Body Fluids Midterm
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
211 Terms
Factors standardized for urine microscopic exams
Microscopes are optically equivalent
Same volume of urine sediment
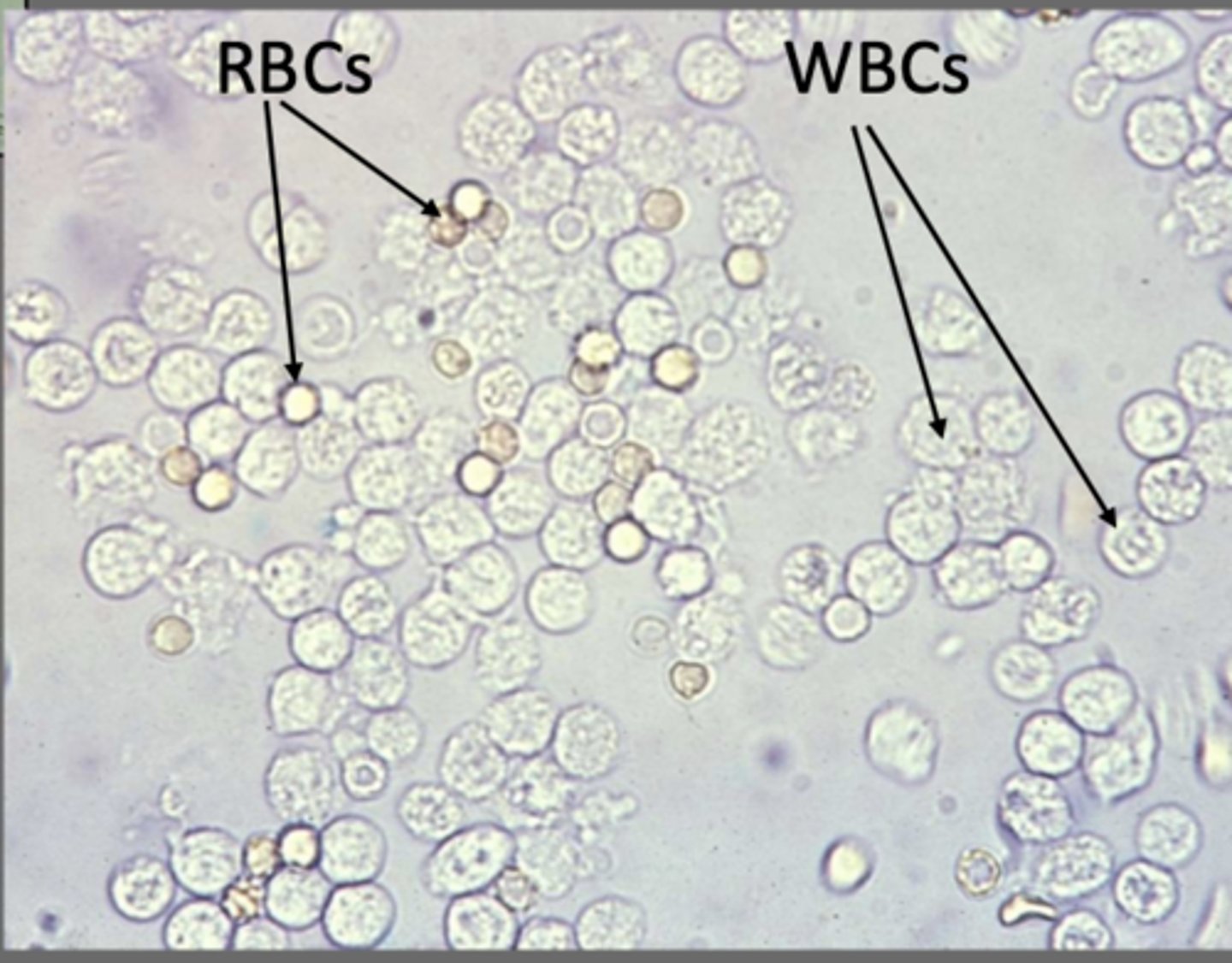
RBC
lack nuclei, homogenously clear center, can see biconcave center
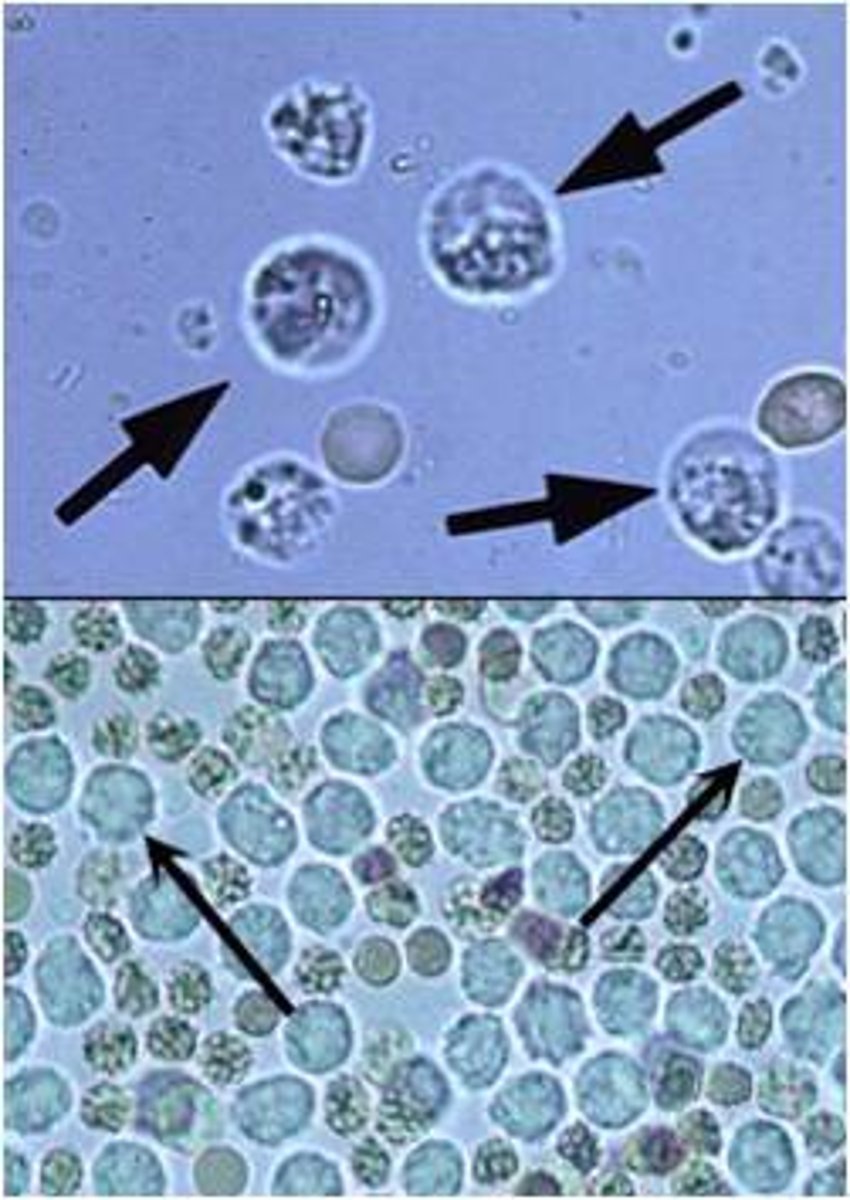
Glitter cell
Neutrophils exposed to hypotonic urine absorb water and swell. Brownian movement of the granules within this larger cells produce sparkling appearance.
Squamous epitelial
Origin in urethra
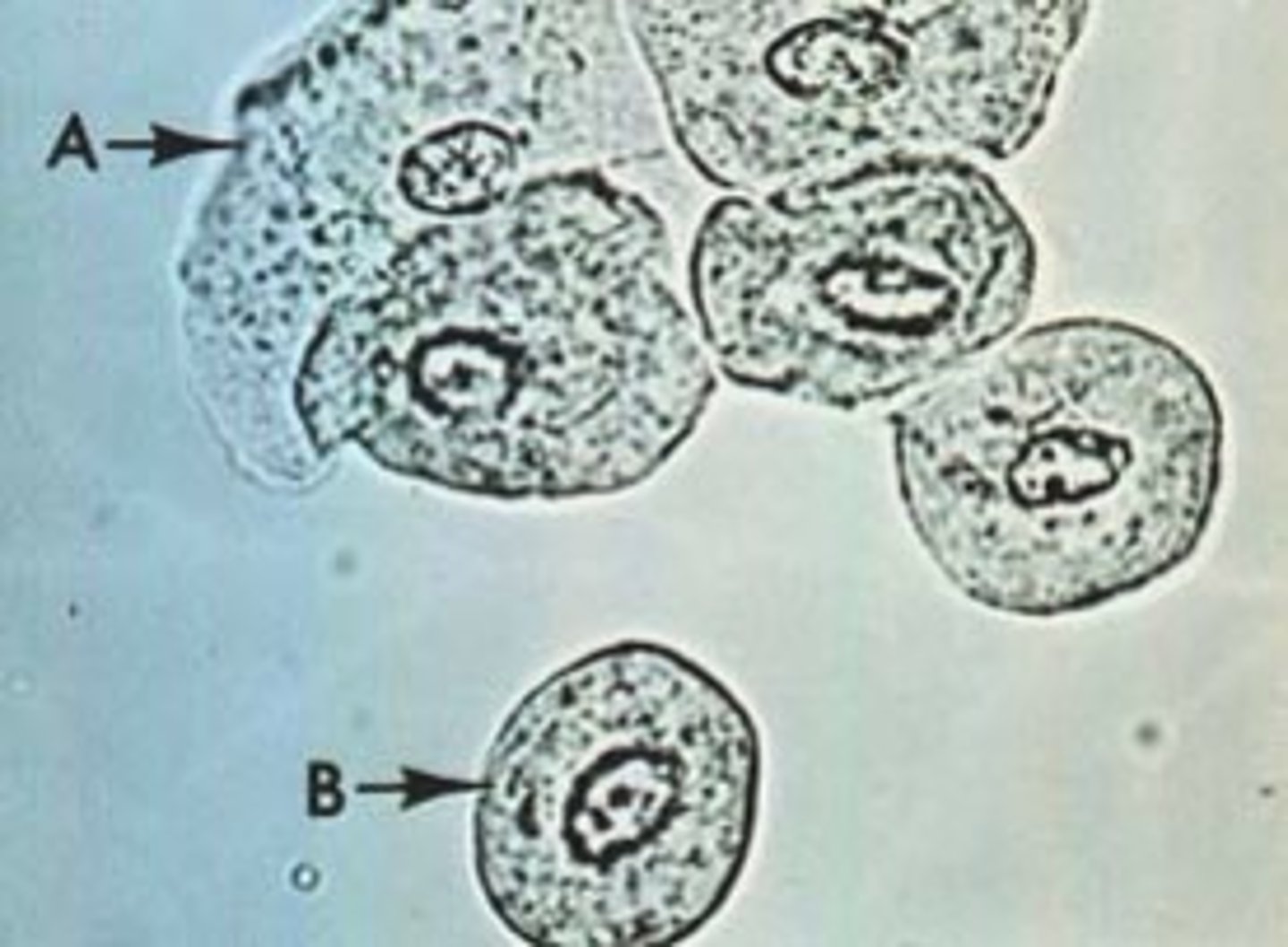
Increased sloughing of epithelial cells from the urinary tract
UTIs and other infections seen with what
Differentiation between RBCs and Yeast
RBCs with lyse with the addition of aceti acid. Yeasts are more refractile and may have buds and will not stain or dissolve
Difference between WBCs and renal tubular cells
WBCs are smaller and have a lobed nucleus
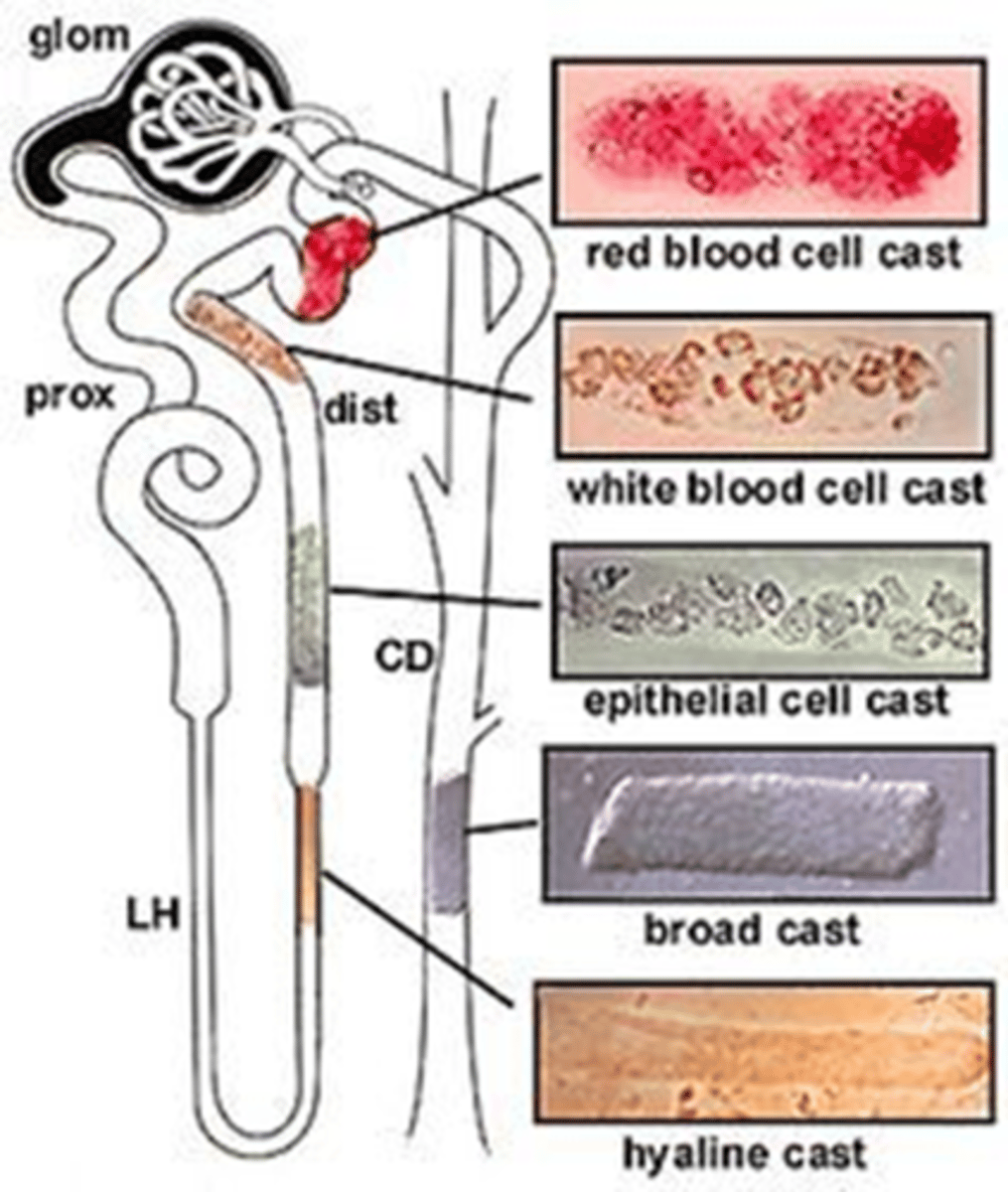
Urinary cast formation
RT cells in the ascending Loop of Henle and DCT produce uromodulin, which traps particles when the urine is highly concentrated, forming a matrix, which will break free and be seen as a cast in the urine
Factors affecting cast formation
Acidic urine
Solute concentration
Increased plasma proteins
Urinary stasis
Hyaline casts
Increased exercise, fever, dehydration, glomerular damage cause in increase in what?
Hyaline cast appearance
Colorless, low refractive index

cellular casts appearance
Cells trapped in the cast matrix
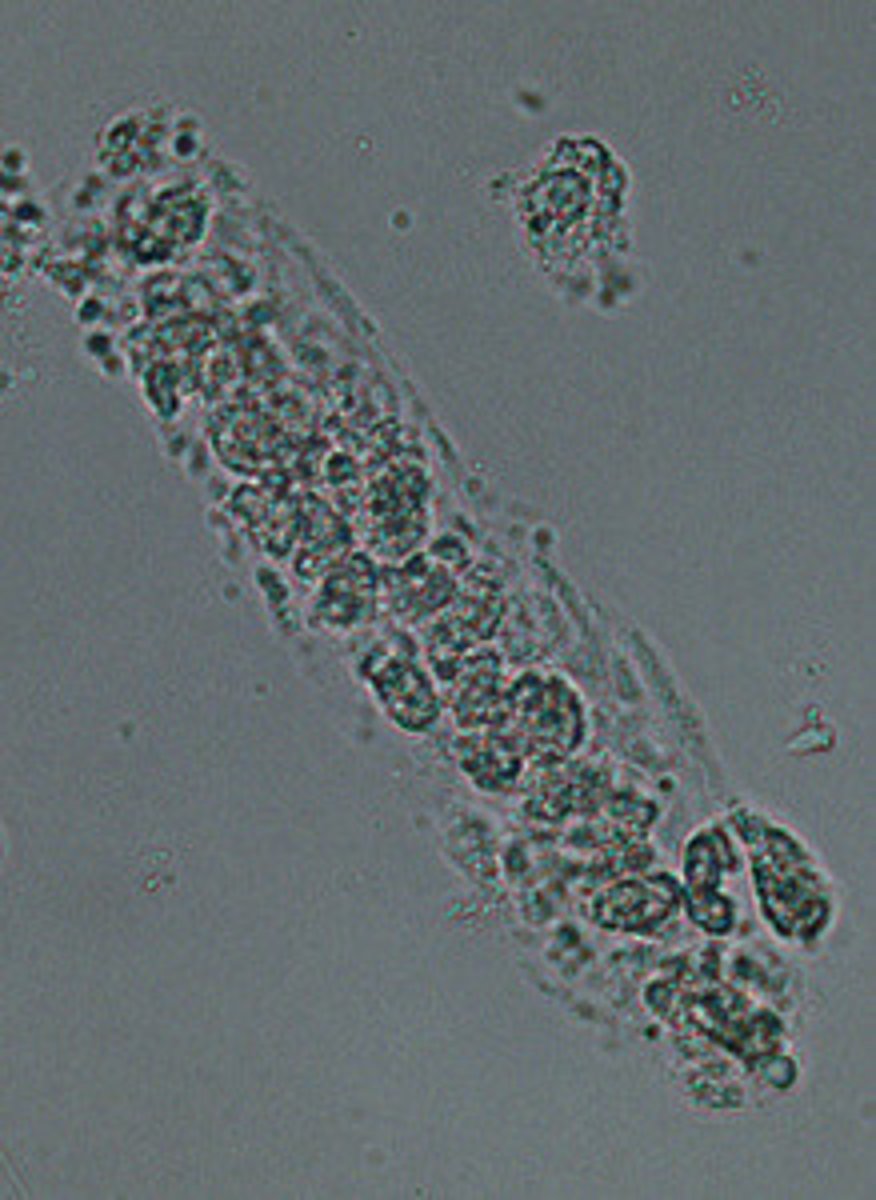
Blood casts
RBCs get stuck in casts and are lysed, releasing hemoglobin, which oxidizes to appear brown
Glomerular damage, bleeding due to kidney stones, cancer; possible after contact sports
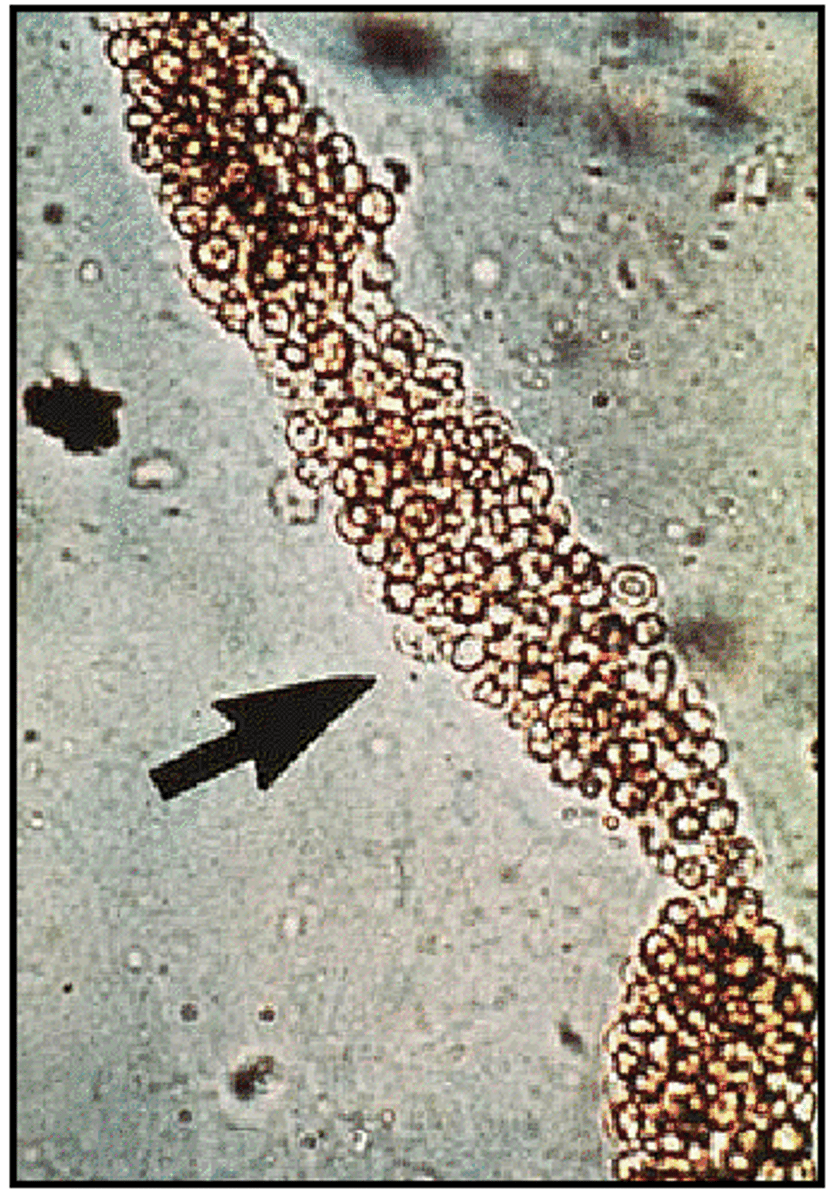
Granular cast
Grainy appearance, fine vs. granular due to size of particles
Degeneration of cells that were trapped within the cast matrix; sometimes found in healthy urine
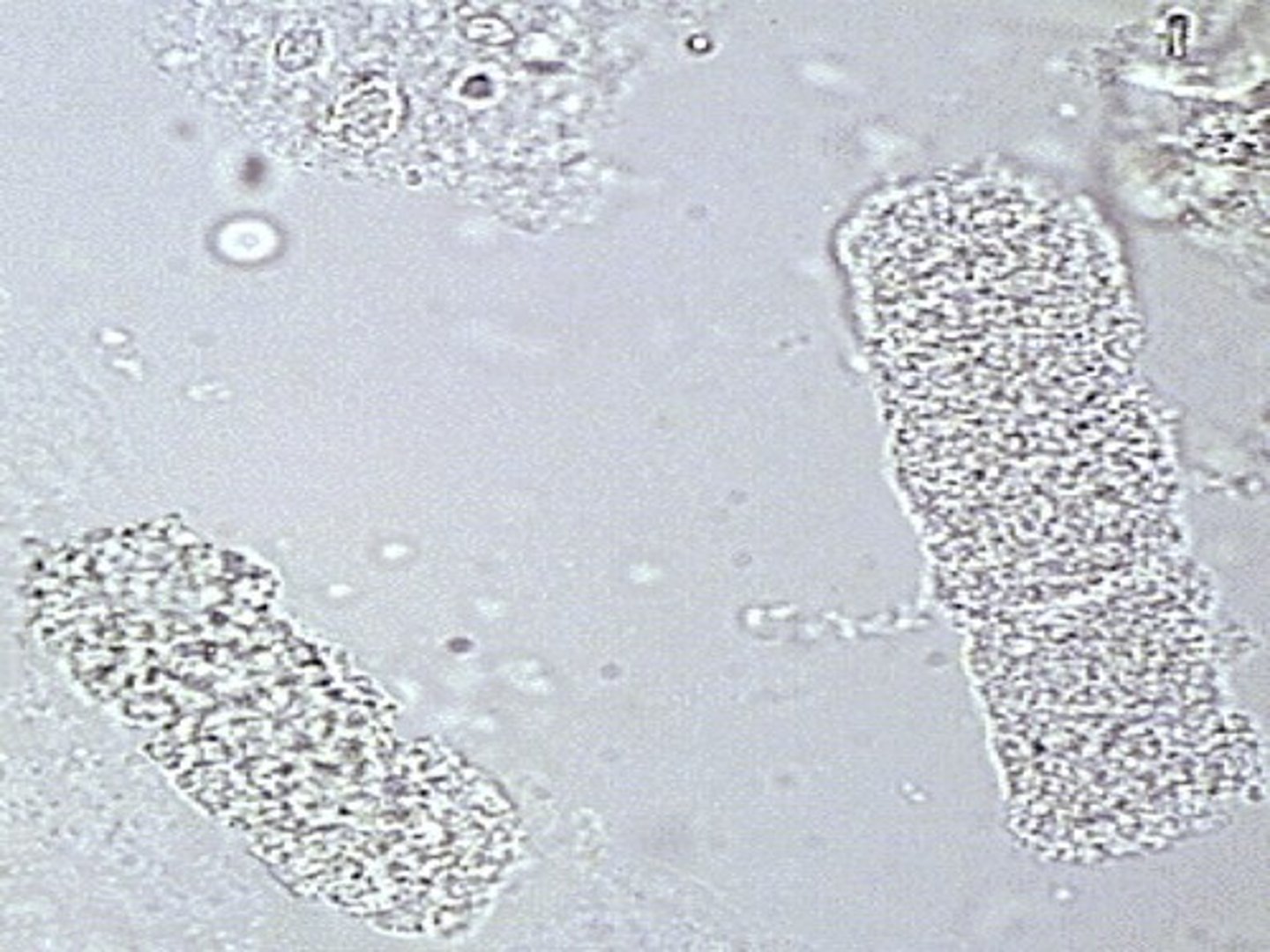
Hyaline, not enough cells to have diagnostic significance
If a cast has a single cell in the cast, what type of cast is it?
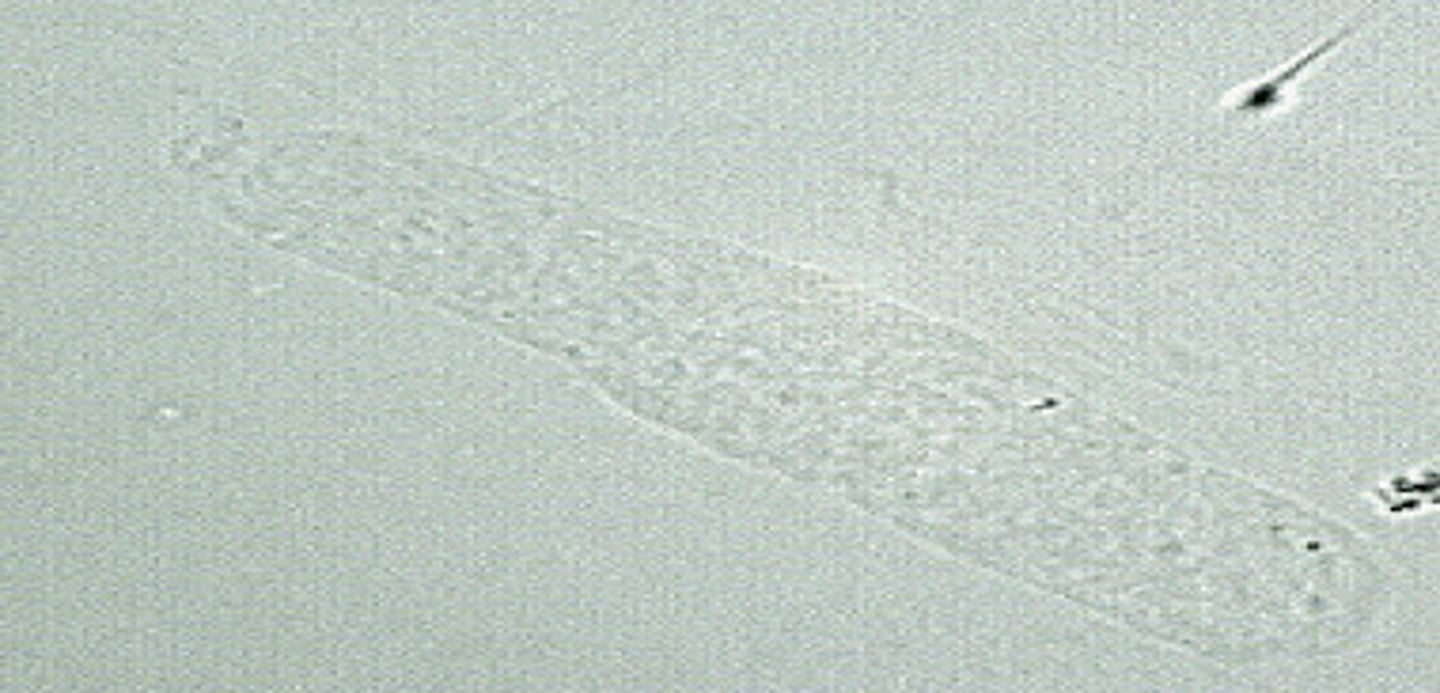
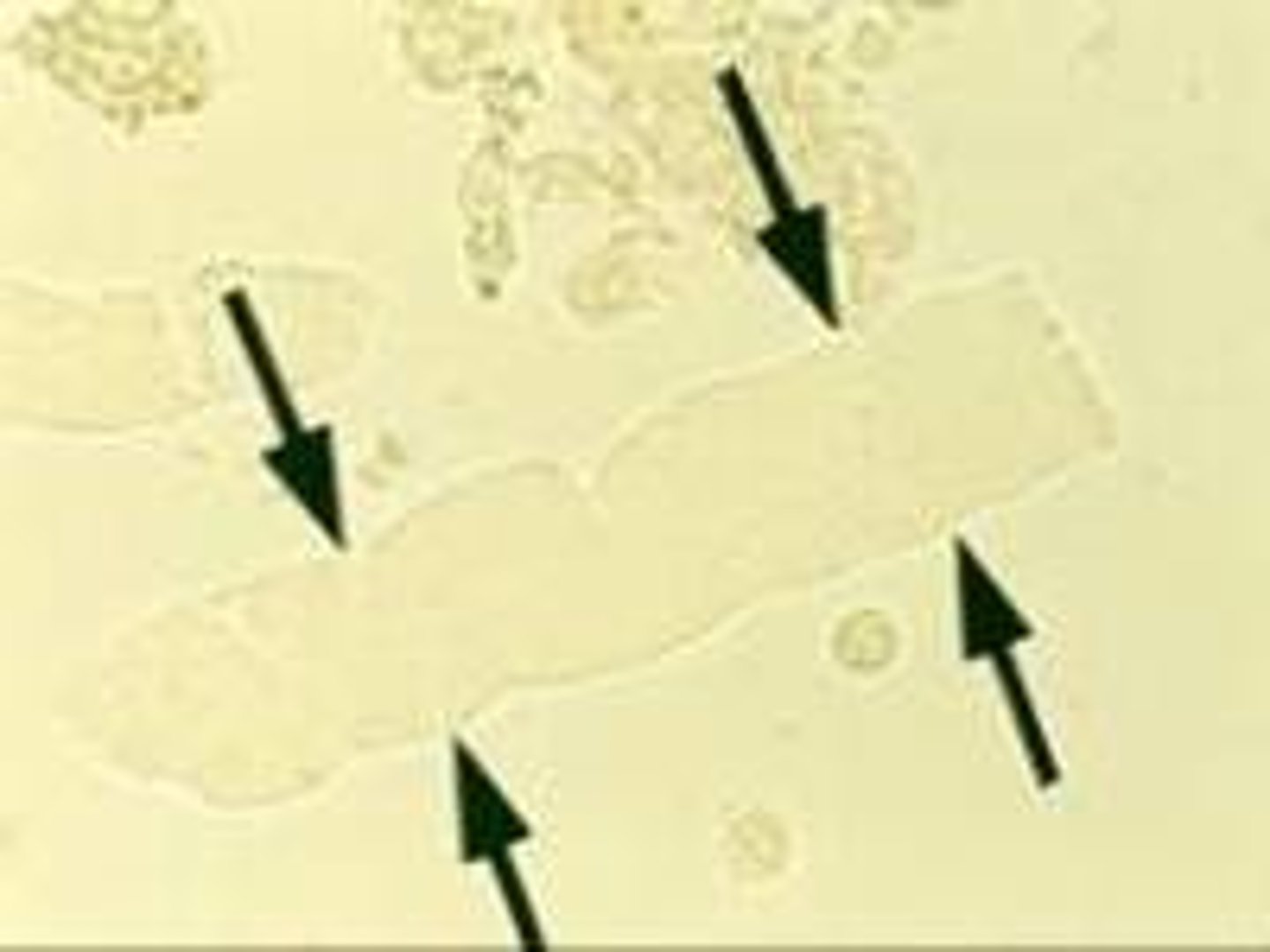
Waxy casts
High refractive index, blunt ends with cracks or fissures across them
"Renal failure" casts, indicates urine is not flowing well; glomerulonephritis, malignant hypertenstion, renal transplant rejection
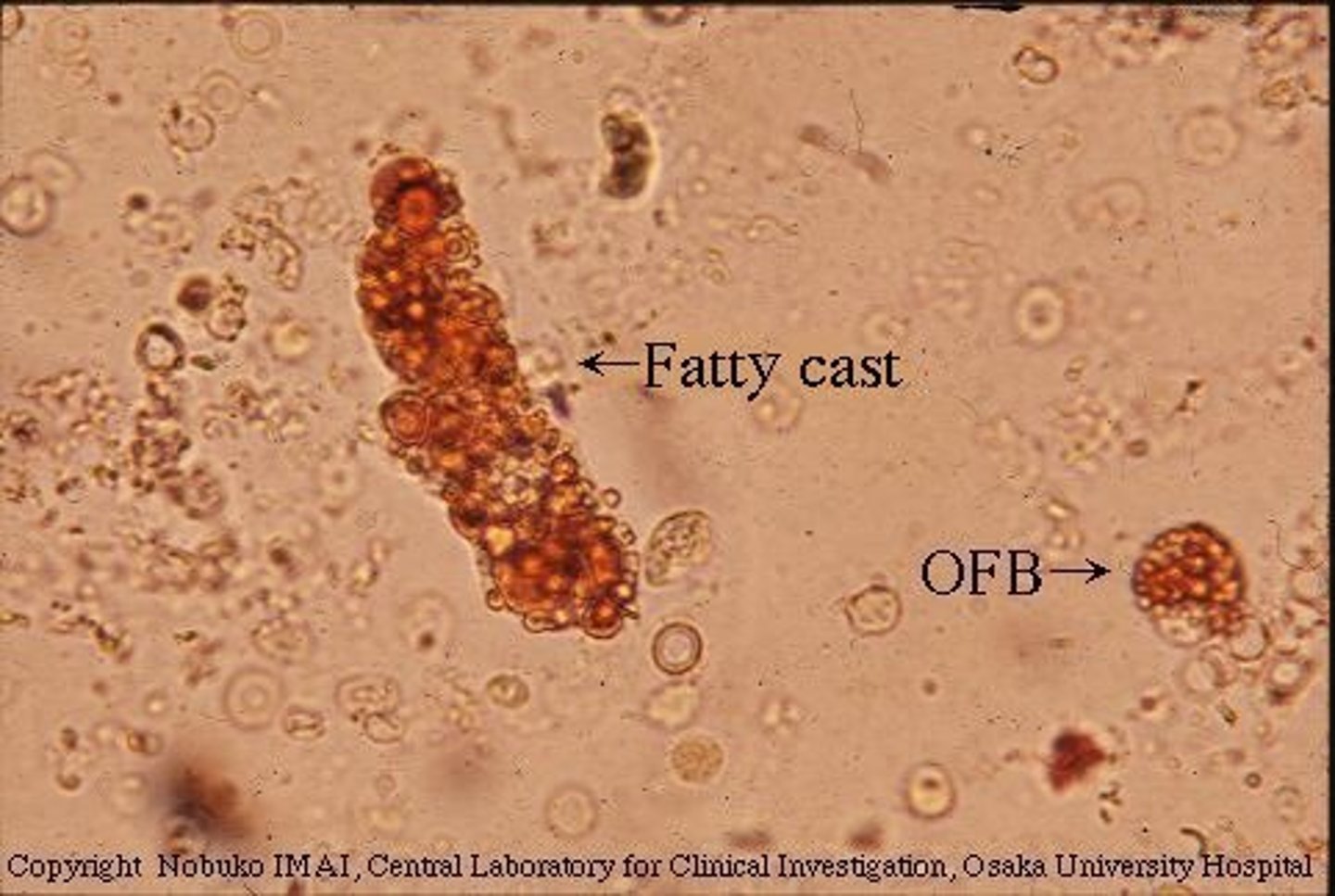
Fatty cast
Casts with fat droplets in them
Glomerular filtration barrier is not functioning
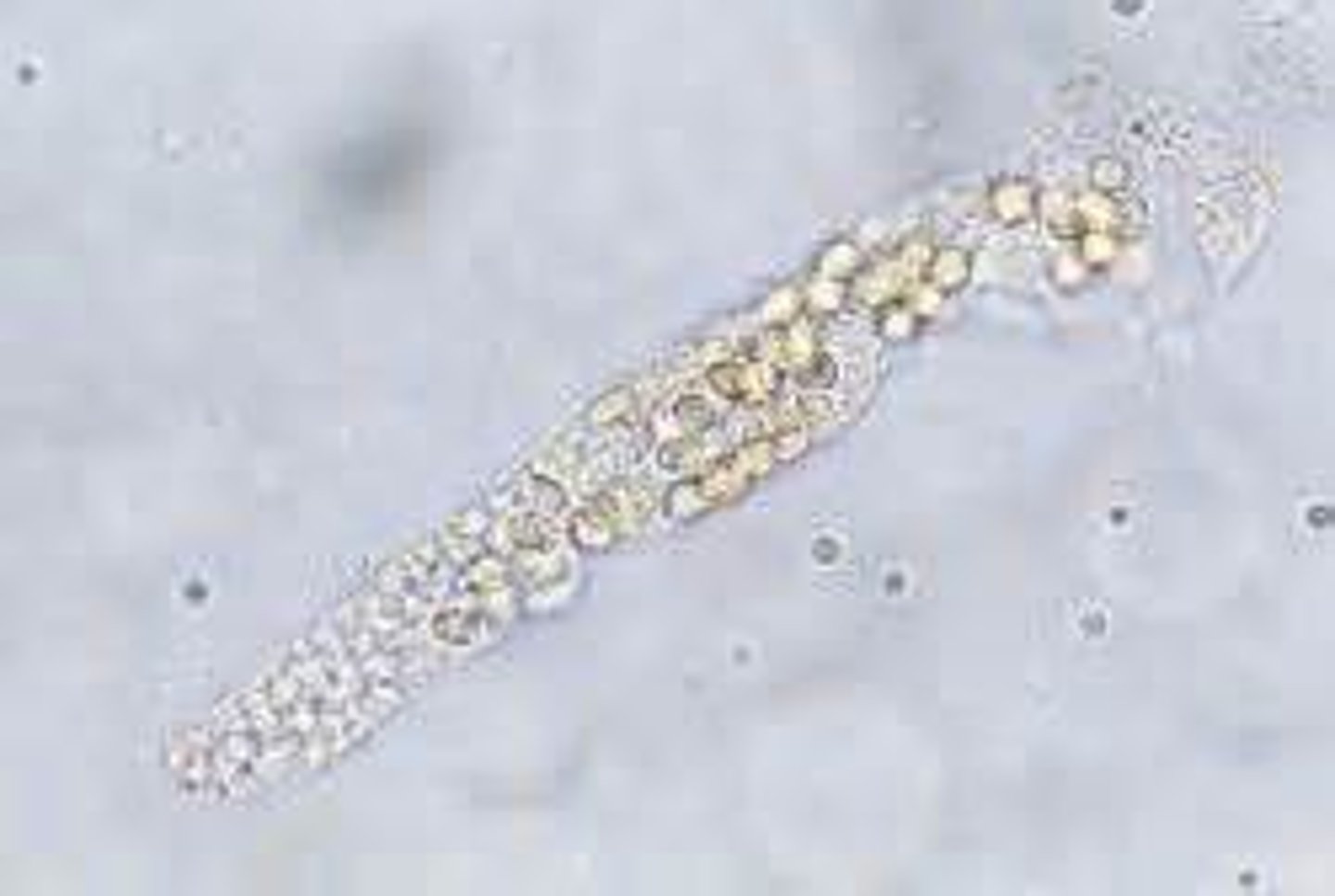
Polarizing microscopy
Cholesterol has maltese cross in what
Waxy cast and diaper fiber difference
A diaper fiber with polarize light, and will have edges that are not parallel. The edges will also have many spots running parallel to the long edge
Renal tubular cells
What types of epithelial cells can be present in casts?
Upper UTI or pyelonephritis (kidney infection)
What is a condition associated with WBC casts?
Acute glomerulonephritis
What is a condition associated with RBC casts?
Nephrotic syndrome
What is a condition associated with fatty casts?
Can be seen 2-3 days after a hemolytic event
What is the significance of hemosiderin in the urine?
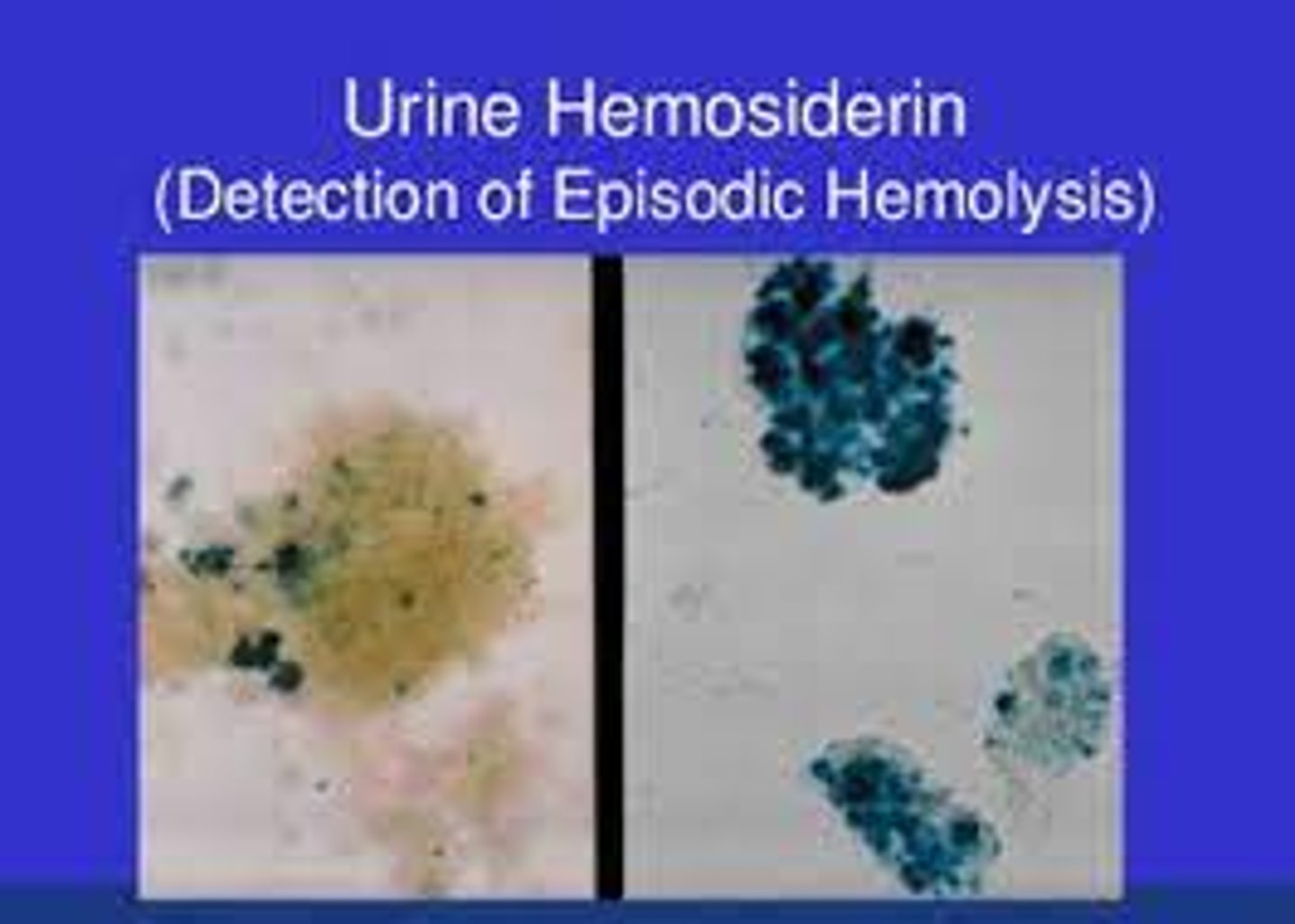
Potassium ferrocyanide stain, observed for coarse Prussian Blue granules
What can be used to identify hemosiderin in urine?
Lower UTI UA results
Protein - small
Blood - small, usually small
Leukocyte esterase - usually positive
Nitrites - usually positive
Micro with increased WBCs, RBCs, TEs and bacteria present
Upper UTI UA results
Protein - small
Blood - small, usually small
Leukocyte esterase - usually positive
Nitrites - usually positive
Specific gravity - normal to low
Micro with increased WBCs (with clumps), RBCs, REs, increased casts (WBC casts!!, granular, renal cell), bacteria present
Chronic pyelonephritis UA results
Protein - moderate
LE - usually positive
Specific gravity - low
Micro with increased WBCs, casts (granular, waxy, few WBC)
causes of acute interstitial nephritis
Antibiotic use
Leukemia
*Renal transplant rejection*
Heavy metal exposure - acute damage
Drug abuse - slow destruction
acute interstitial nephritis UA results
Protein - small
Blood - positive
LE - positive or negative
Micro with increased WBCs, eosinophils, RBCs, RE cells; WBC casts, granular; drug crystals possible if due to drug use
Cystinosis
more severe and is due to defective metabolism of cystine
Cystinuria and cystinosis UA results
Blood - positive
Protein - mild (Cystinosis)
Micro with increased RBCs and cystine crystals
Fanconi Syndrome
Loss in proximal tubule resorption, causing many solutes to be lost in the urine
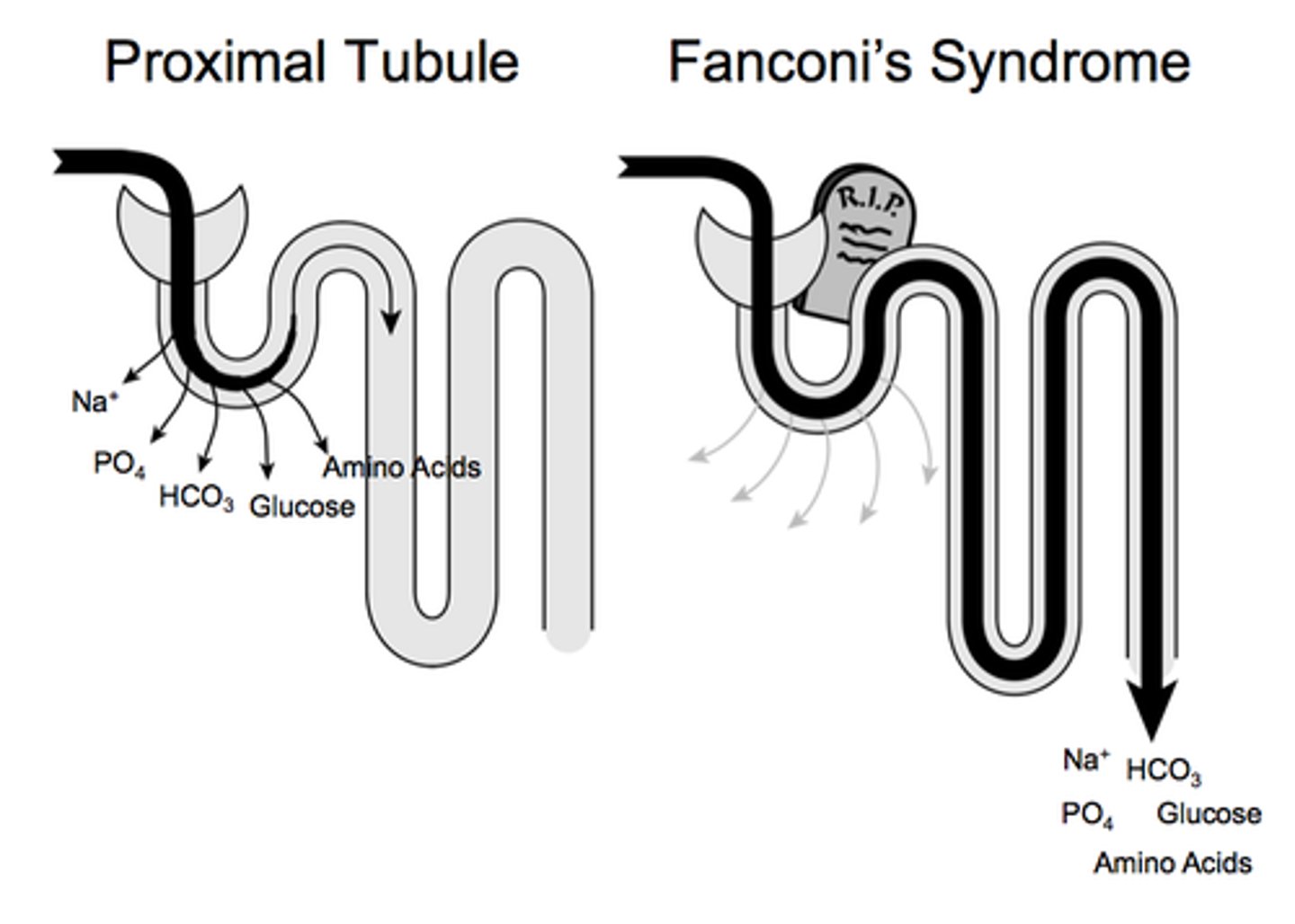
Fanconi syndrome UA results
Protein - moderate
Glucose - positive (variable)
Micro within normal limits
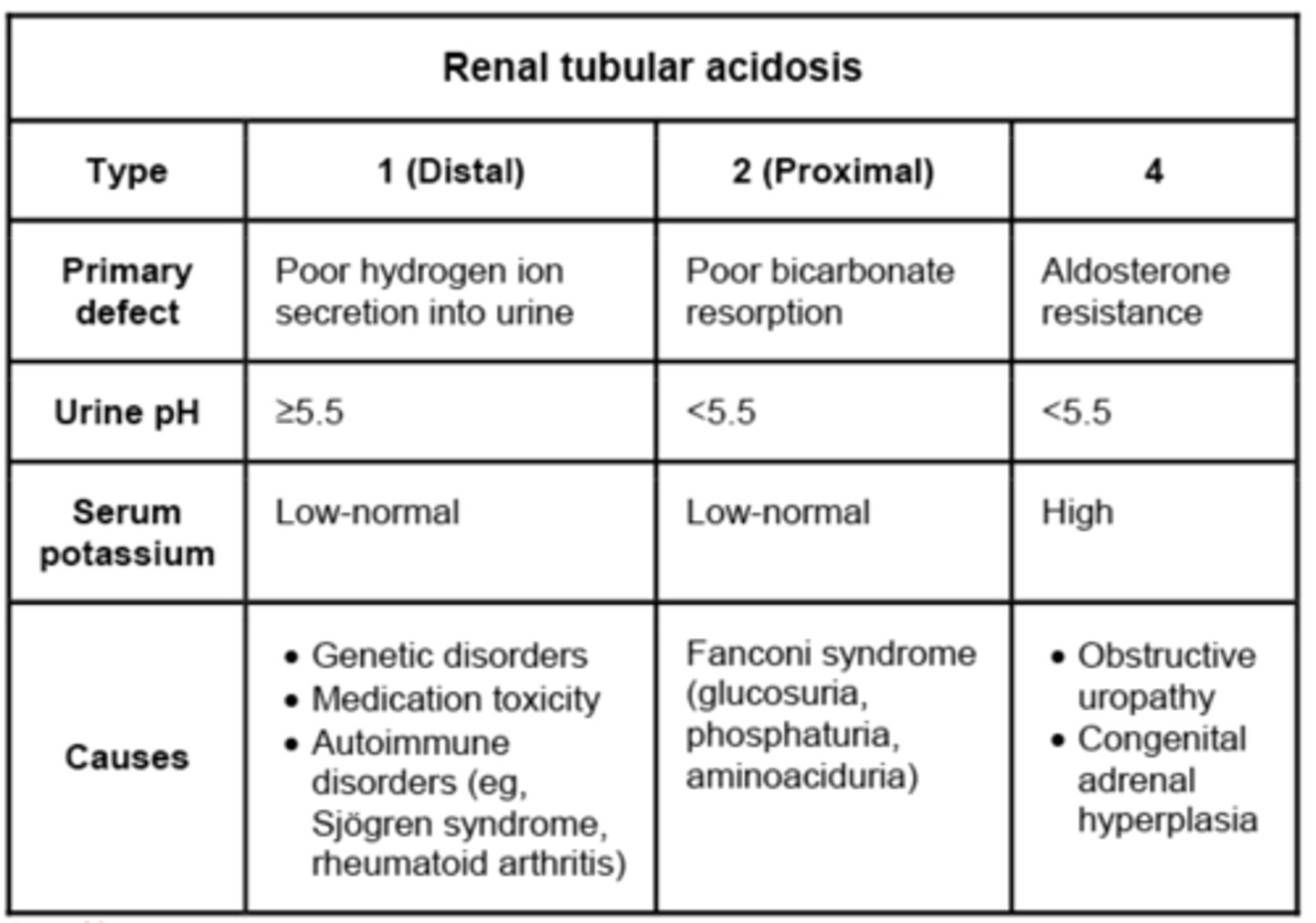
renal tubular acidosis
The inability of the renal tubules secrete H+ ions to acidify the urine by defect of one of 4 mechanisms:
Type I: Ammonia production
Type II: Bicarbonate reabsorption
Type III: Combination of I & II
Type IV: Impaired Na/H+ ion exchange
nephrotic syndrome
A group of clinical symptoms that occur in some glomerular disorders:
Loss of >3.5g/dL of protein per day, resulting in hypoproteinemia in the blood.
Lipid (fat) loss into the urine
Hyperlipidemia in the blood due to liver stimulation compensation of loss into blood
acute glomerulonephritis
Typically due to post-streptococcal infection, children will have fever, nausea, oliguria, hematuria, and proteinuria. Micro UA will have RBC casts
rapid progressive glomerulonephritis
Typically follows an infection in adults, or people with lupus. These patients typically have an antibody that targets the glomerular basement membrane. Patients will have fever, nausea, oliguria, hematuria and proteinuria. Micro UA will have RBC casts.
chronic glomerulonephritis
Hyaline-like protein material covers that glomeruli, and the renal tubules have atrophied. Kidneys lose their function, and patients typically require dialysis or transplant
minimal change disease
Believed to be due to defective T cell response, following an infection or immunization, which can cause the most common nephrotic syndrome in children
IgA nephropathy
IgA complexes get trapped in glomeruli following respiratory, GI, or UTI that stimulated IgA synthesis
Half of patients go into chronic glomerulonephritis
acute and chronic glomerulonephritis UA differences
Protein: Mild (acute), heavy (chronic)
Blood: positive (small for chronic, variable for acute)
Specific gravity: normal (acute), low (chronic)
Micro: increased RBCs (may be dysmorphic in acute) and WBCs, RTs, casts
ischemic acute tubular necrosis
when blood flow is decreased to renal tubular cells and they don’t get enough oxygen to maintain cells (sepsis, trauma, heart failure), cells from collecting ducts shed in urine
steps of Kohler illumination
1. Bring specimen into focus via coarse adjustment
2. Adjust fine focus knob
3. Close field iris diaphragm
4. Adjust condenser height knob
5. Center condenser with centering screws
6. Open field diaphragm just past field
7. Adjust condenser diaphragm until maximum contrast is obtained
MUST ADJUST WITH EACH NEW OBJECTIVE LENS USED
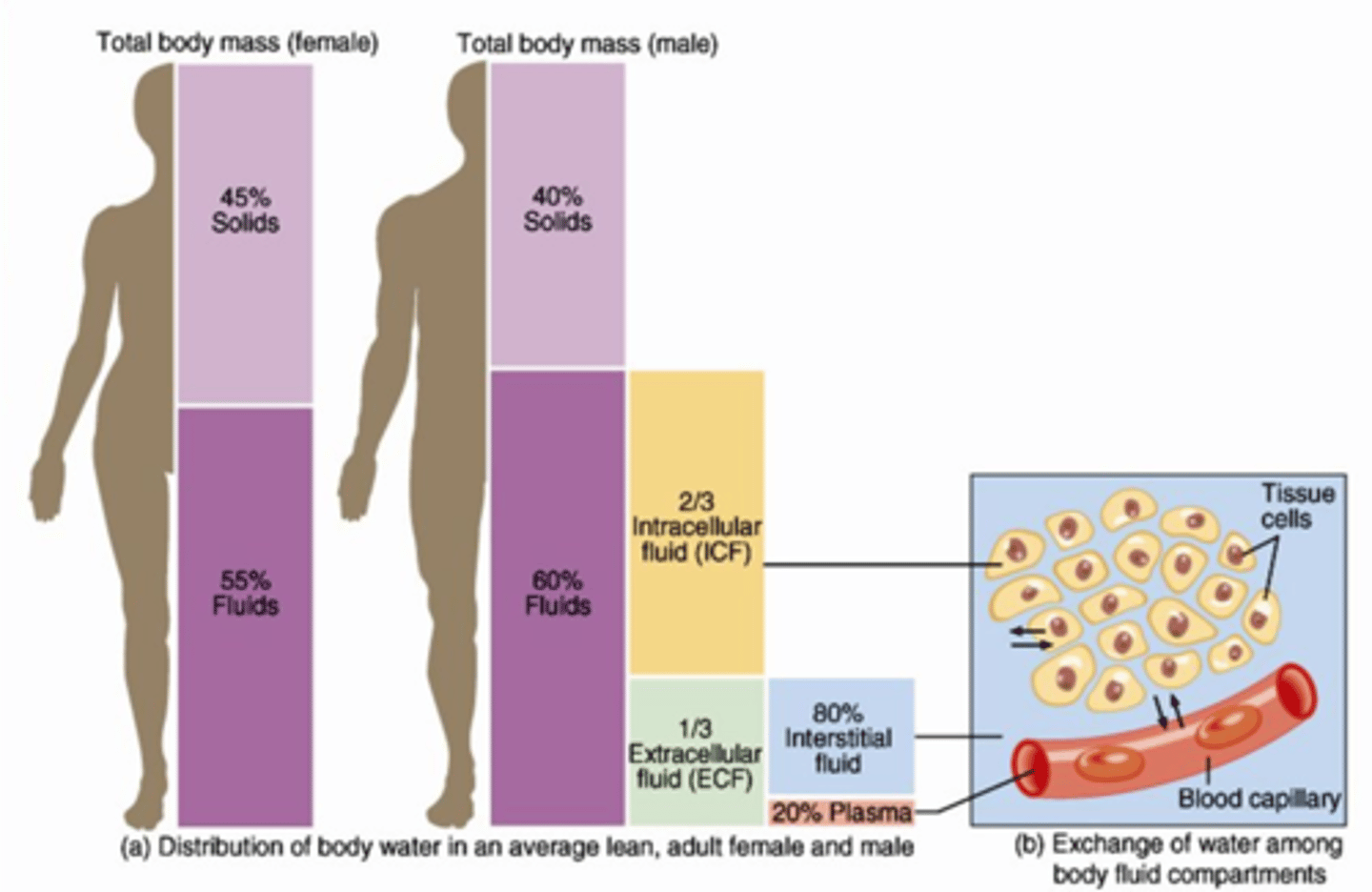
normal distribution of water in the body
60% of the body weight is water: 40% intracellular, 20% extracellular
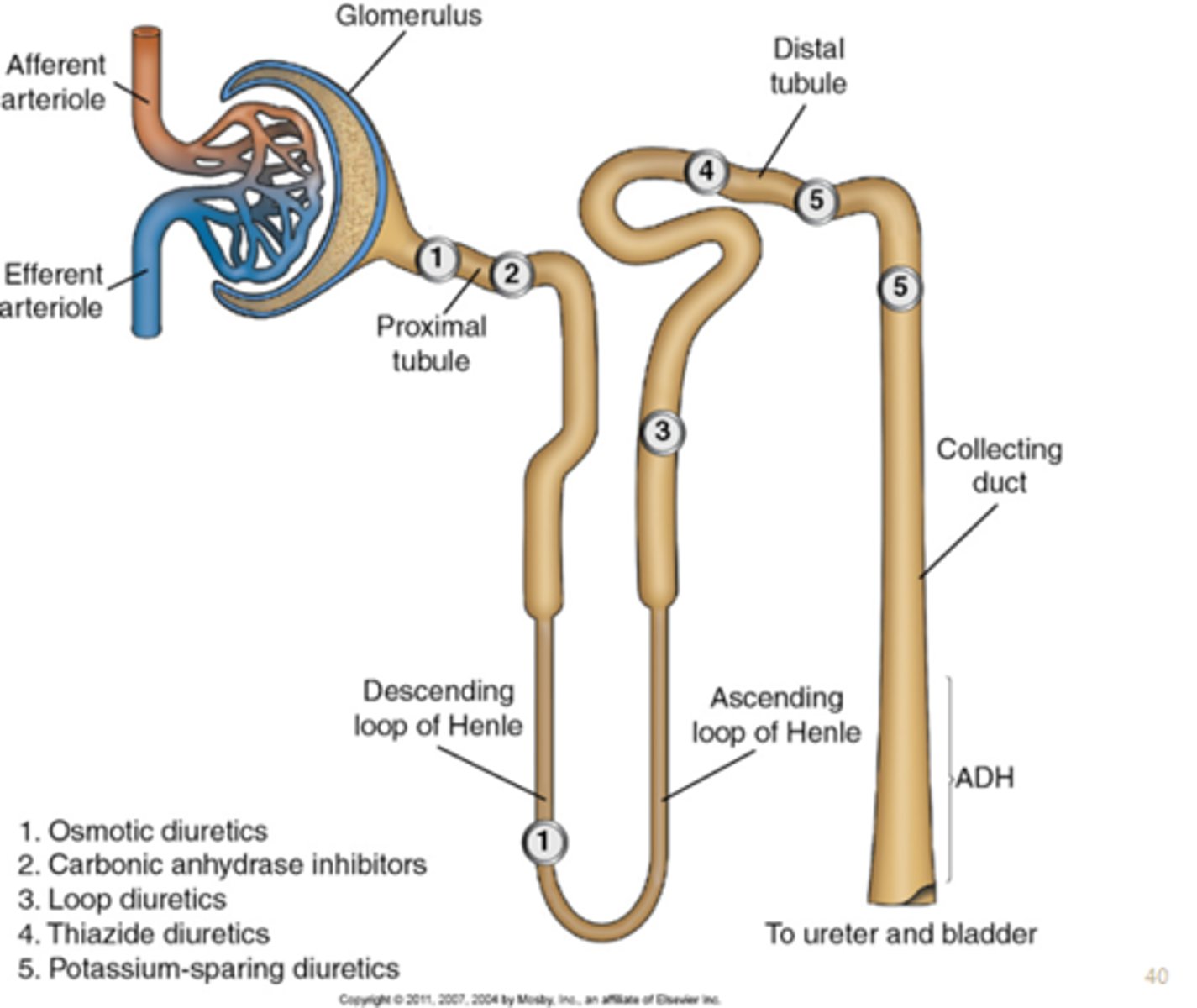
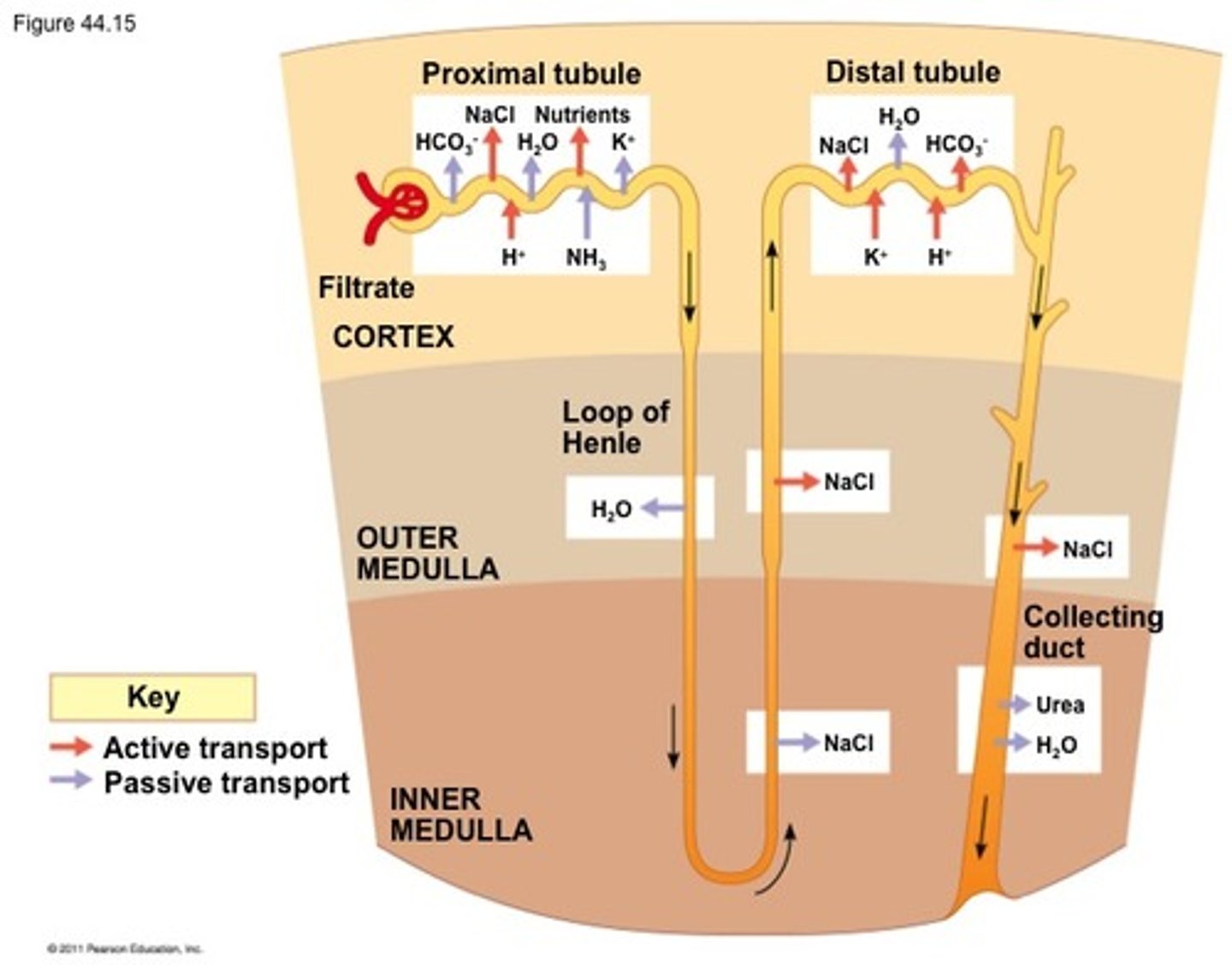
path of water through the nephron
From the Bowman's Capsule, filtrate passes through the proximal convoluted tubule, to the Loop of Henle, to the distal convoluted tubule,
and then to the collecting ducts.
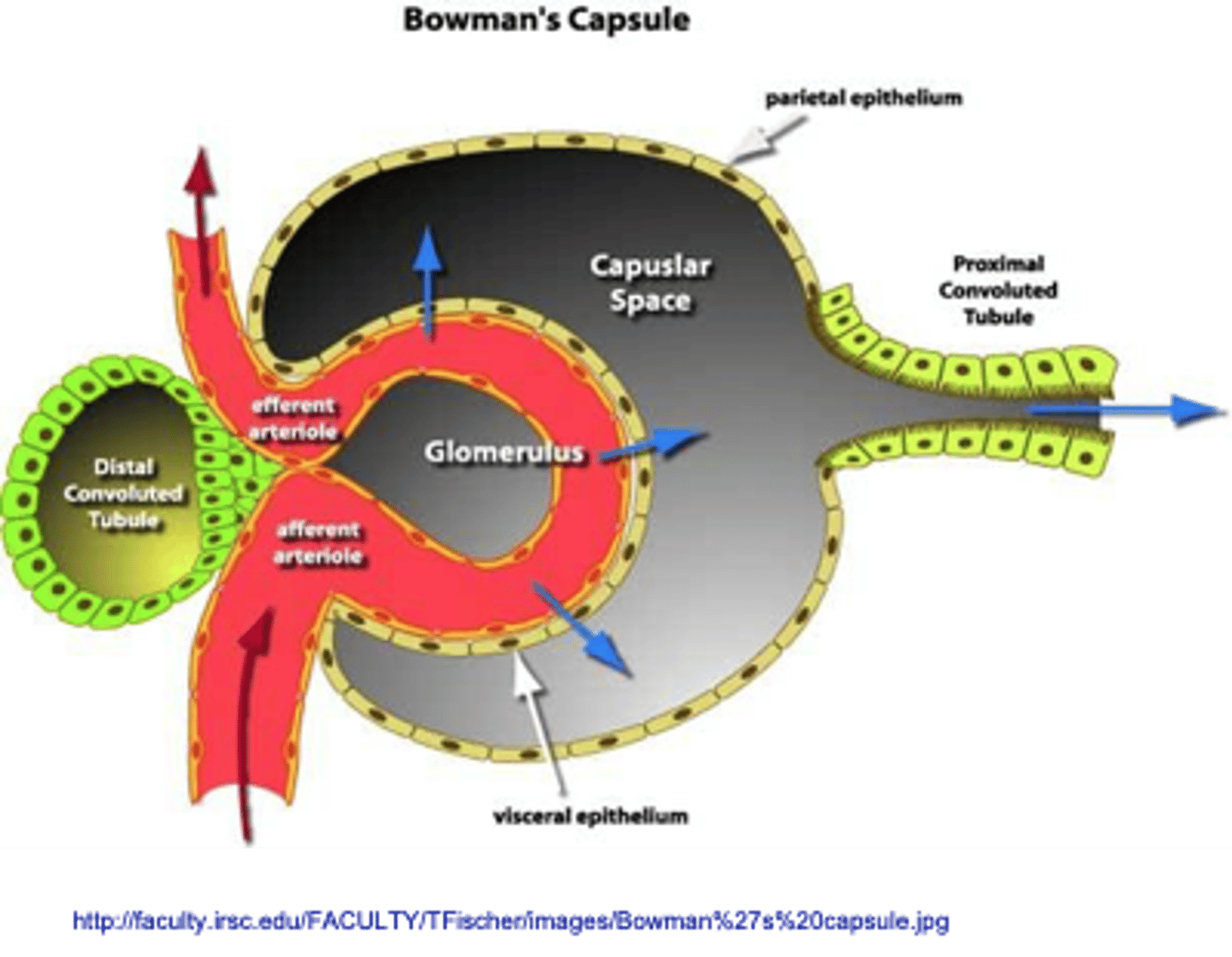
Bowman's capsule
Liquid plasma is filtered into a urinary ultrafiltrate
Plasma ultrafiltration
Selected solute reabsorption
Selected solute secretion
What are the three processes involved in urine formation?
Proteinuria (albumin)
What finding in urine is typically the first sign of glomerular damage?
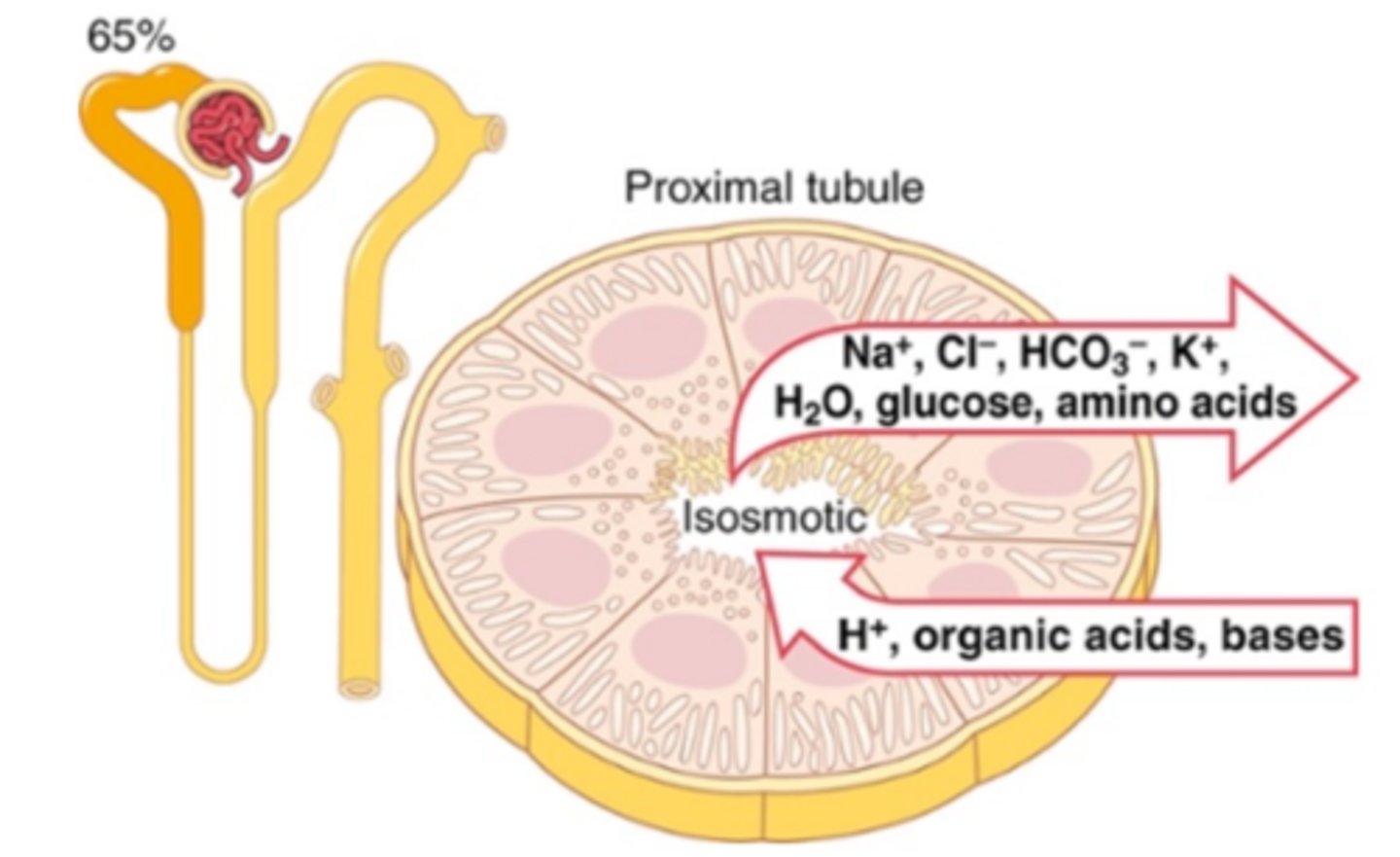
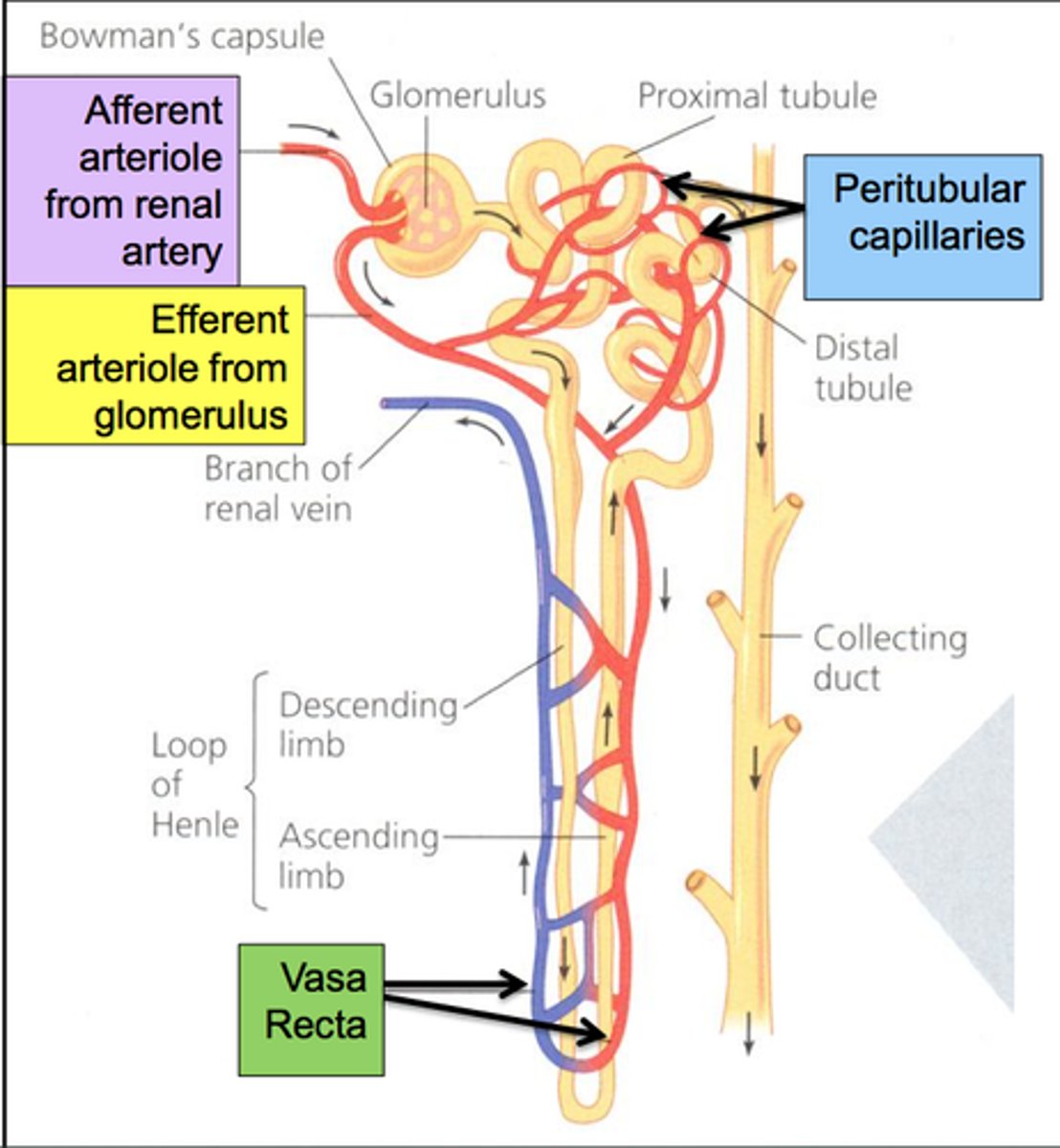
proximal convoluted tubule
Reabsorption of Water, potassium, chloride, and urea by passive transport
100% of the glucose, amino acids and protein and 66% of sodium reabsorbed by active transport
Secretion of H+, NH3, weak acids and bases
Loop of Henle
Passive resorption of water, urea, and sodium chloride ions.
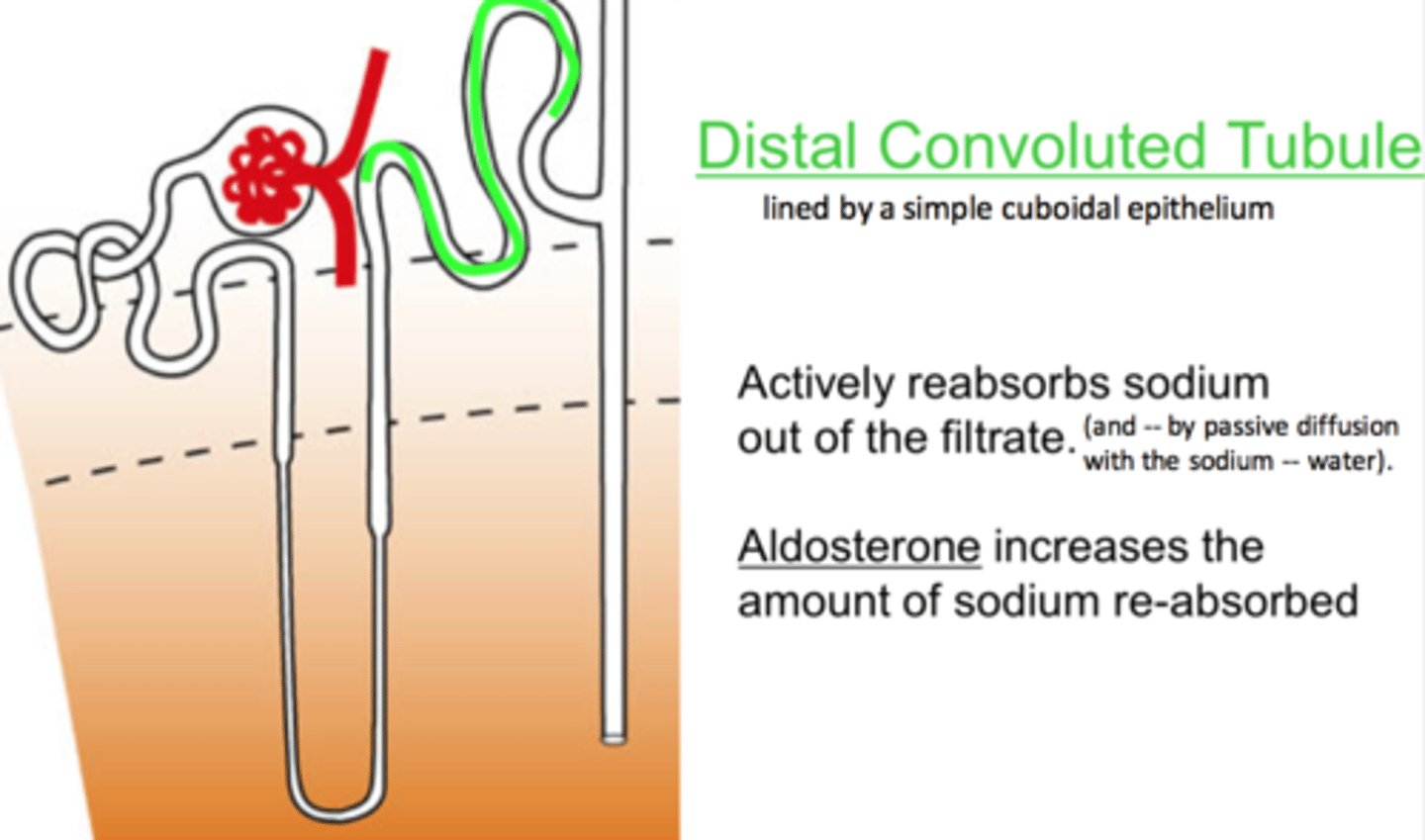
distal convoluted tubule
Active transport back into circulation of sodium, chloride, sulfate and uric acid
Secretion of H+, K+, NH3, uric acid
collecting duct
Final concentration of urine
Secretion of H+, K+, NH3
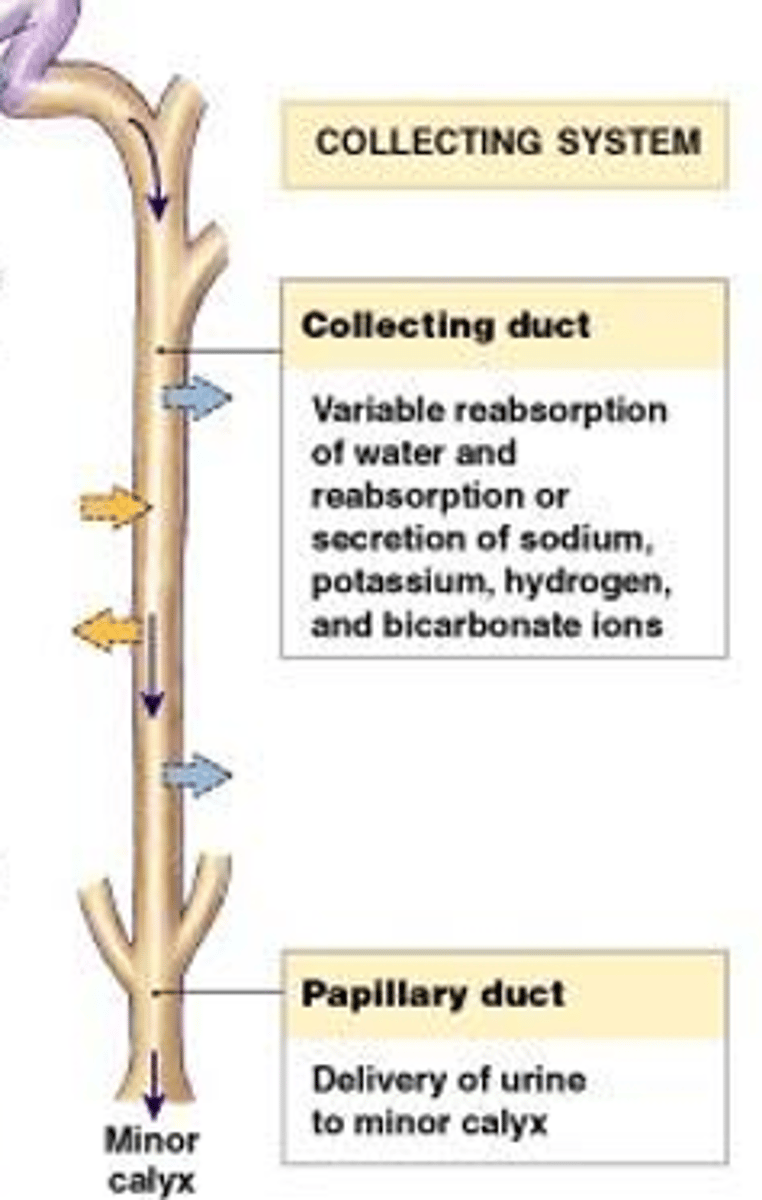
How the kidney concentrates and dilutes urine
The collecting ducts pass through the renal medulla, and it is the hypertonicity of the interstitial fluid, maintained by the processes occurring in the Loop of Henle, that allow the collecting ducts to concentrate the urine into its final concentration.
blood supply of the nephron
The circulation of the kidney starts as an arteriole and then subdivides into a capillary bed, becomes an arteriole again, and then subdivides into second capillary network. It forms a specialized network of capillaries within the glomerulus. These capillaries are in direct contact with the Bowman's Capsule and it is here that the blood pressure must be high enough to result in the liquid plasma moving from the capillaries into the Bowman's space.
fresh urine samples processing
Fresh, left at room temperature - within 2 hours of voiding
physical changes of unpreserved urine
Color changes - oxidation of chemical components (Hgb, red, to methemoglobin, brown)
Clarity changes - as urine cools, crystals can form; bacteria can grow, these increase turbidity of sample
chemical changes of unpreserved urine
pH - falsely increased, typically
Nitrite - falsely increased
Glucose - falsely decreased
Ketones - falsely decreased
Bilirubin - falsely decreased
Urobilinogen - falsely decreased
microscopic changes of unpreserved urine
Casts can decrease due to dissolution
RBCs and WBCs shape can change, or cells can deteriorate
Bacteria continues to grow, falsely elevated
Trichomonas can die quickly in unpreserved urine
Yellow
normal, due to urochrome, urobilin
Any molecule that will dissolve in urine, glucose, hemoglobin, bilirubin
What solutes do not affect the clarity of urine?
Hematuria
Blood in urine, intact RBCs, cloudy or turbid urine; many RBCs on microscopic
specific gravity
the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of water
affects of specific gravity of a urine sample
The size and number of solutes present
oliguria
Low urine volume output (<400mL/day)
urine specimen prep for microscopic analysis
The urine is centrifuged for 5 minutes at 450rpm. The brake is not used because this could disturb the urine sediment. 1mL Kova pipette is used to carefully remove 11mL of the supernatant. The urine sediment is then gently resuspended in the remaining 1mL
Pink/red and clear
Describe the color and clarity of a urine specimen that has hemoglobin present but no intact red blood cells
Pink to red and slightly cloudy, cloudy, or turbid, depending on the number of RBCs present
Describe the color and clarity of a urine specimen that has both hemoglobin and intact red blood cells present
Pathological: Red cells, bacteria, white cells, yeast, crystals, renal cells
Non-pathological: crystals, squamous epithelial cells, lotions/powders, bacterial contaminants
List at least three pathological and four non-pathological substances that can cause a urine specimen to be slightly cloudy or cloudy
principle for determining specific gravity by reagent strip
The reagent strip measures ionic specific gravity, not a true specific gravity. The salts of the urine combine with a polyelectrolyte embedded in the pad. This releases hydrogen ions, as the salts take their place. The release of the hydrogen ions results in a decrease in pH. This results in a color change in the pH indicator embedded in the pad.
Specific gravity is affected by dissolved compounds in the solution. The cells are not dissolved in the solution, only suspended.
Why do urine sediment components such as RBCs, WBCs, and epithelial cells NOT affect specific gravity by any method?
Very dense dyes, like radiographic contrast
List one substance that can cause the urine specific gravity to be greater than 1.050
Specificity
the test's ability to react with only one compound, and not with closely related compounds
range of detection
The range of results that can be accurately determined using a particular method
ie. Glucose assay from 50g/dL to 500g/dL
1.002 - the lowest concentration closest to pure water, as the kidneys are not able to excrete pure water
1.040 - equal to the concentration of the hyperosmotic renal medulla; greater than 1.040 is physiologically impossible, and indicate the presence of another compound, like contrast dyes
What are the minimum and maximum possible measurements of specific gravity and their physiology?
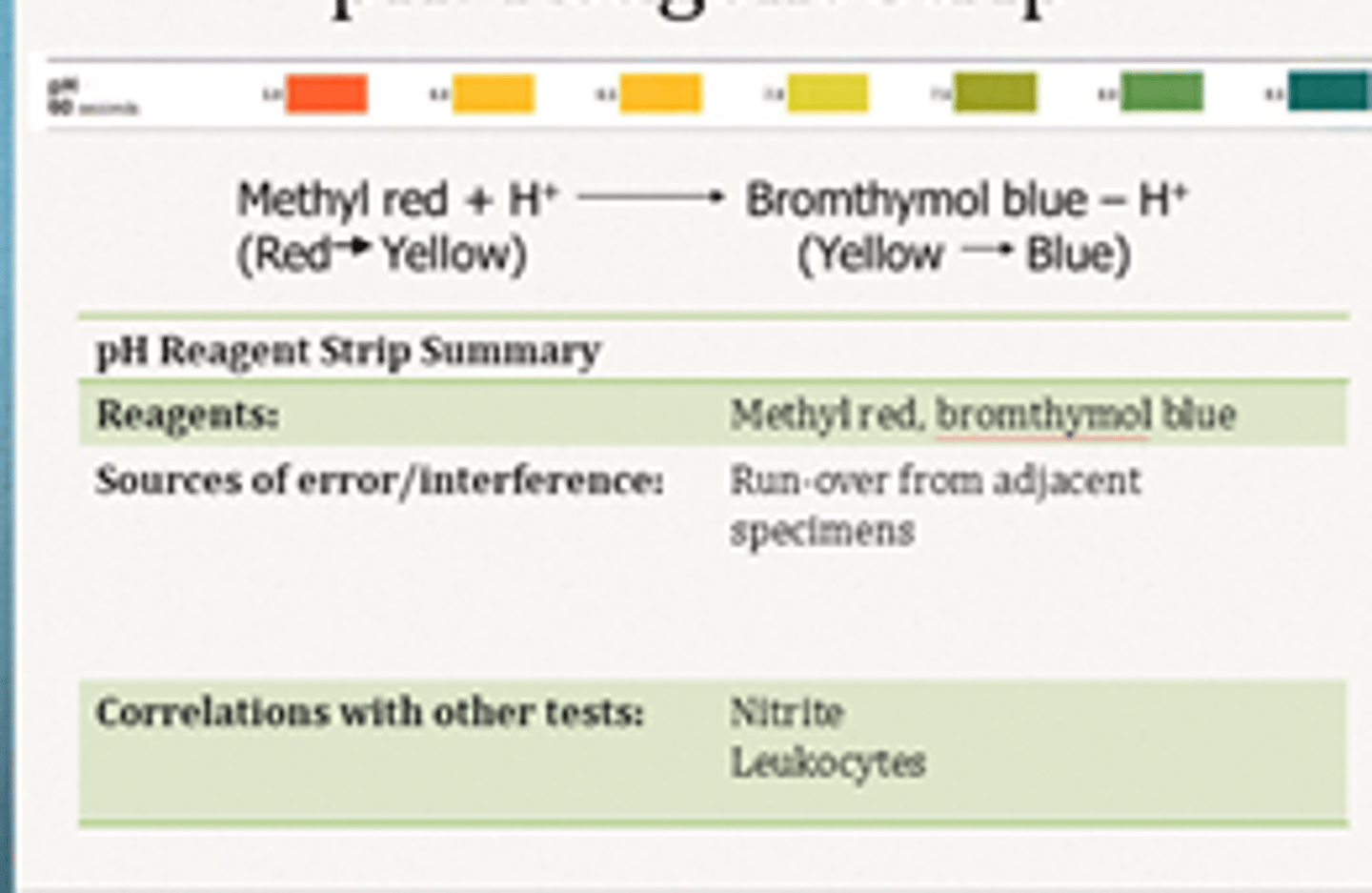
principle of the reagent strip pH test
Two different pH indicators, bromothymol blue and methyl red are embedded into the pad. The combined colors of the indicators produce a range of colors
principle of the reagent strip blood test
The heme portion of the hemoglobin molecule reduces
the peroxide present and oxidizes the chromagen tetramethylbenzidine that is present in the pad. The result is a color change from the yellow chromagen to the green, oxidized chromagen.

myoglobinuria causes
Traumatic: muscle injury, extreme exercise
Atraumatic: muscle ischemia, acute overdose
blood test false positives
Urine has been contaminated with menstrual blood or blood from hemorrhoids
Presence of strong oxidizing agents
blood test false negatives
High nitrites or specific gravity
Presence of ascorbic acid
leukocyte esterase
An enzyme that is found in azurophilic granules of granulocytic leukocytes
No, if the white blood cells that are present are lymphocytes, the pad will not react because lymphocytes do not contain granules that have this enzyme
If leukocyte esterase is negative on reagent strip, does this mean there is no patient infection?
principle of the reagent strip leukocyte esterase
reacts with esters embedded in the pad to produce aromatic compounds. These aromatic compounds react with diazonium salts also present in the pad to produce a purple azo-dye, changing from beige to purple or violet

leukocyte esterase false negatives
Non-granulocytic WBC infection (mostly lymphs)
Strong oxidizing agents
Drugs
leukocyte esterase false positives
Contamination - vaginal secretions, medications or foods that change color of urine
No, nitrite is simply a screening test used to detect nitrites produced by bacteria
Does a negative nitrite rule out infection?
principle of the reagent strip nitrite test
If nitrites are present, they will react with an aromatic amine
embedded in the pad to form a diazonium salt. The diazonium salt will then react with another aromatic compound in the pad to form a colored (pink) azo-dye compound

Nitrite test false positives
Colored substance interference (medications, beets)
Improper storage and bacterial proliferation
Nitrite test false negatives
Too fresh urine specimen (<4h)
Bacteria lacking nitrate reductase
Dietary nitrites
Ascorbic acid
Acidic urine causes
high protein diet, metabolic/respiratory acidosis
pre-renal proteinuria
AKA overflow proteinuria
Excess protein production leads to elevated concentration of proteins in the urinary filtrate. Because the concentration exceeds the renal threshold, small molecular weight proteins will end up in the urine

Normal: hemoglobin, myoglobin, acute phase proteins
Abnormal: immunoglobulin light chains
What are normal and abnormal proteins found in pre-renal proteinuria?
glomerular proteinuria
some type of damage to the glomerular filtration barrier, allowing proteins not normally able to pass through are now able to enter the urinary filtrate
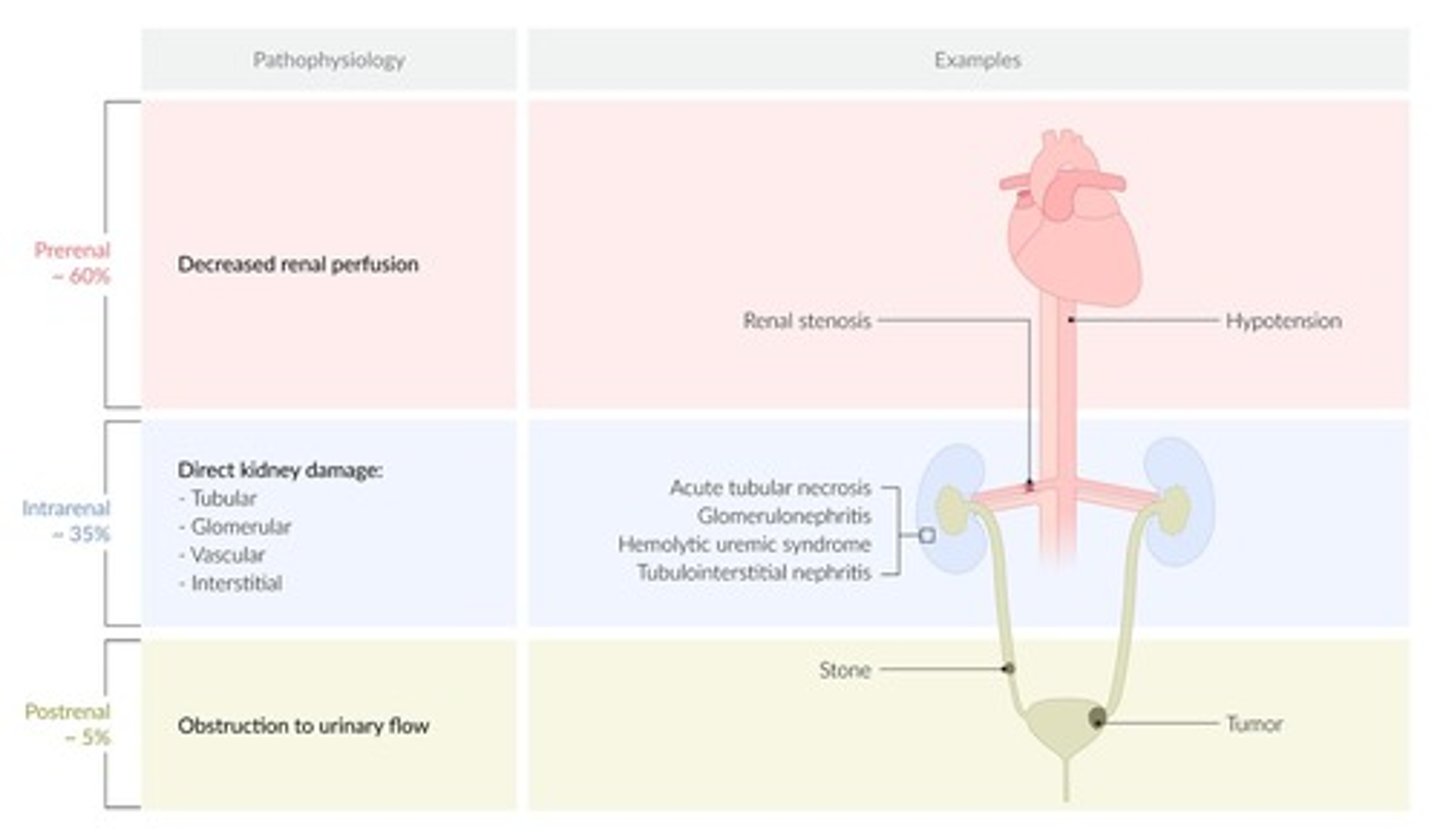
glomerula proteinuria causes
diabetes, hypertension, peripheral vascular disease
postural proteinuria
Protein only gets into the urine when the patient is standing up. It is thought that being in an upright position increases the renal venous pressure, which results in the blood "backing up" which increases the pressure in the glomerulus
principle of the reagent strip protein test
Certain indicator dyes will release hydrogen ions when in the presence of proteins. The hydrogen ions are picked up by the proteins, so the pH of the pad isn't really changing, but the loss of the hydrogen ions by the indicator shows the presence of protein
protein test false positives
Highly alkaline urine
Highly buffered urine
protein test false negatives
Non-albumin proteins present
post-renal proteinuria
Proteins that enter the urine after it has already been formed
Due to infection, injury, kidney stones, or tumor
pre-renal glycosuria
Glucose in the urine is not kidney related, and is the result of high glucose concentrations in the plasma (Diabetes, liver disease)