundation: Patient opens eyes, looks at you, responds slowly, and is somewhat confused.
Stupor: Patient arouses from sleep only after painful stimuli. Verbal responses are slow or absent. Patient lapses into unresponsive state when stimulus ceases and has minimal awareness of self or environment.
Coma: Patient is unarousable and eyes are closed. There is no evident response to inner need or external stimuli.
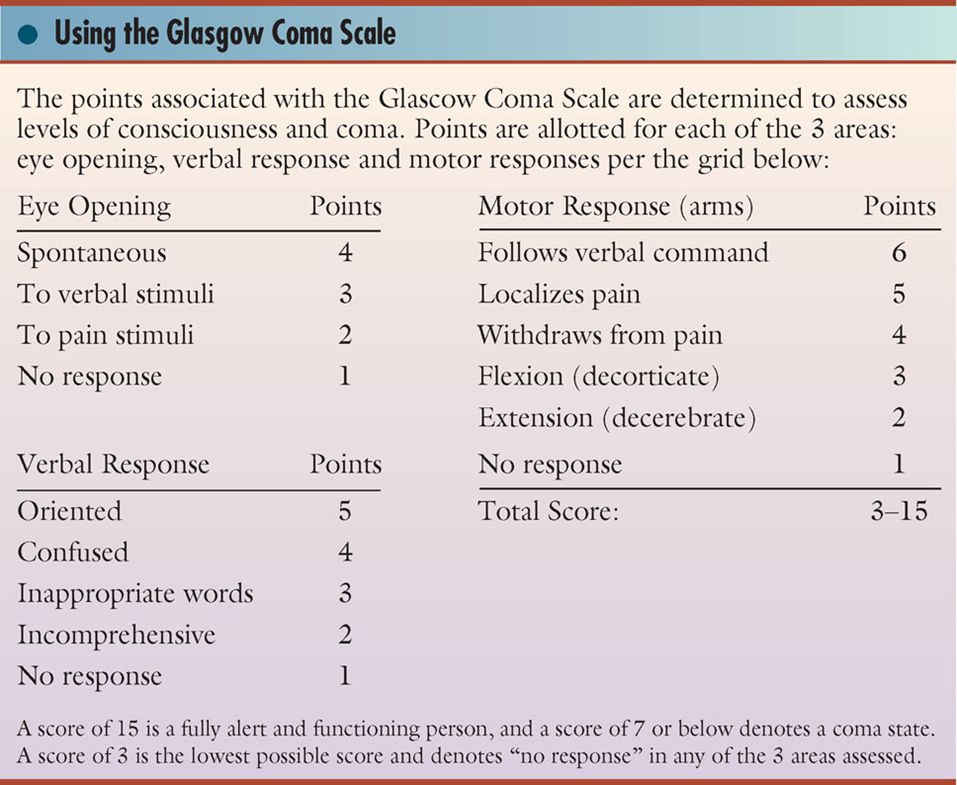
Glasgow Coma Scale
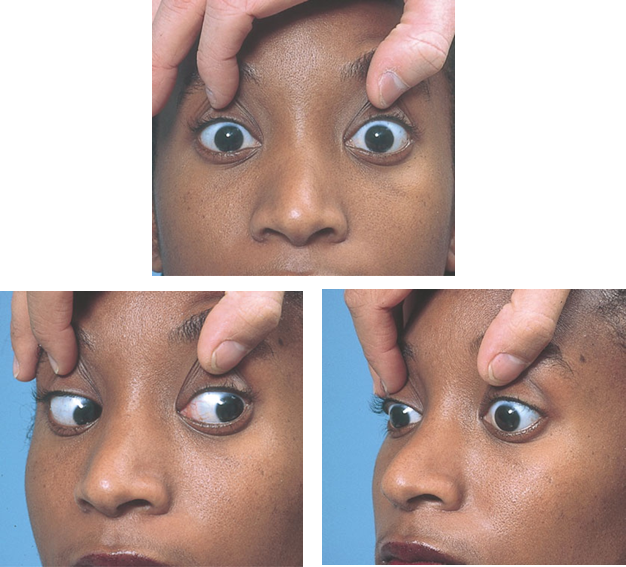
Neurological evaluation of comatose patient
Respirations
Pupils
Ocular movement
Oculocephalic reflex
Posture and muscle tone
If no there is spontaneous movement, apply painful stimuli.
Classify results:
Normal/avoidant: pushes the stimulus away
Stereotypic: evokes abnormal response
Flaccid paralysis or no response
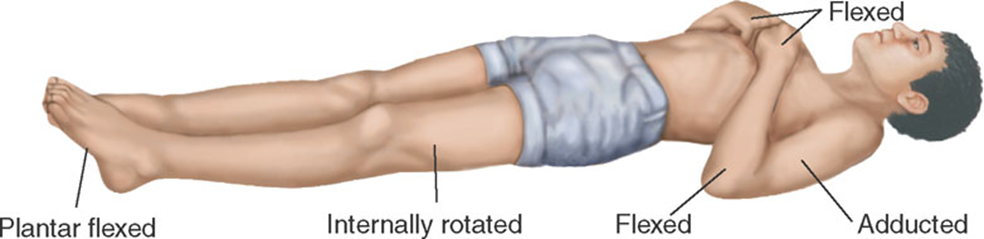
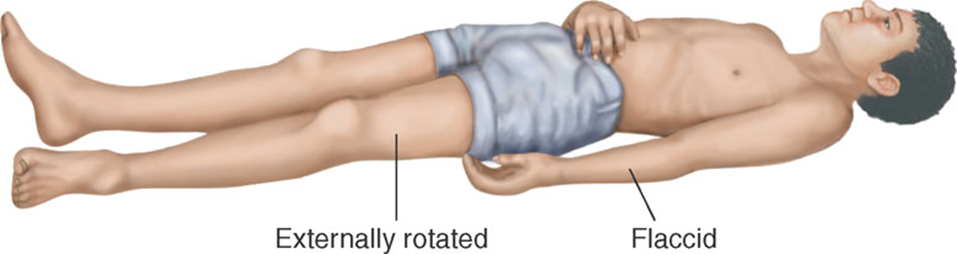
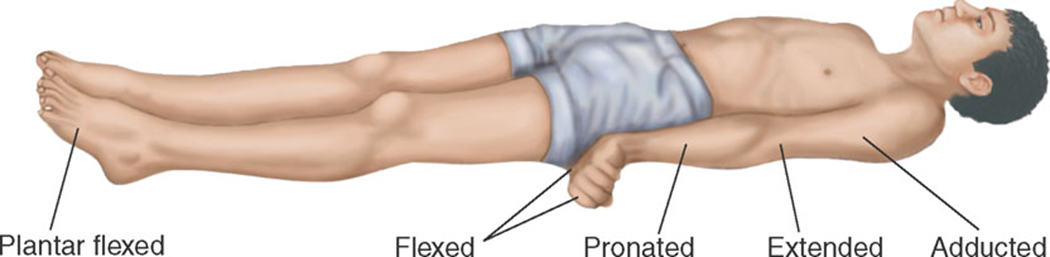
Neurological evaluation for comatose patient
Decorticate Rigidity
Hemiplegia (Early)
Decerebrate Rigidity
Recording Your Findings
Mental status
Cranial nerves
Motor
Sensory
Reflexes
Health Promotion and Counseling
Important topics for health promotion and counseling
Preventing strokes or transient ischemic attack
Reducing risk of peripheral neuropathy
Preventing stroke and transient ischemic attack Health Promotion and Counseling
Stroke
Third leading cause of death
Leading cause of long-term disability
Symptoms and signs depend on vascular territory affected in brain.
Most common: middle cerebral artery
Stroke warning signs
Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg
Sudden confusion or trouble speaking or understanding
Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, or loss of balance or coordination
Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
Sudden severe headache
Stroke risk factors: primary prevention
Hypertension
Smoking
Hyperlipidemia
Diabetes
Excess weight
Lack of exercise
Heavy alcohol use
Stroke risk factors: secondary prevention
After a TIA, focus on any secondary risk factors.
Atherosclerotic large vessel disease
Cardiac emboli secondary to atrial fibrillation
Small vessel lacunar disease
Idiopathic
Reducing risk of peripheral neuropathies
Diabetes is the most common cause of peripheral neuropathies.
Distal symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy
Autonomic dysfunction
Mononeuritis multiplex
Diabetic amyotrophy