Chapter 6: The Skeletal System
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/91
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
1
New cards
5 skeletal system functions (SMP BS)
1. Support (bone and cartilage)
2. Protection (skull, ribs, sternum, vertebrae)
3. Movement (tendons, ligaments)
4. Storage (Ca++, P, fat)
5. Blood cell production (bone marrow)
2. Protection (skull, ribs, sternum, vertebrae)
3. Movement (tendons, ligaments)
4. Storage (Ca++, P, fat)
5. Blood cell production (bone marrow)
2
New cards
Which type of cartilage do most bones develop from?
hyaline cartilage
3
New cards
What is the matrix of hyaline cartilage made of?
collagen fibers (strength) and proteoglycans (resiliency)
4
New cards
Chondroblasts
specialized cells that form the matrix of hyaline cartilage
5
New cards
Chondrocytes
specialized cells in lacunae that maintain the matrix of hyaline cartilage
6
New cards
Perichondrium
Dense irregular connective tissue membrane covering cartilage
7
New cards
Articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage that covers ends of bones in joints
8
New cards
Does articular cartilage have a perichondrium?
no
9
New cards
Appositional growth in cartilage
when chondroblasts in the perichondrium add new cartilage to the (outside) edge of the existing cartilage
10
New cards
Interstitial growth in cartilage
when chondrocytes divide within the cartilage
11
New cards
Bone matrix composition
35% organic collagen fibers (proteoglycans also) that provide flexible strength & 65% inorganic hydroxyapatite (CaPO4 crystals) that bear weight
12
New cards
What would happen if the calcium was removed from the bone?
the bone would be too bendy
13
New cards
What would happen if the collagen was removed from the bone?
the bone would be too brittle
14
New cards
Which of these is correctly matched?
A. Organic: collagen
B. Inorganic: collagen
C. Organic: hydroxyapatite/CaPO4crystals
D. Inorganic: protein fibers
A. Organic: collagen
B. Inorganic: collagen
C. Organic: hydroxyapatite/CaPO4crystals
D. Inorganic: protein fibers
A. Organic: collagen
15
New cards
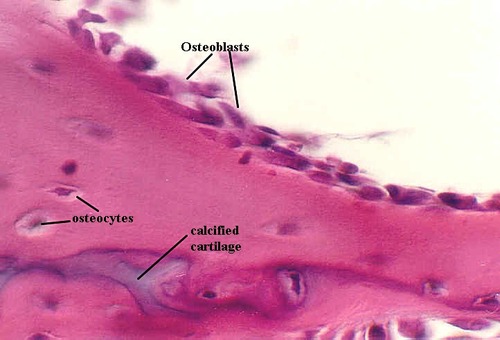
Osteoblasts
cells surrounded by bone matrix that carry out ossification/osteogenesis and communicate through gap junctions
16
New cards
Osteocytes
mature bone cells found in lacunae that maintain matrix

17
New cards
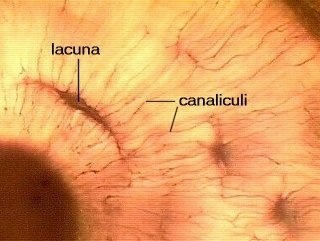
Lacunae
occupied spaces by osteocyte cell body
18
New cards
Canaliculi
occupied canals by osteocyte cell processes
19
New cards
Osteoclasts
large, multi-nucleated cells with a ruffled border formed by the contact of the PM of osteoclasts/bone matrix that breakdown/reabsorb already existing bone via H+ ions (decalcify the bone matrix) and enzymes (digest protein component of matrix)
20
New cards
How do osteoclasts break down bone?
by secreting H+ and protein-digesting enzymes that dissolve calcium phosphate in bone
21
New cards
Stem cells (Osteochondral Progenitor cells)
become either chondroblasts or osteoblasts
22
New cards
Woven bone
immature bone present during fetal development or in the early stages of repair where collagen fibers are randomly oriented
23
New cards
Lamellar bone
mature bone present after remodeling where collagen fibers are oriented in one direction in each lamella
24
New cards
lamellae
concentric, circumferential, and interstitial layers of the bone matrix
25
New cards
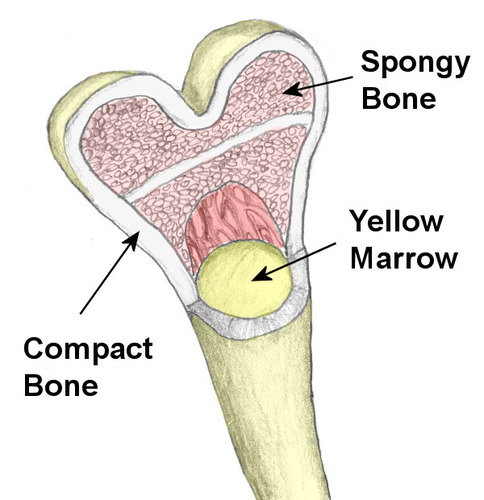
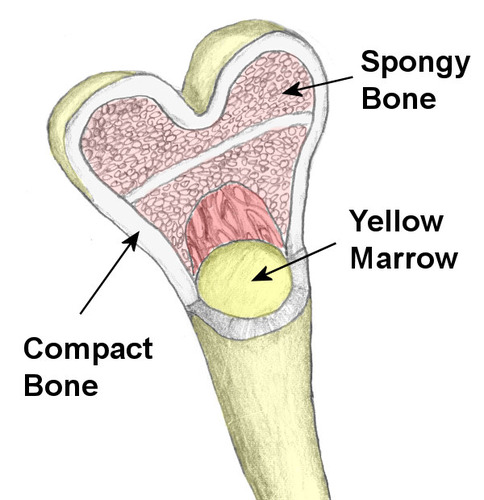
Cancellous/Spongy bone
bone made of trabeculae that have spaces filled with blood vessels and bone marrow, are covered with a single layer of cells (osteoblasts/clasts), and are oriented along stress lines
26
New cards
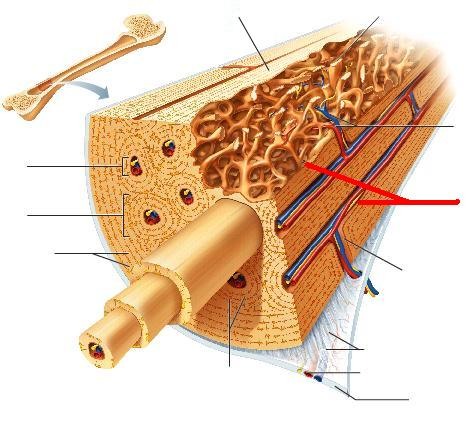
trabeculae
interconnecting rods or plates of bone (like scaffolding
27
New cards
Compact bone
denser bone with fewer spaces, so the blood vessels enter the bone itself
28
New cards
Central/Haversian canals
grooves that run parallel to the bone shaft contain blood vessels, nerves, & L. C. T.
29
New cards
endosteum
membranous lining of the hollow cavity of the bone
30
New cards
periosteum
A dense fibrous membrane that covers the surface of bones and serves as an attachment for tendons and muscles
31
New cards
Perforating/Volkmann's canals
grooves that run perpendicular to the bone shaft and serve as entry points for blood vessels from the periosteum or endosteum
32
New cards
Osteon/Haversian system
the microscopic, functional, and repeating unit of compact bone that consists of a Haversian canal, its contents, lamellae, lacunae w/ osteocytes, and canaliculi
33
New cards
How do osteocytes receive nutrients and remove waste?
the canal system
34
New cards
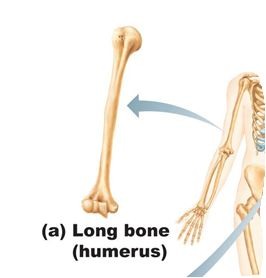
Long bone shape
bones that are longer than wide (Ex: upper and lower limbs)
35
New cards
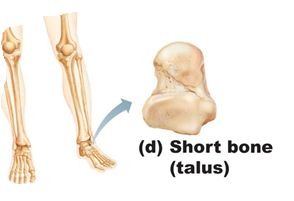
Short bone shape
bones that are nearly cube shaped (Ex: carpals and tarsals)
36
New cards
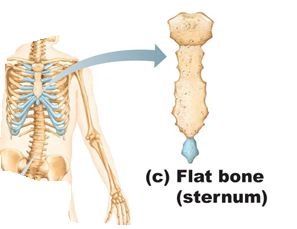
Flat bone shape
bones that are thin, flattened, or curved (Ex: ribs, sternum, skull, or scapulae
37
New cards
Irregular bone shape
bones that are complex shapes (Ex: vertebrae, facial bones)
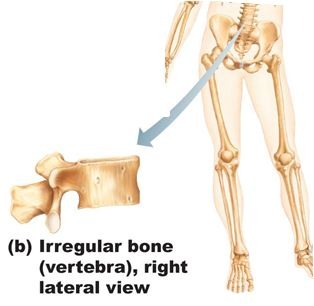
38
New cards
Diaphysis
shaft of a long bone (compact bone mostly)
39
New cards
Epiphysis
end of a long bone (cancellous bone mostly)
40
New cards
Epiphyseal plate
growth plate made of hyaline cartilage until growth stops
41
New cards
Epiphyseal line
remnant of the epiphyseal plate that forms after the bone stops growing in length
42
New cards
Medulary cavity
central, hollowed-out area in the shaft of a bone that contains red blood marrow (all red marrow in children but yellow marrow in the limb bones & skull in adults)
43
New cards
Sharpey's fibers
periosteal fibers that penetrate through the periosteum into the bone that strengthen tendon or ligament attachment
44
New cards
Do flat bones have a diaphysis?
no
45
New cards
Which paired terms are most correct?
A. Epiphysis - shaft of long bone
B. Epiphysis - most is made of compact bone
C. Diaphysis - flat, short, irregular bones
D. Diaphysis - shaft of long bones
A. Epiphysis - shaft of long bone
B. Epiphysis - most is made of compact bone
C. Diaphysis - flat, short, irregular bones
D. Diaphysis - shaft of long bones
D. Diaphysis - shaft of long bones
46
New cards
What does it mean when you see the epiphyseal line?
A. The diaphyseal plate has closed
B. The epiphyseal plate has closed
C. Active cartilage growth is taking place
D. Growth in length is continuing
A. The diaphyseal plate has closed
B. The epiphyseal plate has closed
C. Active cartilage growth is taking place
D. Growth in length is continuing
B. The epiphyseal plate has closed
47
New cards
Intramembranous ossification
bone develops in a connective tissue membrane from embryonic mesenchymal cells
48
New cards
Process of intramembranous ossification (9 steps)
1. Mesenchymal cells in the membrane become osteochondral progenitor (OCP) cells
2. The OCP cells become osteoblasts
3. The osteoblasts produce bone matrix that surrounds the collagen fibers of the connective tissue membrane
4. The osteoblasts then become osteocytes
5. The osteocytes form tiny trabeculae of woven bone
6. More osteoblasts gather on the trabeculae and produce more bone.
7. The resulting spongy bone cells specialize to form red bone marrow
8. Cells surrounding the developing bone specialize to form the periosteum
9. Osteoblasts from the periosteum lay down bone matrix to form an outer surface of compact bone
2. The OCP cells become osteoblasts
3. The osteoblasts produce bone matrix that surrounds the collagen fibers of the connective tissue membrane
4. The osteoblasts then become osteocytes
5. The osteocytes form tiny trabeculae of woven bone
6. More osteoblasts gather on the trabeculae and produce more bone.
7. The resulting spongy bone cells specialize to form red bone marrow
8. Cells surrounding the developing bone specialize to form the periosteum
9. Osteoblasts from the periosteum lay down bone matrix to form an outer surface of compact bone
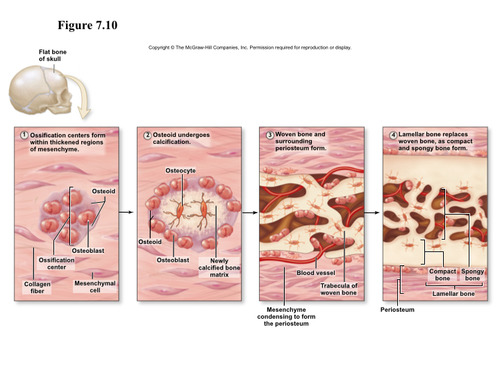
49
New cards
Endochondral ossification
bone develops in cartilage
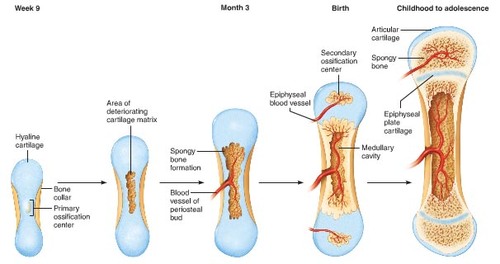
50
New cards
Centers of ossification
locations in the connective tissue membrane where ossification begins then expands to form a bone
51
New cards
Fontanels
large, membrane-covered spaces between developing skull bones
52
New cards
Long bone growth
occurs at the epiphyseal plate and involves the formation of new cartilage by interstitial cartilage growth then appositional bone growth
53
New cards
Appositional bone growth
new layers of bone are added on to the surface of old bone (beneath the periosteum)
54
New cards
Does articular cartilage ossify or persist through life?
it persists throughout life
55
New cards
Zones of epiphyseal plate (5)
1. Resting cartilage
2. Proliferation
3. Hypertrophy
4. Calcification
5. Ossified bone
2. Proliferation
3. Hypertrophy
4. Calcification
5. Ossified bone
56
New cards
Zone of resting cartilage
cartilage attaches to the epiphysis
57
New cards
Zone of proliferation
new cartilage is produced on the epiphyseal side of the plate as the chondrocytes divide and form stacks of cells
58
New cards
Zone of hypertrophy
chondrocytes mature and enlarge
59
New cards
Zone of calcification
matrix is calcified and chondrocytes die
60
New cards
Ossified bone (final zone of the epiphyseal plate)
calcified cartilage on the diaphyseal side of the plate is replaced by bone
61
New cards
Growth at articular cartilage
carried out by chondrocytes near the surface of the articular cartilage and results in the increased size of the epiphyses
62
New cards
Pituitary gigantism
excess growth hormone before growth plates close
63
New cards
Acromegaly
excess growth hormone after growth plates close
64
New cards
Achondroplastic dwarf
improper growth at the growth plate
65
New cards
Factors affecting bone growth (3)
1. Genetics
2. Nutrition
3. Hormones
2. Nutrition
3. Hormones
66
New cards
How does nutrition affect bone growth?
lack of Ca++ and protein during growth causes bones to be small
67
New cards
Rickets
Vitamin D deficiency in children that causes a decrease in mineralization of bone matrix
68
New cards
Osteomalacia
softening of the bone caused by a lack of vitamin D in adulthood
69
New cards
Vitamin C is necessary for
osteoblasts, collagen, wound healing, and teeth to not fall out
70
New cards
Scurvy
Vitamin C deficiency
71
New cards
How do hormones affect bone growth?
1. Growth hormone from the anterior pituitary gland affects interstitial cartilage growth and appositional bone growth
2. Thyroid hormone affects all tissues
3. Sex hormones stimulate growth at puberty and the closure of epiphyseal plates
2. Thyroid hormone affects all tissues
3. Sex hormones stimulate growth at puberty and the closure of epiphyseal plates
72
New cards
Basic multicellular unit (BMU)
a temporary group of osteoclasts and osteoblasts that last about 6 months which remove old bone matrix and replace it with new bone
73
New cards
How long does it take to renew the entire skeleton?
10 years (a decade)
74
New cards
What are the functions of bone remodeling?
bone growth, changes in shape, adjustments to stress, bone repair, and Ca++ ion regulation
75
New cards
How are new osteons formed in compact bone?
osteoclasts break down the matrix and form a tunnel, then osteoblasts form lamellae around the tunnel wall, forming a concentric lamella
76
New cards
4 steps to bone repair
1. Hematoma formation
2. Callus formation
3. Callus ossification
4. Bone remodeling
2. Callus formation
3. Callus ossification
4. Bone remodeling
77
New cards
Hematoma formation
Blood from blood vessels clot
78
New cards
Callus formation
tissue forms at fracture site and connects broken ends
79
New cards
Internal part of callus formation
blood vessels grow into clot, osteoclasts dissolve debris, fibroblasts produce collagen and granulation tissue, chondroblasts produce cartilage, and osteoblasts invade, laying down bone
80
New cards
External part of callus formation
osteoblasts and chondroblasts help the bone/cartilage collar stabilizes into two pieces
81
New cards
Callus ossification
callus replaced by woven, cancellous bone
82
New cards
Bone remodeling
replacement of woven/bone by (lamellar) compact bone
83
New cards
What early structure helps stabilize a fracture during bone repair?
A. Chondroblasts
B. Callus
C. Hematoma
D. Periosteum
A. Chondroblasts
B. Callus
C. Hematoma
D. Periosteum
B. Callus
84
New cards
What cells or tissues do not play a major role in bone repair in the Callus formation stage?
A. Chondroblasts
B. Macrophages
C. Compact bone
D. Osteoblasts
A. Chondroblasts
B. Macrophages
C. Compact bone
D. Osteoblasts
C. Compact bone
85
New cards
Calcium homeostasis
calcium enters bone via osteoblasts and leaves via osteoclasts, affecting blood calcium levels, which are regulated by the parathyroid hormone and calcitonin
86
New cards
How does parathyroid hormone (PTH) affect blood calcium levels?
raises calcium in the blood by stimulating osteoclasts
87
New cards
How does calcitonin affect blood calcium levels?
lowers calcium in the blood by inhibiting osteoclast activity
88
New cards
Effects of aging on the skeletal system
1. Bone matrix decreases and becomes more brittle due to lack of collagen and less hydroxyapatite
2. Bone mass decreases (spongy bone first, then compact bone)
Bone loss causes an increase in fractures, deformity, loss of height, pain, stiffness, stooped posture, & loss of teeth
2. Bone mass decreases (spongy bone first, then compact bone)
Bone loss causes an increase in fractures, deformity, loss of height, pain, stiffness, stooped posture, & loss of teeth
89
New cards
7 types of bone fractures
1. Open (compound) - bone break + open wound where the bone may be sticking out
2. Closed (simple) - no break in skin
3. Incomplete - not across bone
4. Greenstick (incomplete) - fracture on the convex side of the curve of a bone
5. Hairline - two sections of bone do not separate (skull)
6. Comminuted fractures - more than two pieces
7. Impacted - one fragment is driven into the cancellous portion of the other fragment
2. Closed (simple) - no break in skin
3. Incomplete - not across bone
4. Greenstick (incomplete) - fracture on the convex side of the curve of a bone
5. Hairline - two sections of bone do not separate (skull)
6. Comminuted fractures - more than two pieces
7. Impacted - one fragment is driven into the cancellous portion of the other fragment
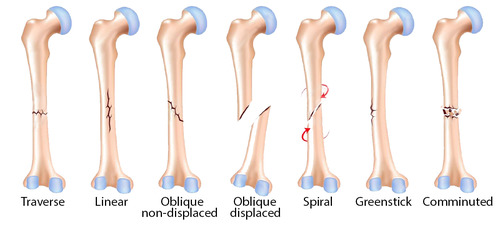
90
New cards
5 classifications of impacted bone fracture
1. Linear
2. Transverse
3. Spiral
4. Oblique
5. Stellate radiating out from a central point
2. Transverse
3. Spiral
4. Oblique
5. Stellate radiating out from a central point
91
New cards
If a 12-year-old were to fracture their epiphyseal plate, the result of the damage could be that the bone:
A. Grows abnormally brittle.
B. May stop growing at the plate.
C. May grow much thicker at the site of the injury.
D. Has a greatly increase potential for a sarcoma.
A. Grows abnormally brittle.
B. May stop growing at the plate.
C. May grow much thicker at the site of the injury.
D. Has a greatly increase potential for a sarcoma.
B. May stop growing at the plate.
92
New cards
What did the Adventist Health Study mentioned at the end of the PowerPoint find? (4 things)
1. Adventist men live 7.3 years longer and Adventist women live 4.4 years longer than other Californians.
2. Five behaviors (not smoking, plant-based diet, nuts several times per week, regular exercise and normal weight), increase life span by up to ten years.
3. Fruits and vegetables lowered risk of heart disease/cancer.
4. Increasing consumption of red and white meat was associated with increased risk of colon cancer
2. Five behaviors (not smoking, plant-based diet, nuts several times per week, regular exercise and normal weight), increase life span by up to ten years.
3. Fruits and vegetables lowered risk of heart disease/cancer.
4. Increasing consumption of red and white meat was associated with increased risk of colon cancer