chapter 14: spinal cord, part 2 - receptors
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
which nervous system provides links TO and FROM the world outside the body?
PNS
the "somatic nervous system" and "autonomic nervous system" (SNS and ANS) are components of?
the PNS's motor (efferent) division
the peripheral nervous system consist of?
ALL neural structures outside the brain and spinal cord
sensory receptors provide information about both ________ and ____________.
external & internal environments
each type of sensory receptor responds BEST to a type of?
stimulus
what is a sensation?
a stimulus we are CONSCIOUSLY aware of
to enter our consciousness, the signals we receive must reach the?
cerebral cortex
what is one way that we categorize sensory receptors?
by the modality of the stimulus, or the stimulating agent
receptors that detect chemicals dissolved in fluid
chemoreceptors
chemoreceptors include
both exteroceptors (eg smell of food) and interoceptors (eg O2 levels in blood)
receptors that detect changes in temperature
thermoreceptors
thermoreceptors can be found in
skin and hypothalamus
receptors that detect changes in light intensity, color, or movement
photoreceptors
photoreceptors are found in
retina of the eye
receptors that detect distortion of cell membrane
mechanoreceptors
mechanoreceptors include receptors for?
touch, pressure, vibration, stretch
baroreceptors
detect changes in blood pressure
proprioceptors
monitor the position and movement of skeletal muscles and joints
specialized receptors
in your skin sense touch; they pick up light touch, vibrations, temperature, and pain
mechanoreceptors can function as
baroreceptors, proprioceptors, tactile receptors, specialized receptors in inner ear
receptors that detect painful stimuli
nociceptors (noci-ceptors)
two divisions of nociceptors
somatic & visceral; chemical, heat, mechanical damage
other than the modality of the stimulus, what is another way we can categorize sensory receptors?
location
receptors that detect stimuli from the external environment
exteroceptors
receptors that detect stimuli from the internal organs
interoceptors
receptors that detect body & limb movements
proprioceptors
skin and mucus membrane receptors are
exteroceptors
special sense receptors are
exteroceptors
SOMATOSENSORY receptors of muscles, tendons, joints are
proprioceptors
other than the modality of the stimulus and location, what is another way we can categorize sensory receptors?
structure of the receptors
in terms of classification by receptor structure, we have two types. they are?
simple receptors for general senses, and receptors for special senses
general senses
TACTILE - temperature, pain, touch, pressure, vibration, proprioception, stretch
special senses
vision, hearing, taste, smell, equilibrium
what helps to determine stimulus duration?
receptor adaptation, the decreased sensitivity to continuous stimulus
a TONIC receptor shows _________ adaptation, and will respond ________________.
slow; continuously as long as the stimulus is present
a PHASIC receptor shows _________ adaptation, and will respond ________________.
rapid; briefly at the onset or offset of a stimulus
explain tonic vs phasic receptors
tonic = monitor steady, ongoing stimuli & thus help maintain awareness of CONSTANT conditions, such as balance or stretch
meanwhile, phasic = quickly respond to a new movement, but dont detect its persistence; ex when u wear a watch, u feel it at first, but after a short time, you stop noticing it unless the watch moves or you take it off
pressure receptors would count as
phasic
pain receptors & head position receptors would count as
tonic
the INACCURATE localization of sensory signals is called?
referred pain
why does referred pain happen?
basically, signals from the VISCERA are perceived as originating from the skin or muscle; this is bc somatic & visceral receptors often send signals via the SAME ascending tracts in the spinal cord, so sometimes the somatosensory cortex cant tell the tru source
referred pain: heart attack pain may be referred to? why?
pectoral region & medial arm; sympathetic innervation of the heart & innervation of these skin regions both come from T1-T5 segments of spinal cord
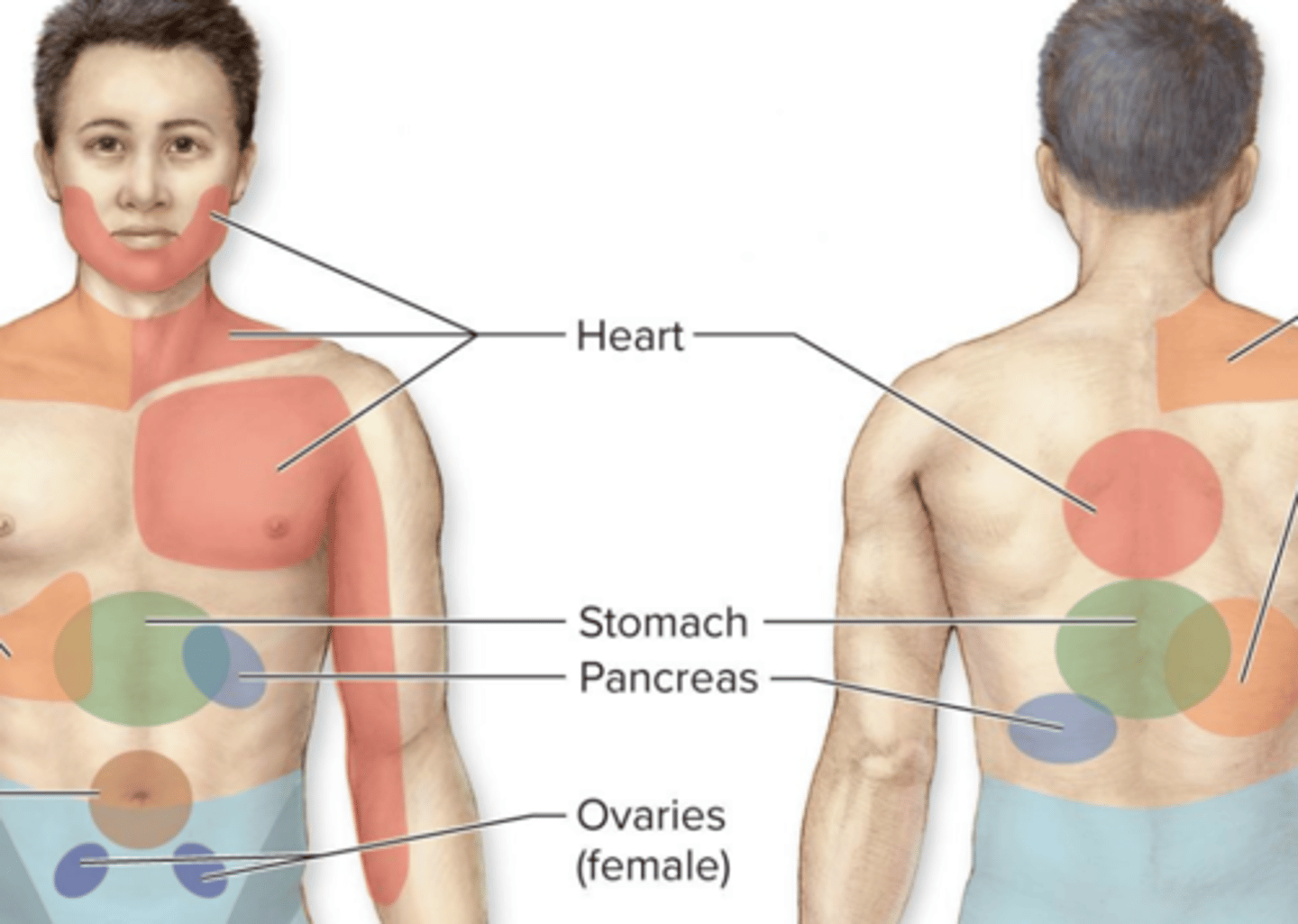
referred pain: kidney/ureter pain may be referred to? why?
INFERIOR abdomen, bc T10-L2 spinal nerves
referred pain: visceral pain is often conveyed along ________ nerves, but occasionally on ___________ nerves. for example
sympathetic, parasympathetic; bladder pain can be conveyed via sacral parasympathetic nerves = referred to buttocks