BIOL 208: Lecture 9 - Autotrophs
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is trophy? What does the word have to do with?
has to do with food
Autotroph vs. Heterotroph, Define the terms
Autotroph:
Make their own complex carbs from inorganic C sources = CAN FIX C
Heterotrophy:
use organic sources of carbon synthesized by other = CANNOT FIX C (need to eat C)
What are the 2 types of Autotrophy?
Photosynthesis
Chemosynthesis
*****True or False: Trophic strategies have evolved Independently?
True
Which Domain of Life (prokaryotes or Eukaryotes) are the MOST DIVERSE in trophic strategies?
Prokaryotes
What type of trophic Strategdo Fungi + animals use?
Plants use mostly what trophic strategy?
Autotroph —> Photosynthesis
****Chemo synthesizers only exist among _____
PROKARYOTES
*******Autotrophs: Photosynthesis vs. Chemosynthesis, What do they each derive their ENERGY FROM?
Photosynthesis = Derived from light
Chemosynthesis = derived from OXIDATION
*****What is PAR + What does it stand for?
Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR)
Visible light
What type of light are absorbed most by chlorophyll?
Blue + Red
that why we see green
******What is PPFD, What does it stand for?
Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density
Number of Photons per meter squared per second
how much usable light for photosynthesis” plants receive.
Plants receive variable amounts of light. What 2 aspects of light affect the photosynthetic rates?
Quantity
Quality
****What 4 things affect the quantity + quality of light?
Latitude (angle of solar radiation)
Clouds
Landscape features
Position of Plant relative to other plants
Par- Light partitioning in forests: Where is there the least amount of PAR and where is there the most?
Most = Canopy
Middle
Low vegetation + Forest floor = least
How have different Plants dealt with the difference in PAR depending on their positioning in the forest?
Adapt to High or Low par
How does Water depth affect PAR?
PAR decreases as you go down, so does the spectrum of light that reaches
What color light is absorbed first in Water + which is last?
First:
Red
Orange
Yellow
Purple
Green
Blue
Last
How do ORGANIC + INORGANIC material affect PAR in water?
Particles in water layers ABSORB light
High # particles = less PAR gets through
*****What color are DEEP WATER ALGAE/ autotrophs + WHY?
Surface:
RED light = ABSORBED
Green = reflected (see green)
Deep water:
No red light reaches, BLUE reaches = Absorbed instead
RED reflected
ADAPTED TO USE BLUE LIGHT PAR
Deep water algae/autotrophs = RED
Can a plant do unlimited amounts of photosynthesis?
NO
Net photosynthesis rates (NPR) increases as PPFD increases to a SATURATION POINT
*****What are Photosynthetic Response Curves?
Graphs of NPR (net photosynthesis rate) as a function of PPFD (Photosynthesis proton flux density)
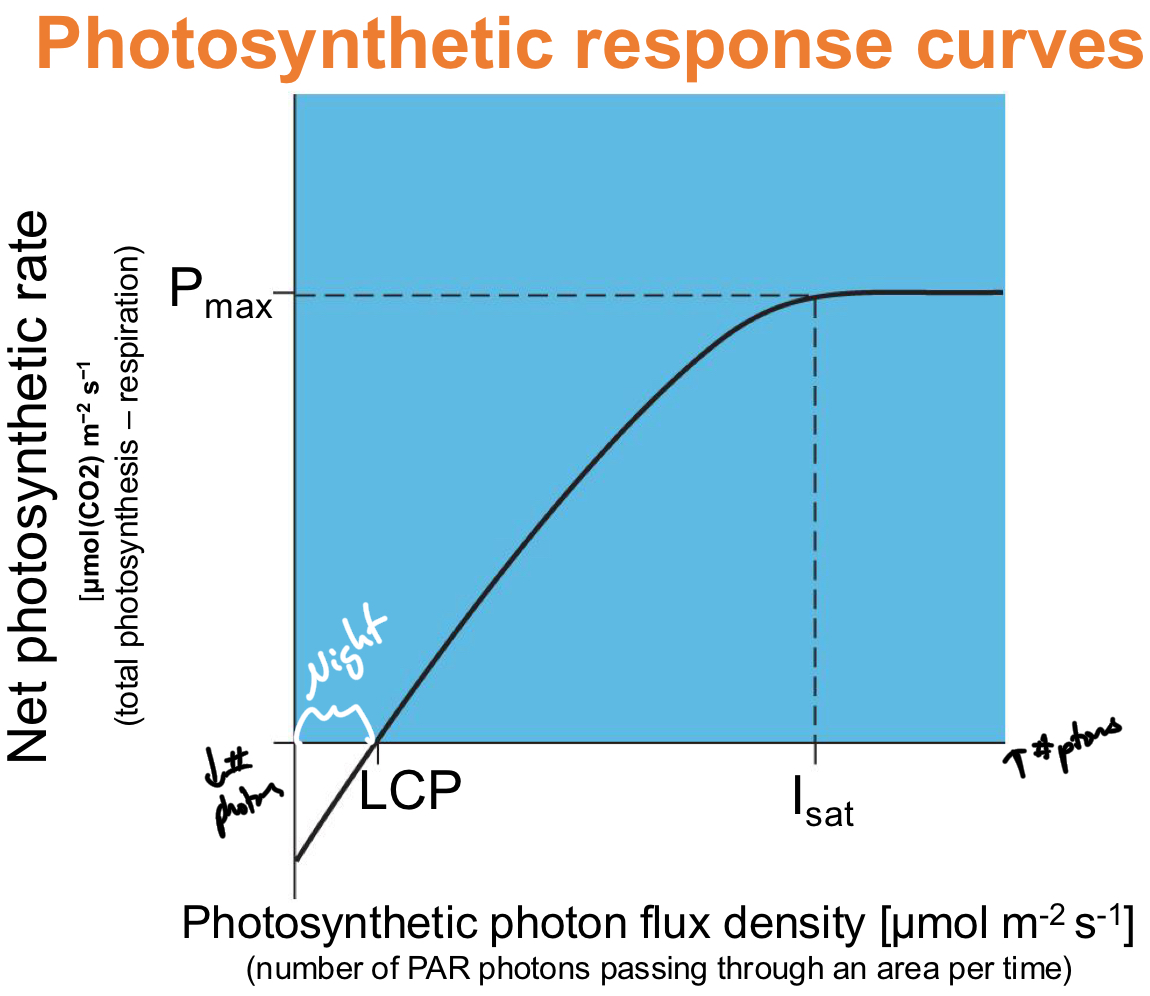
What is Isat, LCP + Pmax on the photosynthetic response curve?
Isat = Irradiance at saturation
Max amount of photons a plant can use at a time
LCP = Light compensation point
Light intensity at which photosynthesis = cellular respiration (amount of glucose prod = amount of glucose used)
Pmax = max net photosynthesis
***What occurs above + below LCP respectively?
Above = Plant making more sugar than it uses
Below = Consuming sugar product
not enough light to produce enough carbs
What what time is Rate of photosynthesis BELOW LPC?
NIGHT
no light to perform Photosynth.
Sugars required = greater than sugars made
Are Photosynthetic curves among the same species the SAME?
NO
Photosynthetic response curves can DIFFER among individuals WITHIN SPECIES
How does a seedling of the same species differ in the Photosynthetic Response Curves if they were grown in the OPEN vs. in the SHADE?
Open:
Pmax + I sat = Higher
Shade
Pmax + I sat = Lower
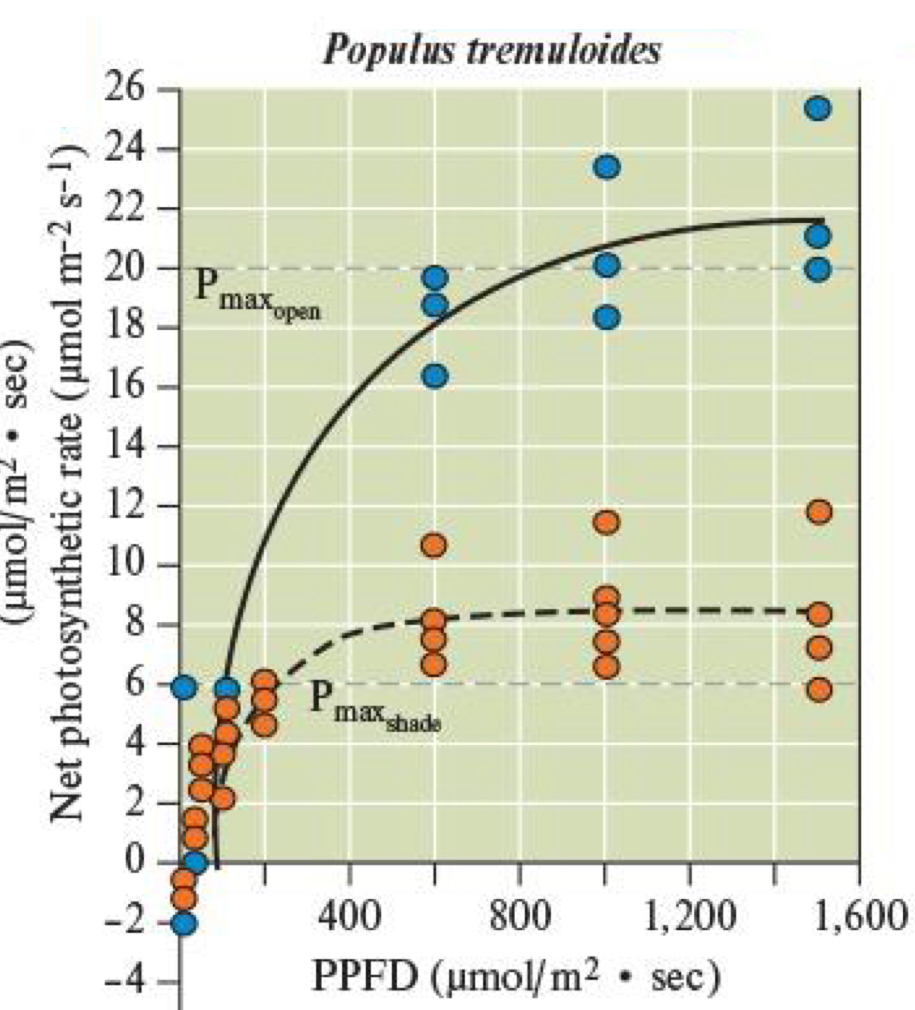
****Compare how SUN plants vs. SHADE plants in their PPFD usage
Sun = INEFFICIENT at using LOW PPFD
Shade = more EFFICIENT using llwoo
****Compare how SUN plants vs. SHADE plants in their I sat + how that affects their ability to survive + reproduce in different conditions?
Sun = High I sat
FAIL to reprod in SHADED areas
Shade = Low I sat
DAMAGED in SUNNY areas
Photosynthesis can be divided into what 2 processes?
Light dependent
Light independent
Where do each of the photosynthetic processes occur in the plant?
Light dependent = Thylakoid membrane of chloroplast
Light independent = Stroma of chloroplast
*****What RXNs occur in each Processes of Photosynthesis?
Light dependent
Photons —> ATP + NADPH + O2 (by product)
Light independent
ATP + NADPH + CO2 —> CHO
What is the light independent processes also known as?
Calvin cycle
What is the net equation of photosynthesis?
6 CO2 + 6 H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6 O2
How do Plants get the CO2?
enter through STOMATA via DIFFUSION
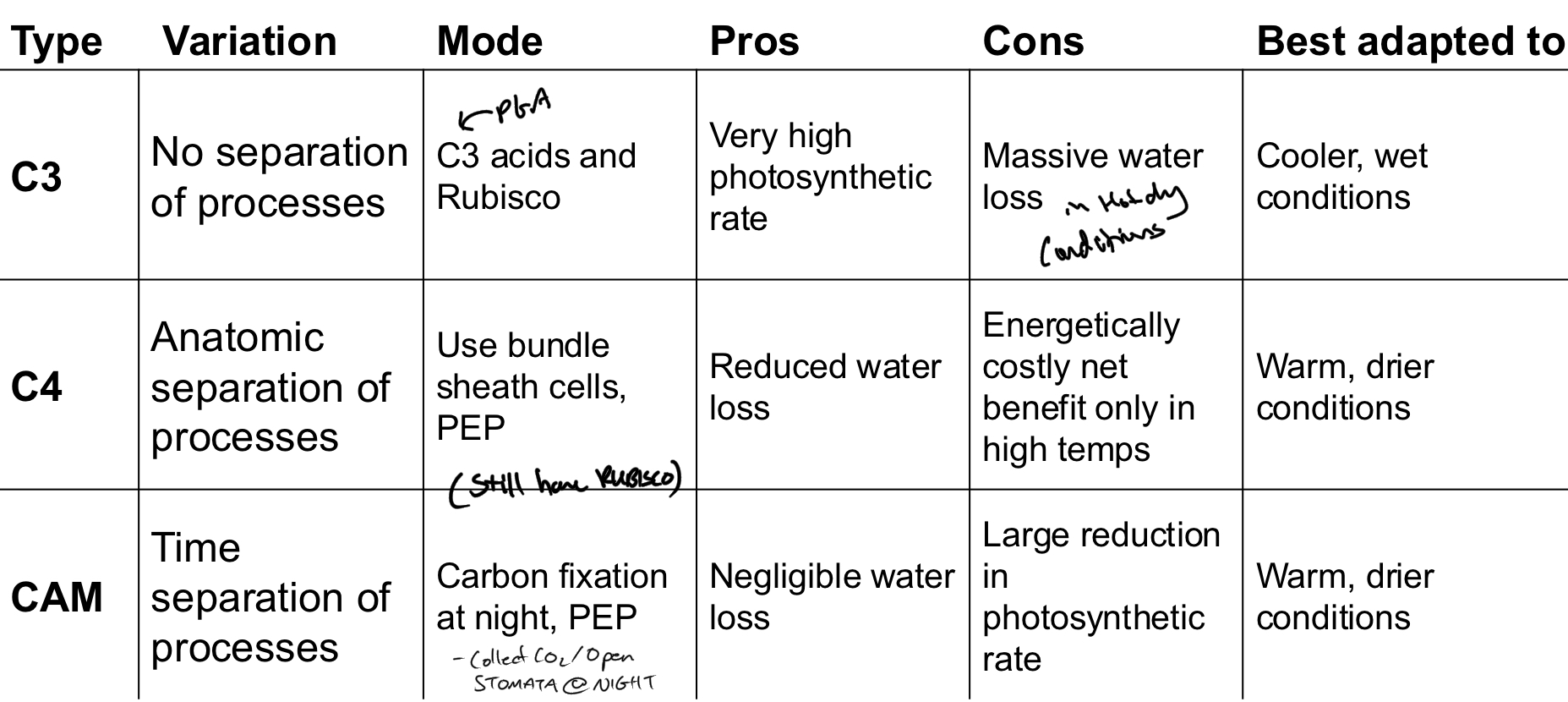
What are the 3 types of Photosynthesis?
C3
C4
CAM
***What is the Difference between the 3 types of Photosynthesis?
C3 = NO anatomical or Temporal separation of photosynthetic processes
C4 = ANATOMICAL separation of photosynthetic processes
PAM = TEMPORAL separation of photosynthetic processes
****In what CELLS does photosynthesis occur?
Mesophyll cells
contains lots of chloroplasts
****How does C3 Photosynthesis work? Where does Initial C Fixation occur what about The Calvin cycle + what TIME?
Both Initial carbon fixation + Calvin cycle occur in MESOPHYLL + during the DAY
*****What PROCESS occurs during the Initial C Fixation occur and The Calvin cycle for C3?
Step | Process | Description |
|---|---|---|
Initial Carbon Fixation | CO₂ combines with RuBP | Enzyme fixes CO₂ to RuBP (5-carbon) → forms 3-PGA (C₃ compound) |
Calvin Cycle | (Light-independent reactions) | 3-PGA is reduced using ATP + NADPH (from light reactions) → forms G3P, used to make glucose and regenerate RuBP |
*****What ENZYME does the initial C fixation of CO2 to RuBP?
RUBISCO = binds CO2 to RuBP
******What is the DISADVATANGE of C3 photosynthesis?
Rubisco = INEFFICIENT at HOT temps
Photosynth. = inefficiently at hot temps
******What is Photorespiration?
RuBisCO binds oxygen (O₂) instead of carbon dioxide (CO₂) during photosynthesis and produces CO2
uses ATP + Glucose to do so
*****Under what conditions do C3 plants undergo Photorespiration? WHY?
HOT DRY days
STOMATA CLOSES to conserve water but no CO2 for Photosynthesis
What are the 2 solutions to C3 photosynthesis?
C4 = Anatomical separation
CAM = Temporal separation
****How does C4 Photosynthesis work? Where does Initial C Fixation occur what about The Calvin cycle + what time?
CO2 = Initially bound to an enzyme in the MESOPHYLL cells to form C4 Acid
C4 acid is transported to BUNDLE SHEATH CELL
C4 acid = broken down to CO2 + Pyruvate
CO2 goes into CALVIN CYCLE in BUNDLE SHEATH CELLS where RUBISCO will Fix it to RuBP
All occurs at same time during the day
****Why does the physical separation into bundle sheath cells prevent photorespiration in Hot dry climates?
Separation of Light dependent MESOPHYLL (O2 prod.) + Independent processes BUNDLE SHEATH
Bundle sheath cells = HIGH in CO2 + Low in O2 = RUBISCO more efficient
This way Stomata can close without worrying about RUBISCO from binding to O2 instead as only CO2 = available in Bundle sheath cells
****What ENZYME does the Initial Fixing of CO2 to form C4 acid. What is the CO2 bound to?
PEP carboxylase = enzyme
PEP = Phosphoenolpyruvate (What CO2 is bound to)
******For C4, what processes occur in Bundle Sheath cells and what occur in mesophyll cells?
Mesophyll:
Light dependent rxn (O2 prod)
Co2 fixation to C4 acid
Bundle Sheath
C4 breakdown = Pyruvate + CO2
RUBISCO fixing CO2 + RuBP
Calvin cycle
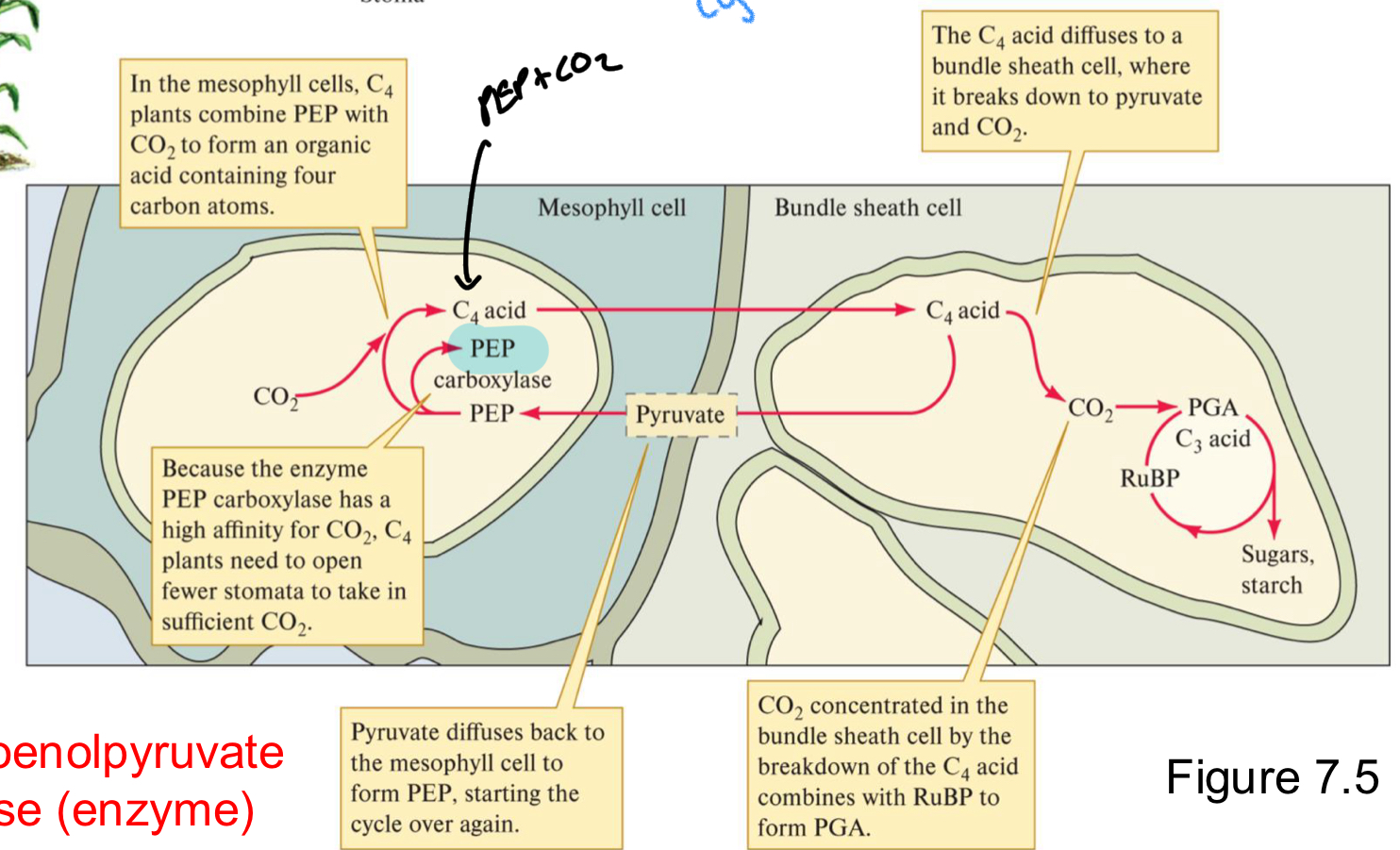
Why is PEP used for the initial fixing of CO2 in C4?
PEP has a high affinity for CO2 regardless of temp
Is C4 photosynthesis common among plants? How does it affect the Primary production from C4 plants.
No only 3% of vascular plants
Still make decent amount of Primary producttion 23%
What is the most prominent C4 plant?
Corn
*******What is the PRO of C4 photosynthesis?
CAN CLOSE STOMATA in hot temps to conserve water and still maintain high CO2 concentrations around Rubisco due to shutting to bundle sheath cells
RUBISCO can still function efficiently in hot temps
*******What is the CON/ trade off of C4 photosynthesis?
Takes energy to create bundle sheath cells
= Takes LONGER to reach reproductive stage
******Is there any advantage C3 has over C4 ?
YES C3 = more ENERGY EFFICIENT
Need to build bundle sheath cells
*****In what environment does C4 Work best?
HOT + DRY
C4 = WATER EFFICIENT
but if water = not limiting there is no point
*****Why are there so few native C4 plants in Edmonton? 2 reasons
Minimum temp = too low for optimal growth
Not dry enough in Edmonton that C4 would provide enough of an advantage
What does CAM stand for?
Crassulacean Acid Metabolism
****How does CAM Photosynthesis work? Where does Initial C Fixation occur what about The Calvin cycle + what time?
ALL functions occur in MESOPHYLL CELL
TEMPORAL SEPERATION
Night: PEP + CO2 —> C4
Day: CALVIN CYCLE
****How + Why does the Temporal separation prevent photorespiration in Hot dry climates for CAM? Aka what specifically occurs at night and what occurs at day?
Night: Not as hot = don’t risk water loss
STOMATA OPEN
PEP carboxylase makes C4 using CO2 (From open stomata) and Pyruvate (made during the day)
Day: Hot = risk water loss
STOMATA CLOSED
C4 breaks down in to CO2 + Pyruvate
CO2 = fixed to RuBP by RUBISCO ==> CALVIN CYCLE (light independent)
CONSERVE WATER
*****Rank the 3 methods of Photosynth. from most to least efficient + why?
C3 = most efficient
C4 = Needs E to make bundle sheath cells
CAM = Can only get carbon during the NIGHT
*****What type of evolution does C4 + CAM have with each other?
CONVERGENT e
Distantly related organisms independently evolve SIMILAR TRAITS (PEP)
*****Rank the 3 methods of Photosynth. from best to worst at water conservation + why?
CAM = stomata closed at day when it is the hottest, there is no water loss at all
C4 = Stomata can close when it is hot = reducing water loss
C3 = If stomata closes in hot temps = no photosynthesis = stomata open in hot dry temps
*******Compare the 3 types of photosynthesis in their 1) Way of dealing with photorespiration 2) what they use + how they do photosynthesis 3)Pros vs. Cons 4) what environment they are best suited for