Week 6: Learning and Consciousness Overview
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
Learning
Permanent change in behavior from experience.
Unlearned Behaviours
Innate behaviors like instincts and reflexes.
Reflexes
Automatic responses to specific stimuli.
Instincts
Innate drives leading to complex behaviors.
Habituation
Decreased response to repeated stimuli.
Sensitization
Increased response to a stimulus after exposure.
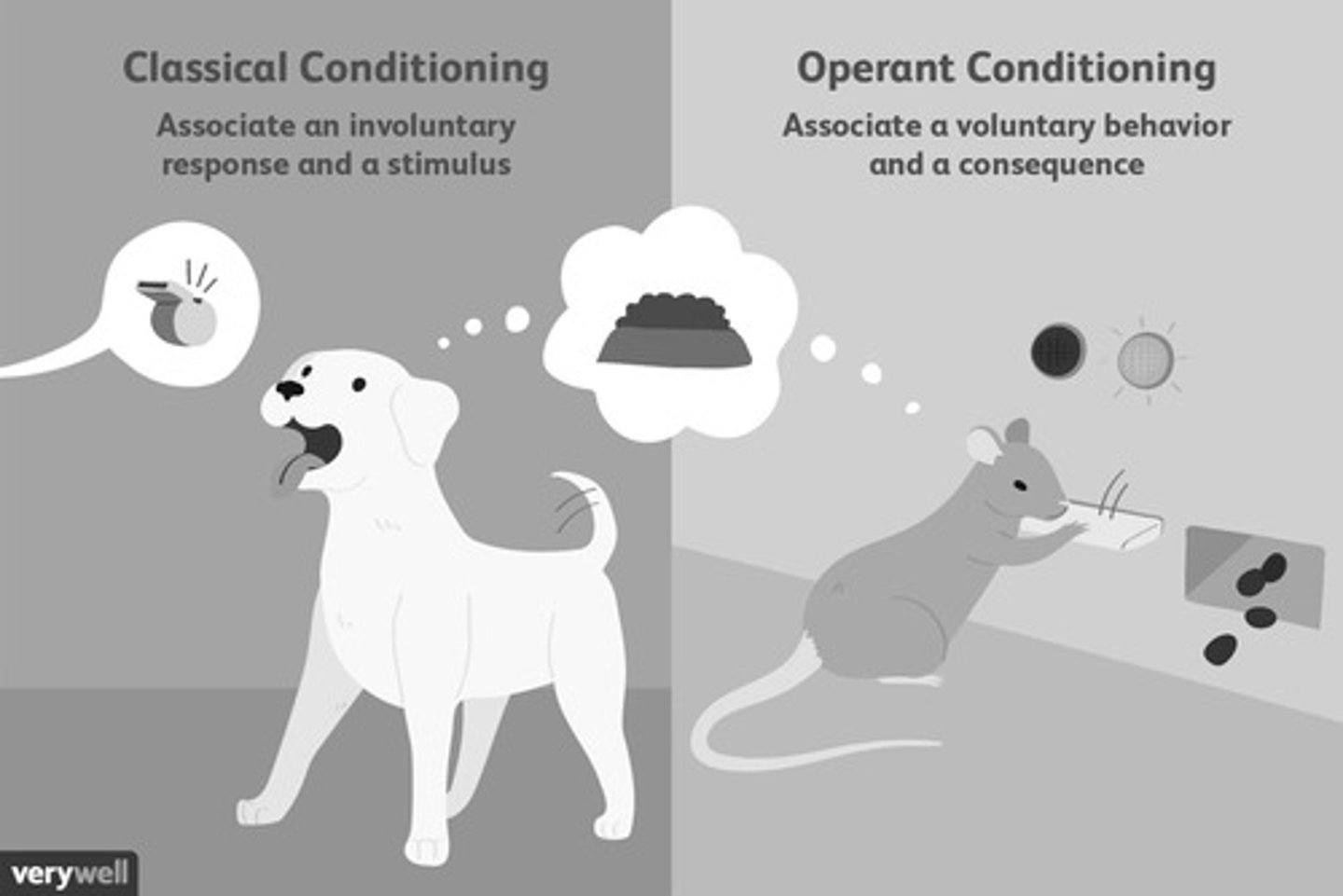
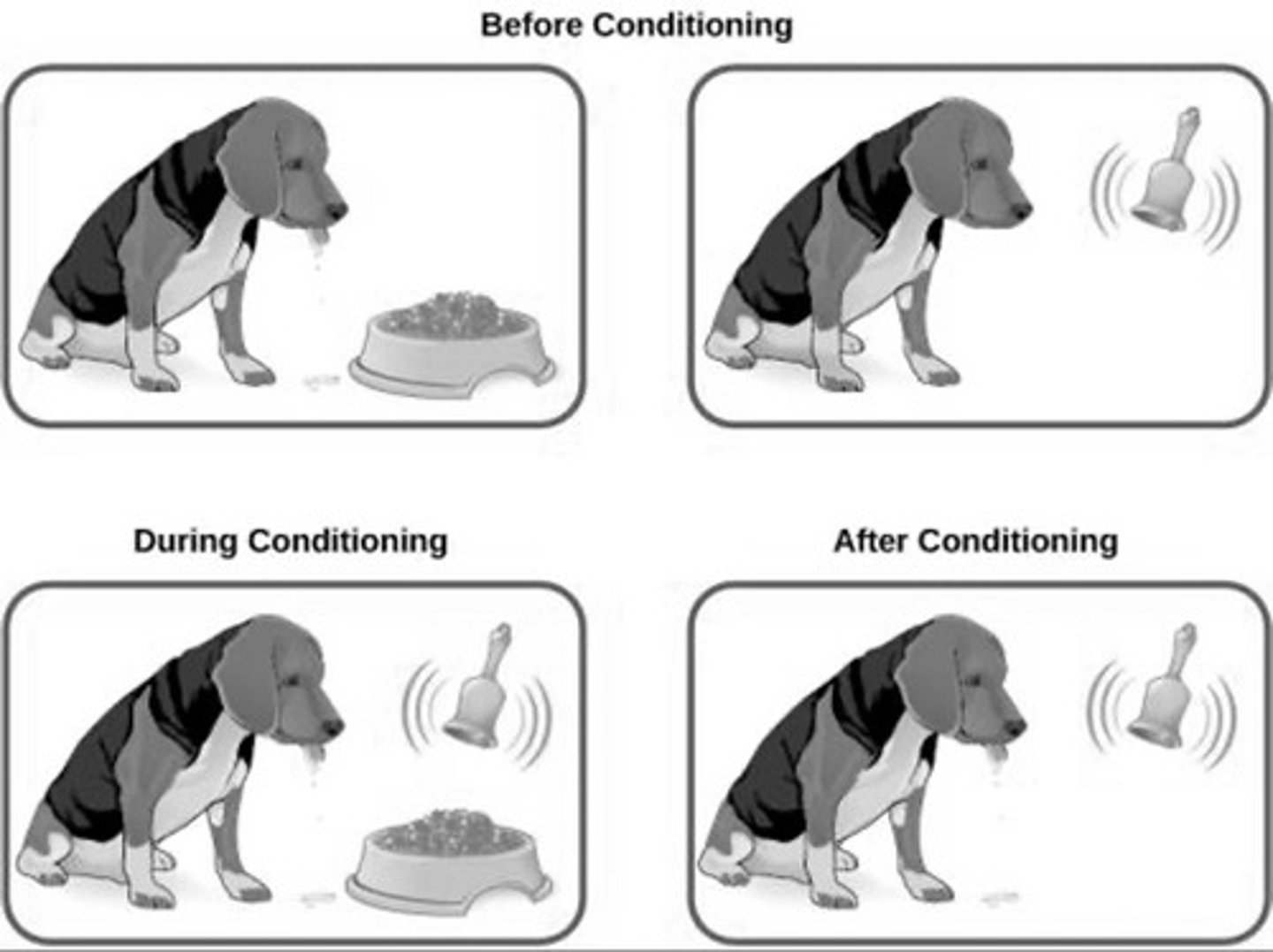
Classical Conditioning
Learning to associate stimuli to anticipate events.
Neutral Stimulus
Stimulus that initially elicits no response.
Unconditioned Stimulus
Naturally triggers an automatic response.
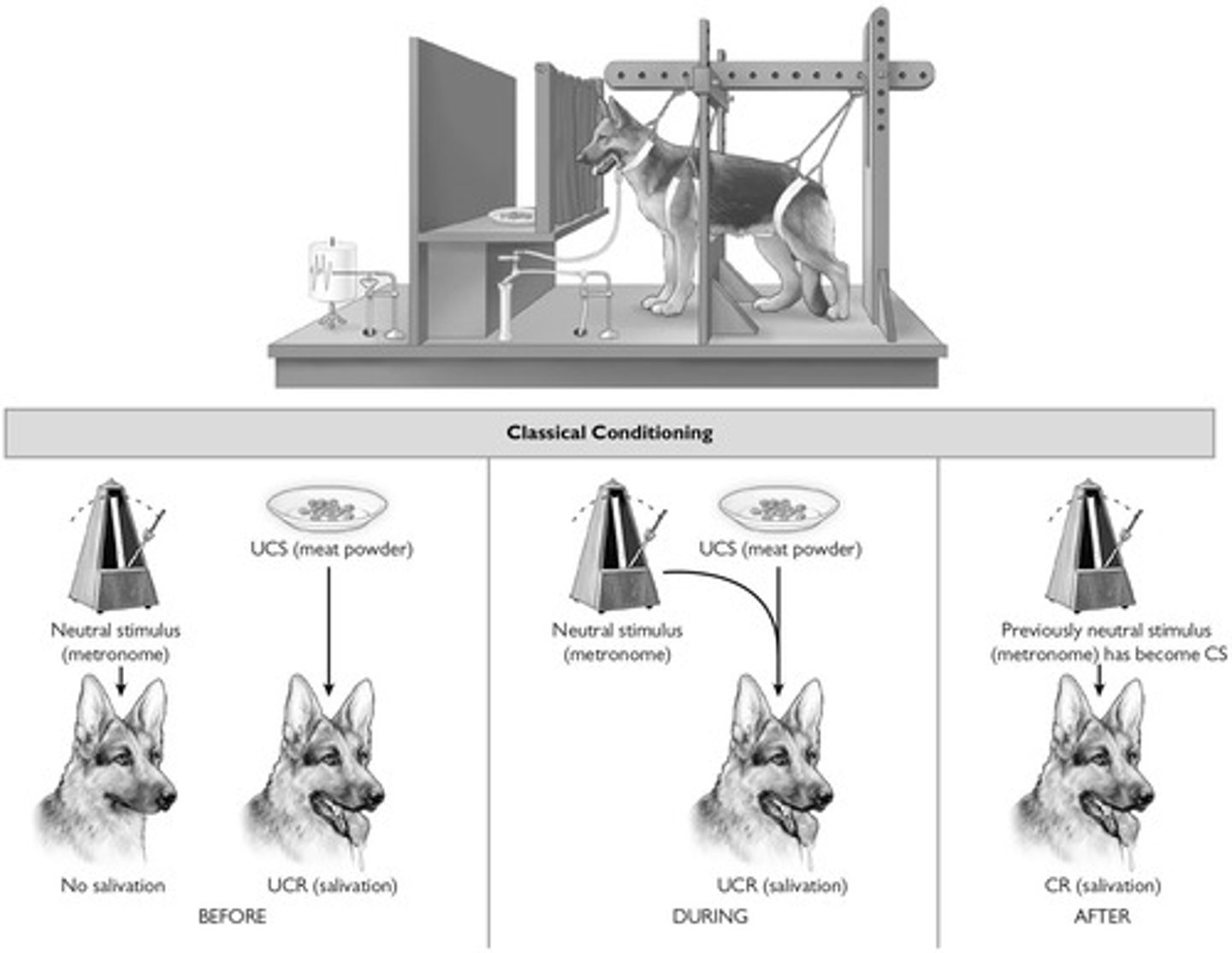
Unconditioned Response
Natural reaction to an unconditioned stimulus.
Conditioned Stimulus
Previously neutral stimulus that triggers response after conditioning.
Conditioned Response
Learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus.
Acquisition
Process of learning a conditioned response.
Extinction
Conditioned response decreases and disappears.
Spontaneous Recovery
Conditioned response reappears after extinction.
Renewal Effect
Response reappears in original environment.
Stimulus Generalization
Similar stimuli elicit the same conditioned response.
Stimulus Discrimination
Distinct stimuli trigger different responses.
Little Albert
Experiment demonstrating classical conditioning of fear.
Fetishes
Sexual attraction to nonliving objects.
Marketing Conditioning
Pairing products with appealing stimuli for response.
Conditioned Taste Aversion
Develops after one trial, long delays possible.
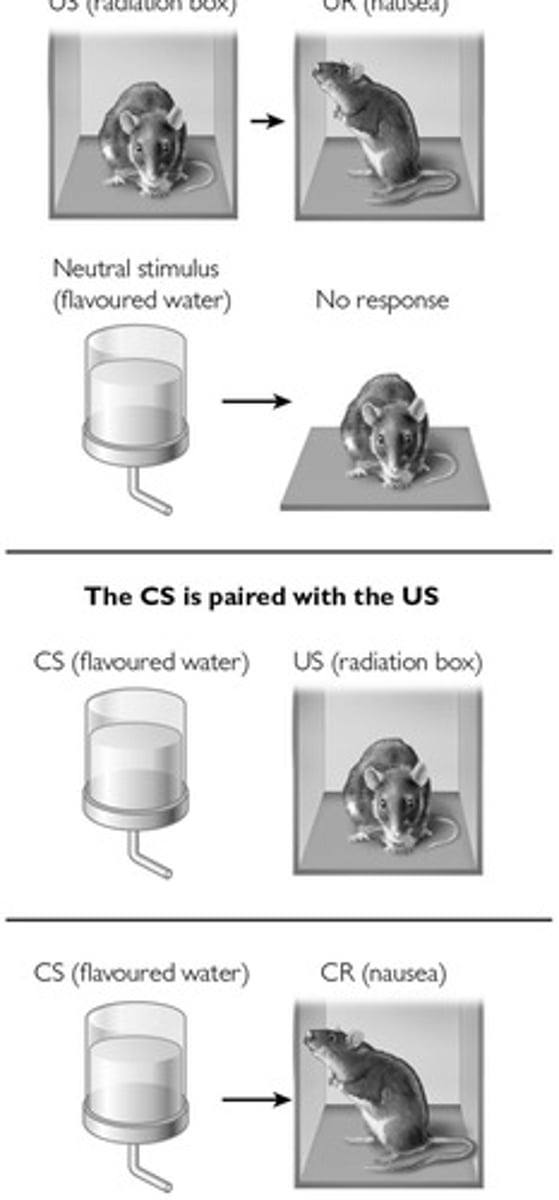
Biological Preparedness
Primed to learn specific associations naturally.
Operant Conditioning
Associating behavior with consequences like reinforcement.
Positive Reinforcement
Adding something to increase behavior likelihood.
Negative Reinforcement
Removing something to increase behavior likelihood.
Positive Punishment
Adding something to decrease behavior likelihood.
Negative Punishment
Removing something to decrease behavior likelihood.
Law of Effect
Reward increases behavior likelihood; punishment decreases it.
Stimulus Discrimination
Ability to distinguish between different stimuli.
Stimulus Generalization
Responding similarly to similar stimuli.
Instinctive Drift
Animals revert to innate behaviors despite reinforcement.
Continuous Reinforcement
Reinforcing behavior every time it occurs.
Partial Reinforcement
Occasional reinforcement leads to slower extinction.
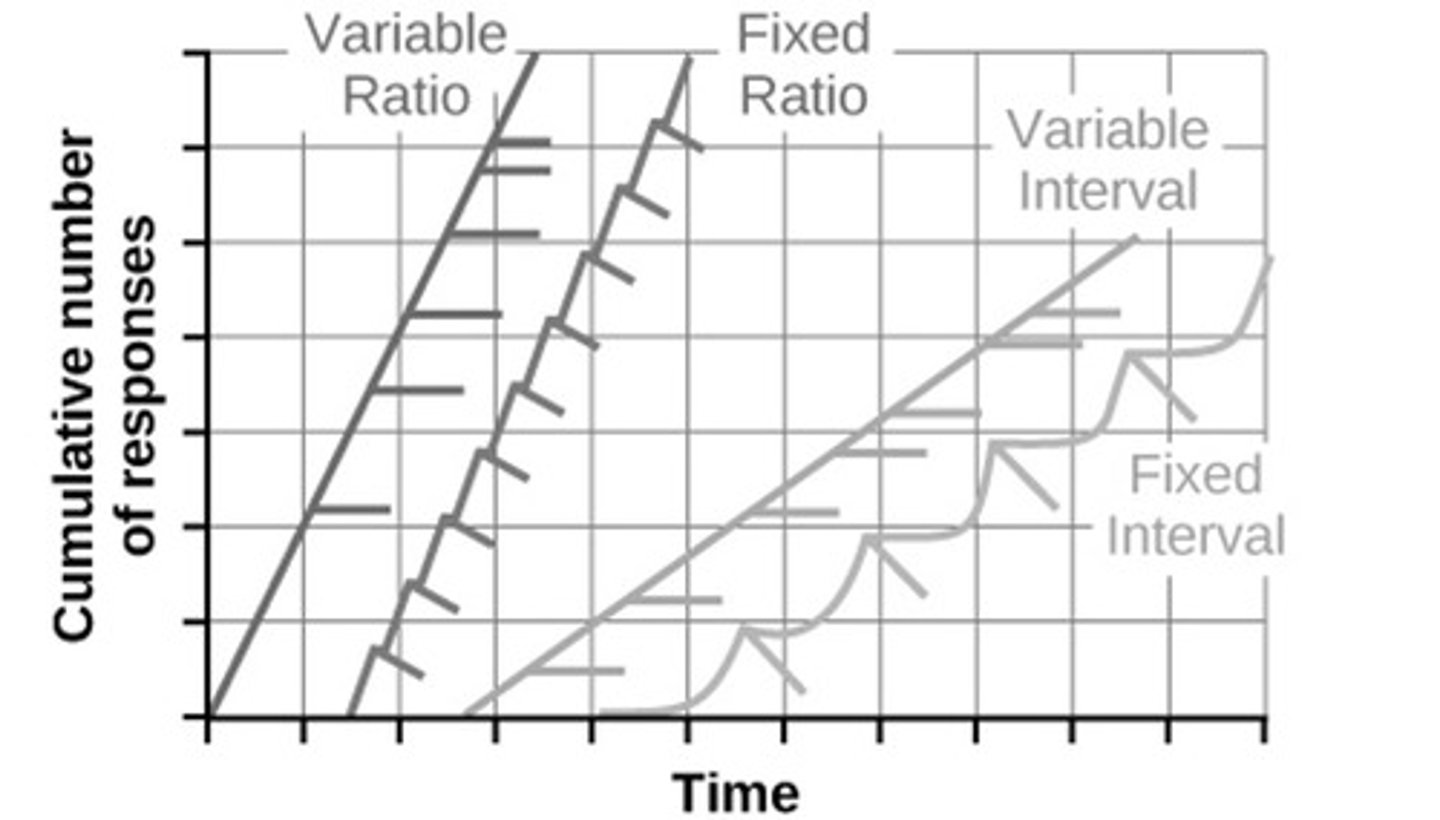
Fixed Interval Schedule
Reinforcement at predictable time intervals.
Variable Interval Schedule
Reinforcement at unpredictable time intervals.
Fixed Ratio Schedule
Reinforcement after a set number of responses.
Variable Ratio Schedule
Reinforcement after an unpredictable number of responses.
Latent Learning
Learning without immediate reinforcement, revealed later.
Cognitive Maps
Mental representations of spatial information learned.
Observational Learning
Learning by watching others' behaviors.
Media Violence
Exposure to violence in media influences real-world behavior.
Superstitious Behavior
Behavior learned through accidental reinforcement.
Cognitive Approaches to Learning
Mental processes play a role in learning.
Violence in Media Statistics
Children exposed to extensive violence before adulthood.
Alien Communication
20% of college students believe aliens communicate via dreams.
Alien Encounters
10% of people claim to have met aliens.
Sleep Paralysis
Awake but unable to move, often terrifying.
Cultural Influence
Culture shapes experiences of sleep paralysis.
Waking Consciousness
Subjective awareness of the world and self.
Altered States
Includes sleep paralysis, hypnosis, and drug effects.
Sleep Definition
Low activity and reduced awareness state.
Hormones in Sleep
Melatonin, FSH, LH, and growth hormone secreted.
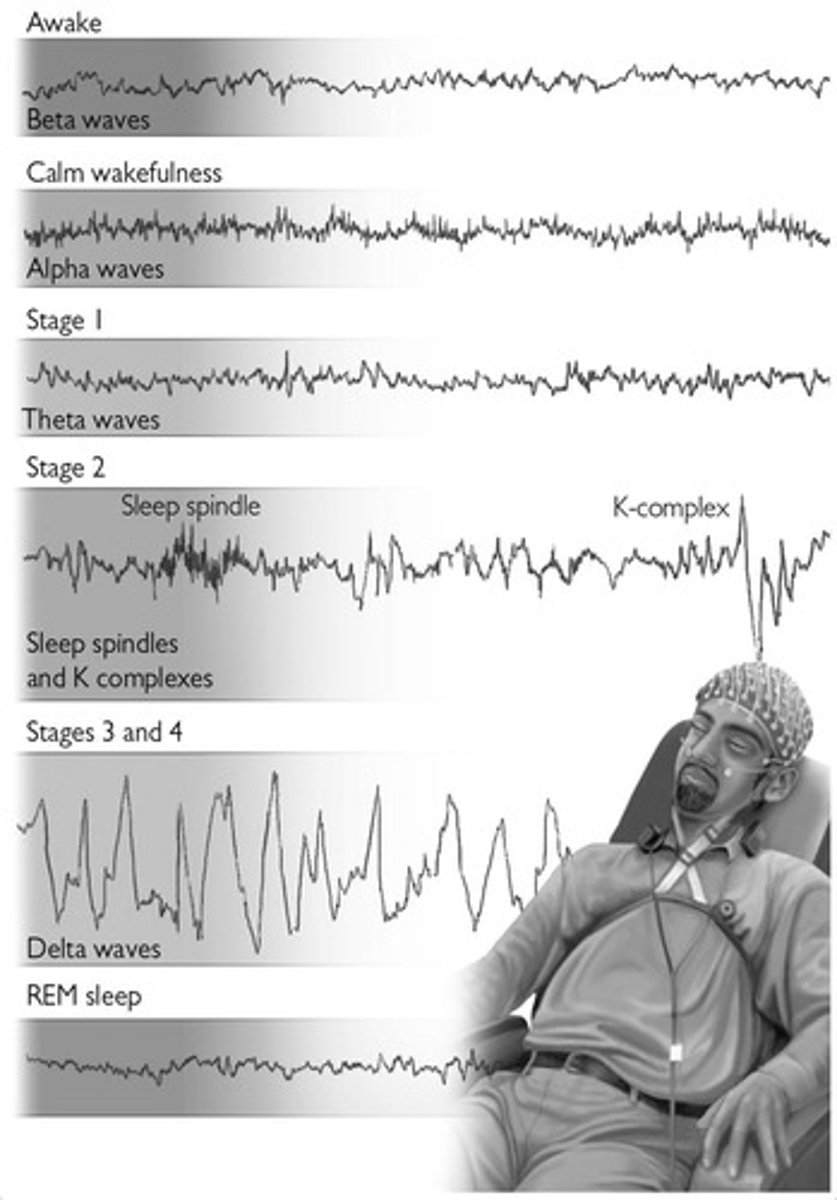
NREM Stages
Stages 1 to 4, no eye movements, fewer dreams.
REM Sleep
Stage 5 with vivid dreams and eye movements.
Deep Sleep Benefits
Recharges body, boosts immune and cardiovascular health.
Hypnagogic State
Pre-sleep consciousness with vivid imagery.
Myoclonic Jerk
Sudden muscle contraction during the transition to sleep.
Stage 1 Sleep
Transition phase lasting a few minutes.
Stage 2 Sleep
Includes sleep spindles, comprises 65% of sleep.
Delta Waves
Brain activity in deep sleep stages 3 and 4.
Sleep Efficiency
Children spend more time in deep sleep than elderly.
REM Rebound
Increased REM sleep after deprivation.
Adaptive Sleep
Sleep necessary for growth and development.
Restorative Sleep
Restores cognitive function and memory consolidation.
Sleep Needs
Average sleep duration varies among individuals.
Sleep Requirements
7-8 hours needed, varies by age.
Sleep Deprivation
Increases stress and emotional reactivity.
Emotional Regulation
Biological basis affects emotional responses.
Amygdala Activation
Reacts to neutral images as emotional.
Peter Tripp
Staged 200-hour wakeathon, experienced severe effects.
Sleep Hygiene
Practices for better sleep quality.
Circadian Rhythm
Biological rhythm occurring over 24 hours.
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
Brain's clock, regulates circadian rhythms.
Melatonin
Hormone that promotes sleep, regulated by light.
Jet Lag
Fatigue from internal clock misalignment.
Rotating Shift Work
Changing work schedules disrupt normal rhythms.
Bright Light Therapy
Realigns biological clock with external environment.
Shift Work Effects
Ages brain by over 6 years.
Dream Function
Explores meaning and purpose of dreams.
Freud's Dream Theory
Dreams fulfill unconscious wishes, latent vs. manifest.
Dreams-for-Survival Theory
Dreams process daily life concerns for survival.
Kurdish vs. Finnish Study
Kurdish children report more intense threatening dreams.
Sleep-Wake Cycle
Linked to natural light-dark environmental cycles.
Sleep Deprivation Symptoms
Includes slurred speech, hallucinations, personality changes.
Sleep Environment
Quiet and comfortable space promotes better sleep.
Caffeine Avoidance
Avoid after lunch for improved sleep quality.
Activation-synthesis theory
Dreams interpret random brain activity during sleep.
Limbic system
Emotional center active during REM sleep.
Insomnia
Difficulty sleeping at least 3 nights weekly.
Insomnia prevalence
9-20% of people experience insomnia.
Insomnia in students
~25% of students suffer from insomnia.
ADHD and insomnia
ADHD increases insomnia risk by 3.48 times.
Insomnia treatments
Psychotherapy and hypnotics like Lunesta, Ambien.
Paradoxical insomnia
Belief of sleep deprivation despite normal sleep.
Sleep-state misperception
Misunderstanding of one's actual sleep state.
Night terrors
Sudden waking with screaming and confusion.
Sleep apnea
Airway blockage during sleep causing breathing issues.
SIDS
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome related to sleep apnea.
Narcolepsy
Sudden sleep onset directly into REM sleep.