Hearing Science Final
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Particles of a medium move______ to the sound wave, making sound waves _________
parallel, longitudinal
Time = 1/f in an inverse relationship is
f = 1/T
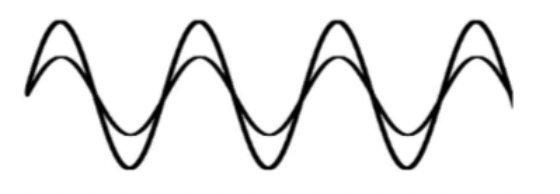
What is different about these two waves?
Amplitude
Period is
the duration of one complete cycle of a wave.
Amplitude is
the maximum displacement of a wave from its rest position.
Phase is
the position of a point in time on a waveform, often expressed in degrees or radians.
Frequency is
the number of cycles of a wave that occur in one second, measured in Hertz (Hz).
One sinusoidal wave has a period of 10 ms, the other has a period of 2 ms. When the two waves are added together the results are …
the period is 10 ms (It is the longer period of the two waves)
What would be the best tool for analyzing the frequency components of a complex sound?
Frequency spectrum
How is energy represented on a spectrogram?
The color/shade
Sound travels fastest in…
solids due to closer molecular packing.
True or false, sound travels in a vacuum
False, it does not occur, as there are no molecules to transmit the sound waves.
A sound wave is…
longitudinal
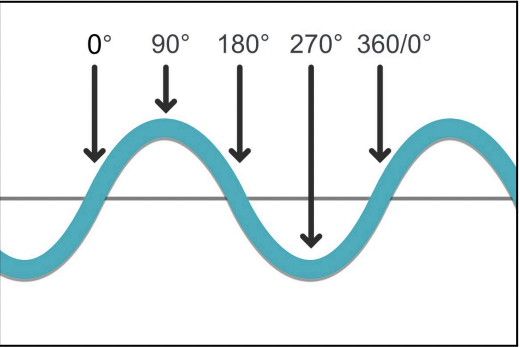
What is the phase measured in?
Degrees and radians
What makes a complex wave?
A complex wave is made up of multiple simple sine waves combined at different frequencies and amplitudes, resulting in a waveform that sounds richer than a single frequency. Ex. Combination of 2 sine waves combination of 3 or more sine waves.
Visual representation of how energy is distributed across frequency in a complex sound at a specific time point
Is called a Spectrum
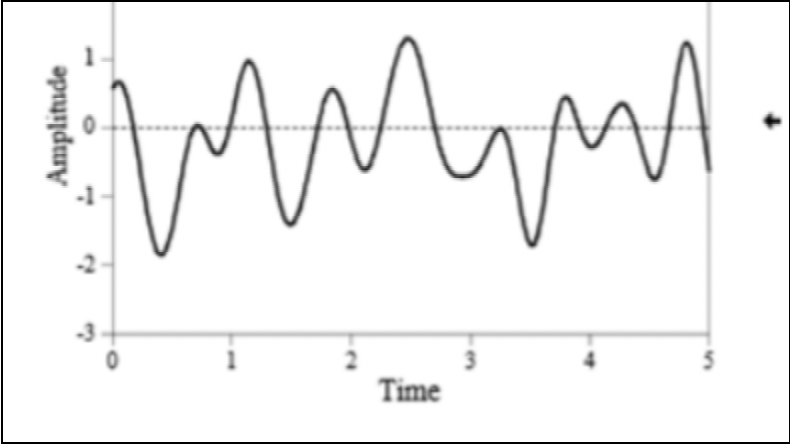
What information does this graph represent?
Time, Domain
What are the functions of the pinna and ear canal?
Collects sound, protects the ear from infection, enhances the sound level at the eardrum for specific frequencies
What structure separates the middle ear and the inner ear?
Oval window
What structure separates the outer and middle ear?
Tympanic membrane
What leads to the largest increase to overcome the impedance mismatch between the outer and middle ears?
Area Difference
The base of the BM is ________ with less mass; activated by _________
Stiffer; higher frequencies
Apex of the BM is _______ with more mass; activated by ________
more flexible; lower frequencies
True or False: An intensity discrimination threshold is the lowest intensity a stimulus can be detected (usually 50% of the time)
False: This describes the absolute threshold
In audiometric testing, there is a speech perception test in which listeners hear “say the word: thought” and are asked to repeat the word. What auditory behavior is being measured?
Recognition
True or False: Humans are most sensitive to frequencies between 1,000 - 5,000 Hz
True
In clinical setting, _____ is used to document and communicate about hearing thresholds
Audiogram
Minimum audible pressure (MAP)
Sound level is measured at the eardrum
Minimum audible field (MAF)
Sound level is measured in the sound field
The difference in level between the loudest and quietest sounds that a person can hear is…
Dynamic range
The difference in level between the loudest and quietest sounds that a person can hear…
Dynamic range
What represents the softest sound you can hear?
Minimum audibility curve
True or False: A sound of 50 dB SPL is 2x the sound pressure as the same sound of 25 dB SPL
False: due to the logarithmic nature of the decibel scale, a 50 dB SPL sound is actually 100 times the sound pressure of a 25 dB SPL sound.
What is the reference point for dB SL scale?
Threshold of the individual listener
If a person’s threshold at 1000 Hz is 10 dB HL and a 1000 Hz pure tone is presented at 45 dB SL, what is the HL presented at?
10 dB HL + 45 dB SL= 55 dB HL
What is the Method of Adjustment?
It is finding a threshold where the observer adjusts the stimulus, NOT THE EXPERIMENTER
What are the potential problems with classic psychophysics methods in measuring threshold?
Time consuming, require complicated programming, cannot separate observer’s internal response and criterion
The measure of minimal amount of change in a stimulus that can be detected is called…
Discrimination threshold
In a psychometric function, the x-axis is typically _____________ and the y-axis is typically ________
Physical characteristics of stimulus, percent of response
Loudness is a ______ variable
Perception
Intensity is a _______ variable
Stimulus
In a loudness growth function, sounds above 40 dB double in intensity when
increased by 10 dB
Loudness recruitment is …
With increase in stimulus, their perception of loudness increases faster than that of listeners with typical hearing
When does phase locking to pure tones work best?
Below 4000 Hz
What measures the discrimination threshold for pitch?
Frequency difference limen (Sounds lower than 4000 Hz: FDL is lowest, pitch discrimination is best)
The lowest frequency component of a complex tone is…
Fundamental
In the phenomenon of missing fundamental, what pitch is heard with the complex tone?
The pitch of the fundamental frequency
The ability to hear out one component in a complex sound depends on the listener's…
Frequency resolution, Frequency selectivity, and Auditory filter width
Basilar membrane tonotopic mapping means each location on the BM responds to a limited range of…
Frequencies
Wide Auditory Filter has…
Poor frequency resolution and more difficulty with speech in background noise
Narrow Auditory Filter has…
Better frequency resolution and improved speech perception in background noise
If we change the duration of a pure tone of 1000 Hz from 500 ms to 1 second, it will sound…
The same (No change in loudness but longer in duration because the sound > 300 ms)
In sounds < 300 ms, what is the relationship between duration and absolute threshold?
Linear relationship
True or False: If the absolute threshold for 200-ms 1000 Hz is 5 dB SPL, you cannot detect a 100 ms 1000 Hz tone played at 5 dB SPL
True
The duration window is approximately 200 ms for forward masking and 25 ms for backward masking. Which of these signals is not masked by the noise?
Played 100 ms before the onset of noise masker
In amplitude modulation detection, what result indicates better performance?
Listener can detect shallower modulation
If a sound source is 0 degrees azimuth and 180 degree elevation, where is it located?
Back of the head
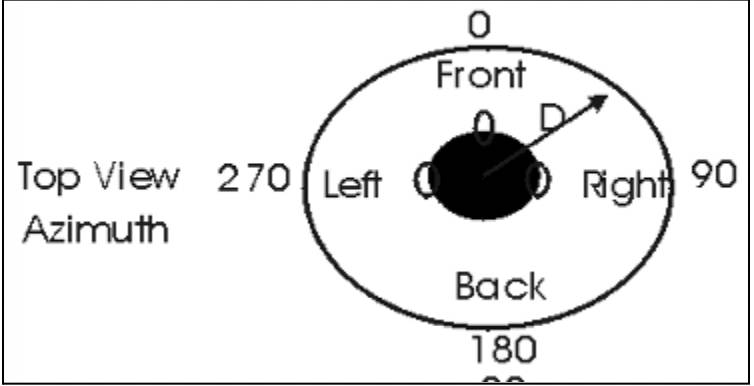
ILD is based on ________ between ears
Intensity differences
ITD is based on _______ between ears
Time differences
True or False: The Head-Related Transfer Function (HRTF) is a monaural cue
True
True or False: According MAA (Minimum Audible Angle), we are more sensitive to the position of sound source when it is next to us than when it is front of of us
False: Smaller when the sound is closer to 0 degree azimuth (right in front of the head), and smaller at low frequency
Where does the most extreme Interaural Time Difference (ITD) occur?
To the right/left
What is a binaural cue for sound localization?
Interaural Level Difference (ILD) and Interaural Time Difference (ITD)
When is ITD a more dominant cue for localization?
Lower frequencies (below 2kHz)
What does not work well in the cone of confusion?
Binaural cues
A visual representation of sound with a small time window, good time resolution, and poor frequency is a characteristic of what?
Wideband spectrum
Speech intelligibility would improve with
Less energetic masking, more favorable signal-noise-ratio, and better audibility
What is a typical measure of speech intelligibility?
Speech recognition score
True or False: With the same SNR, speech intelligibility in fluctuating noise is typically lower than that in steady-state noise.
False: Speech intelligibility is generally higher in fluctuating noise compared to steady-state noise because fluctuations can improve the detection of target speech.
When does energetic masking happen?
When speech and noise have similar energy distribution on the spectrum
Sounds move like a ______ wave, and are graphed as a ______ wave
Longitudinal, sinusoidal
To look at the amplitude of individual frequencies in a complex sound what would you need?
Spectrum, or a spectrogram which shows how frequencies change over time
What mechanisms are used to overcome impedance mismatch?
Area difference of TM and oval window (17x), buckling effect of the TM, and lever action of ossicles (1.2x)
Level of the auditory hierarchy:
Detection (basic), Discrimination, Identification, and Comprehension (complex)
In amplitude modulation detection, it is easier to hear a sound through a masker with ______ modulation
Deeper
If you change the duration of a 1k Hz pure tone from 100 ms to 200 ms, what happens to the sound?
Sound becomes louder
What is the effect when a signal is presented after the masker?
Forward masking
Low harmonics phase lock to…
Pure tones
High harmonics phase lock to the…
Envelope
Frequency difference limen is…
the smallest detectable difference in frequency that can be perceived by an auditory system. It is measured using method of constant stimuli
What is true about the minimum audible angle?
It is the smallest angular separation between two sound sources that can be reliably detected by the auditory system.
True or False: The ear canal resonance effect amplifies frequencies of 1k Hz - 5k Hz.
True: It enhances sound sensitivity in this frequency range, improving perception of speech and other sounds.
The method of limits …
Presenting stimuli starting from high or low intensities to determine a threshold
Functions of the inner ear:
Separating sounds into individual frequencies, sends sounds to the auditory pathway, and tuning mechanical vibration into neural activity
Speech intelligibility task is…
When a participant is presented a stimuli and asked to repeat back what they hear
Characteristics of the base of the BM
More stiff, less mass, and resonates with higher frequencies