Biology chapter 7: Human Nutrition
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Lack of Vitamin C:
Scurvy
Symptoms:
tooth loss
swelling
anemia
Prevent by:
Eating citrus fruits
Lack of Vitamin D:
Rickets
(Poor bone development)
Vitamin D is crucial for the absorption of calcium
Ways to prevent:
Eating food contains calcium, vitamin D like fish, egg, butter
Calcium, D:
Vitamind D helps the body to absorp calcium, required for strong bones, teeth
Strong teeth, bones, involved in the clotting of blood
Milk, Cheese, eggs
Iron:
To make haemoglobin, the pigment in RBC
Liver, red meat, pork
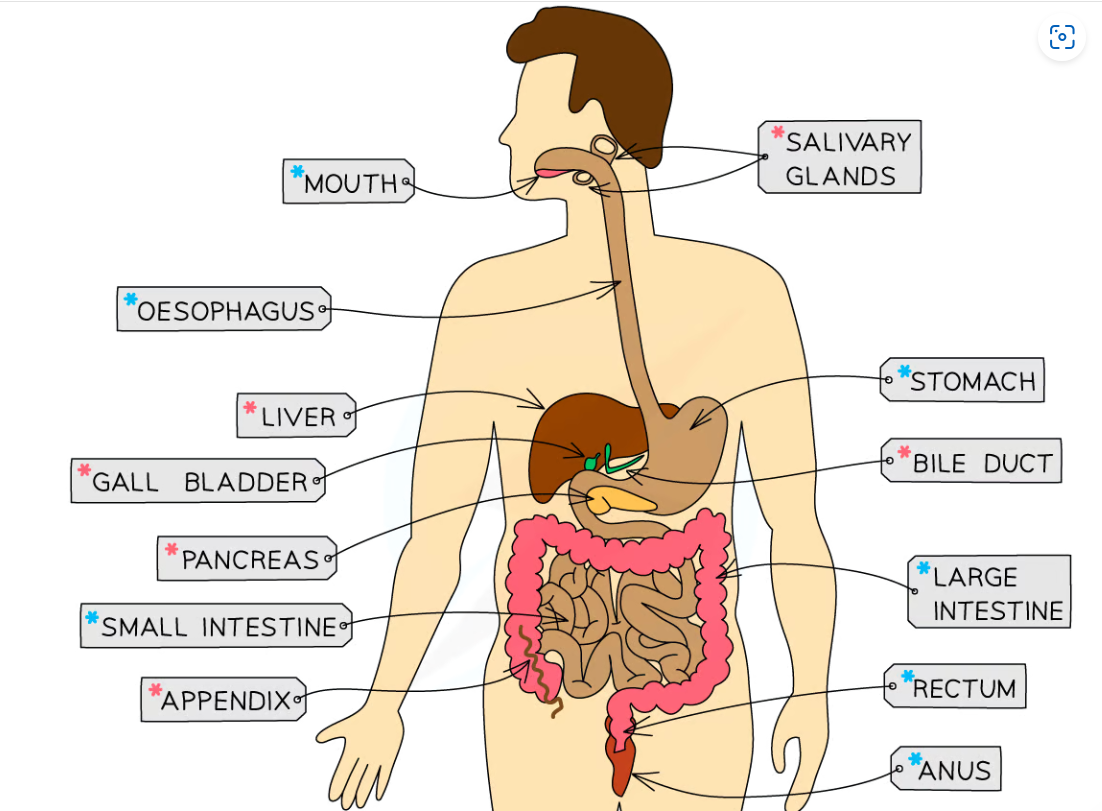
The pathway of food in Human’s body
Mouth
Oesophagus
Stomach
Small intestine:
Duodenum
Ileum
Large intestine:
Colon
Rectum
Anus
The digestive system
Types of teeth + roles
hey
Stomach
Produced Pepsin, breaking down protein in acidic condition
The lining contains muscles
Physically squeeze and mix it with HCl
Digest the food for several hours
Substance produced by Liver + Their roles:
Produced Bile, secreted it into the duodenum
Bile roles:
Neutralise HCl from the stomach, Which helps to create an optimum pH conditions for Enzymes in the Small Intestine to work
Emulsify lipids, for lipase to digest it easier
Gall bladder
Where bile is stored
Pancreas
PANCREAS ONLY PRODUCE ENZYMES. The enzyme will be secreted into the duodenum.
Produced Amylase, breaking down Starch into Maltose.
After this, Maltose will be broken down into Glucose by Maltase in the small intestine
Produced Trypsin, help to break down proteins
Produce Lipase, help to break down lipids
Absorption (Nutrients + water)
Movement of digestive food molecules into the blood (glucose and amino acids) and lymph (fatty acids and glycerol)
Nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine
Water: small intestine + colon
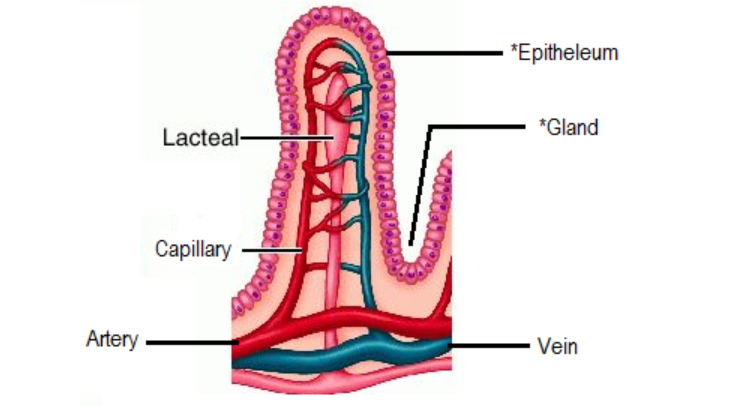
Adaptations of the small intestine
Long, highly folded surface, containing millions of villi => Increase SA, allowing absorption to occur faster + more efficiently
Presence of villi
Villus:
Has epithelium cells on outer surface, the EC contains microvilli on the outside. SA higher
Epithelium cell is one cell thick => More efficient diffusion of nutrients
Lacteals: absorption of FA + G
Capillaries: good blood supply