BIOL 2110L - Iowa State Practical 2 -
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Iowa State
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms

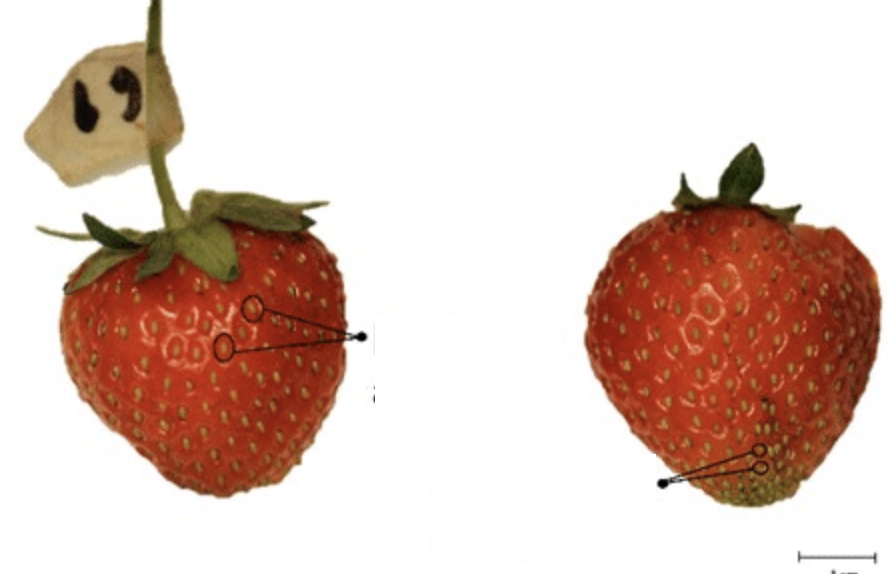
What type of fruit is this image?
Achene, a one-seeded, dry fruit that doesn't split open at maturity. Achenes are typically small and contain a single seed. What we typically call "seeds" in strawberries.
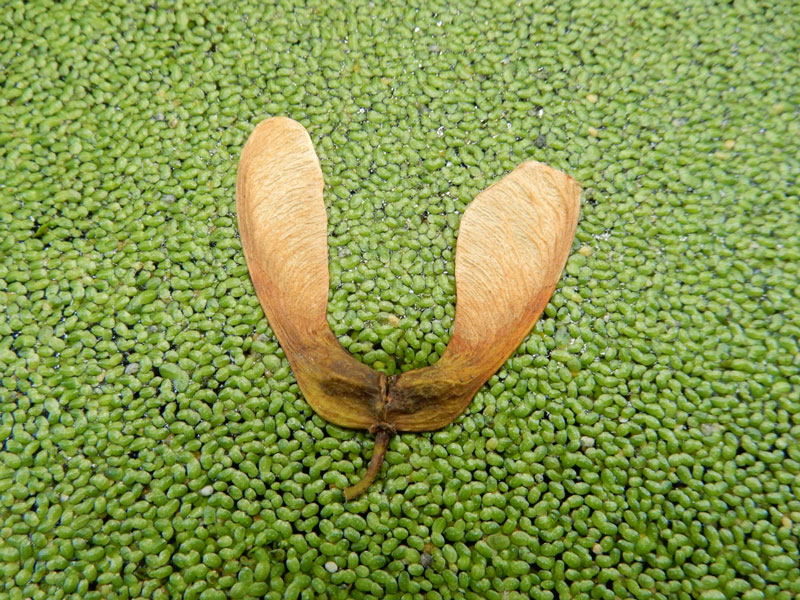


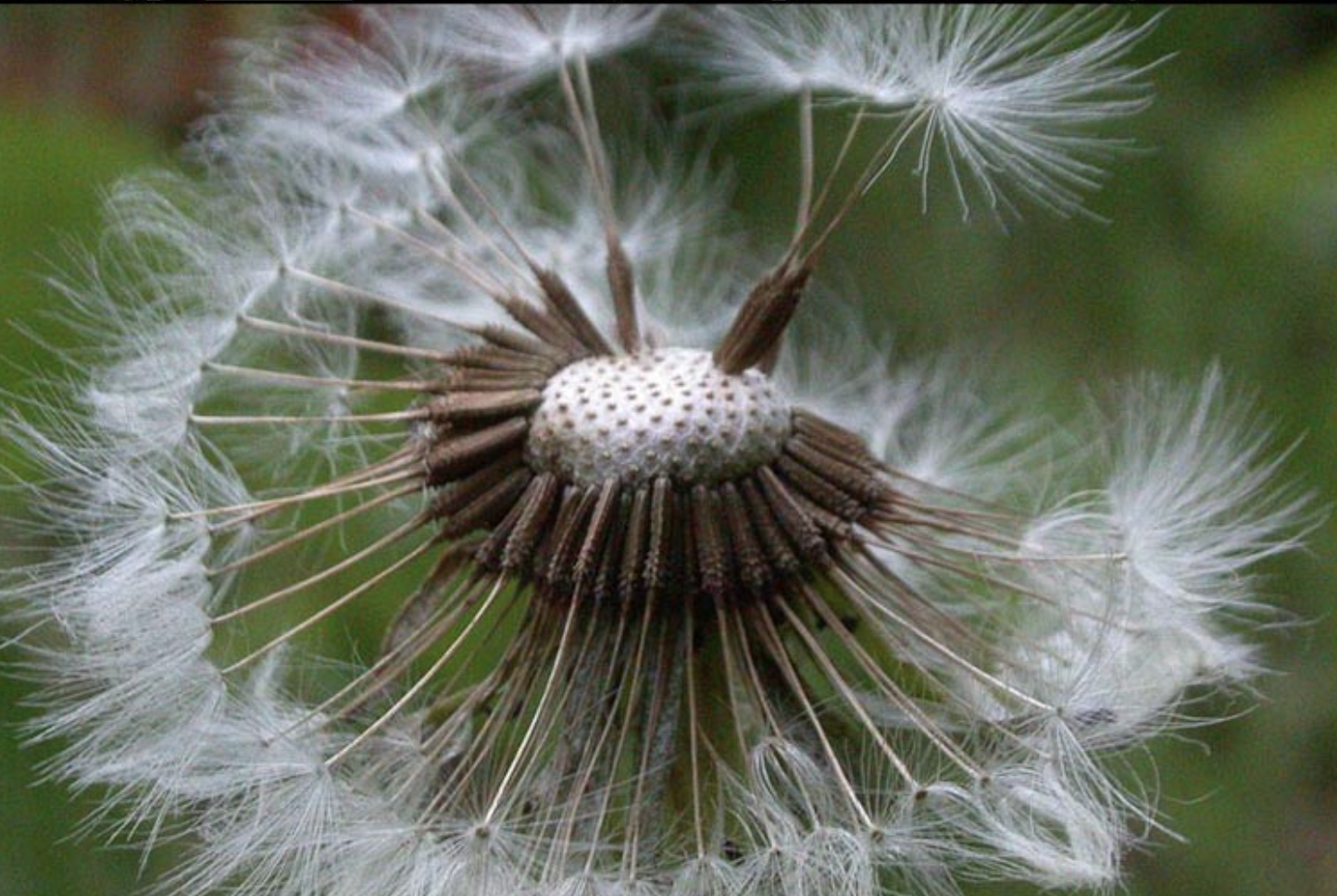
What is the dispersal method of this?
Anemochory, the dispersal of seeds or spores by wind.

What is the pollination of plants by wind called?
Anemophily, which involves the transfer of pollen through the air to fertilize other plants.
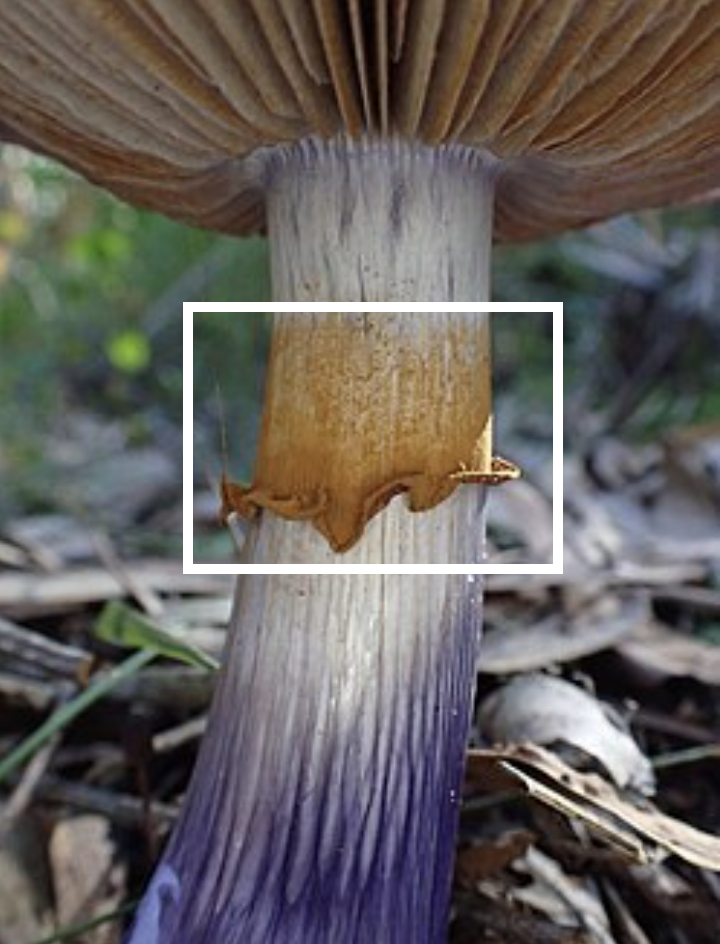

What is in the square?
Annulus, a ring-like structure found on certain fungi, typically marking the location where the veil was attached to the cap.
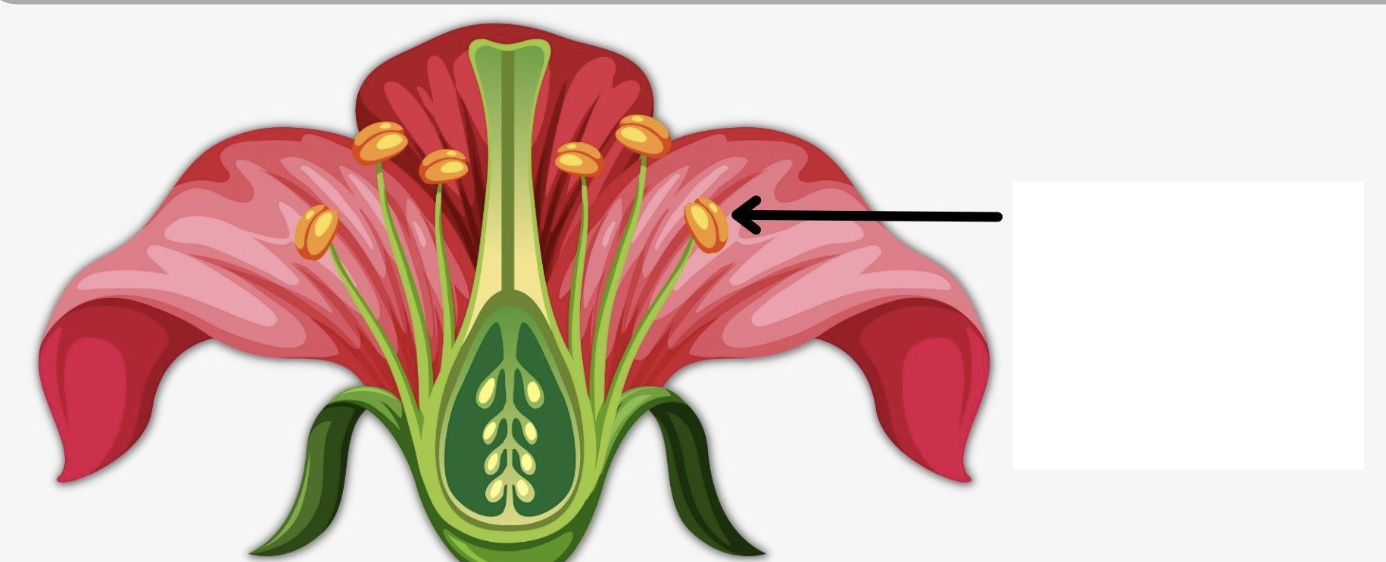
What is the arrow pointing to?
Anther, the part of a flower that produces pollen and is typically located atop the filament.
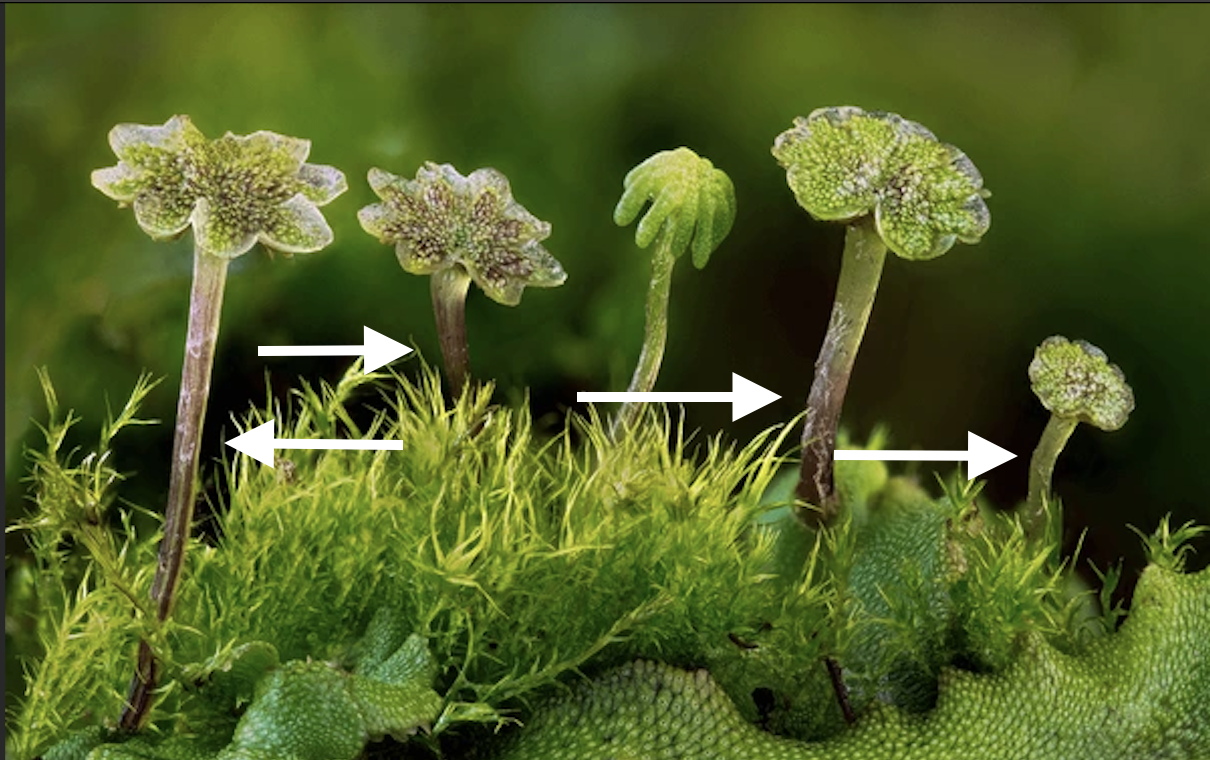

What are the arrows pointing to?
Antheridiophore, a reproductive structure in certain liverworts that bears male gametes (antheridia).
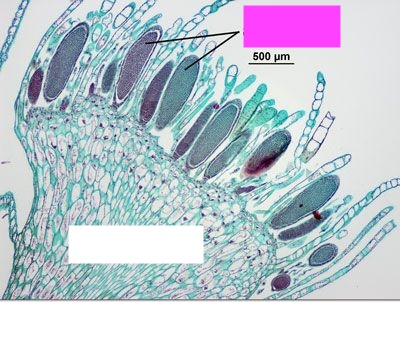
What are the arrows by the pink box pointing to?
Antheridium, the male reproductive structure in certain non-flowering plants that produces sperm.
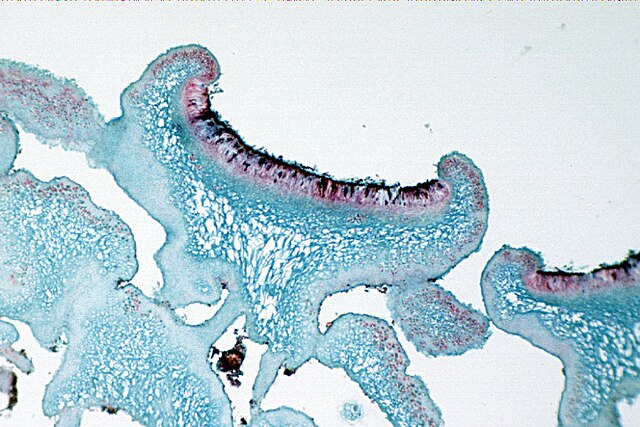
What does the picture display?
Apotheicum, a specialized structure in some fungi that produces ascospores.
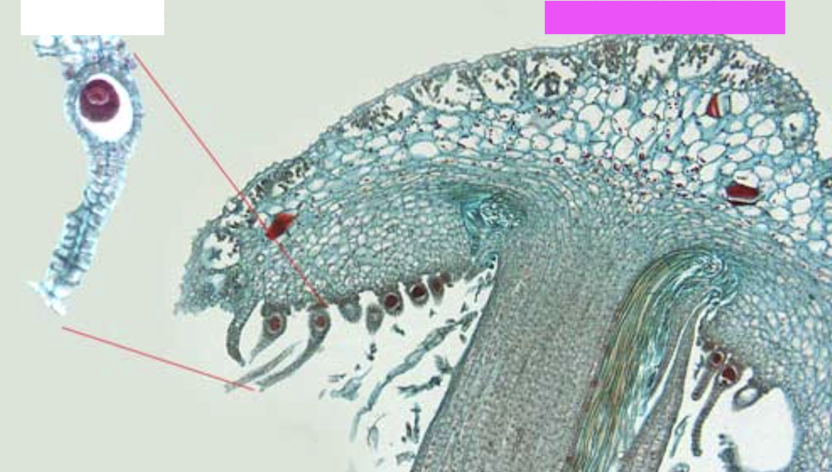
What is the the large structure that the pink box is above?
Archegoniophore, a reproductive structure in certain liverworts that bears female gametes (archegonia).
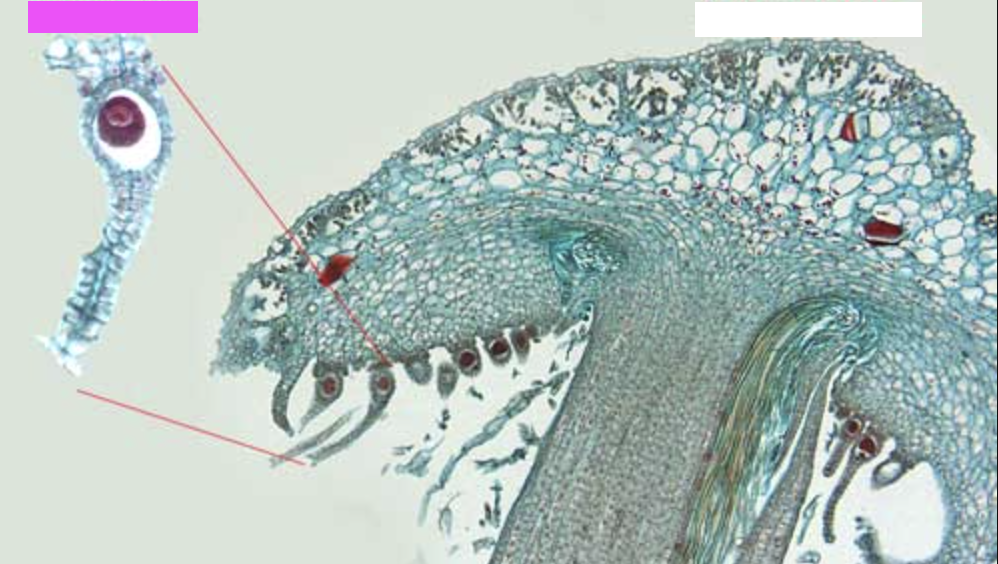
What are the lines by the pink box pointing to?
Archegonium, the female reproductive structure in certain non-flowering plants that produces eggs.
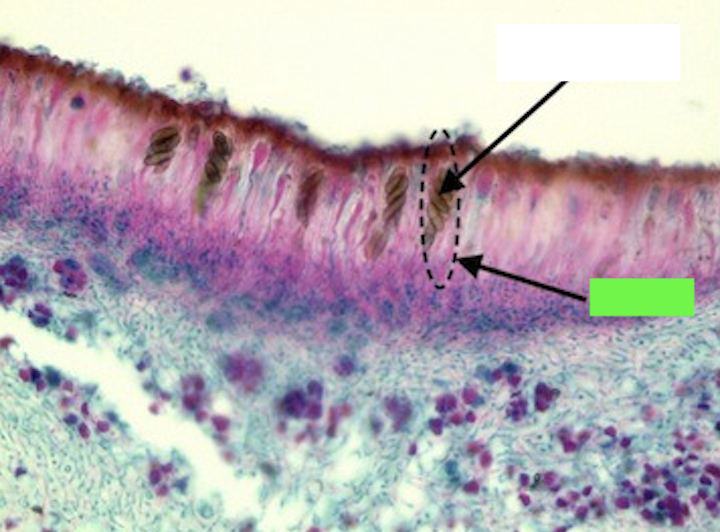
What is the green arrow pointing to?
Ascus, a sac-like structure in fungi that contains and releases ascospores.
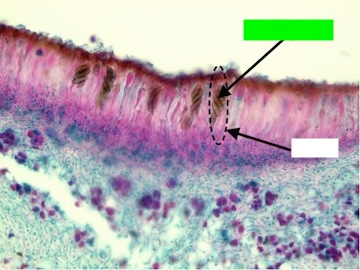
What is the green arrow pointing to?
Ascospore, a fungal spore produced in an ascus during sexual reproduction.
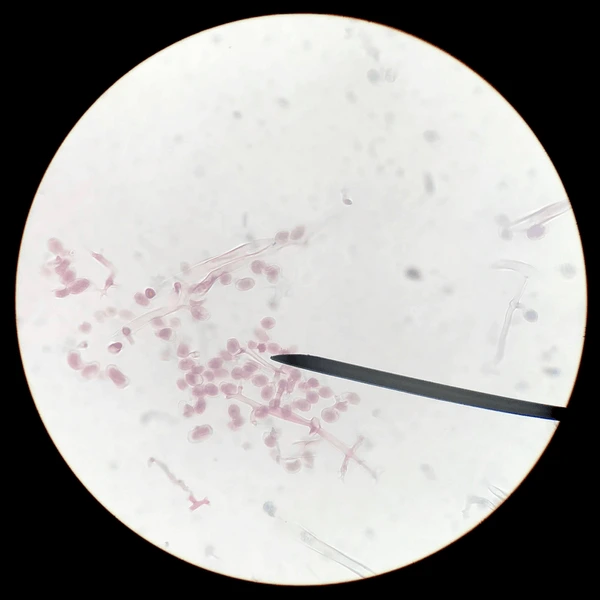
What does this image show?
Asexual spores, the reproductive spores produced by fungi through mitosis.

What type of dispersal occurs with this fruit?
Autochory, the type of dispersal method that where the fruit explodes releasing the seeds?
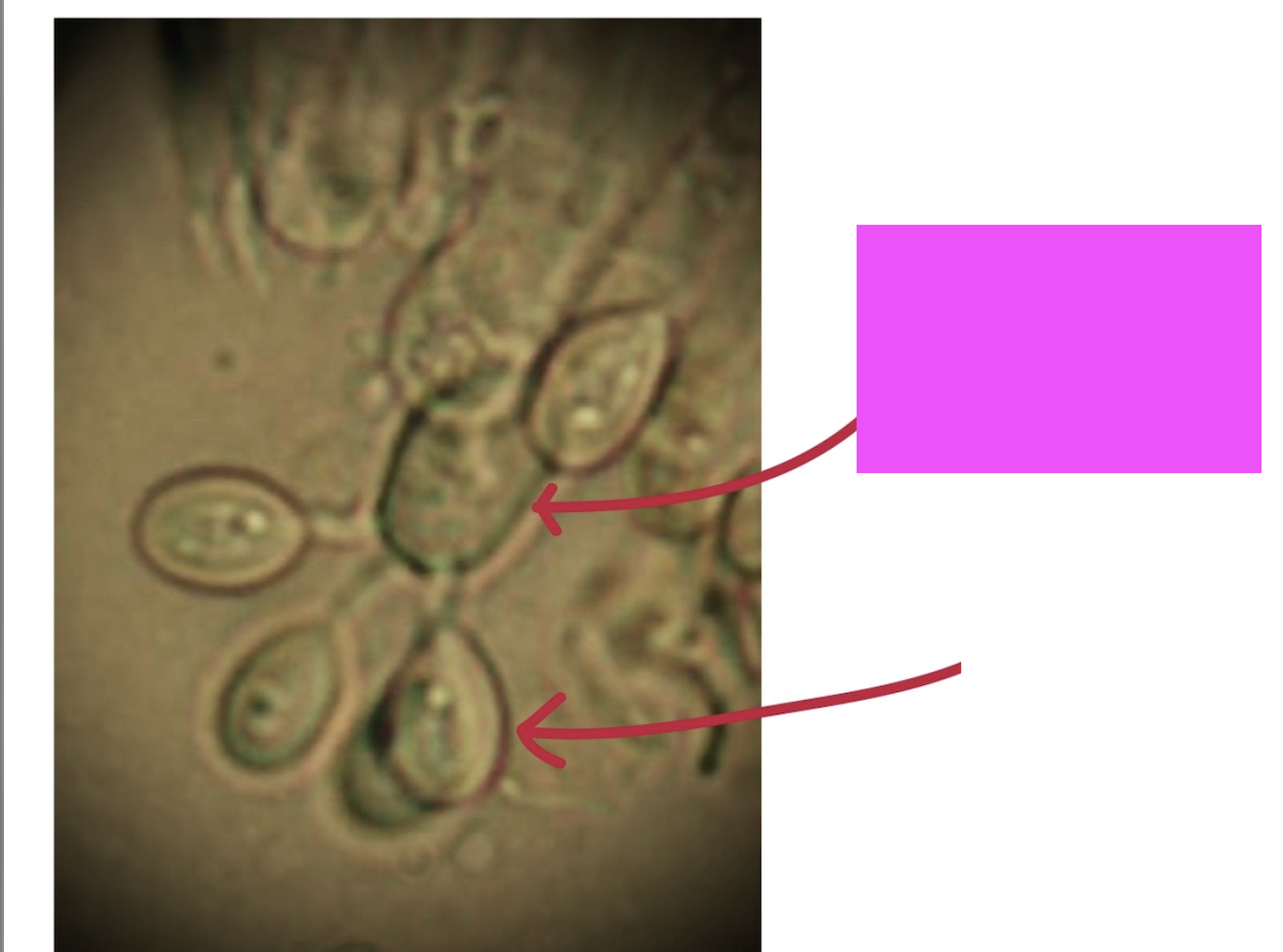
What is the pink arrow pointing to?
Basidium, the spore-producing structure found in certain fungi. It is typically club-shaped and produces basidiospores.
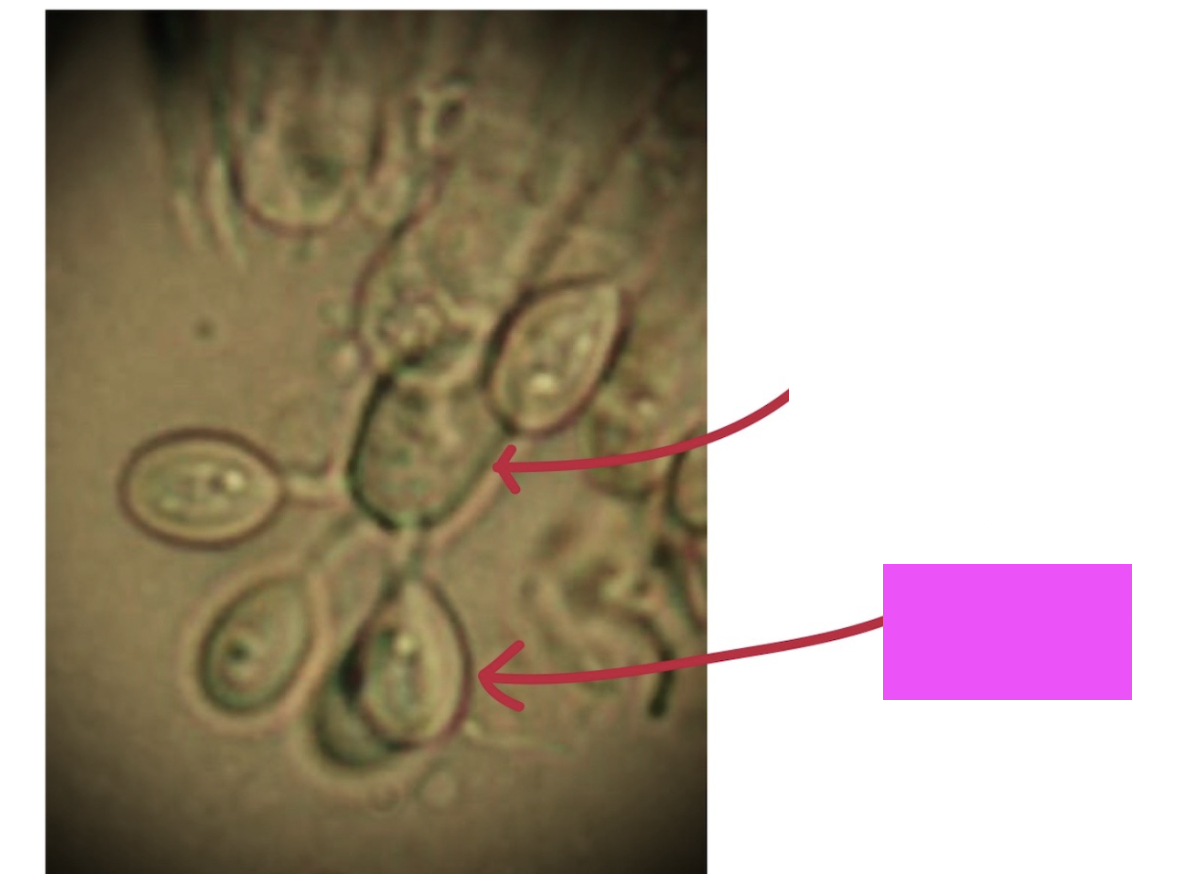
What is the pink arrow pointing to?
Basidiospore, the haploid spore produced by a basidium in fungi.
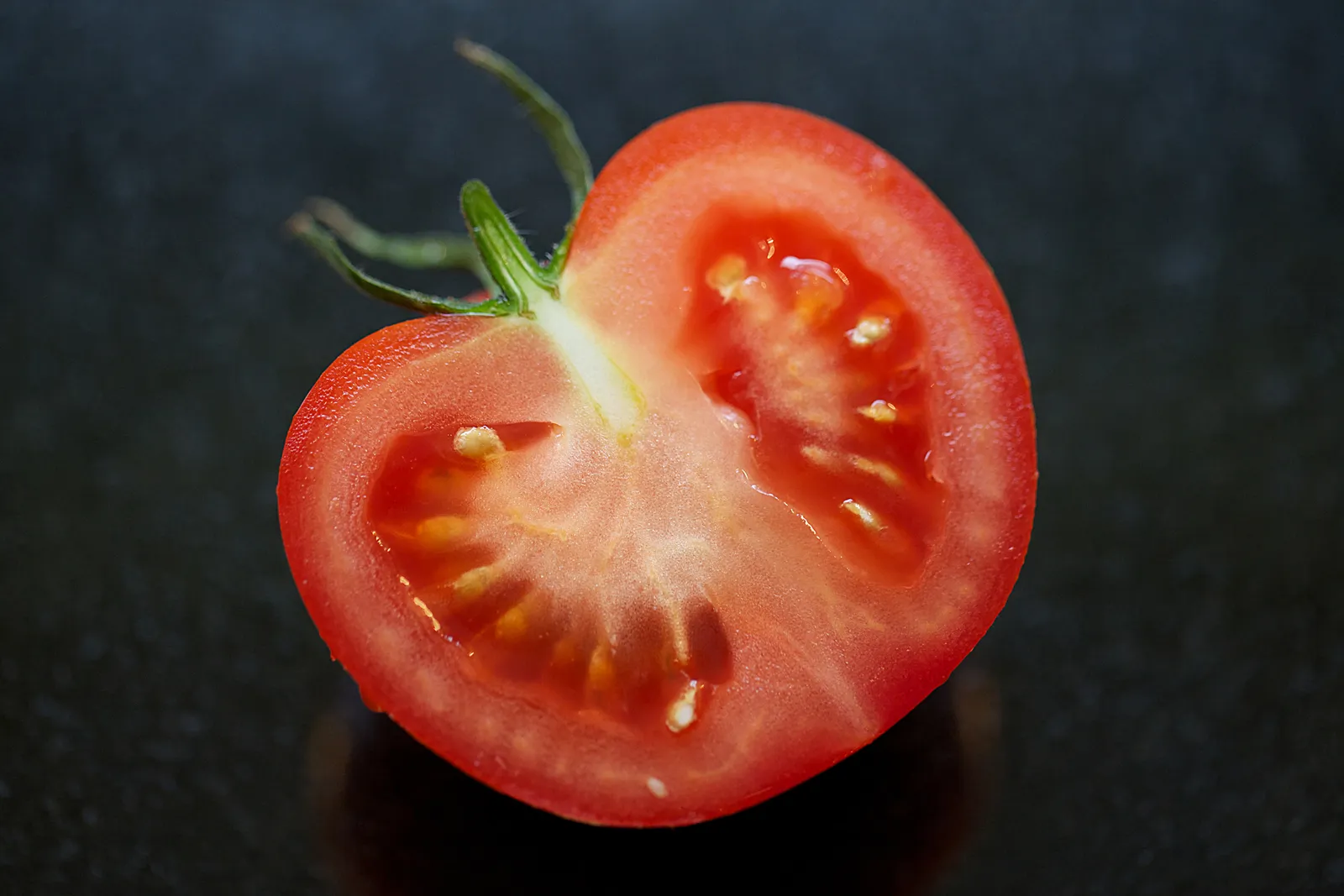

What is this?
Berry, a fleshy fruit that develops from a single ovary, containing multiple seeds.
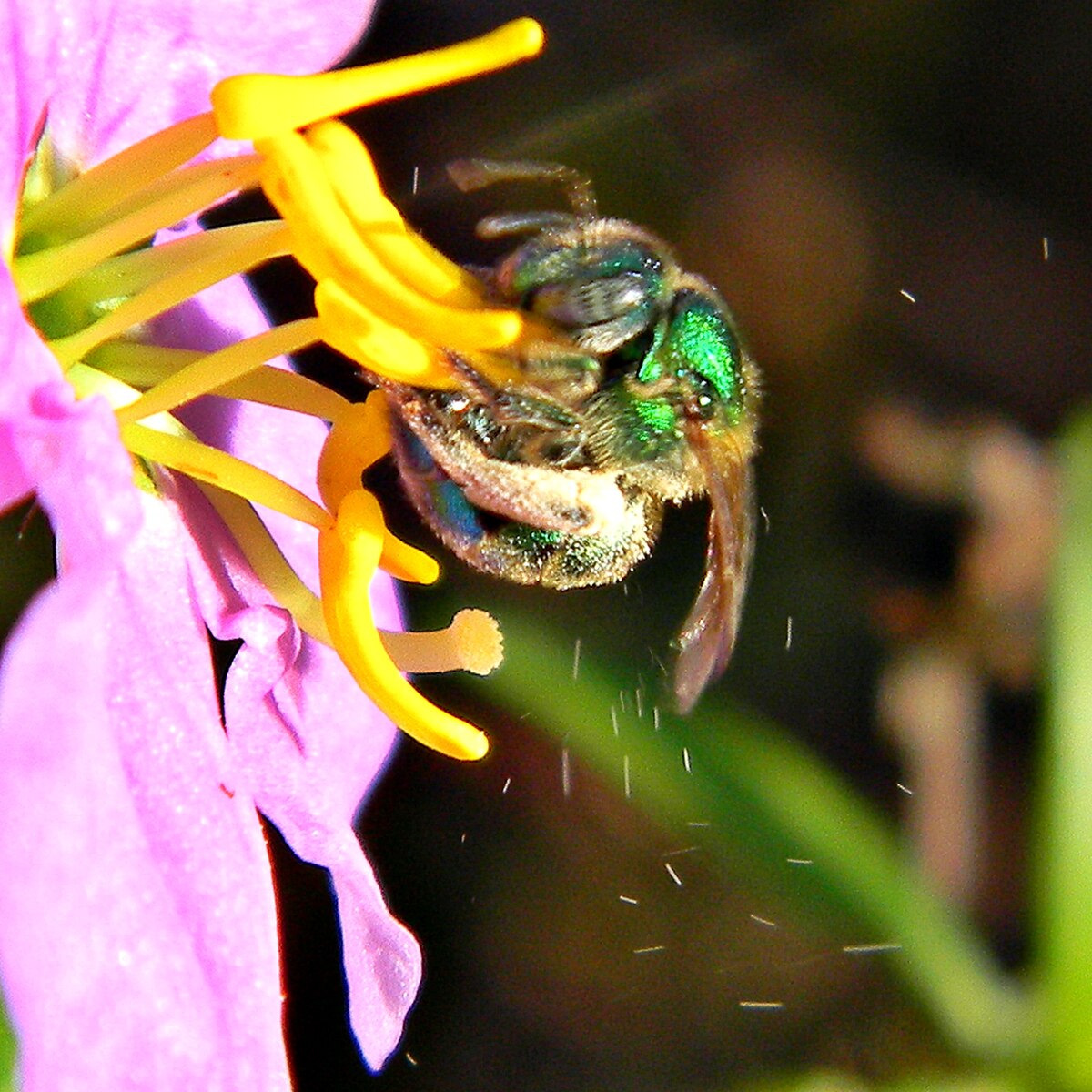

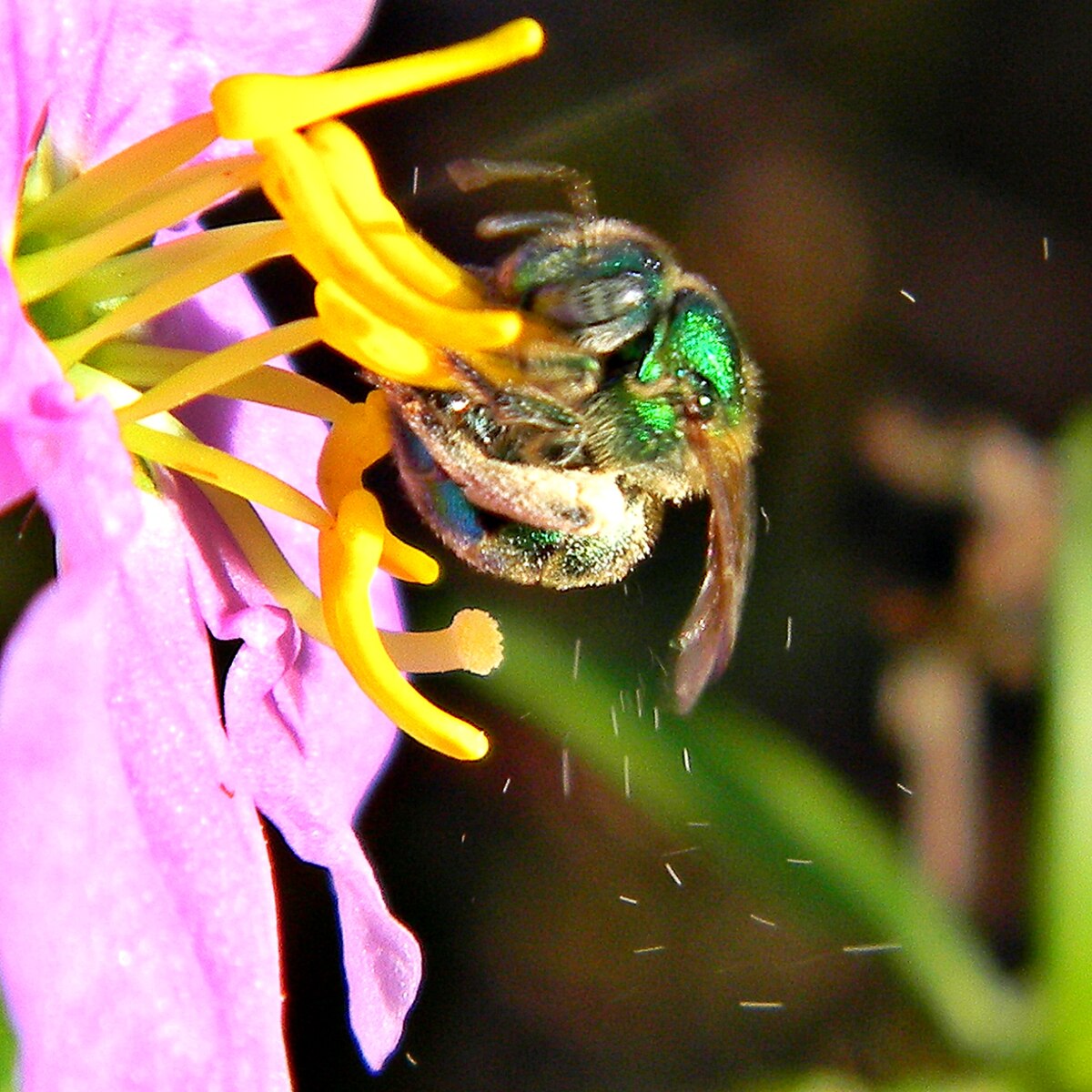
What method of pollination is performed by this?
Buzz pollination, where insects use rapid wing vibration to release pollen from a flower’s anthers.
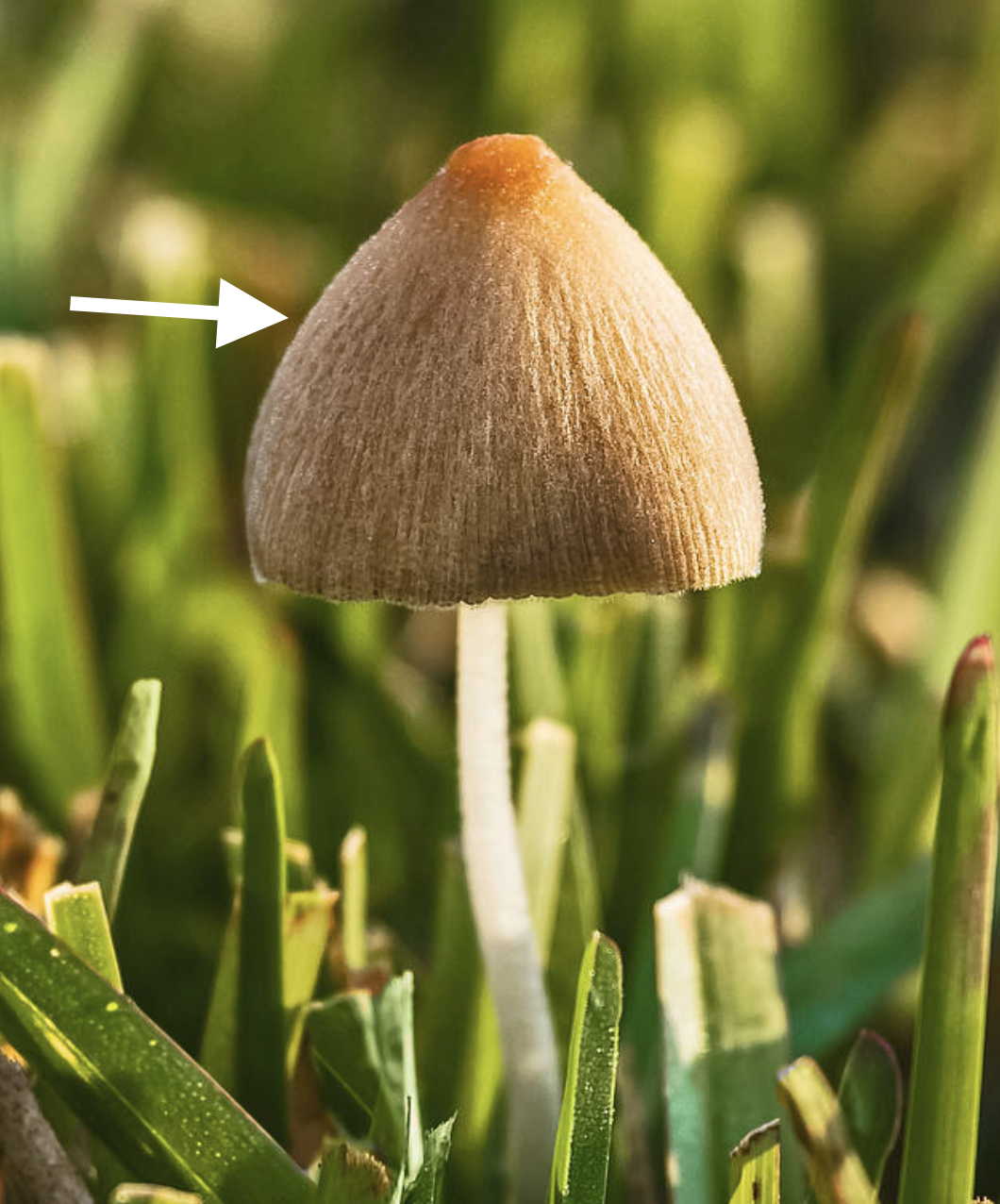

What is the arrow pointing to?
Cap, the top part of a mushroom that houses spores.
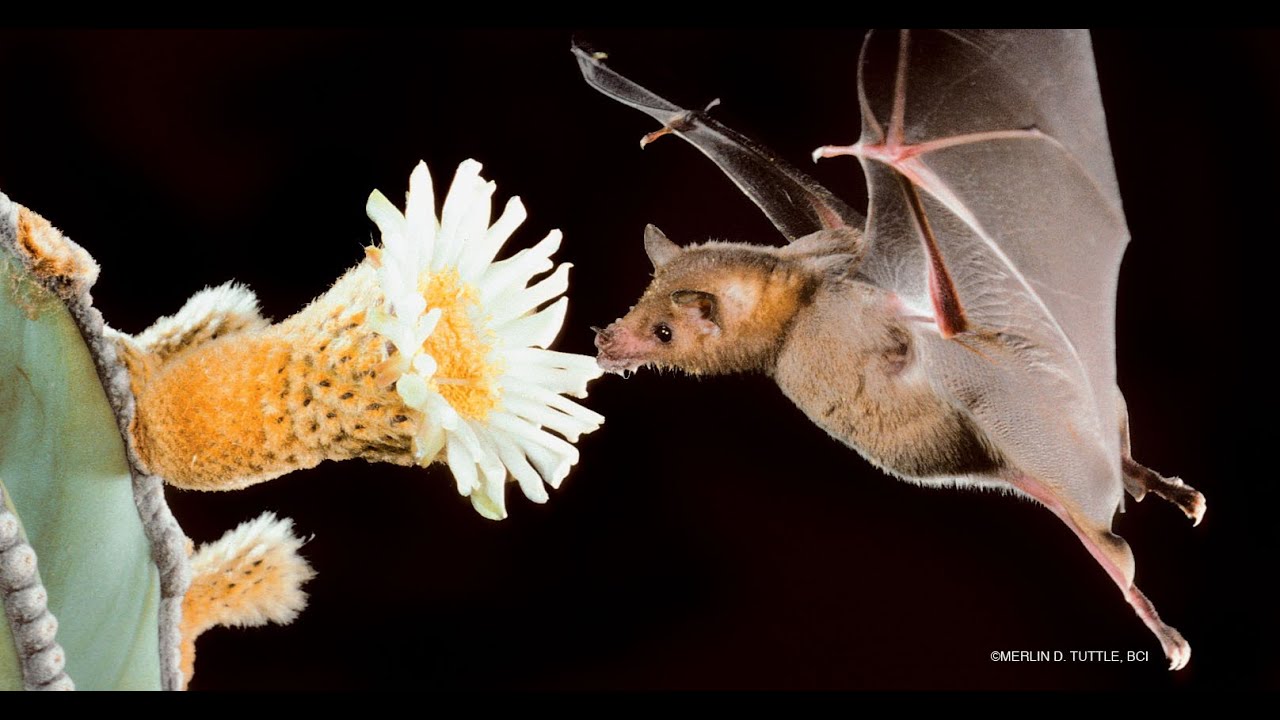

What is the type of pollination occurring in the picture?
Chiropterophily, pollination by bats, often involving large, nocturnal flowers.
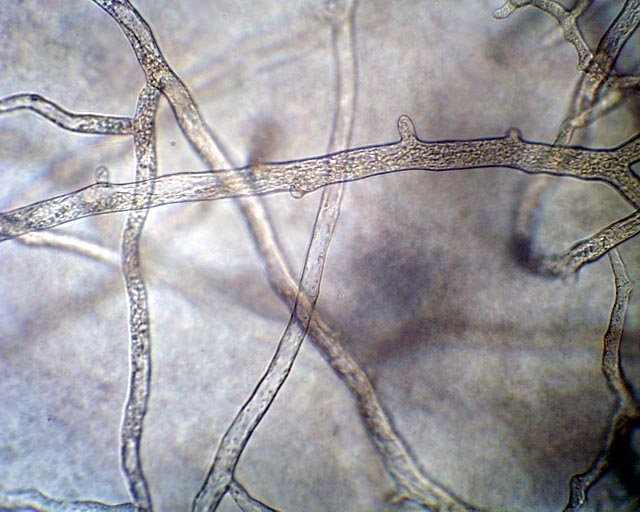
What is shown in this image?
Coenocytic (Aseptate) hyphae, which are hyphae that are multinucleate and lack cross-walls, allowing for continuous cytoplasmic flow.
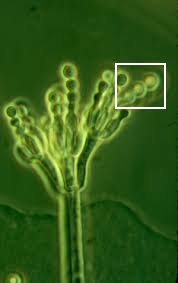
What is pictured in the square?
Conidia
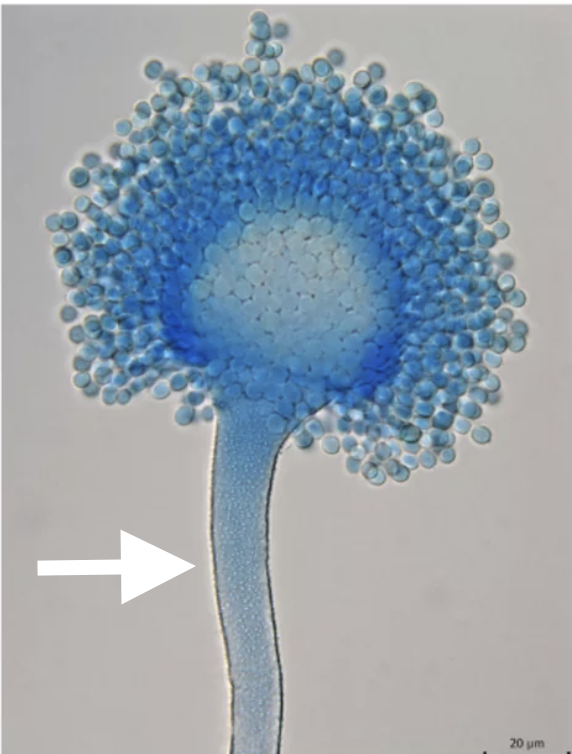
What is the arrow pointing to?
Conidophores, that produce conidia.
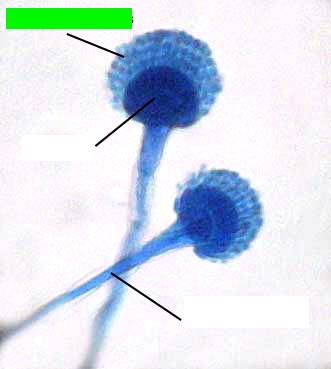
What is the green arrow pointing to?
Conidiospores, which are asexual spores produced at the tips of conidiophores.

What is pictured in the image?
Crustose, a growth form of organisms like lichens and algae that adhere to a surface.
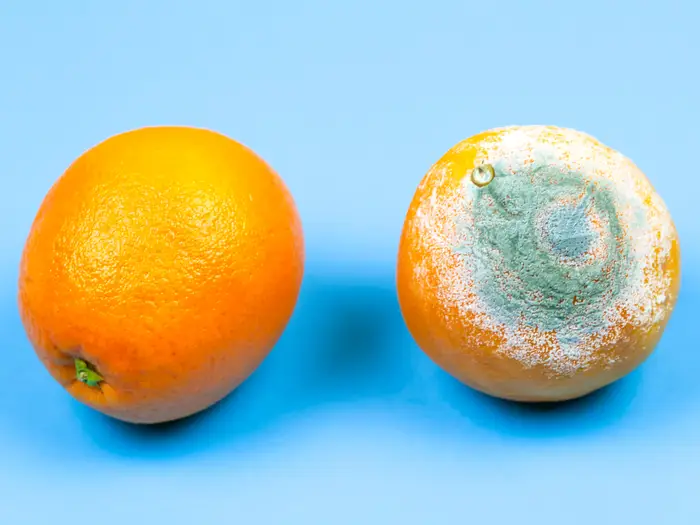

What Phylum does the picture belong to?
Zygomycota
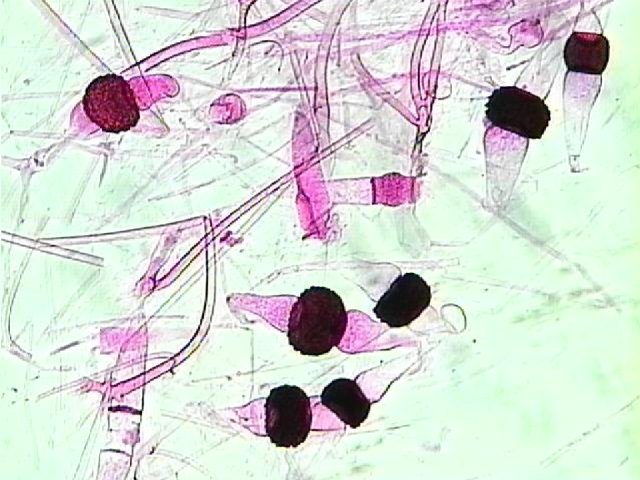
What Phylum does the picture belong to?
Zygomycota
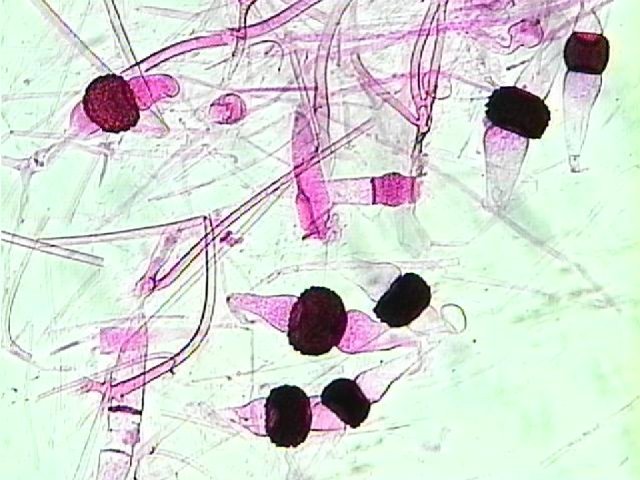
Does the picture display sexual or asexual reproduction?
Sexual
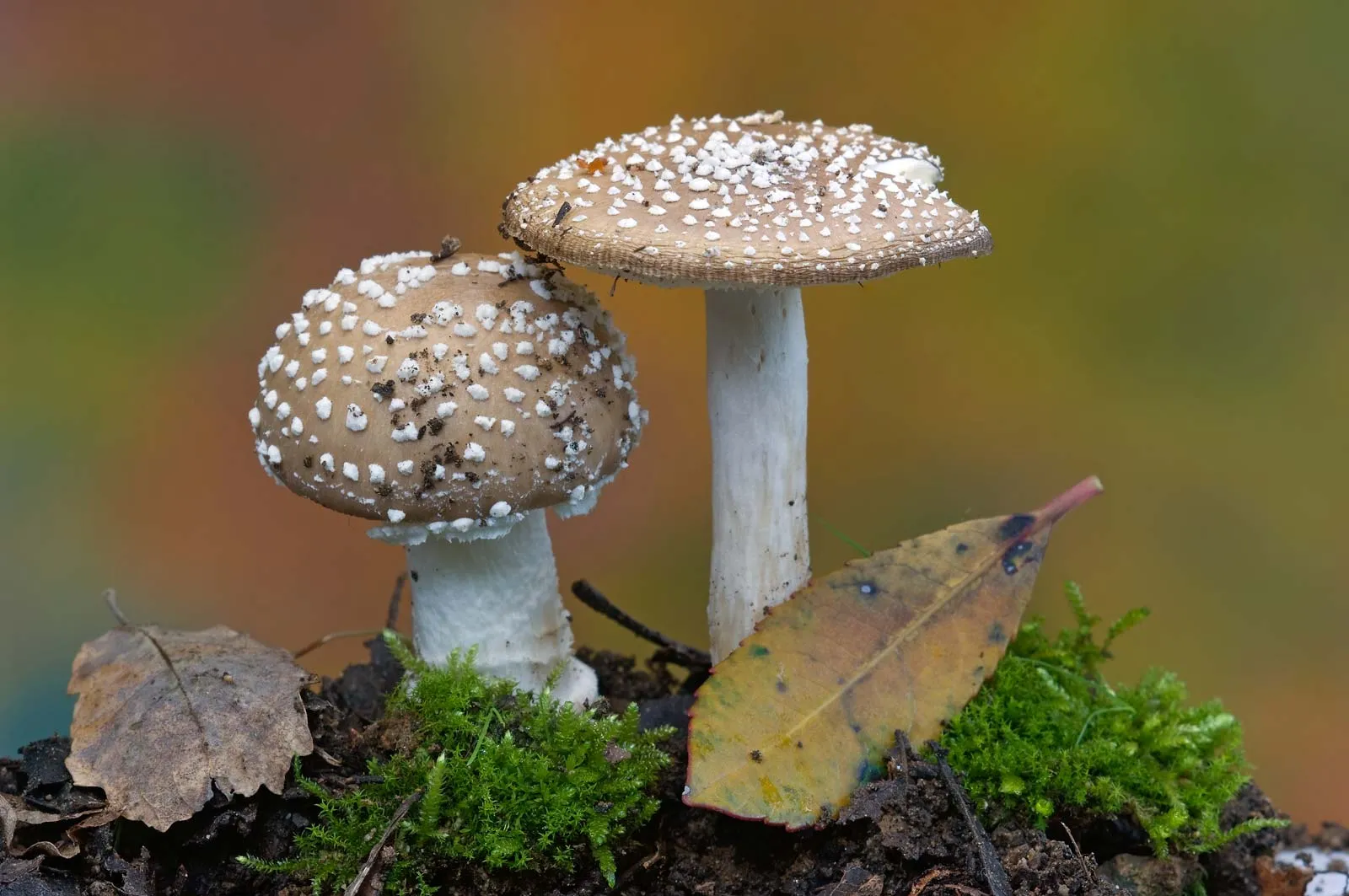

What phylum does this belong to? What is it?
Basidiomycota, Mushroom

What Phylum does the picture belong to? What is it?
Basidiomycota, Bolete
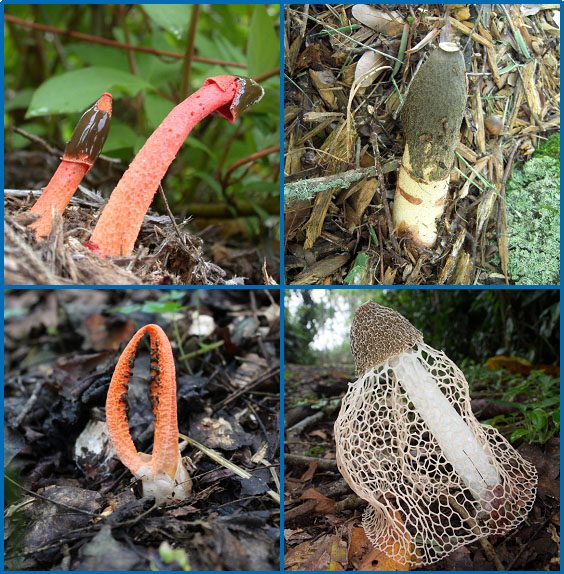

What phylum does this belong to? What is it?
Basidiomycota, Stinkhorn

What Phylum does the picture belong to? What is it?
Basidiomycota, Puffball

What Phylum does the picture belong to? What is it?
Basidiomycota, Bracket
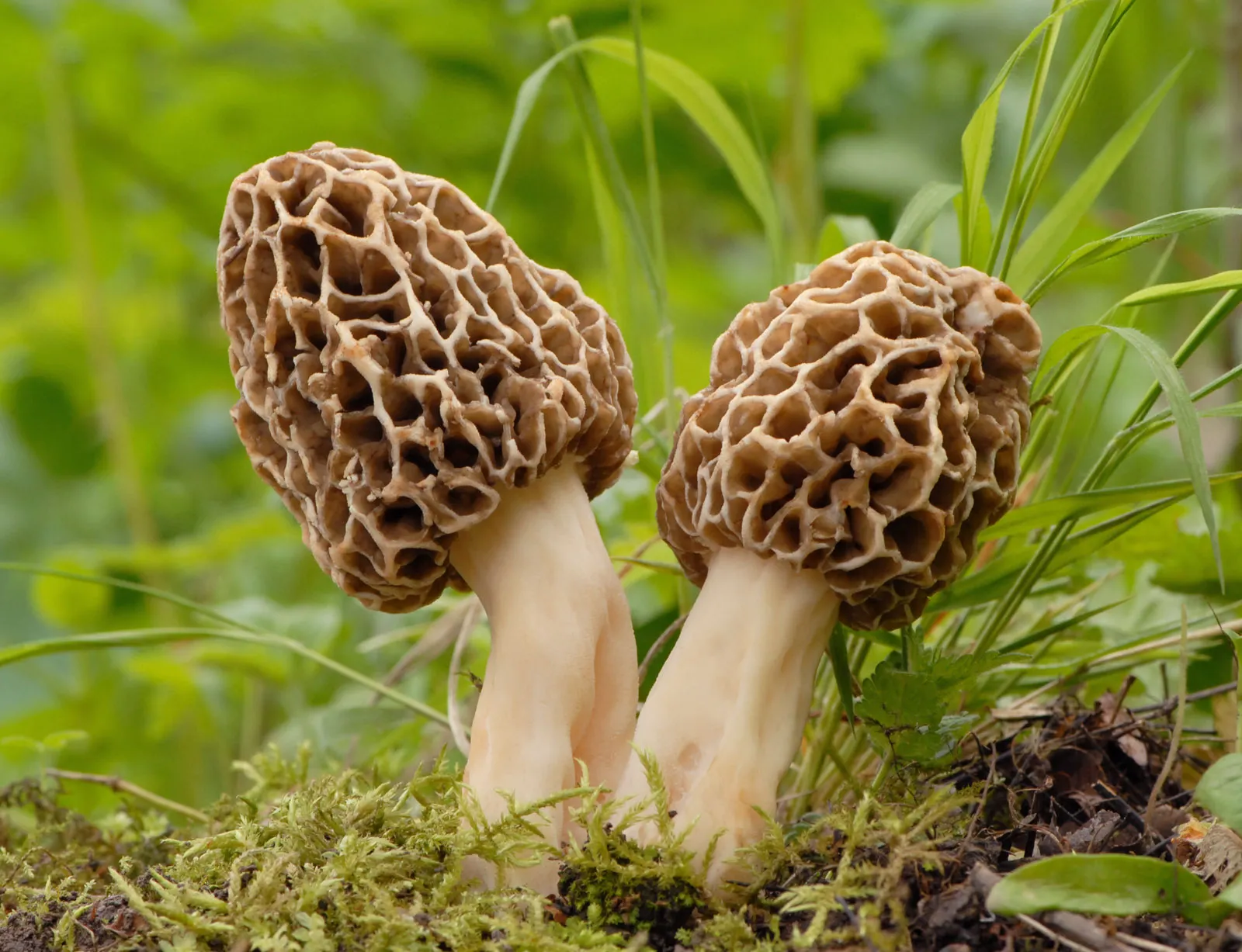

What Phylum does the picture belong to? What is it?
Ascomycota, Morel

What Phylum does the picture belong to? What is it?
Ascomycota, Truffle
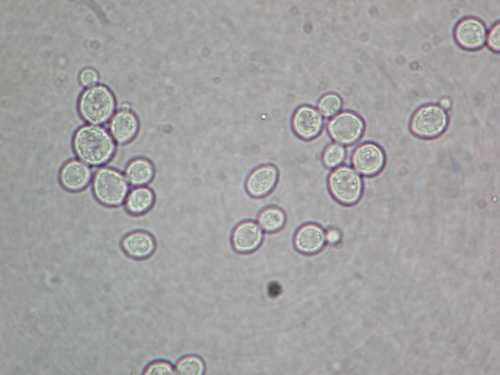
What Phylum does the picture belong to? What is it?
Ascomycota, Yeast
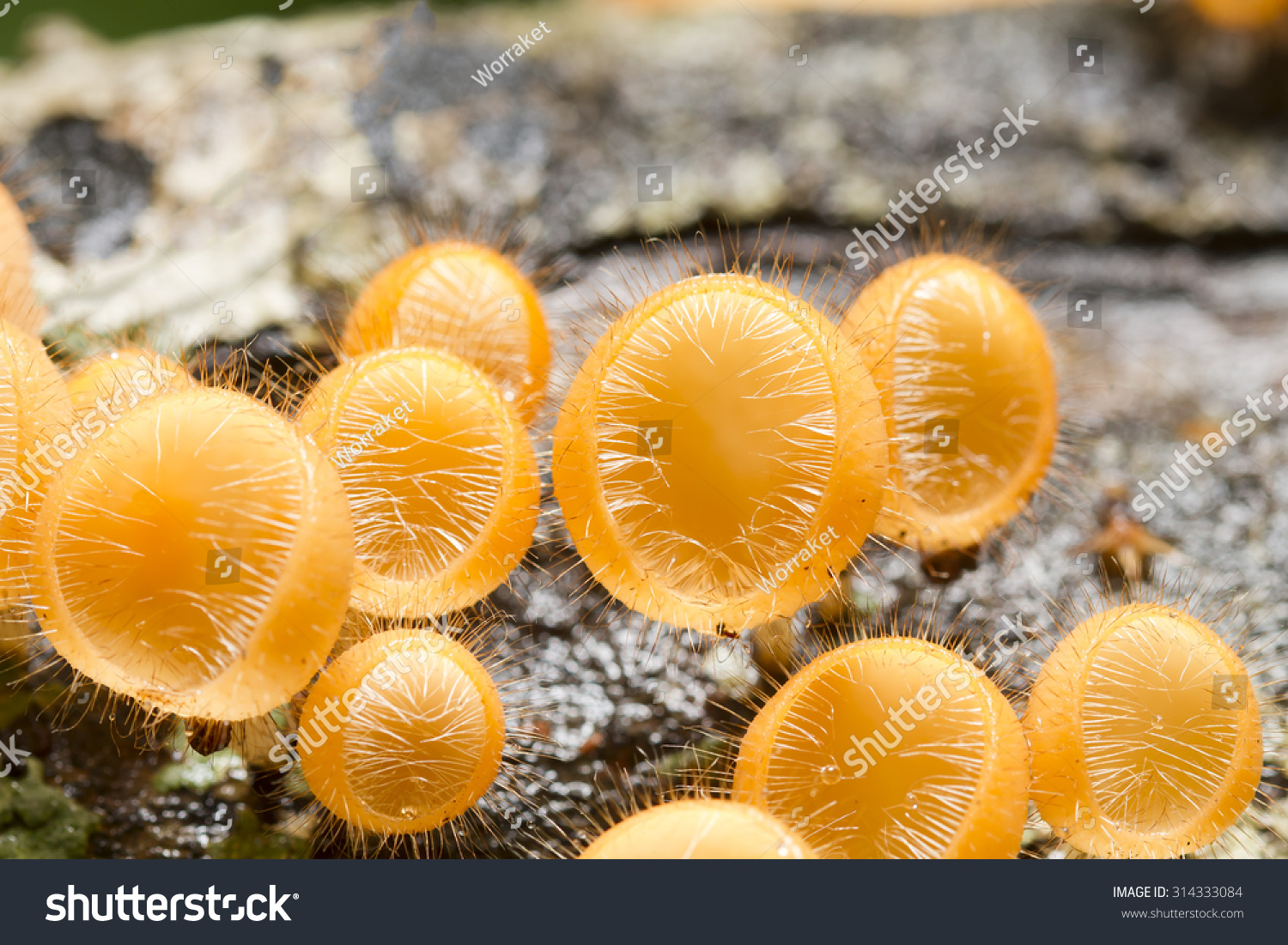

What phylum does the picture belong to? What is it?
Ascomycota, Cup Fungi
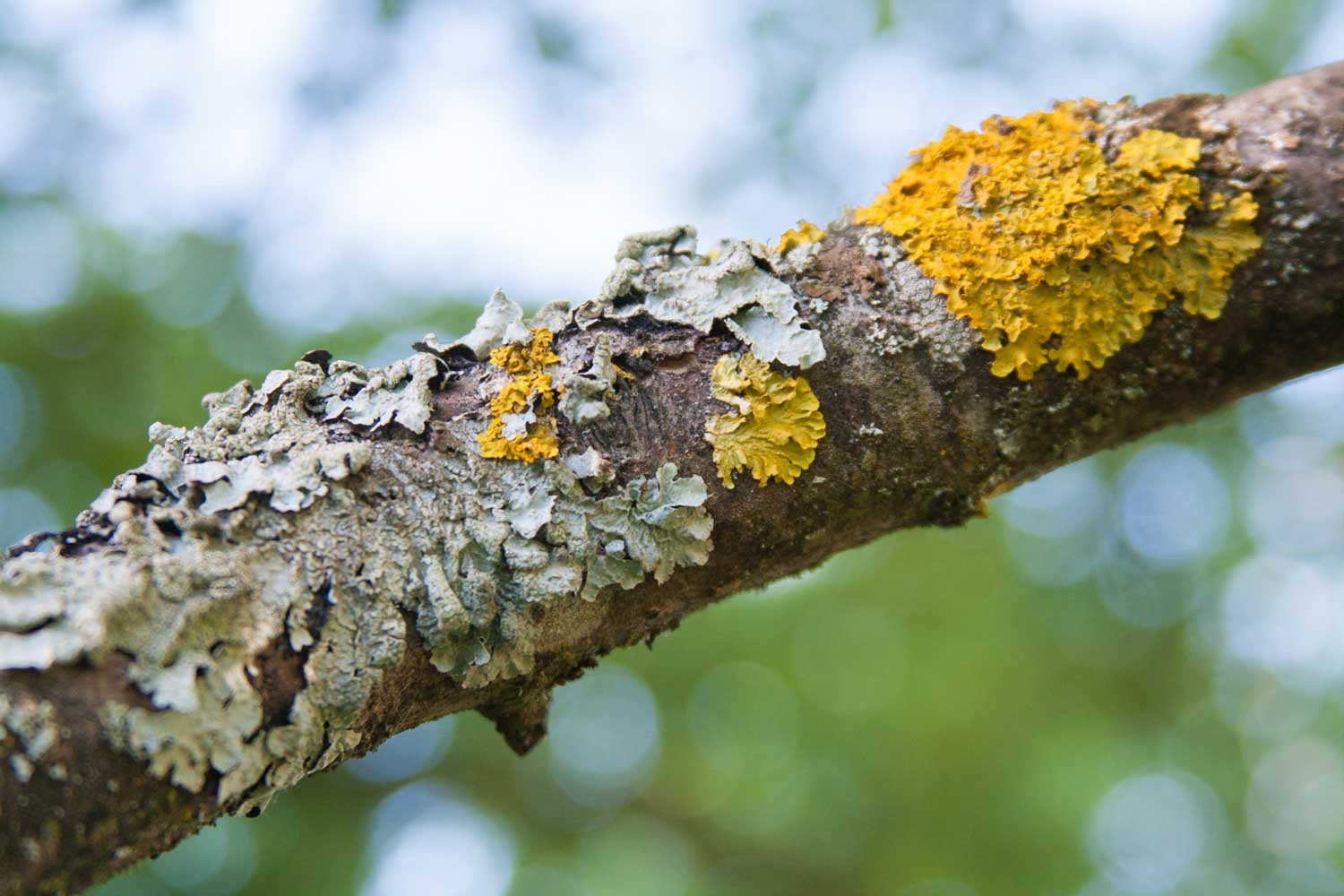

What is pictured?
Lichens
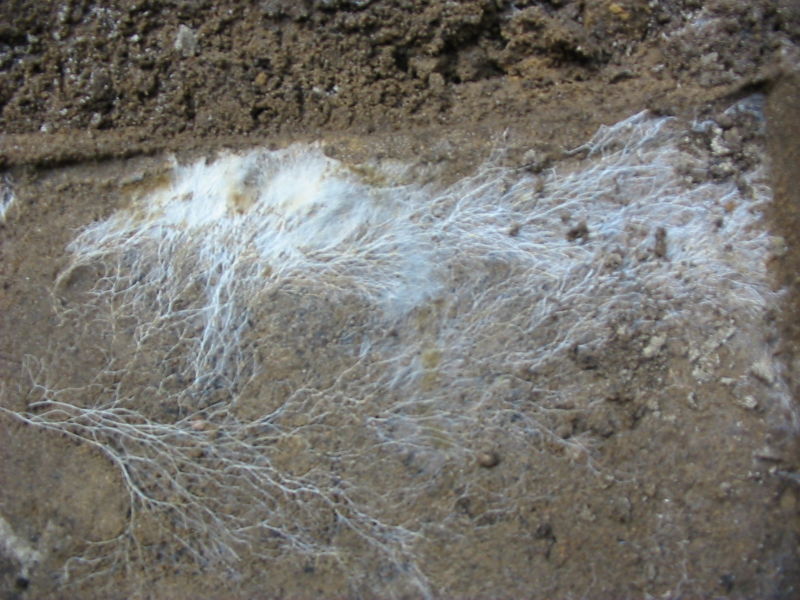

What is pictured?
Mycelium, a mat of fungal hyphae
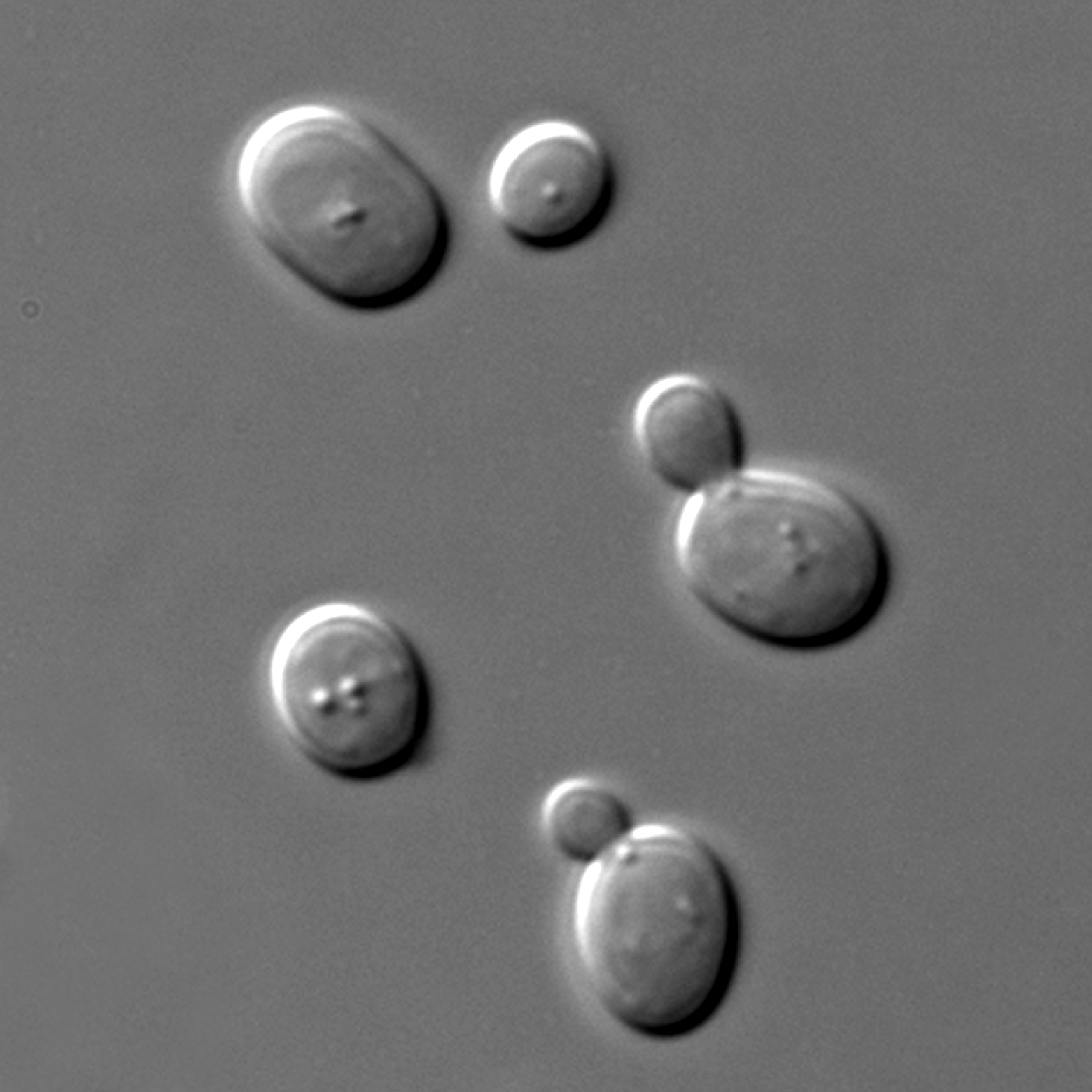
What is pictured?
Yeast budding
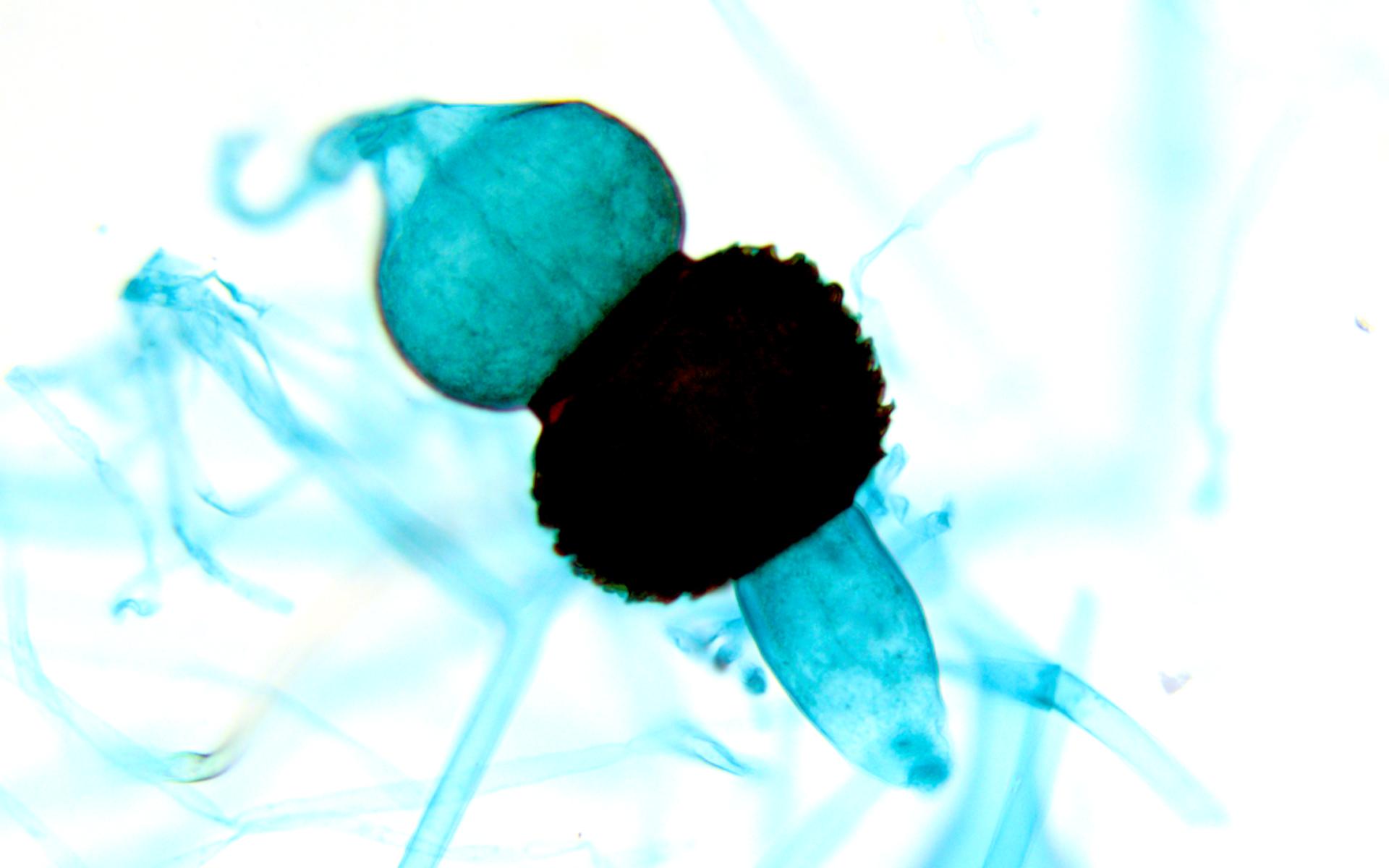
What is pictured? Does it undergo sexual or asexual reproduction? What phylum does it belong to?
Zygosporangia, Sexual, Zygomycota
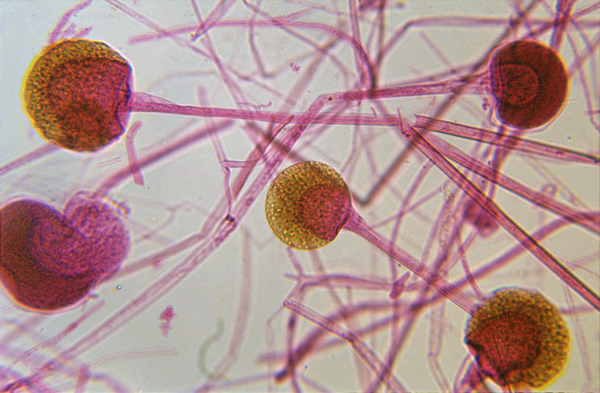
What is pictured? Does it undergo sexual or asexual reproduction? What phylum does it belong to?
Sporangia, Asexual, Zygomycota
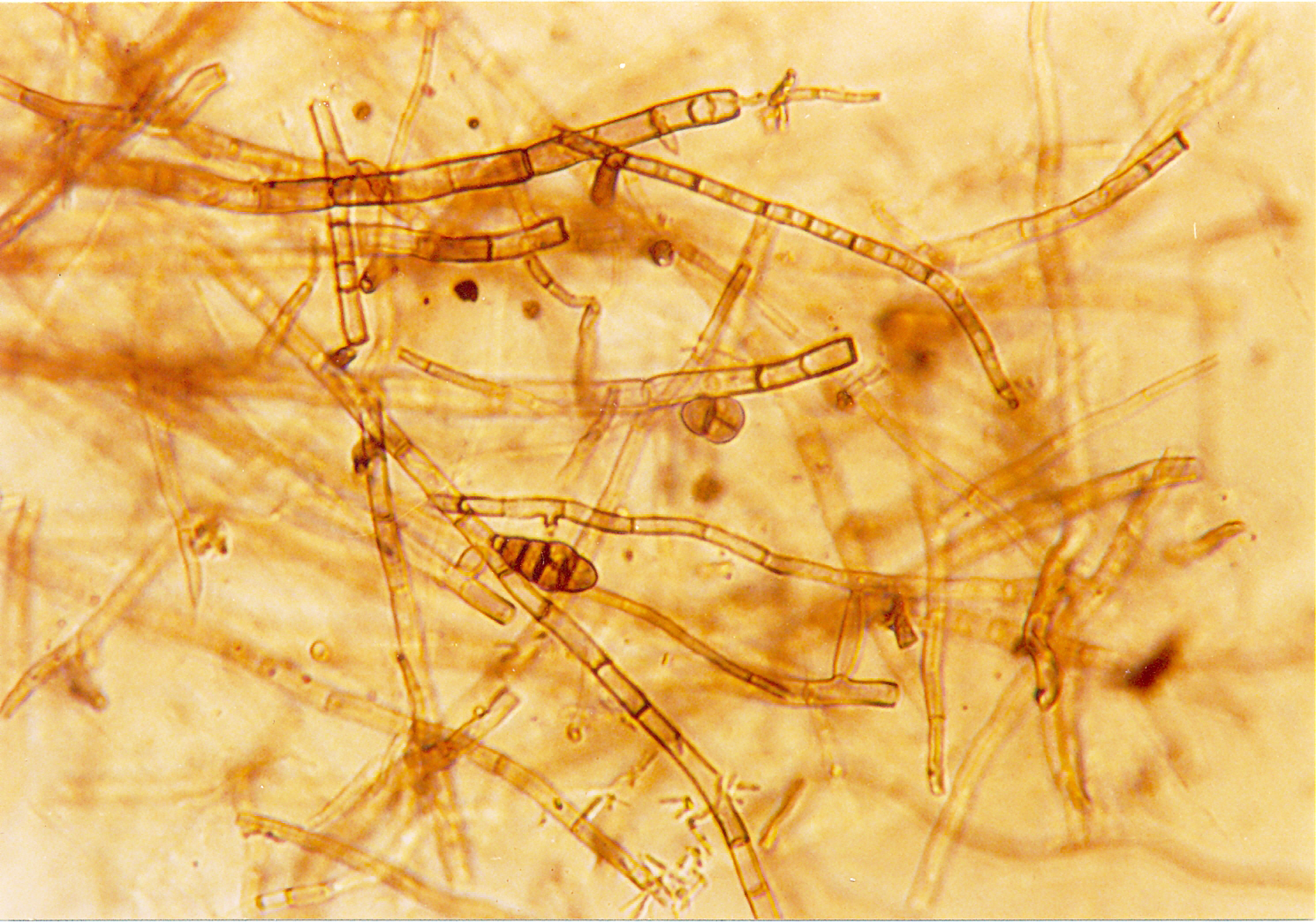
What is pictured?
Septate hyphae

What is pictured?
A basidiocarp, the fruiting body of Basidiomycota
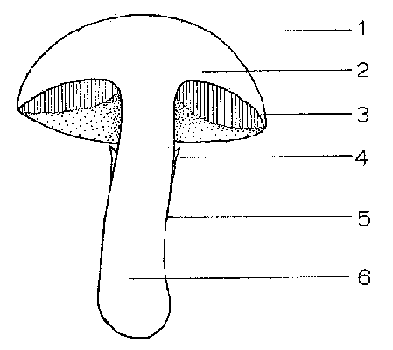
What is 3 pointing to?
Gills
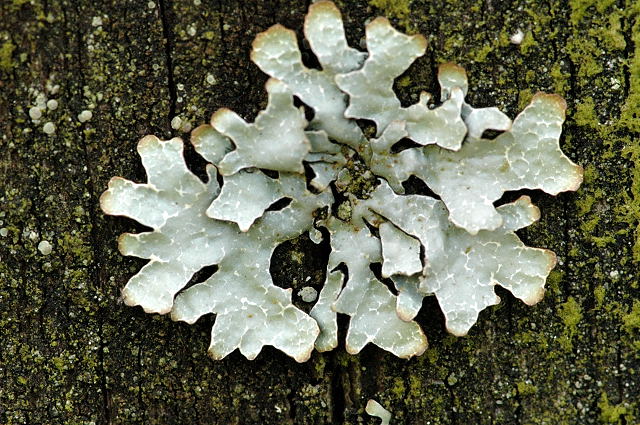

What is pictured?
Foliose Lichen
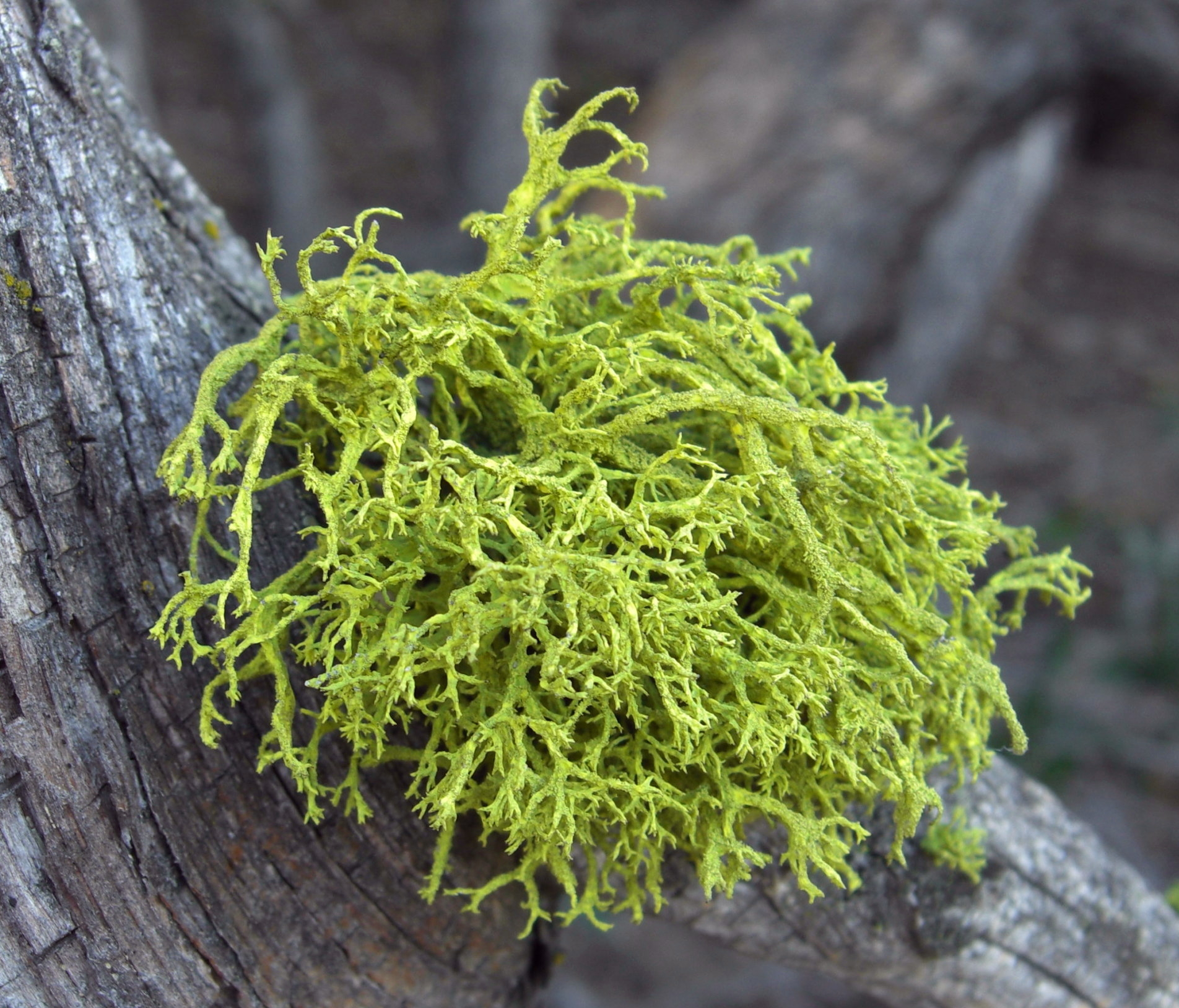

What is pictured?
Fruticose Lichen
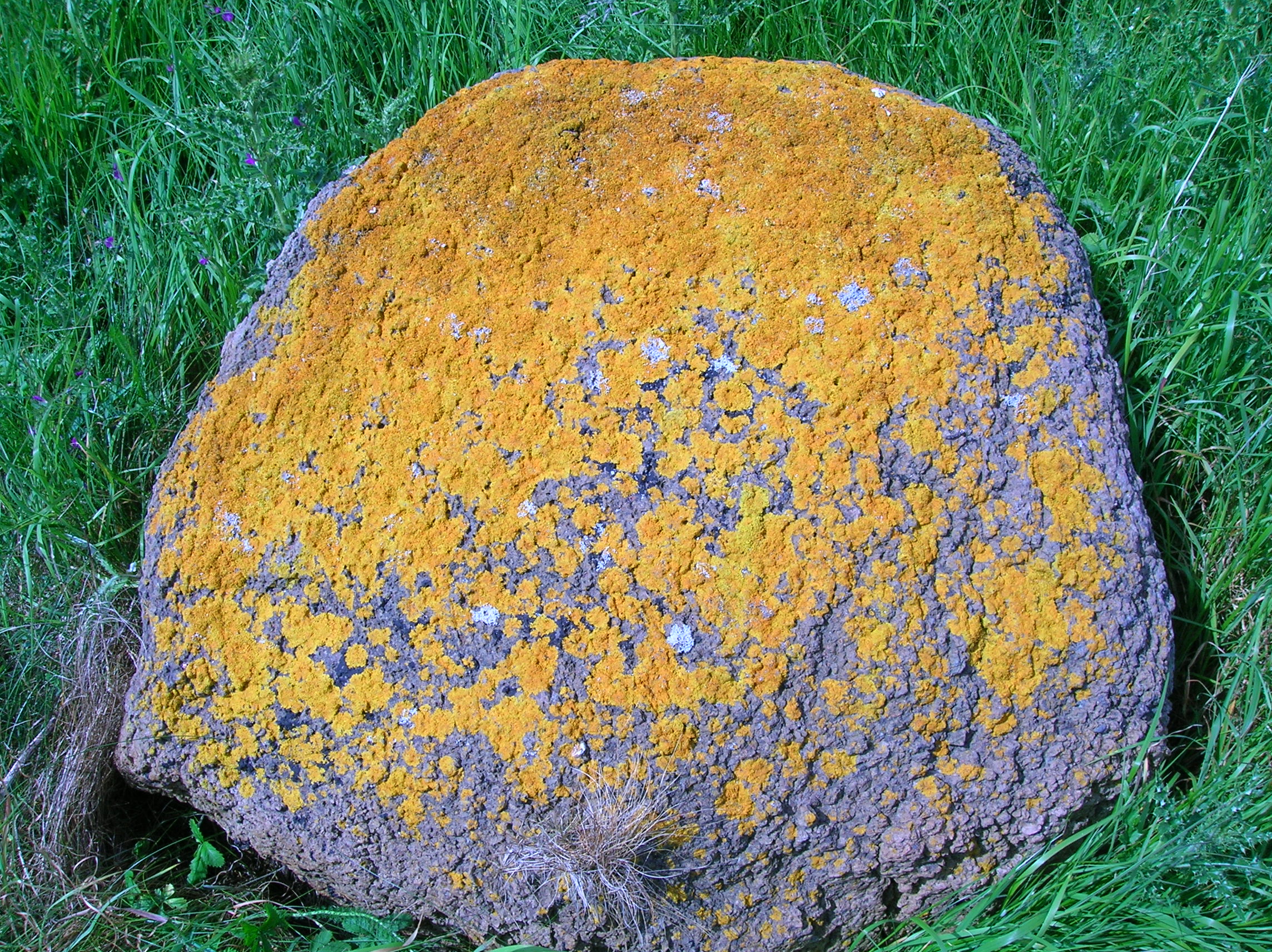

What is pictured?
Crustose Lichen
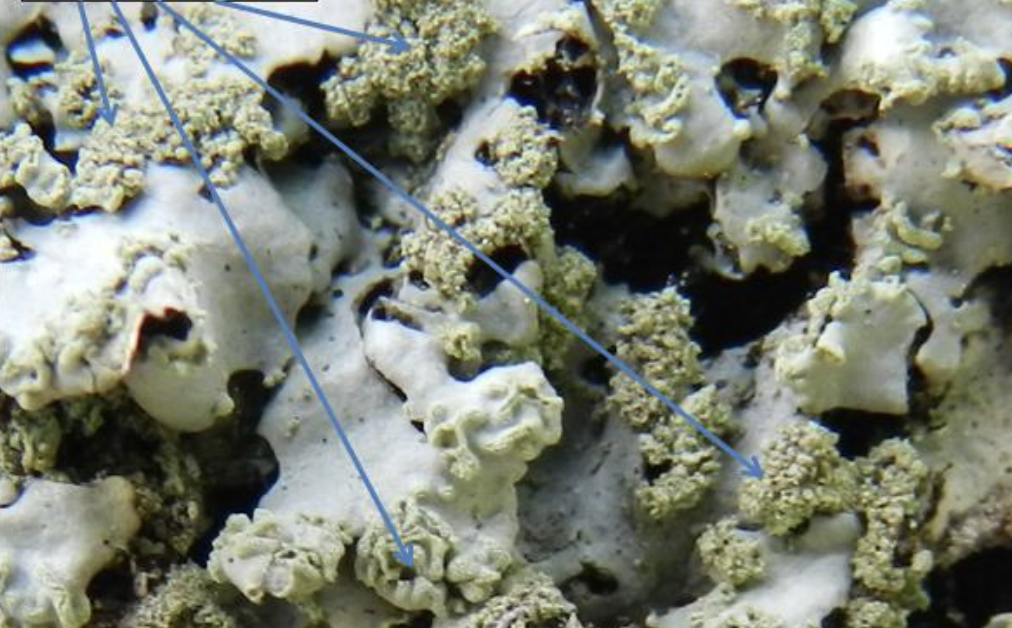

What is pictured?
Soredia
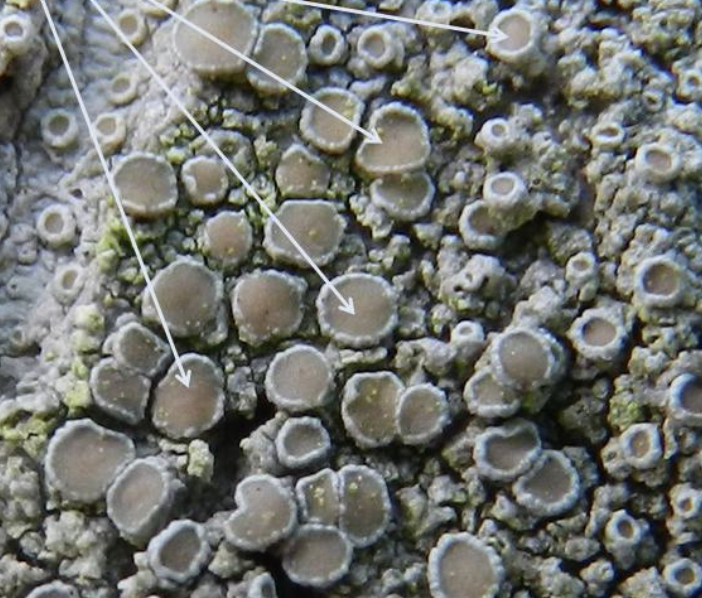

What is pictured?
Apothecia, reproductive structures in lichens that produce spores.
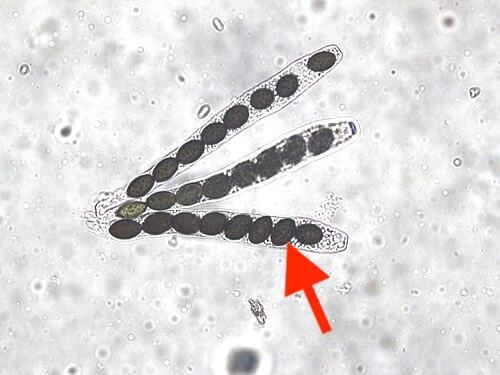
What is the arrow pointing to?
Ascospores, the spores produced by ascomycete fungi,
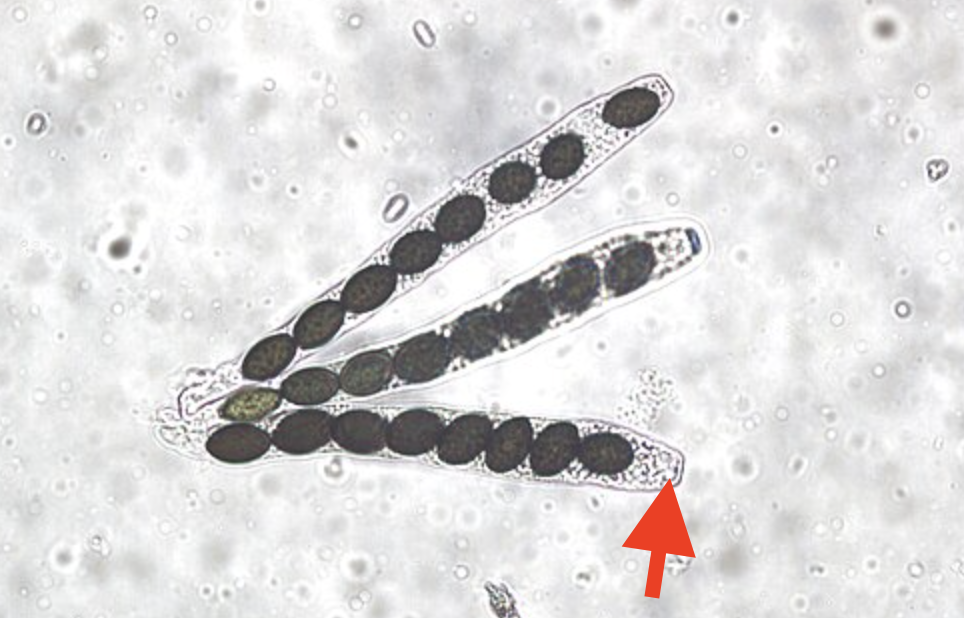
What is the arrow pointing to?
The asci, which holds the ascospores
What ploidy is a mature sporophyte?
2N (diploid)
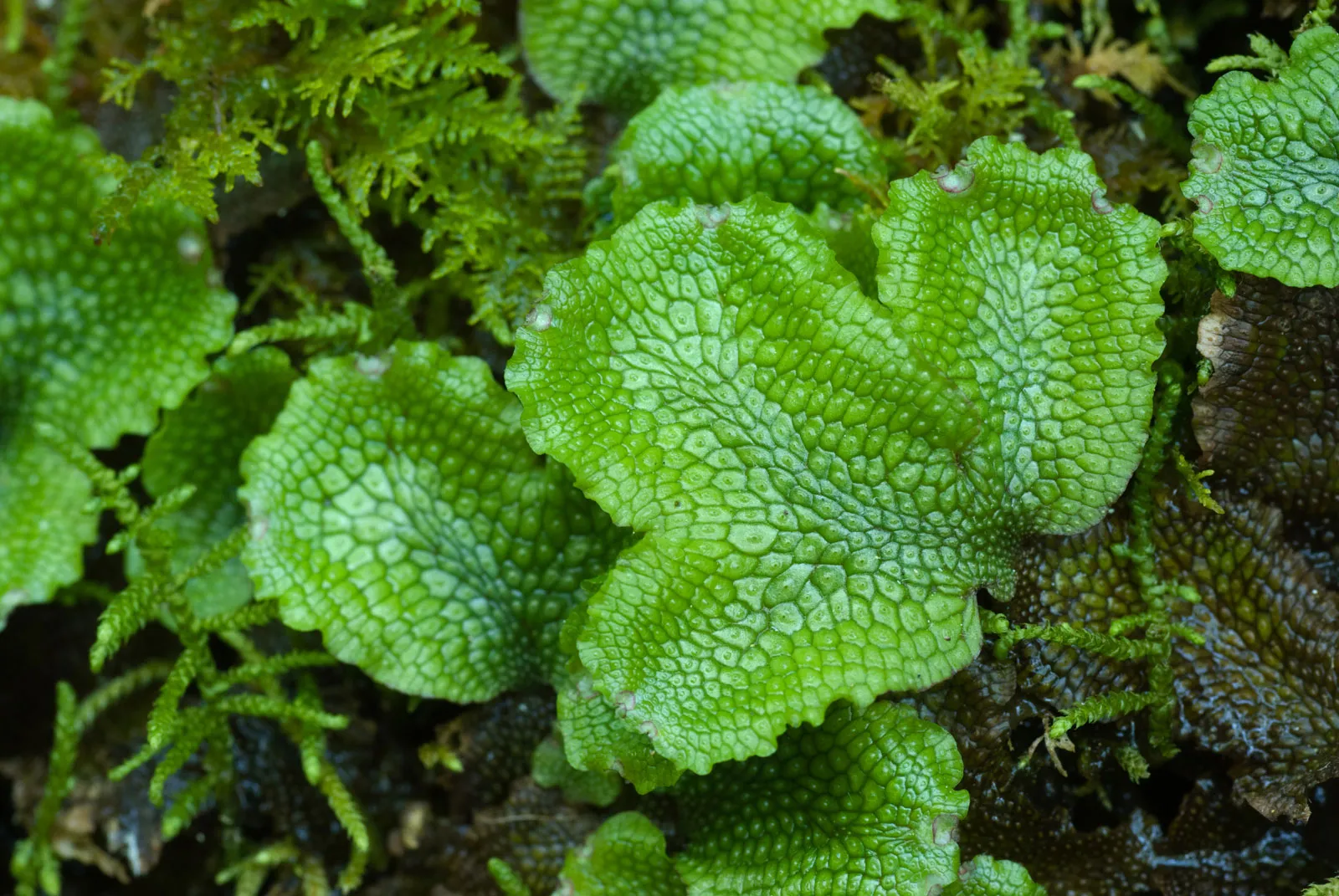

What phylum is pictured? What is the structure?
Phylum Hepaticophyta, Liverworts
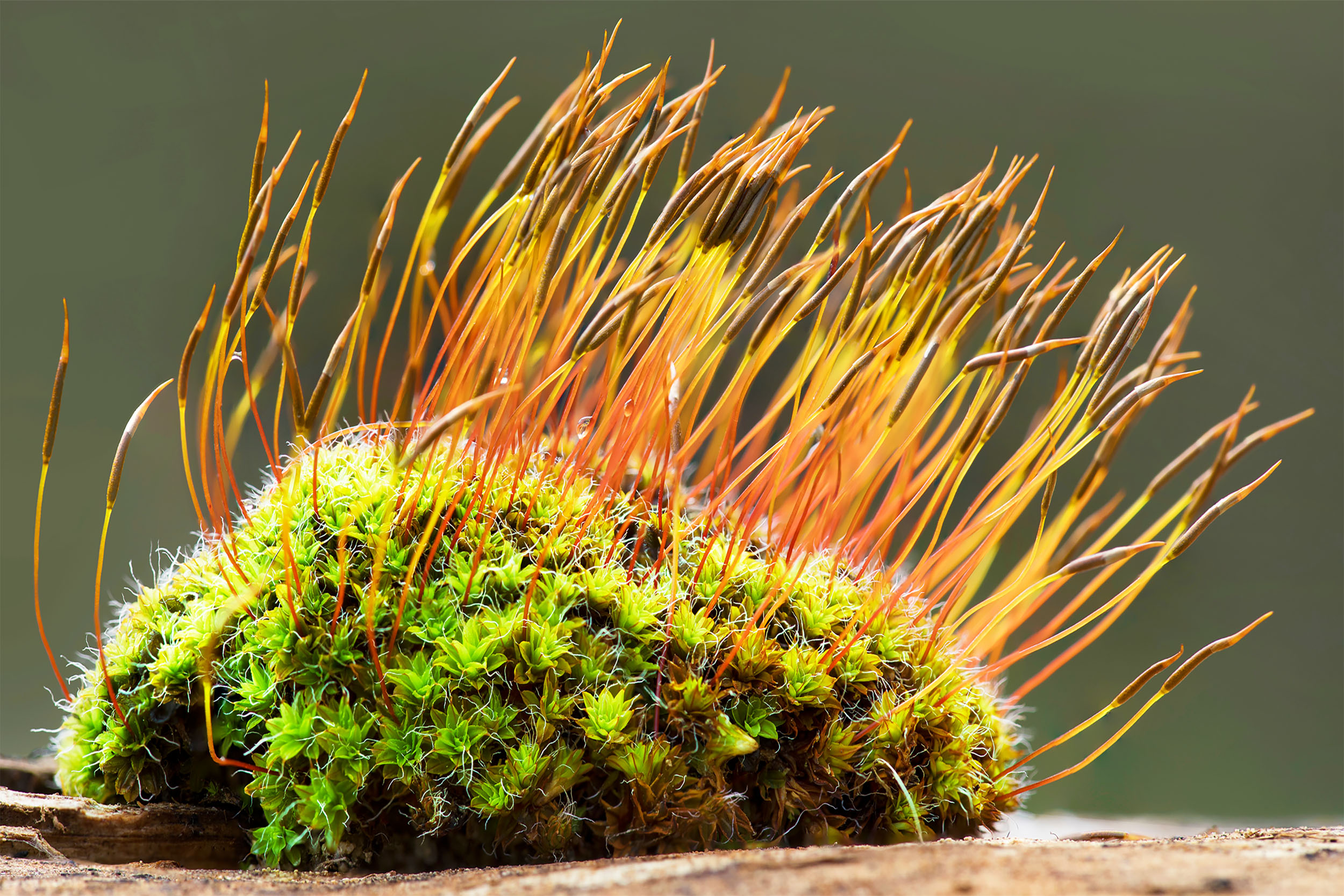

What phylum is pictured? What is the structure?
Phylum Bryophyta, Mosses
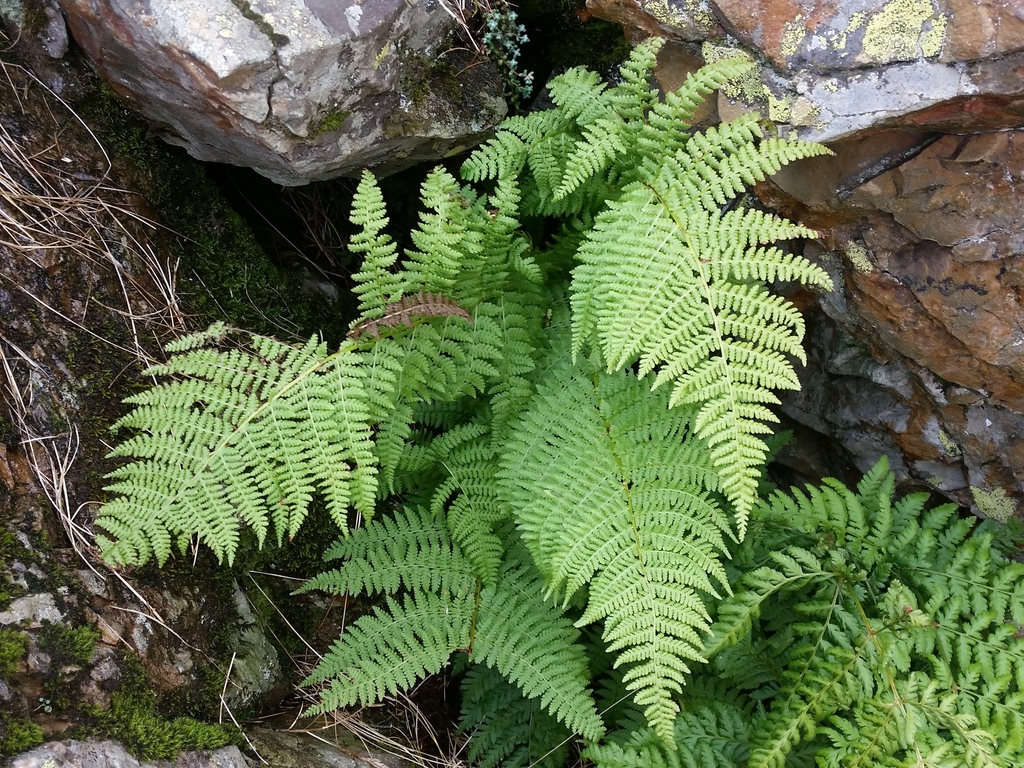

What phylum is pictured? What is the structure?
Phylum Pteridophyta, Ferns

What phylum is pictured? What is the structure?
Phylum Pinophyta, Pines, spruces, firs

What phylum is pictured? What is the structure?
Phylum Anthophyta, Flowering plants
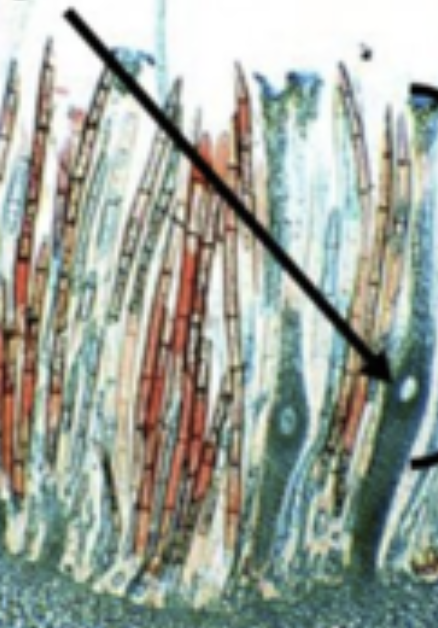
What is the arrow pointing to?
Archegonium eggs
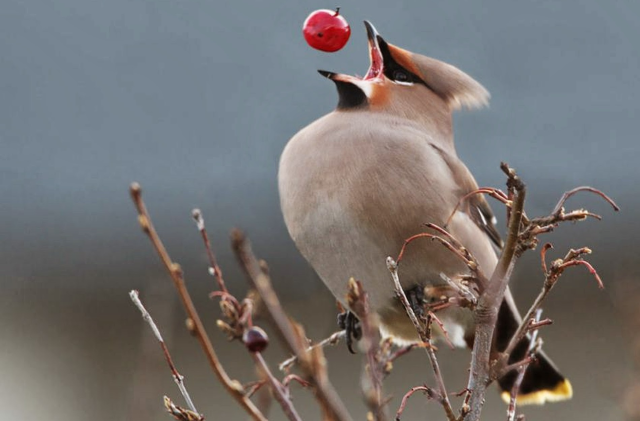

What is demonstrated in the picture?
Endozoochory, a seed dispersal mechanism involving animals that eat fruit and excrete seeds at a different location.

What is demonstrated in the picture?
Epizoochory, a seed dispersal mechanism where seeds attach to the exterior of animals and are carried to new locations.

What is demonstrated in the picture?
False copulation pollination, where a flower mimics an insect’s appearance to increase pollination.
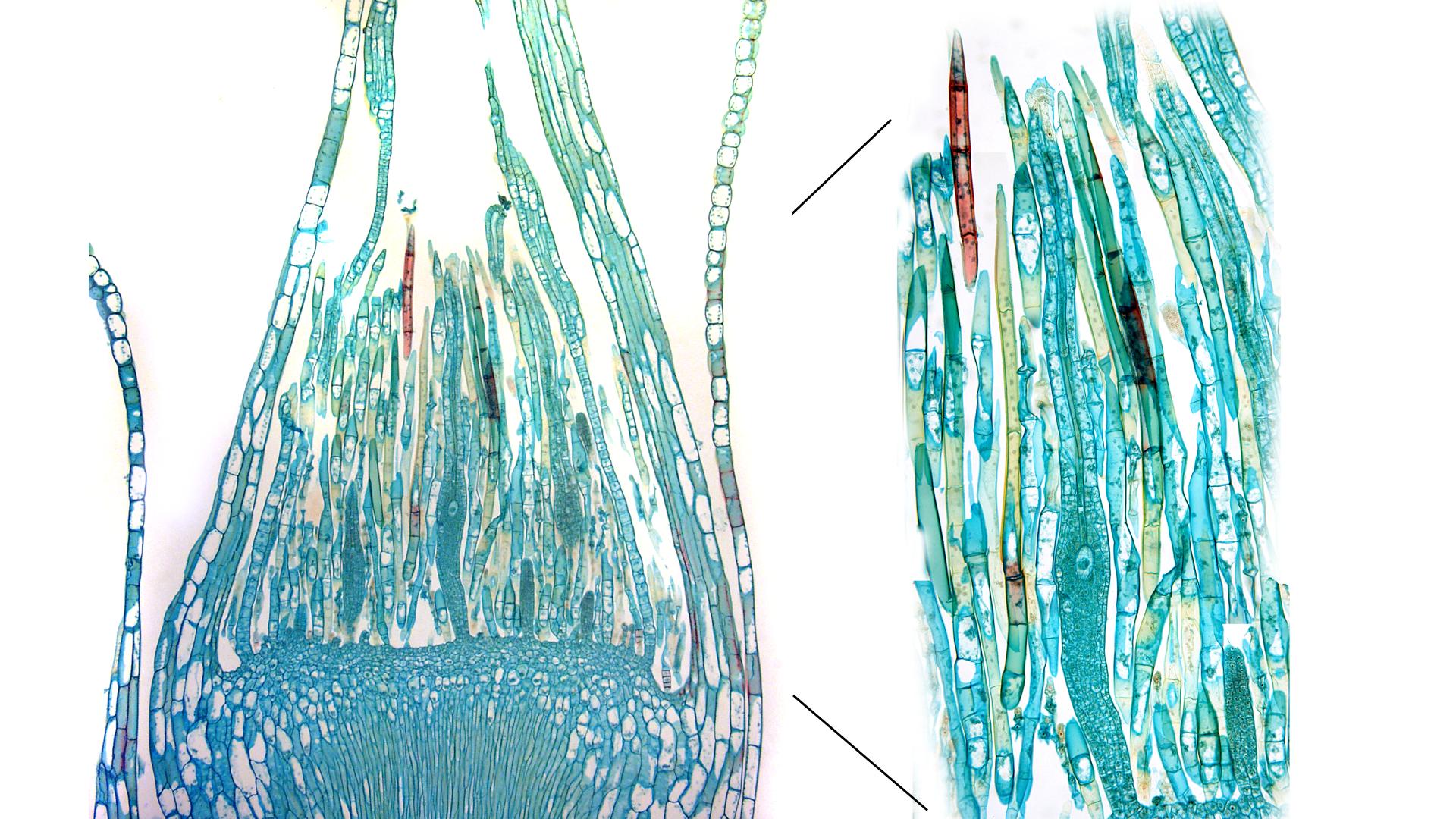
What is the ploidy pictured?
Diploid (2N)