week 1 - what is a chronic disease
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is a 'Chronic Disease'
A disease with prolonged temporal course that does not resolves spontaneously and 'cure' is rarely achieved
What is a common risk factor?
A risk factor that applies for several diseases, for example sedentary lifestyle
What are multiple risk factors?
When you can be at risk for a disease due to many diff causes, for example cardiovascular disease has multiple risk factors such as sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, alcohol, etc.
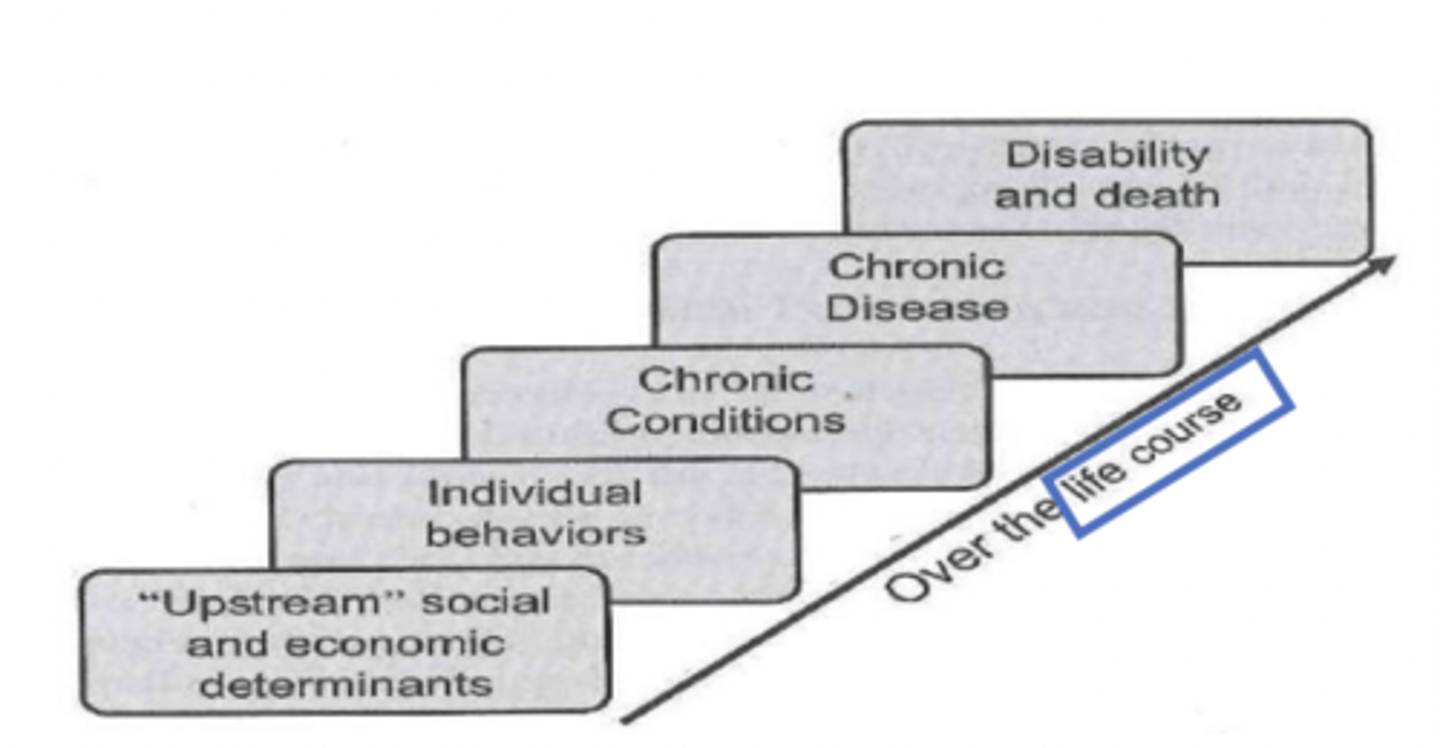
Name stages of chronic disease continuum (start to end)
Why are chronic diseases becoming (increasing) important?
Epidemiological Transition and Demographic Transition
What is Epidemiological Transition
The replacement of infectious diseases by chronic diseases over time
What led to epidemiological transition
➢Expanded public health and sanitation
➢Changes in health behaviours
What is Demographic Transition?
Change in make-up of population
- Think population growth
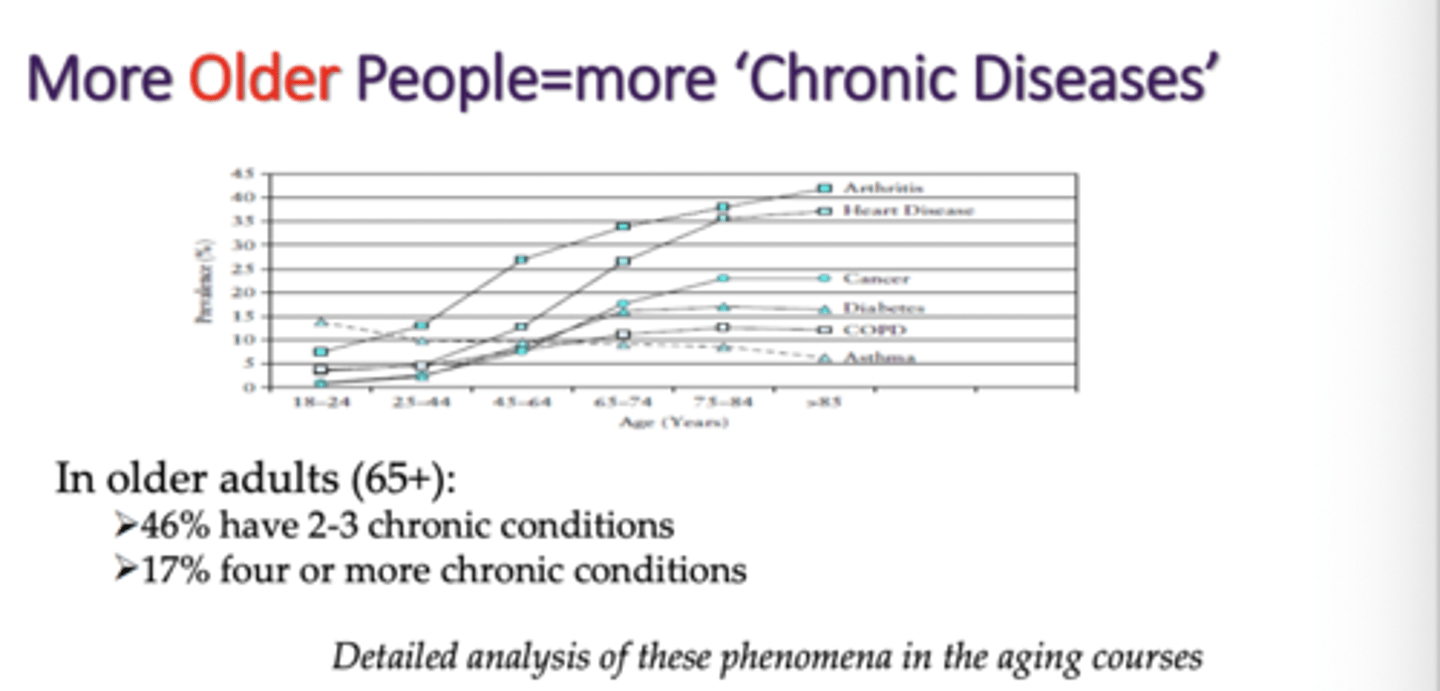
- AGING, On average more old people, less young people
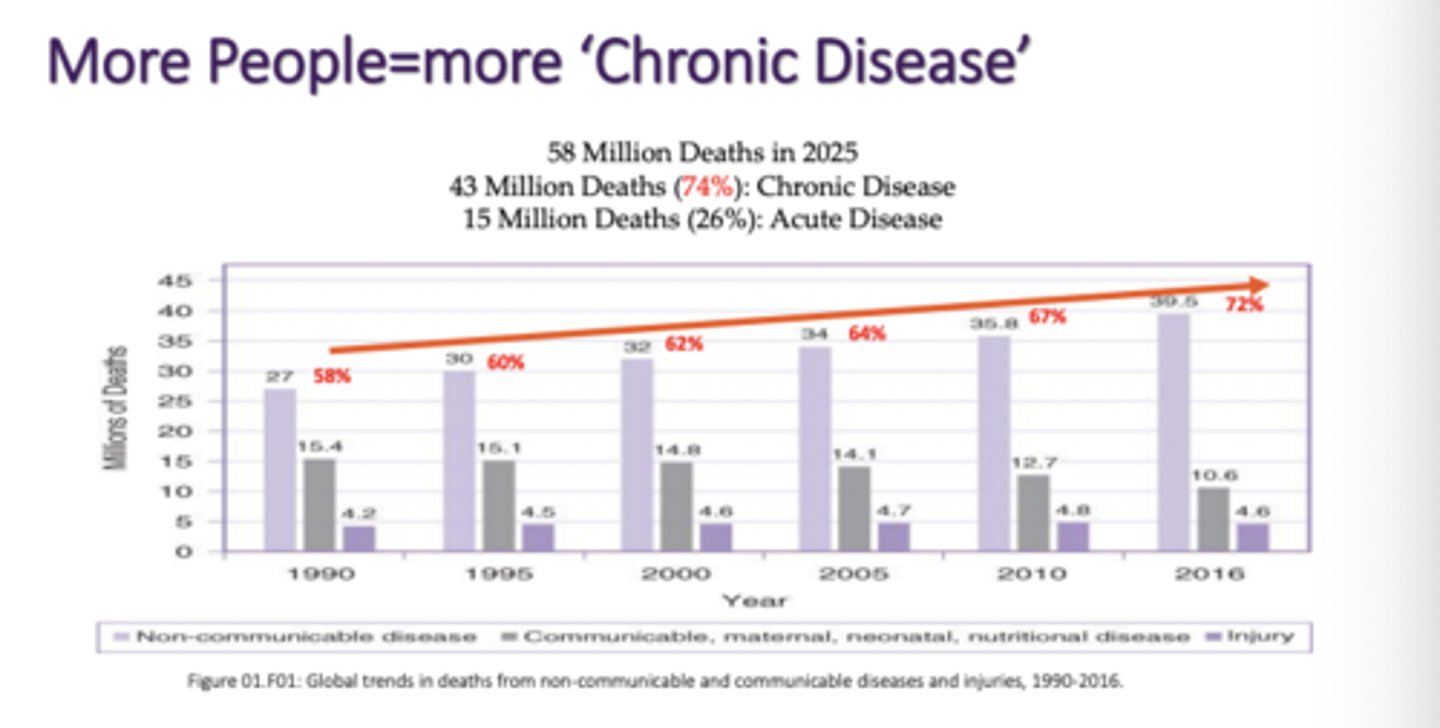
- More People=more 'Chronic Disease'
- More Older People=more 'Chronic Diseases'
What is the epidemiologic approach to chronic disease?
Identification of determinants/risk factors
➢Understanding the natural history
➢Generating evidence
➢We need a model (week 2)
What is the public health approach to chronic disease?
Assessment of Burden & Prevention
What does assessment of burden entail?
➢Burden of diseases
➢Burden of exposure
What is prevention about in a public health & chronic disease context?
Reduce onset of disease, minimize impact of disease (morbidity, mortality and symptoms)
➢Change in perception from inevitability to preventability ➢Based on findings from epidemiological studies - i.e. EVIDENCE-BASED
What discussions has the COVID-19 pandemic opened regarding chronic disease management?
Discussions on inequities and challenges in chronic disease management.
What is the difference that scientists are starting to appreciate in relation to physiological performances? (Covid-19 related)
The difference between acceptable variation in physiological performances (condition) and 'disease'.
Mortality vs Morbidity
(number of death)
➢Versus morbidity (any departure from health)
Name the 10 main chronic diseases that are the leading causes of morbidity & mortality
heart disease, stroke, cancer, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, arthritis, dementia, depression, and anxiety
➢Most common and most burdensome
➢Not necessarily most lethal
Percentage of Canadian older than 20 with at least one of:
➢10 main chronic diseases:
➢One major chronic disease: 21.4%
a) 38.4%
b) 21.4%
Incidence vs. Prevalence
Incidence is the number of new cases in a specific time period
"10 more ppl got x disease this month"
Prevalence is the current number of cases at a time
"964 people have x disease in 2022"
Absolute Disparity - IDKKKKK
?????
Relative Disparity
?????????
The Global Burden of Disease
➢Looking on more aspects of life, a life course approach, DALY
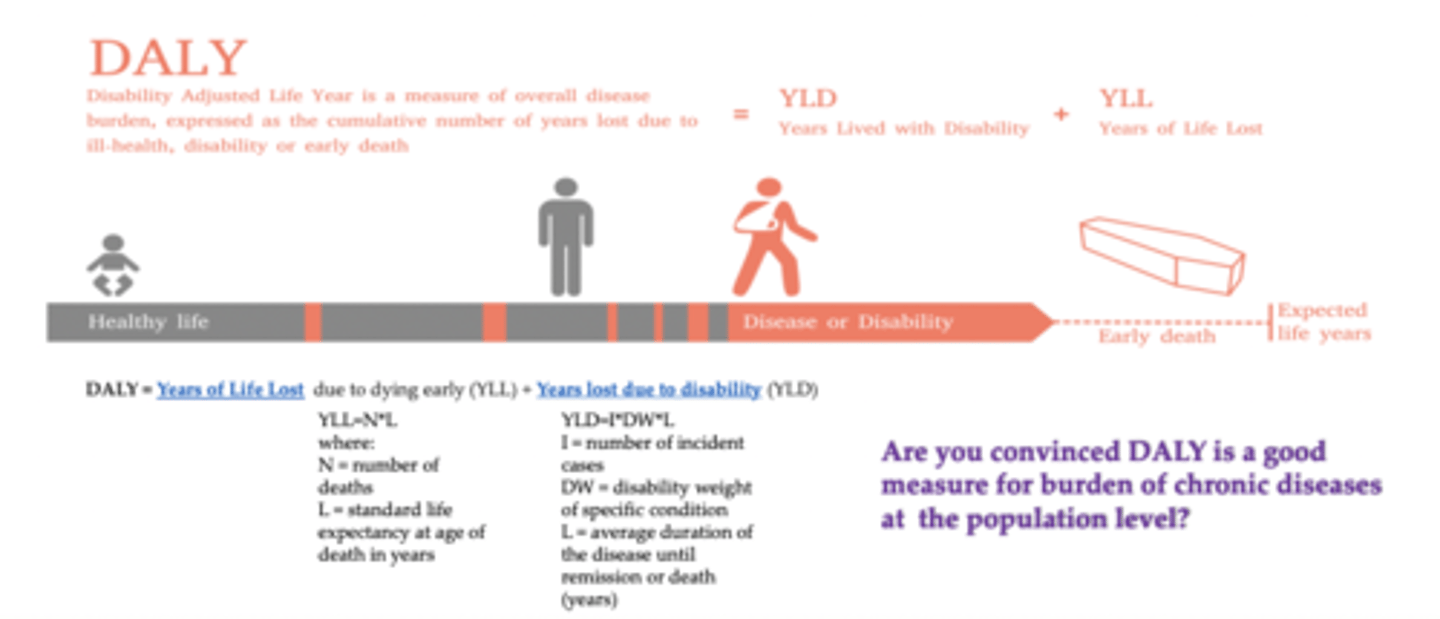
What does DALY stand for?
The disability-adjusted life year (DALY)
What does DALY do?
➢Considers age at death, life expectancy, and degree of disability
➢Is expressed as the number of years lost due to ill-health, disability or early death
➢Combines mortality and morbidity into a single, weighted, comparable metric
Define DALY
disability adjusted life year is a measure of overall disease burden, expressed as the cumulative number of years lost due to ill-health, disability or early death
Burden of Exposure - what does it tell us?
- How much of the occurrence of a disease is due to a particular exposure
- How much of the disease can be prevented if we eliminate the exposure
What is burden of exposure based on? Is the effect reversible?
Is based on the measure of association between the exposure and the outcome
➢Exposure-outcome relationship is real (unbiased) and causal ➢Effect is reversible
Relation between Burden of Exposure & Excess Risk
➢ Means how much of the outcome in the exposed group is really associated with the exposure
➢ Excess risk
What is Excess Risk?
➢ The risk added to the baseline risk due to exposure
➢ Real impact of an exposure (read burden)
➢ Proportion of occurrence that might be reduced if the exposure eliminated
➢ BIG assumption: causal relationship
Burden of exposure significance?
➢ If large, indicative of an important public health problem
➢ Simply can be calculated by subtracting risk in unexposed from risk in exposed
Attributable Risk / Burden of Exposure - Calculation
Amount of disease in current smokers attributable to smoking = 49.6-17.7=31.9 per 100,000 If we eliminate smoking we will get rid of 31.9/100,000 cases of the disease among exposed
**In epidemiology it is called absolute (attributable) risk**

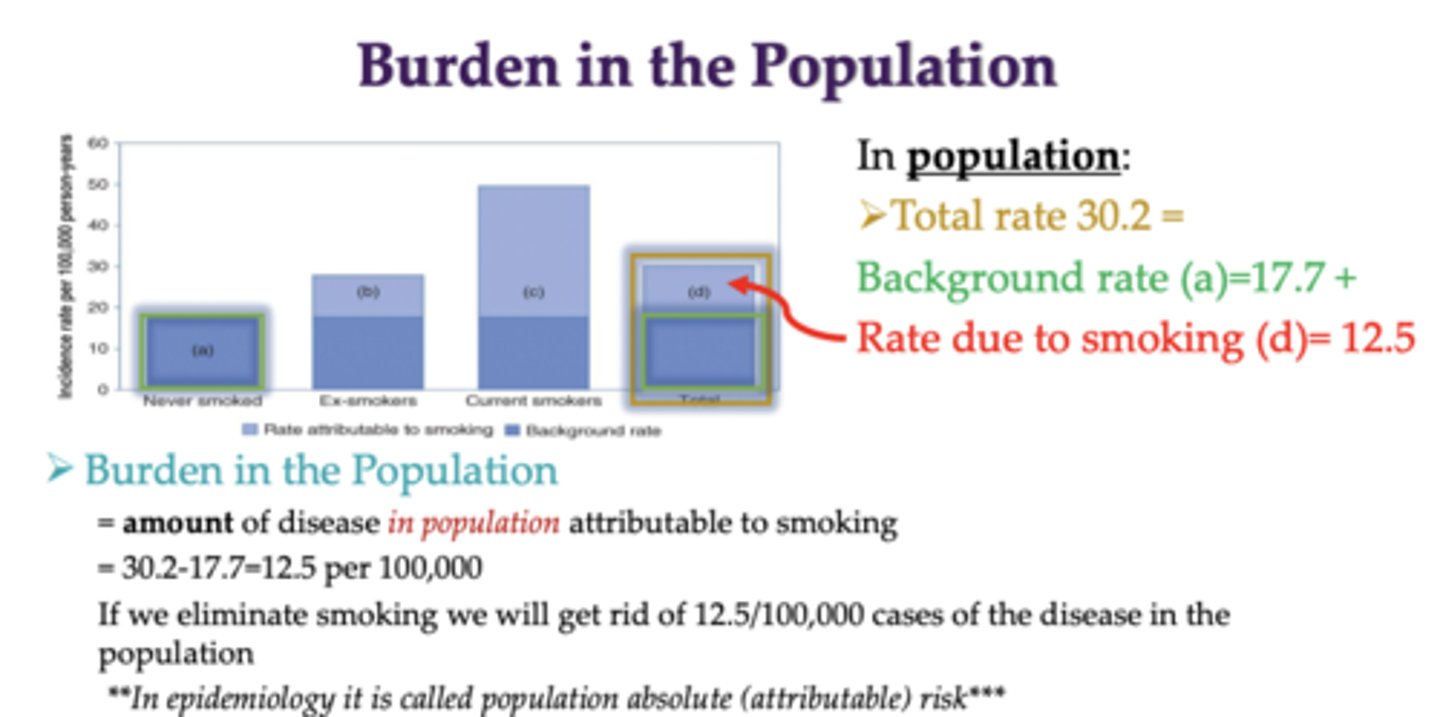
Burden in the Population
Burden in the Population = amount of disease in population attributable to smoking