Patterns in the Sky
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocab for the textbook Understanding Our Universe by Stacy Palen and George Blumenthal 4th edition for Astronomy&101
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Zenith
Point directly above the observer in the celestial sphere
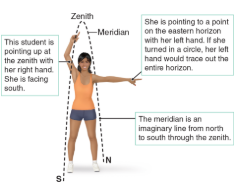
Meridian
The line on the celestial sphere that runs from north to south dividing the sky into an eastern half and a western half
Horizon
The line that separates the sky from the ground. Perpendicular to zenith then spin 360 that’s your horizon

Celestial Sphere
Imaginary sphere with celestial objects in its inner surface.
Initially created by the Ancient Greeks
Constellation
Group of stars that seem fixed pattern on the celestial sphere
Day
Time it takes Earth to rotate on its axis.
A sidereal day is the time it takes for the Earth to complete one full rotation relative to distant stars, approximately 23 hours and 56 minutes.
A solar day, which is about 24 hours, measures the time from one noon to the next, accounting for Earth's orbit around the Sun.
Apparent Daily Motion
The daily path each object takes across the sky.
Altitude
The location of an object above the horizon or the angle formed between the object and the observer's line of sight, measured in degrees.
Latitude
The angular distance north or south from the equatorial plane of a nearly spherical body
Longitude
Circumpolar
Can always be seen from the horizon from a specific location on Earth, appearing to circle around the celestial pole.
Revolve
One object orbits another
Rotate
Spin on an axis
Ecliptic
The annual path of the sun against the stars; this follows the zodiac the 12 constellationsand is the basis for the changing seasons and the positions of celestial objects in the sky.
Summer Solstice
When the north pole is titled towards the sun, the day when the sun is the highest in the sky as it crosses the meridian, the sun rises farthest north of east, sets furthest north of west, marks the first day of summer typically on June 21
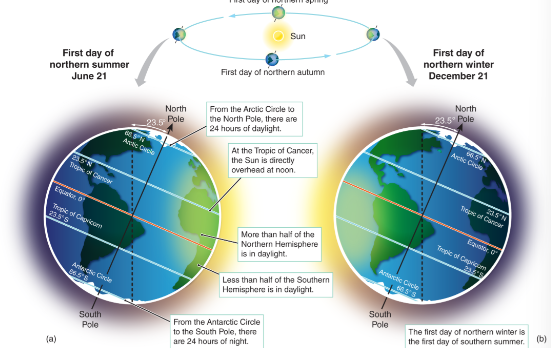
Winter Solstice
When the north pole is tilted away from the sun, resulting in the shortest day of the year, typically occurring around December 21.

Equinoxes
Twice a year when day and night are of approximately equal length, marking the beginning of spring and fall, typically occurring around March 21 and September 23.
Tropical Year
The time between equinoxes which is slightly shorter than 1 solar Earth orbit and is approximately 365.24 days long, marking the cycle of seasons.
Tropics
the regions of Earth located between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5 N and 23.5 S), the sun is directly overheard on the equinoxes
Precession of the Equinoxes
The change of the positon of the equinoxes over time due to the Earth's axial tilt and orbital motion, resulting in a gradual shift in the alignment of the stars as viewed from Earth.
Noon
The time at which the Sun crosses the meridian.

Equator
Imaginary line on Earth dividing it in half.
At the equator all stars rise and set each day.
At other latitudes, the celestial equator intersects the horizon due east and due west. Therefore, a star on the celestial equator rises due east and sets due west. Stars north of the celestial equator rise north of east and set north of west. Stars south of the celestial equator rise south of east and set south of west.
Tropical Year
The time between one crossing ot the vernal equinox and the next. Slightly shorter than the time it takes for Earth to orbit once about the sun.
New Moon
When the moon is between Earth and the sun.
Far side illuminated, from Earth its in darkness.
-UP AT DAYTIME.
Up at daytime
NEVER visible in night
Rises with the sun at sunrise
Crosses the meridian near noon
Sets with the sun in the west.
Cresent
Phase in which the object appears less than half illuminated by the Sun
Gibbous
Phase in which the object appears more than half illuminated by the Sun

Waxing Crescent
Moon visible east of the sun
Most noticeable just after sunset, near the west
Lit on the west side
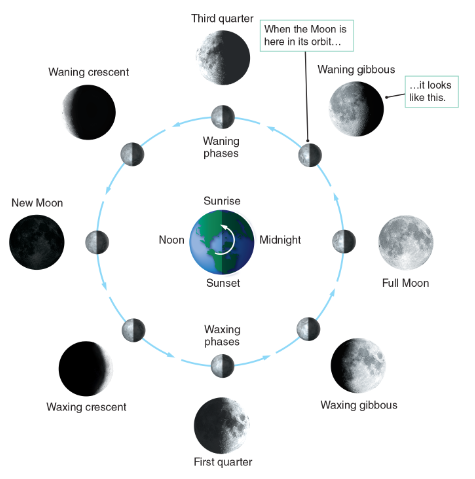
First Quarter Moon
1 week after a new moon
Named due to a fourth of its way through orbit
Rises at noon
Meridian at Sunset
Sets as Midnight
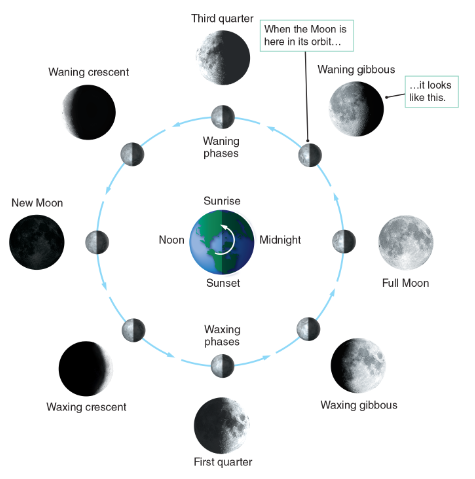
Full Moon
Opposite of the sun
Viewed from Earth fully illuminated by the sun
2 weeks after the new moon
Rises as the sun sets
Meridian at midnight
Sets at sunrises

Third Quarter Moon
Half of the near side is in sunlight and half darkness
Rises at Midnight
Crosses meridian near sunrise
Sets at noon
Eclipse
When the shadow of one astronomical object falls on another
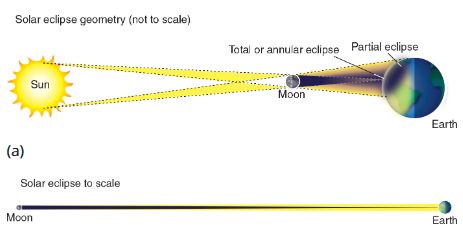
Solar eclipse
When the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun casts a shadow on Earth.
small shadow
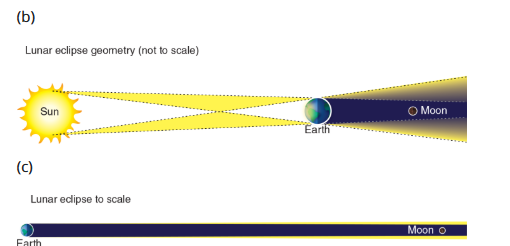
Lunar Eclipse
Moon is in the Earth’s shadow occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, causing the Earth’s shadow to cover the Moon.