Histograms and Scatter Plot Review
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
NC/NC
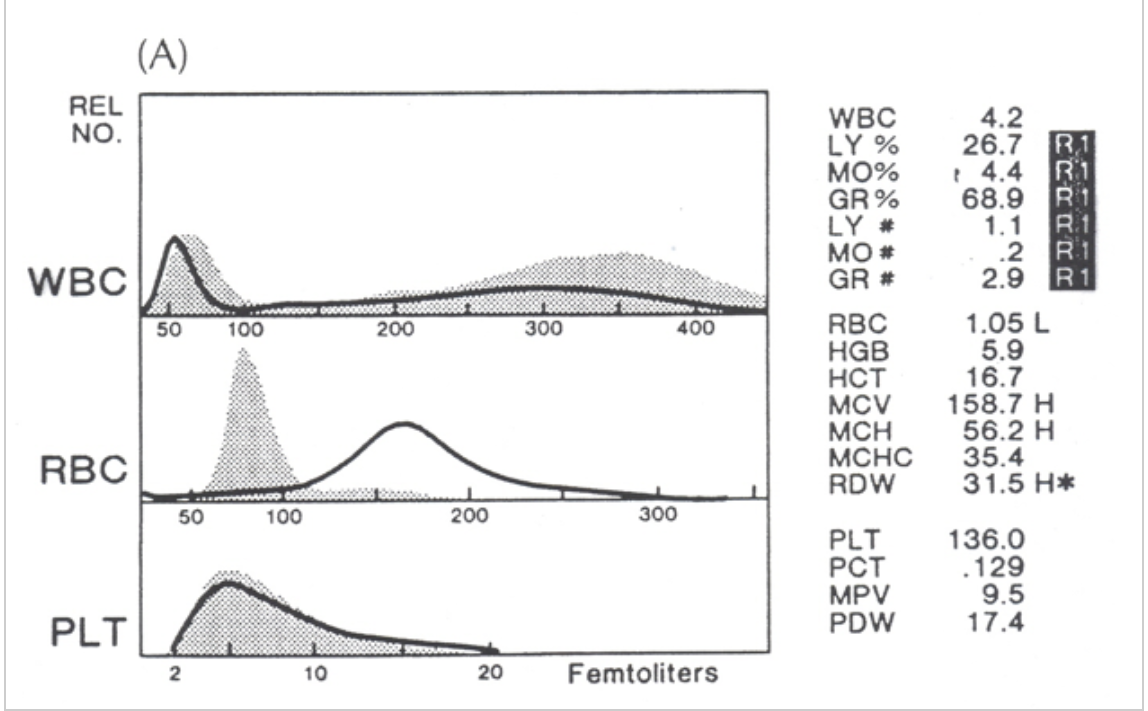
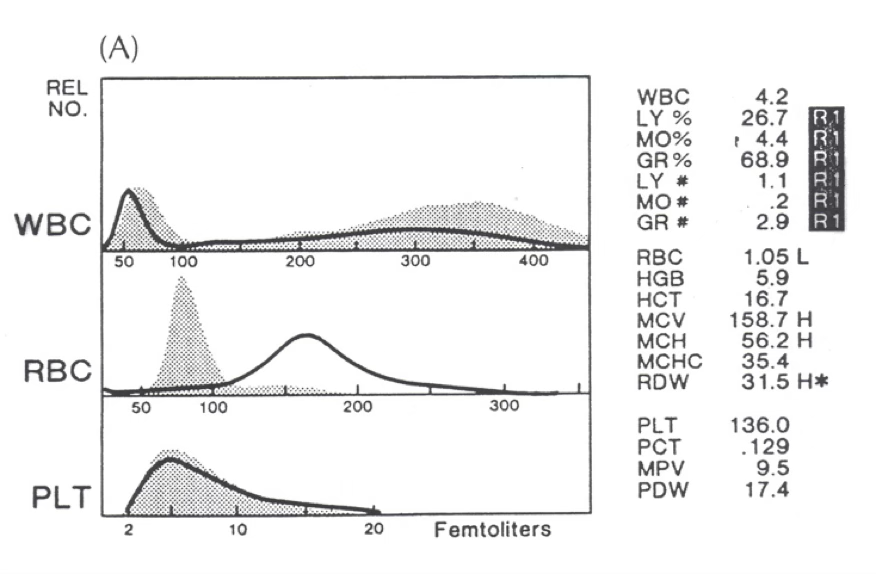
what type of anemia is present?
nRBC/giant platelets
R1 flag
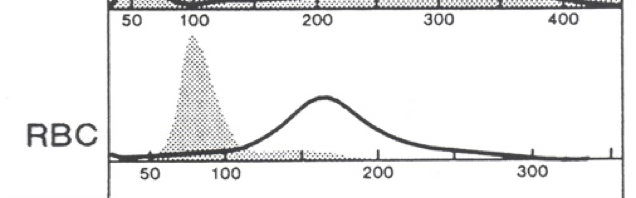
the dark line is the patient. the gray is normal. what flag is present?
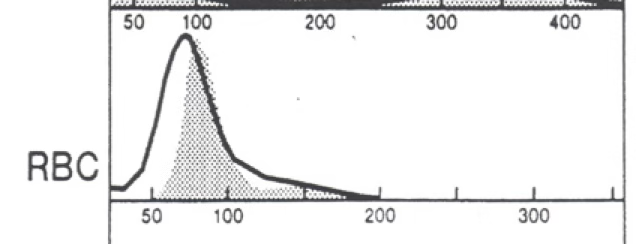
micro/hypo anemia
MCV approx. 77
RDW about 21
the black line is the patient. the gray area is normal. what type of anemia is present?
micro/hypo
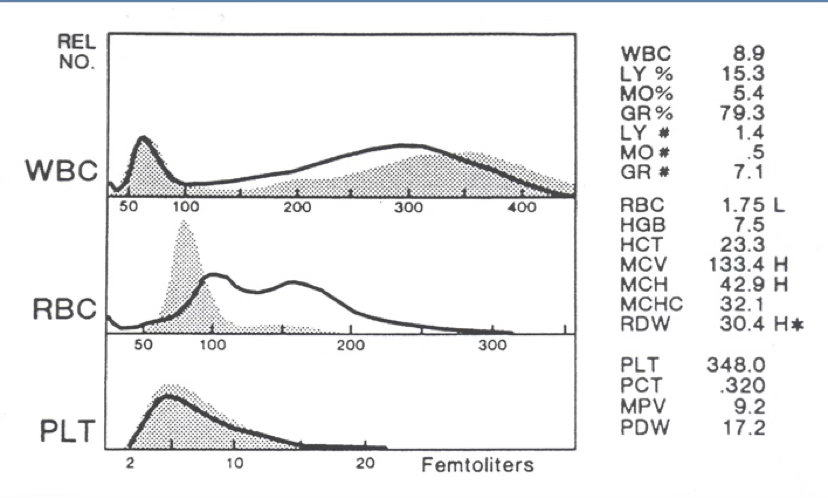
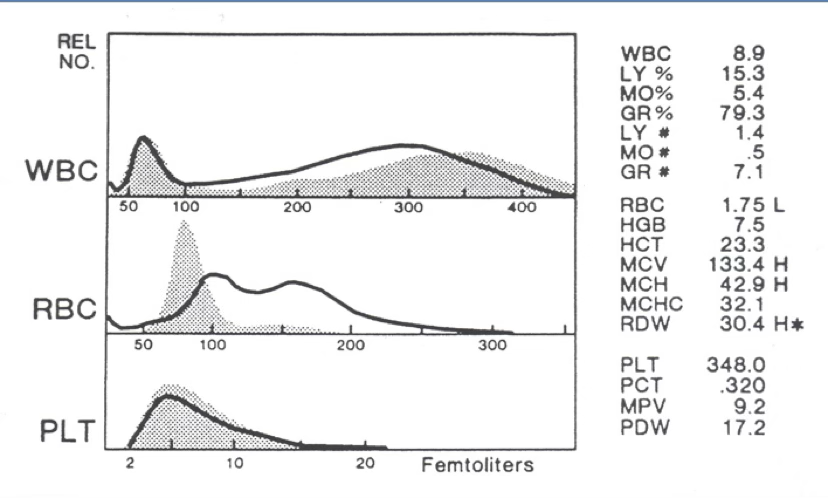
what type of anemia is present?
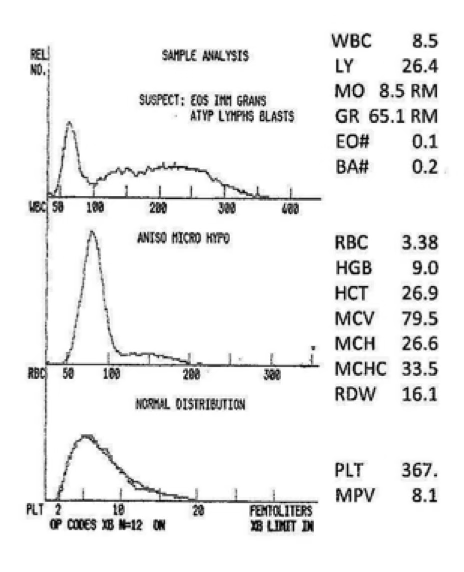
R2 flag
variant lymphs/blasts
black line = patient. gray area = normal. what flag do you expect from this histogram?
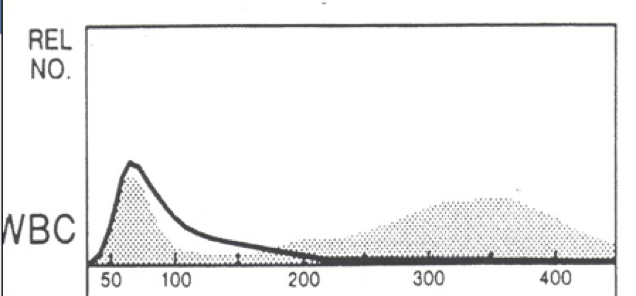
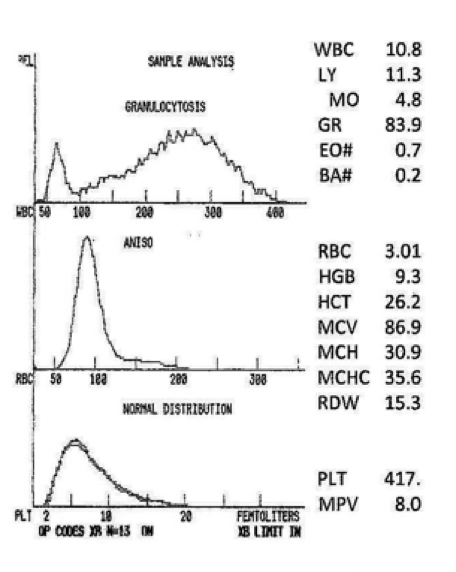
severe NC/NC
what type of anemia do you expect?
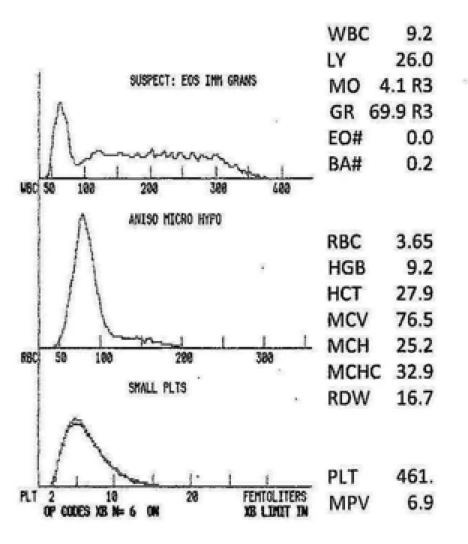
moderate or severe anisocytosis
what does the RDW of 16.7 indicate?
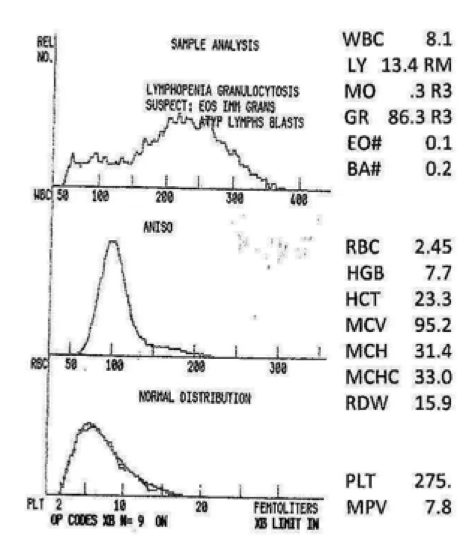
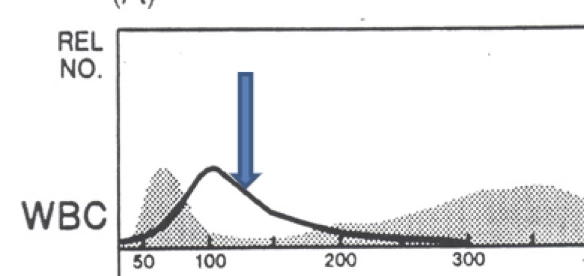
neutropenia resulting from lymphocytosis
what can be said about the granulocytes in this graph?
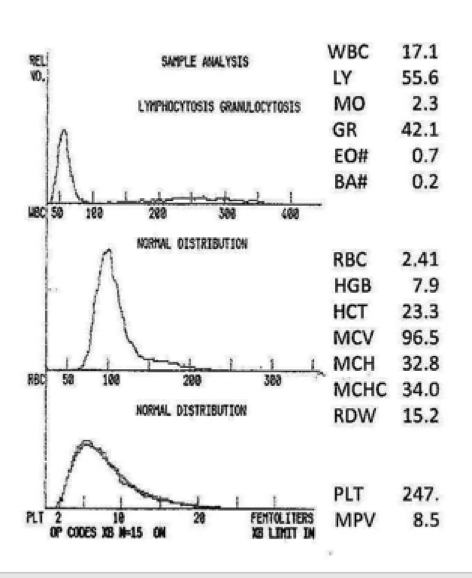
marked decreased
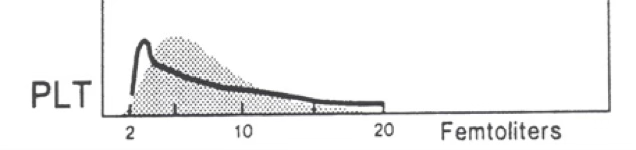
what would you expect this platelet count to be?
blasts/atypical lymphocytes
R2 flag
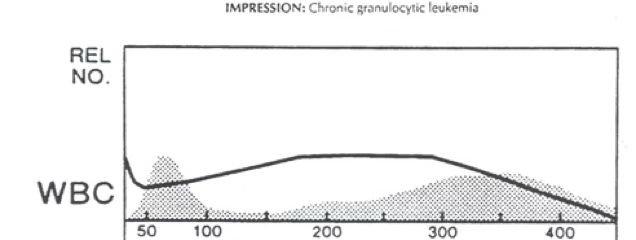
what cells do you expect to see on a differential with the below histogram?
immature granulocytes
increased eosinophils/basophils
nRBCs
what do you expect to find on the WBC relative differential?
macrocytic cells
what type of RBCs do you expect on a smear?
vitamin B12 and folate
what tests do you recommend next?
nutritional deficiency post treatment
micro/hypo anemia post transfusion
what are the 2 most probable causes of a bi-modal RBC histogram?
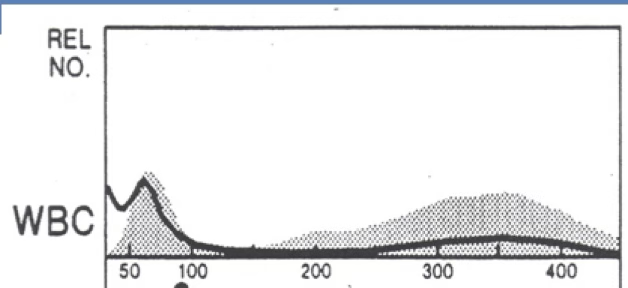
left shift
what can be said about the WBC population?
basophils
what cell type is at #3?
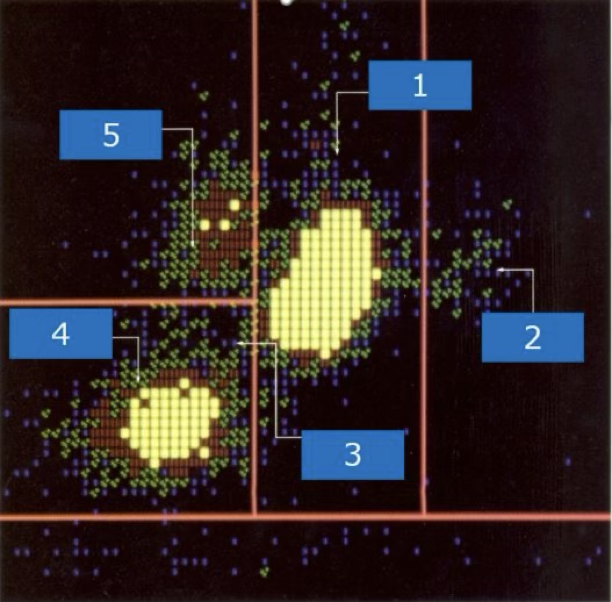
monocytes
what cell type is at #5?
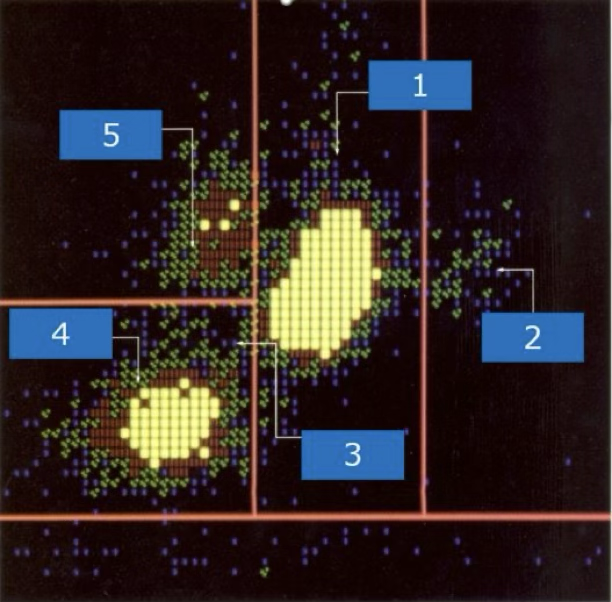
lymphocytes
what cell type is at #4?
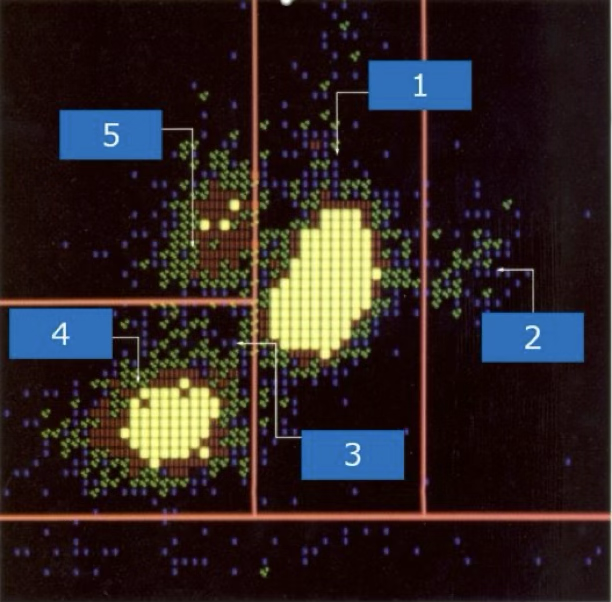
neutrophils
what cell type is at #1?
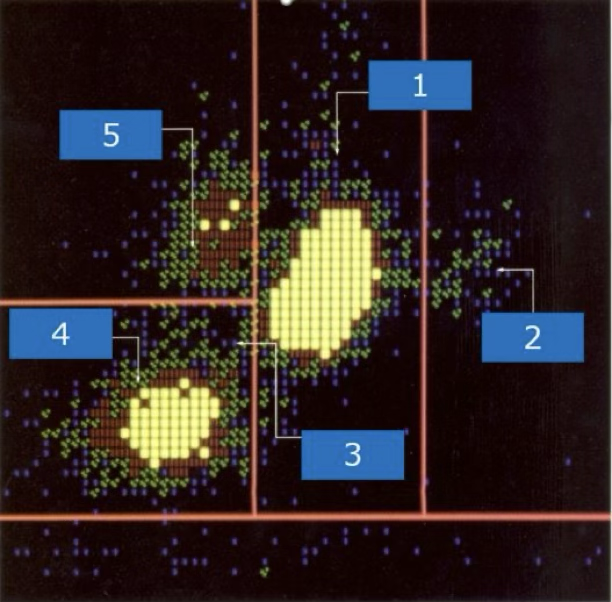
eosinophils
what cell type is at #2?
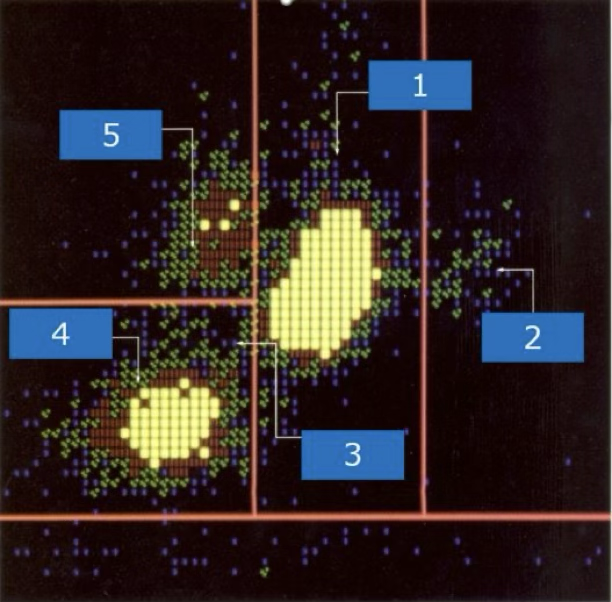
suspect blasts
what type of cells are located at 9,7,1?
immature granulocytes
what cells are located at 2?
nRBC and giant platelets
what is located at 4 and 5?
degenerated cells or debris
what is located at 3?
lymphoblasts
what type of blast is located at 7?
variant lymphs
what is located at 6 and 8?
patient C
which patient shows cold agglutination secondary to infectious mono—values incorrect?
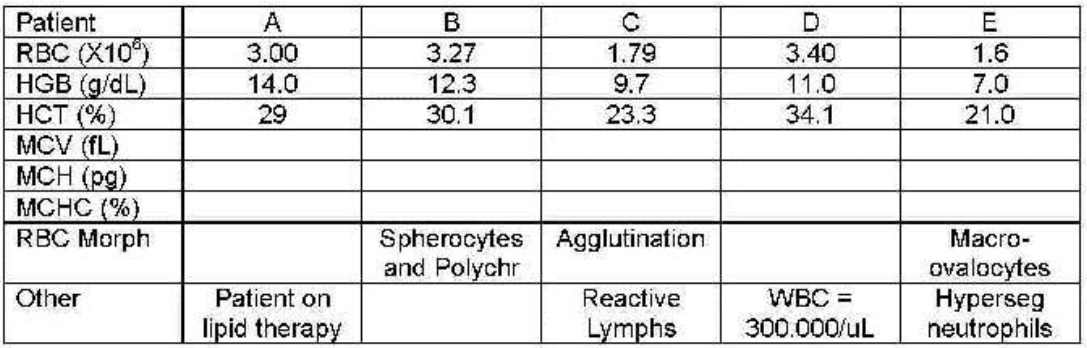
patient A
which patient shows lipemia—hemoglobin not correct?
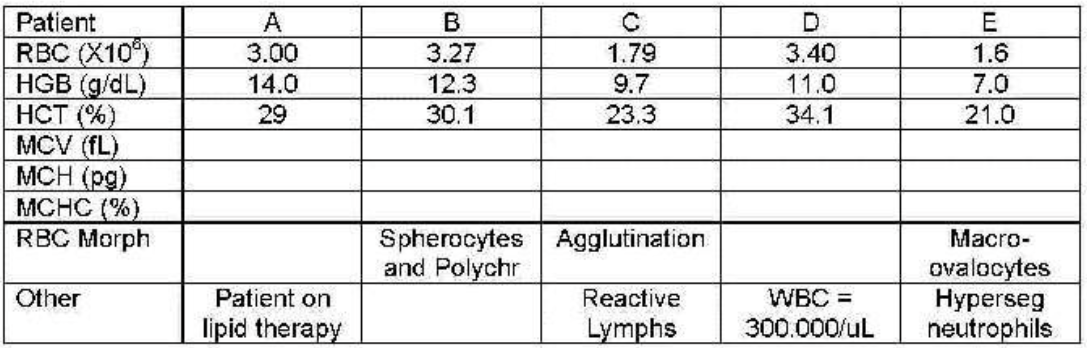
patient B
which patient shows spherocytes—indices abnormal bur correct?
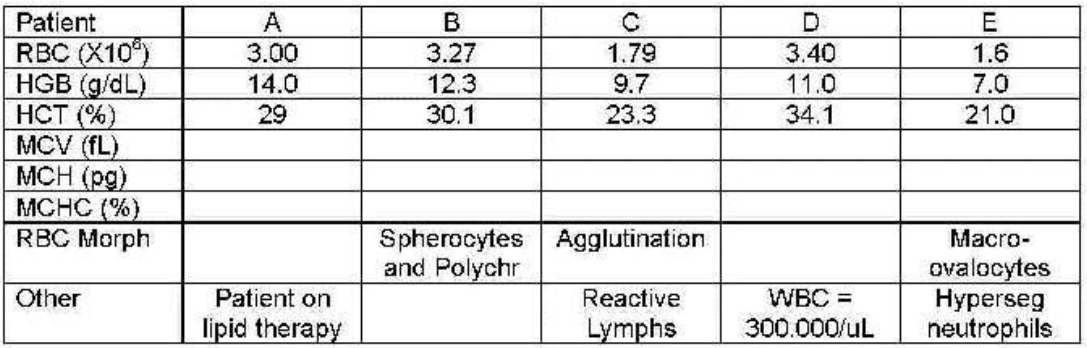
patient E
which patient shows megaloblastic anemia—indices abnormal but correct?
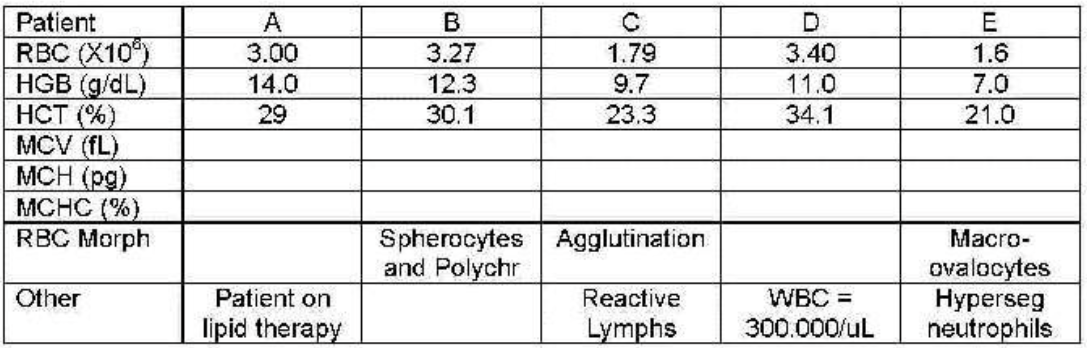
patient D
which patient has an elevated white count interfering—all results incorrect?
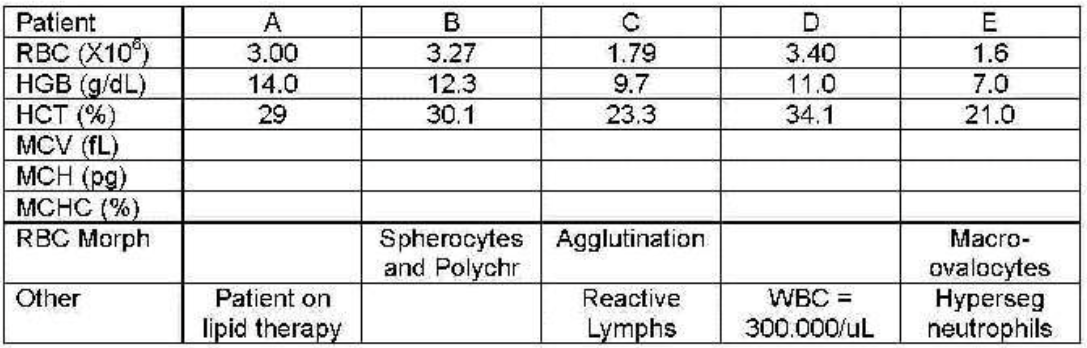
patient D
which patient’s blood needs to be diluted, reran to get WBC then corrected or recalculated other values?
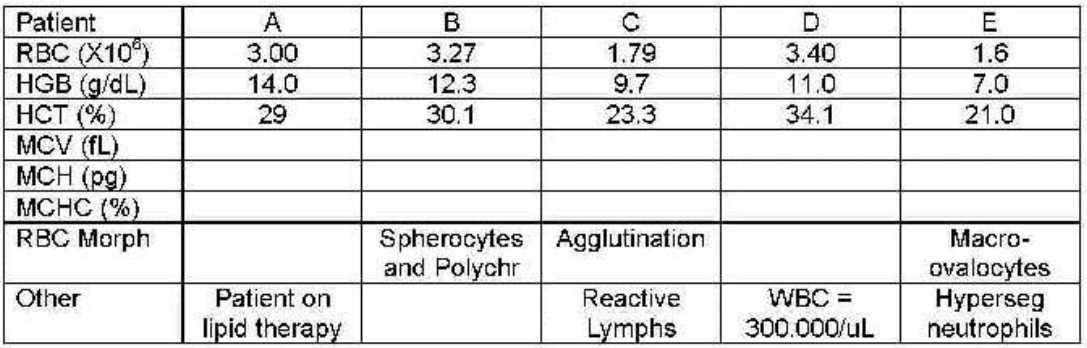
patient C
which patient needs to be warmed to 37℃ and reran?
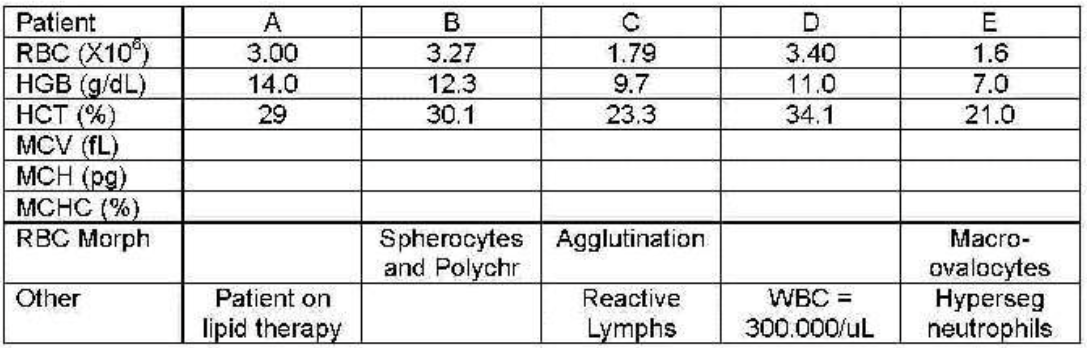
patient A
which patient needs plasma replaced with saline and reran?
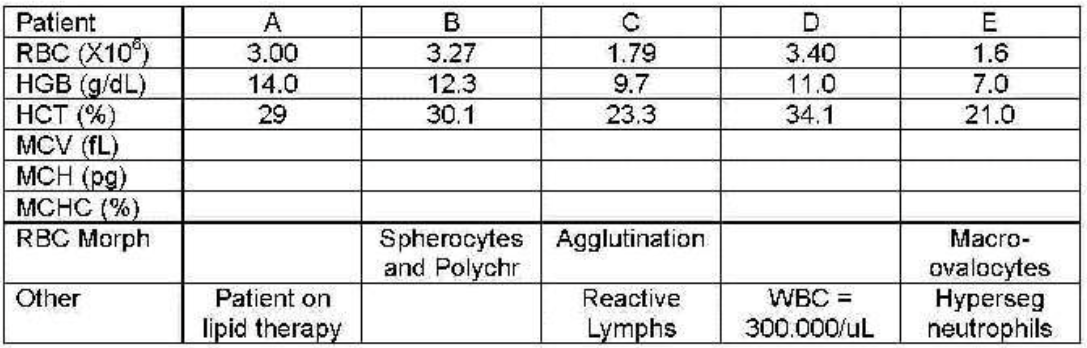
patients B and E
which patients can have their results reported because they are correct?
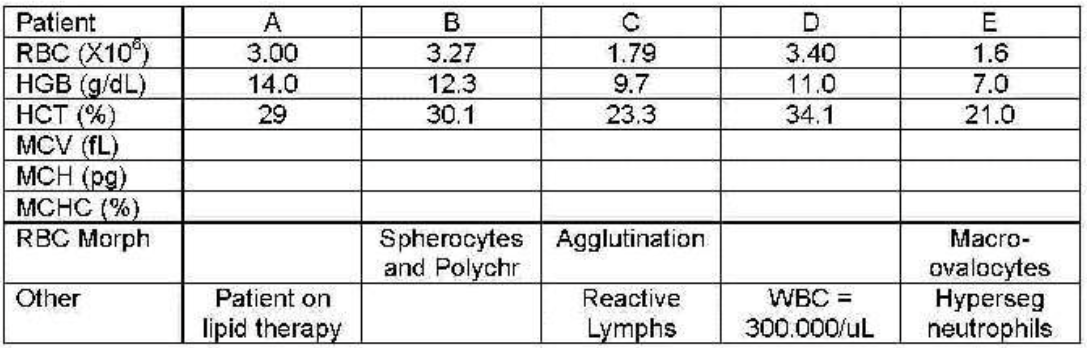
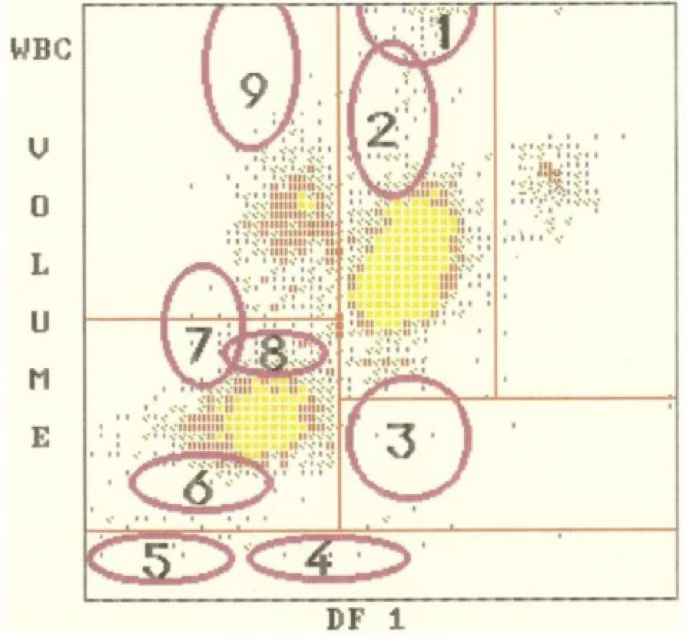
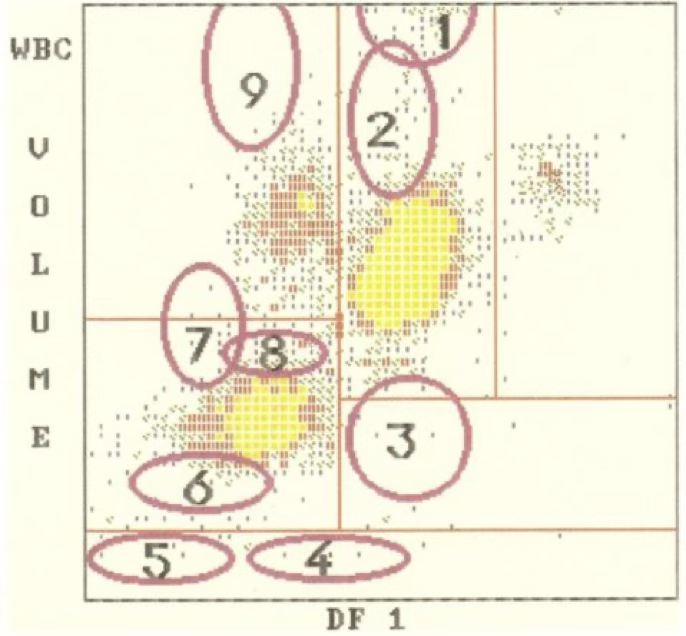
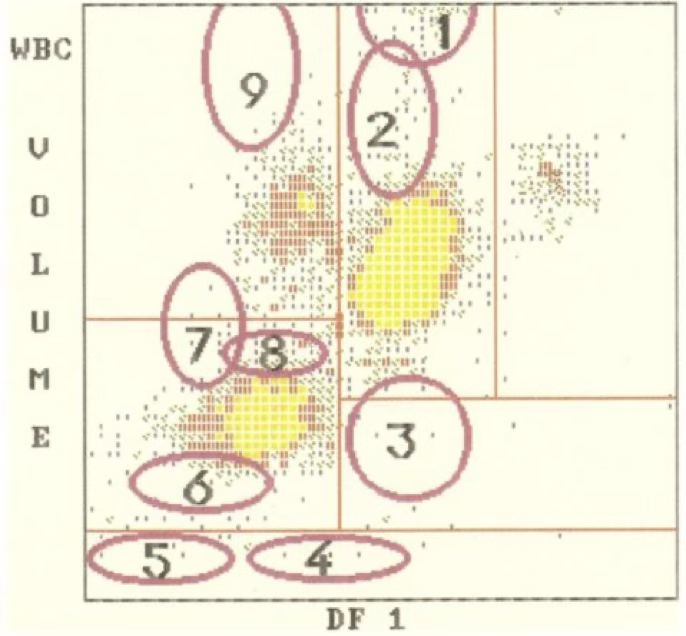
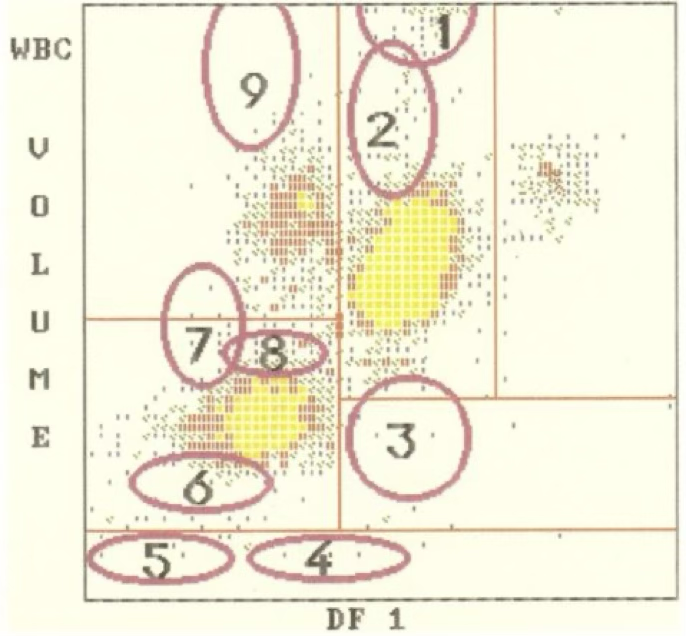
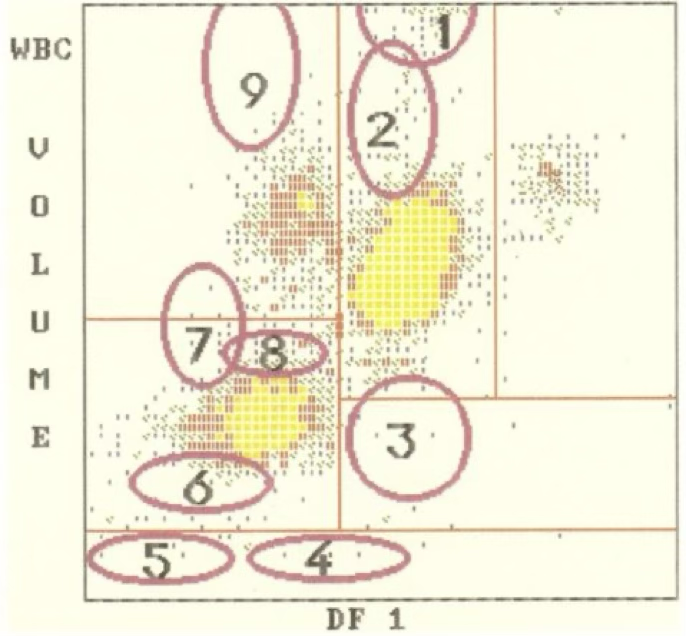
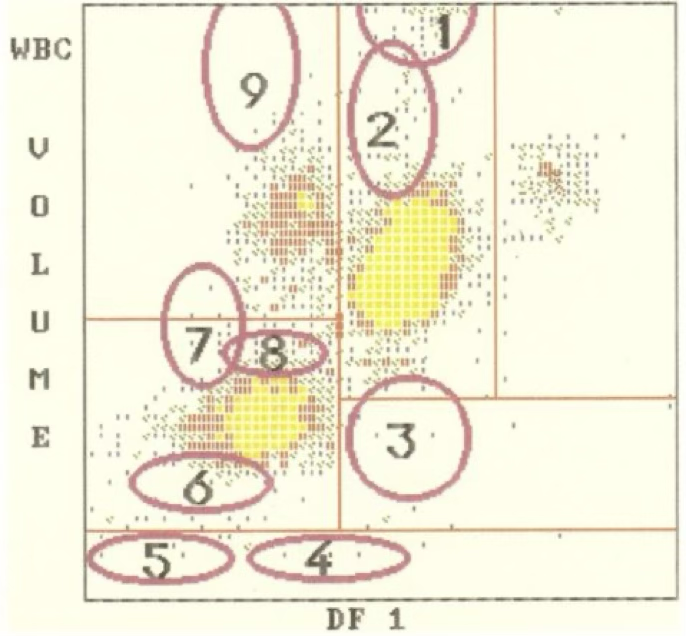
5
where is nRBC?
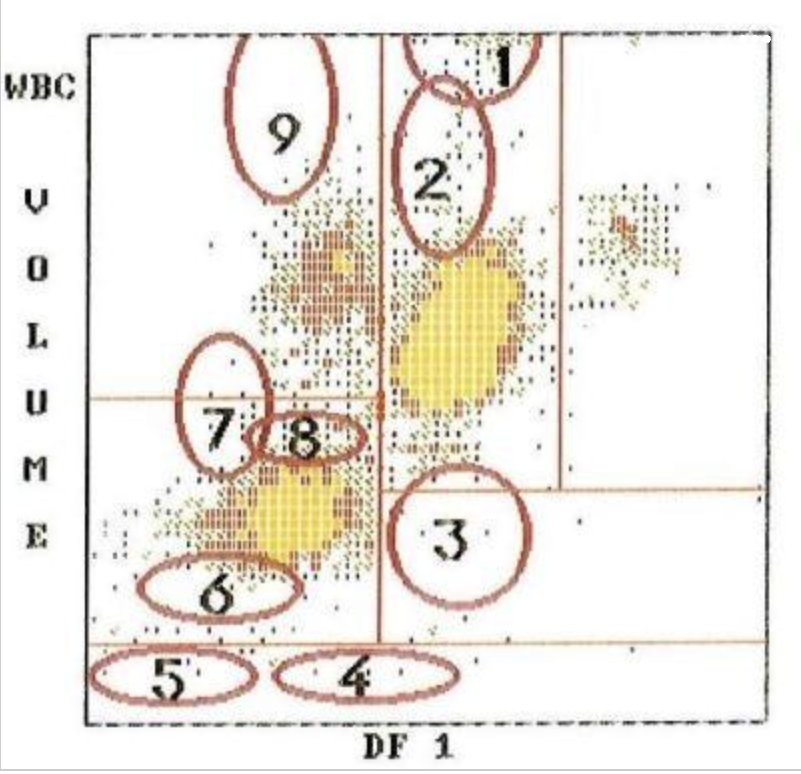
2
where are myelocytes?
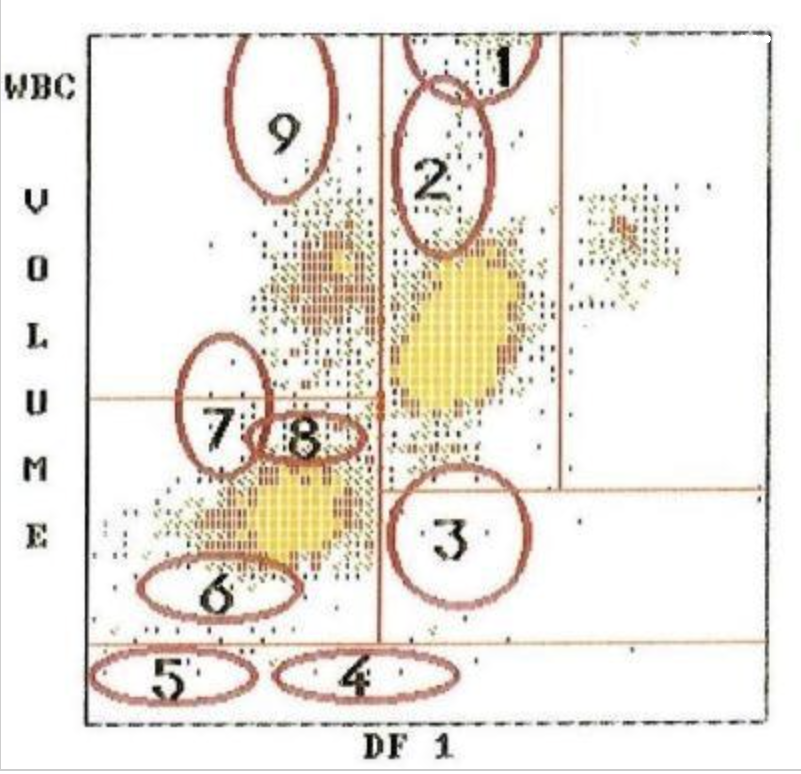
4
where are clumped platelets?
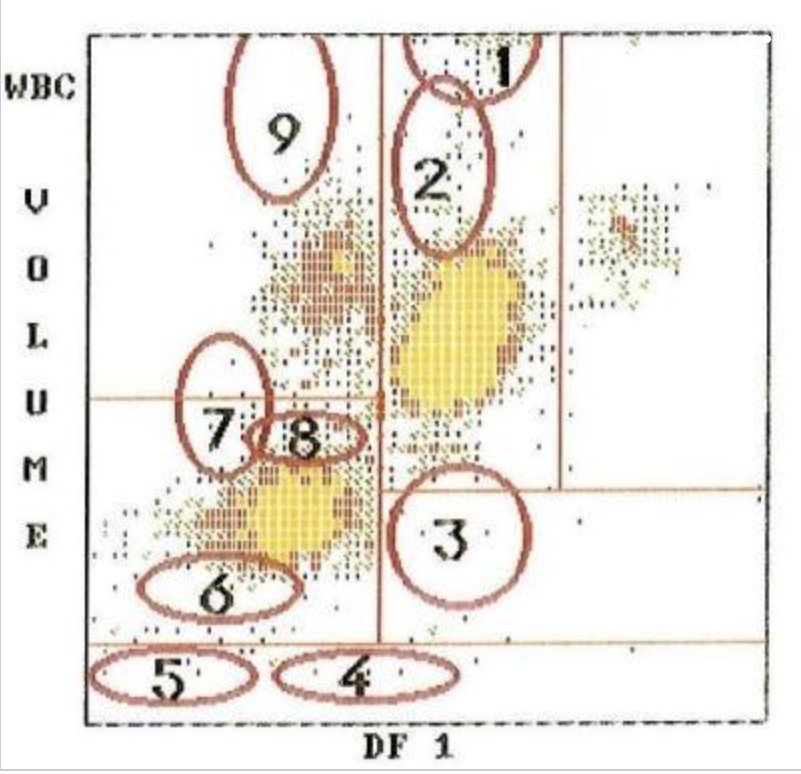
1
where are myeloblasts?
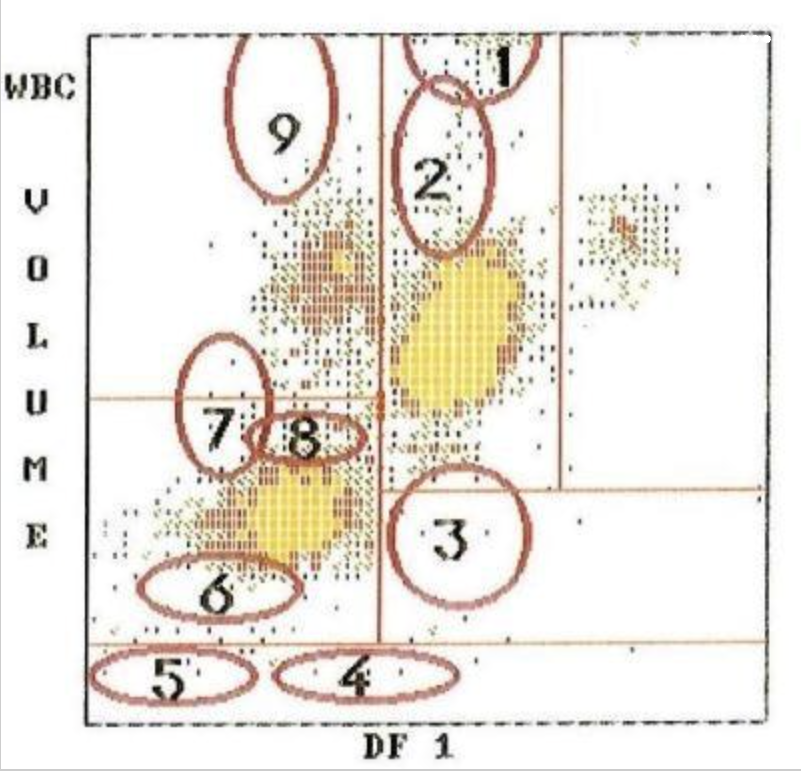
7
where are lymphoblasts?
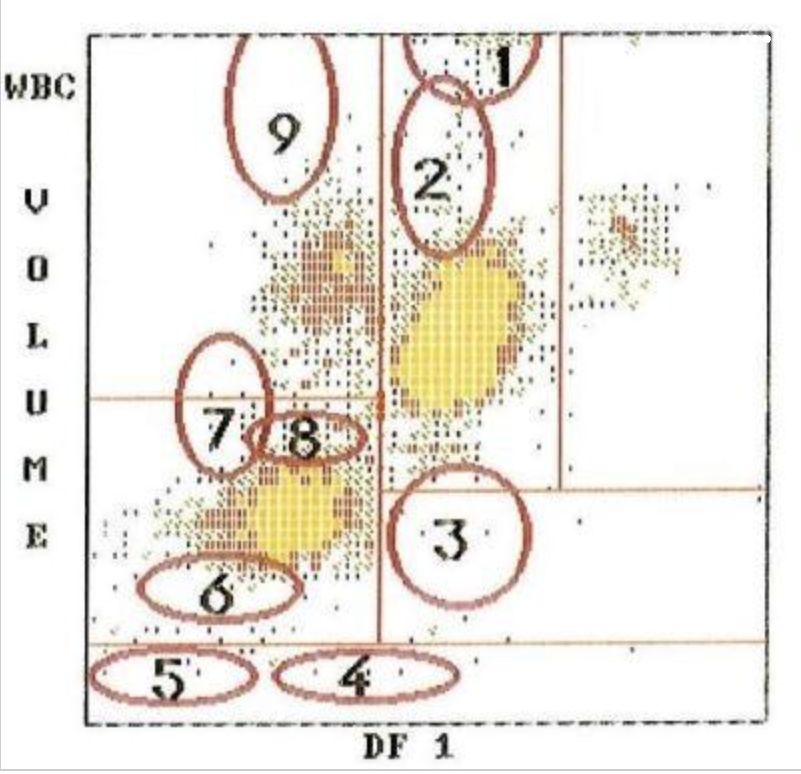
9
where are monoblasts?
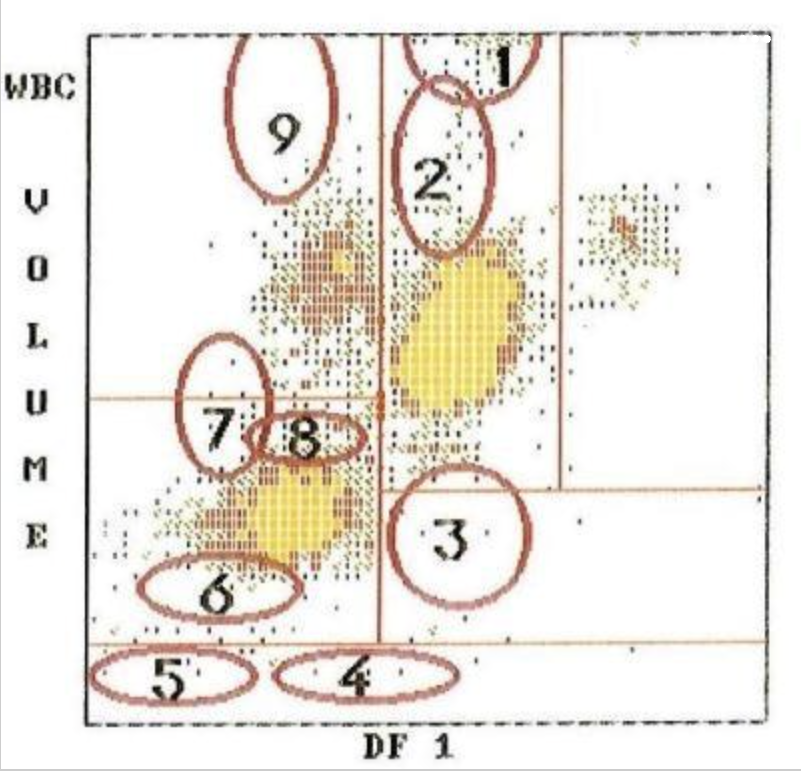
8
where are reactive lymphocytes?
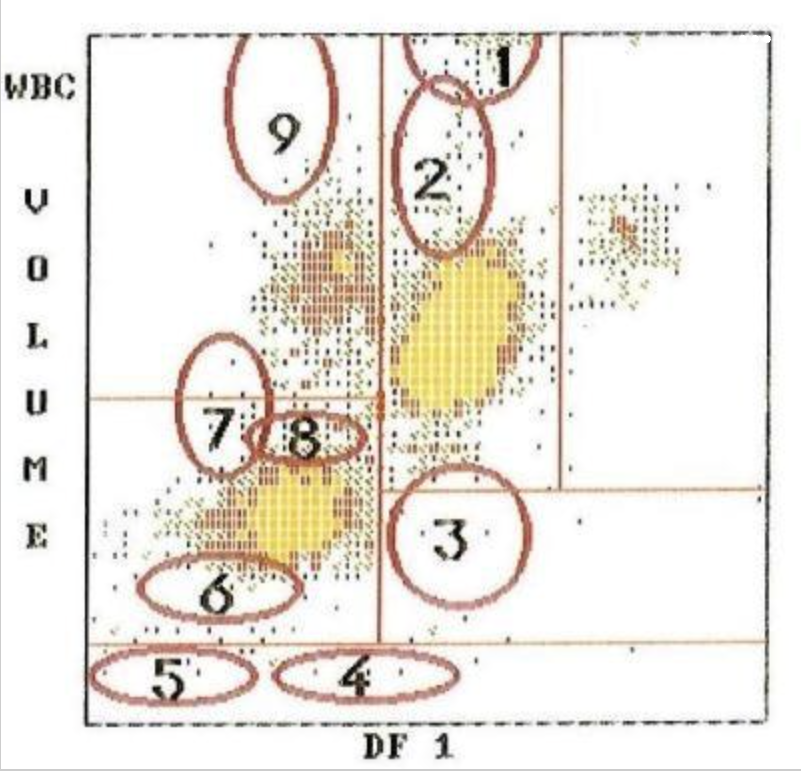
4
where are monocytes?
1
where are large platelets?
5
where are eosinophils?
3
where are blasts?
2
where are the lymphocytes?
5
where are the segmented neutrophils?
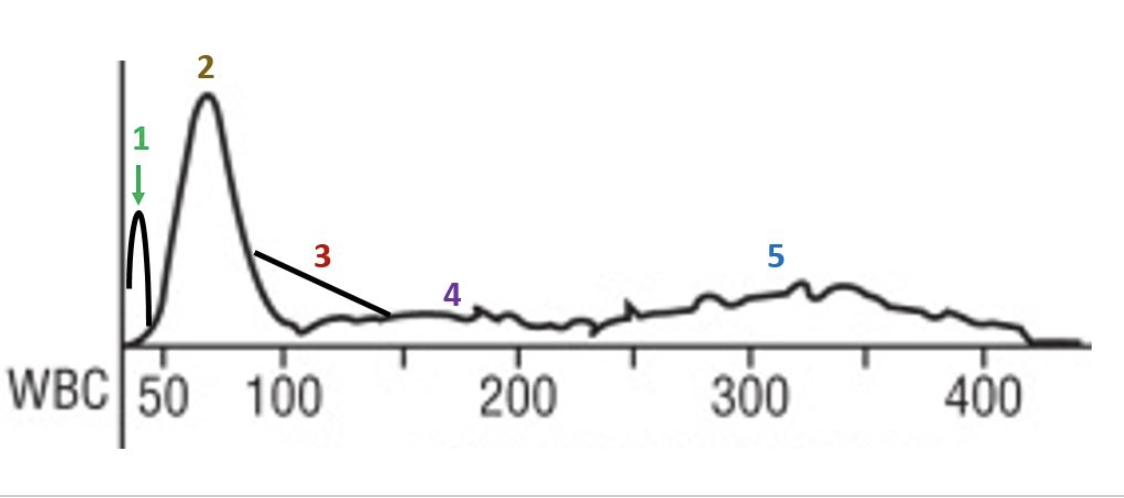
3
where are retics?
1
where are fragments?
4
where are doublets or WBCs?
2
where is the MCV?
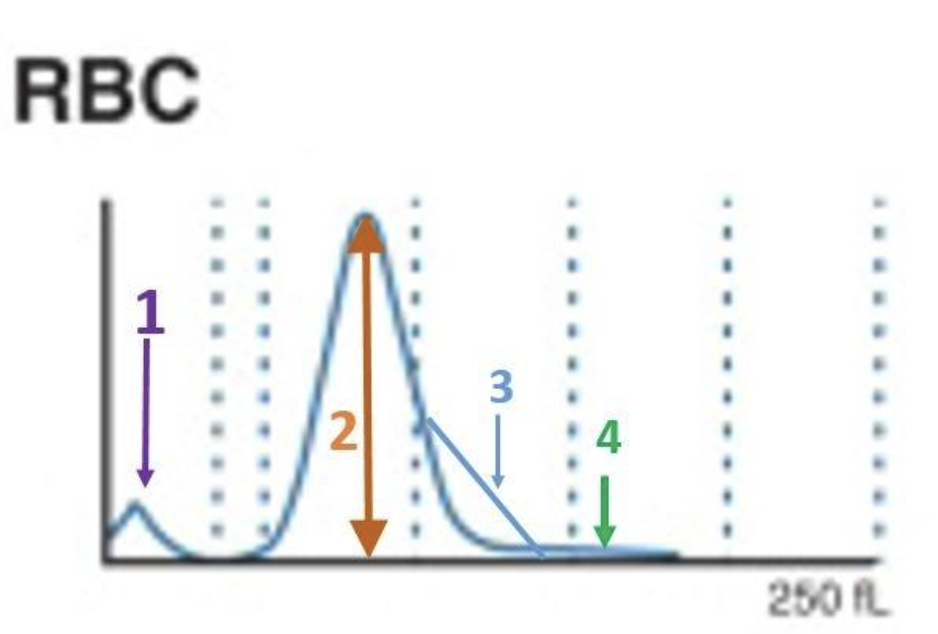
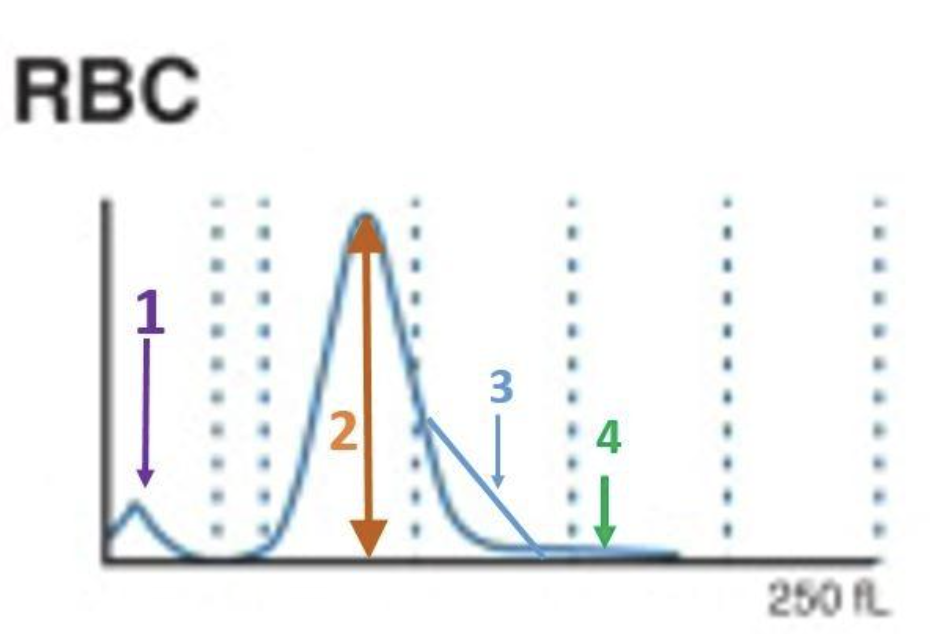
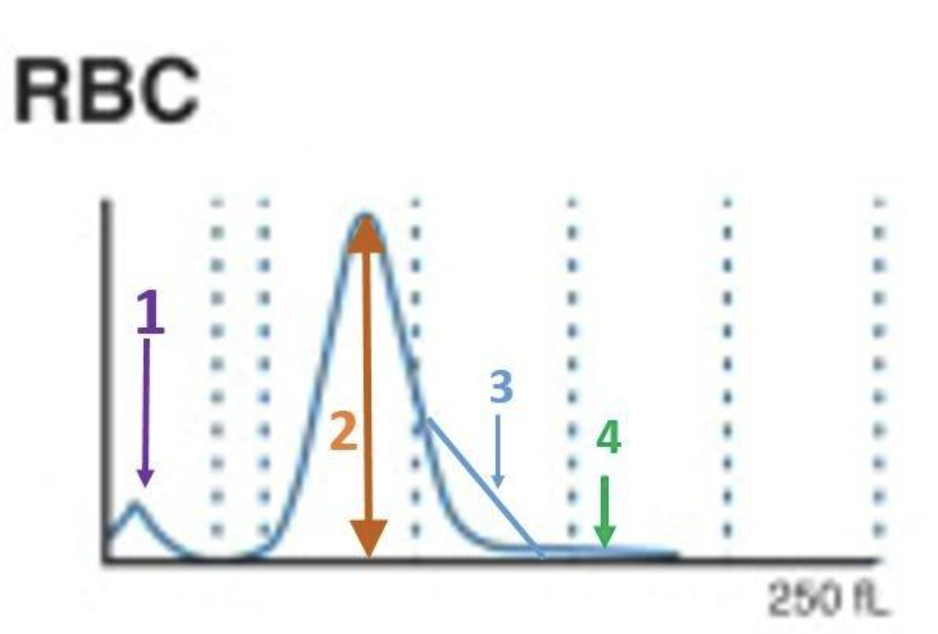
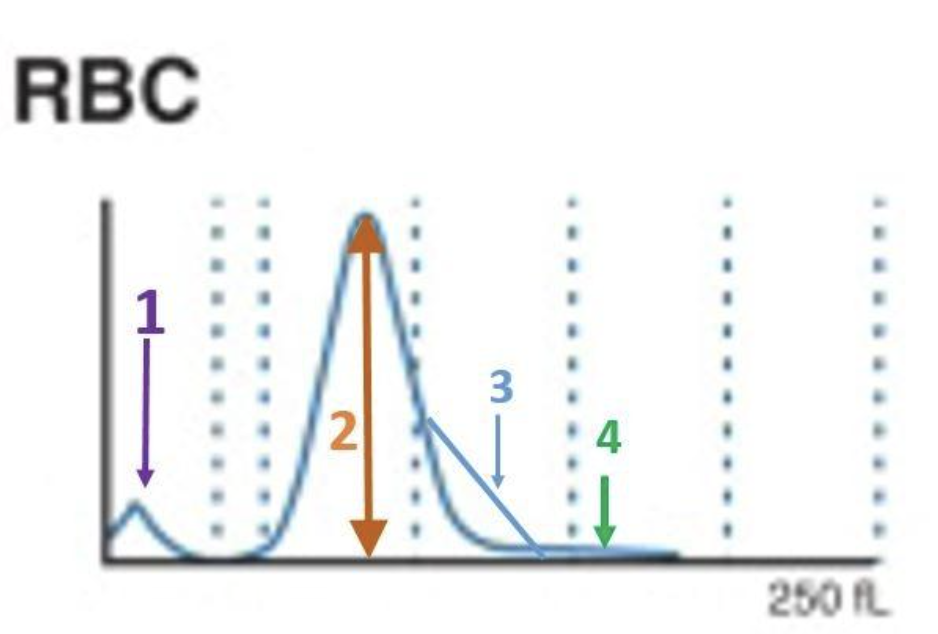
1
where are bubbles?
3
where are large platelets?
2
where are the tiny RBC?
D
where are red blood cells?
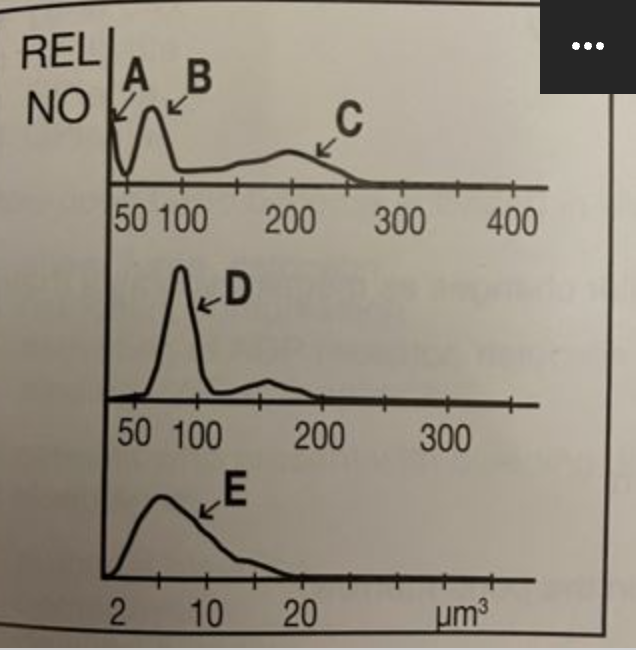
C
where are granulocytes?
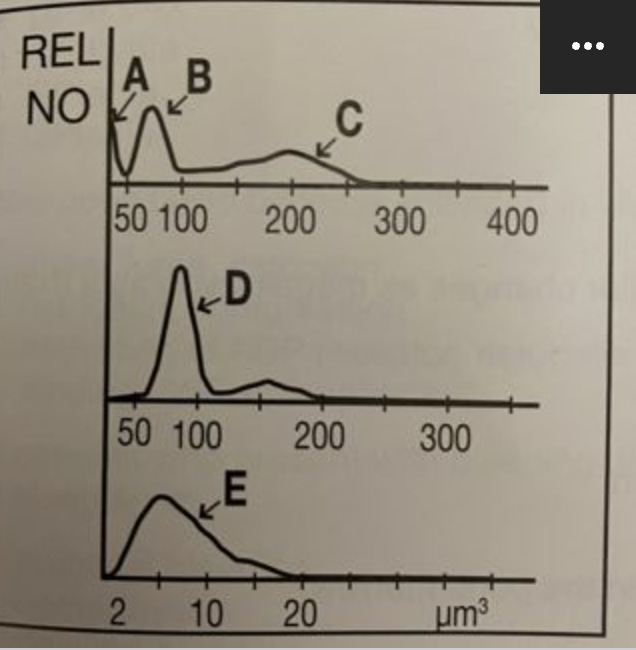
B
where are lymphocytes?
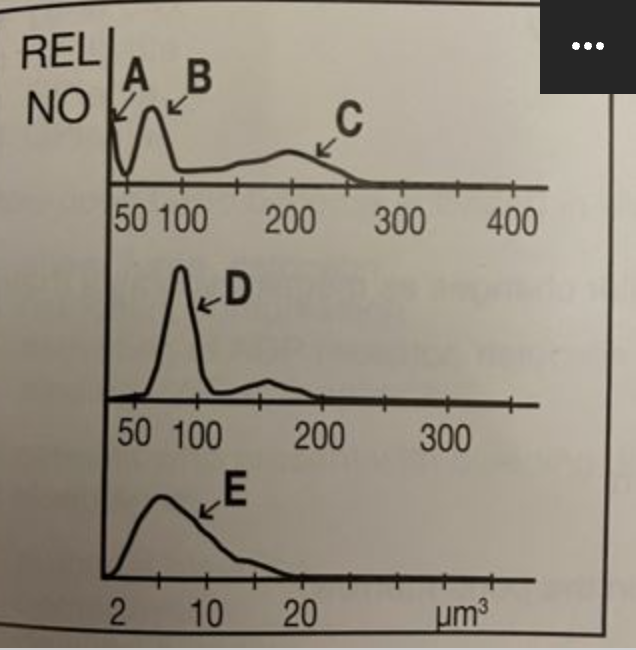
A
where are giant platelets, nucleated red blood cells, sickle cells, and artifacts?
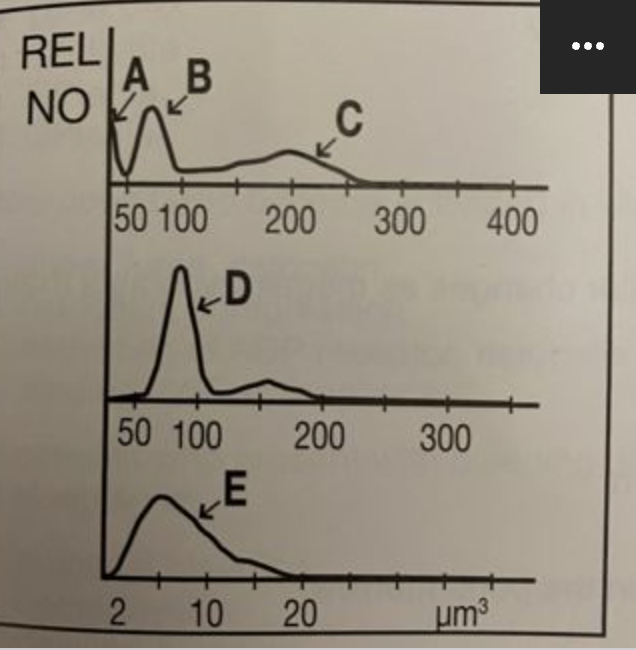
E
where are platelets?
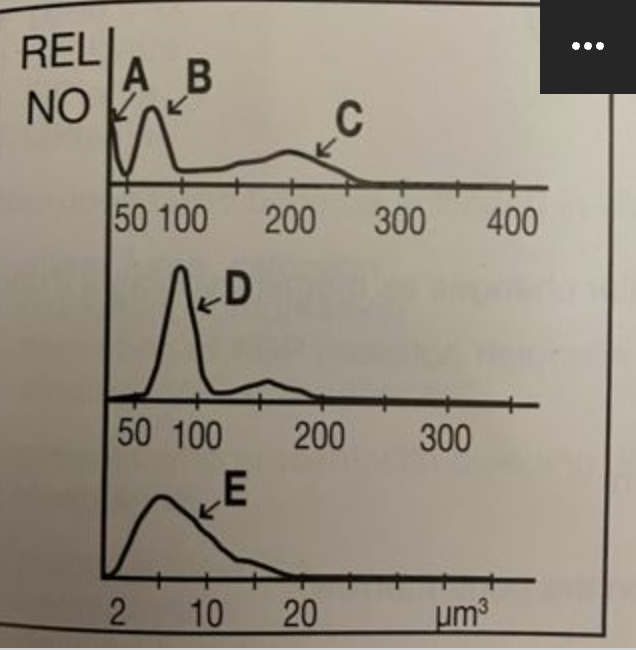
white blood cell count
in an electronic or laser particle cell counter, clumped platelets may interfere with which of the following parameters?
check the light source
hemoglobins are read on a photoelectric colorimeter in the laboratory. while reading the hemoglobins, a problem of drifting is encountered. to access the problem, the first thing to do is:
repeat the control
on initial start up of the automated hematology analyzer, one of the controls is slightly below the range for MCV. Which of the following is indicated?
normal whole blood
which of the following is the standard calibration method for hematology instrumentation against which other methods must be verified?
increased hematocrit and MCV
blood collected in EDTA undergoes which of the following changes if kept at room temperature for 6-24 hours?
true
the Coulter principle is based on impedance of an electronic current when cells are pulled individually through an aperture. the number of interruptions indicates the number of cells and the size of the interruption gives the type of cells?
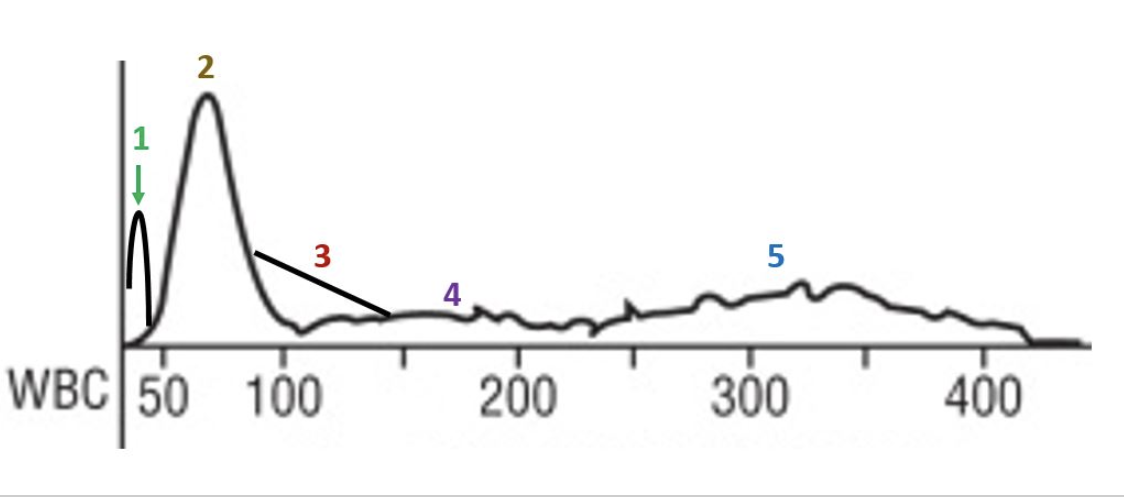
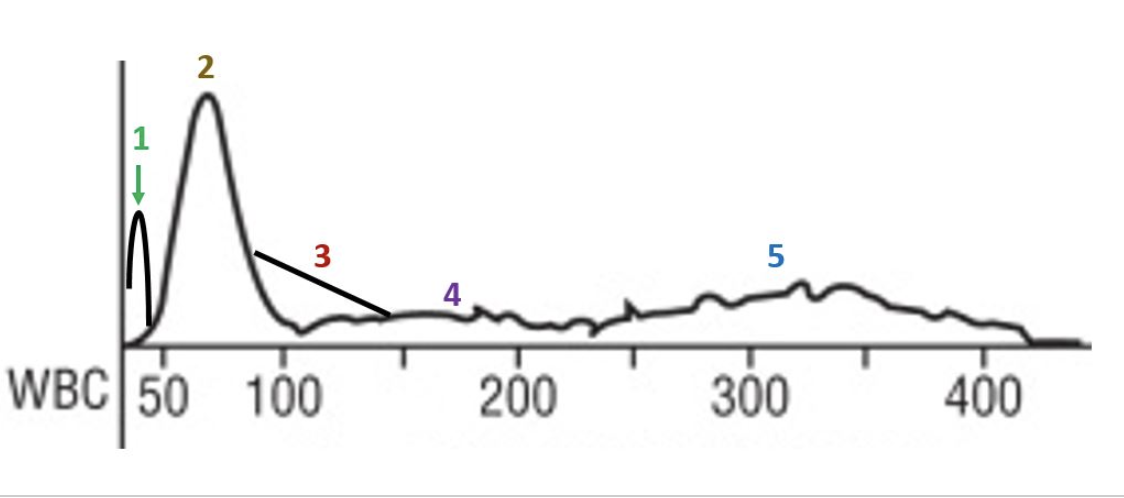
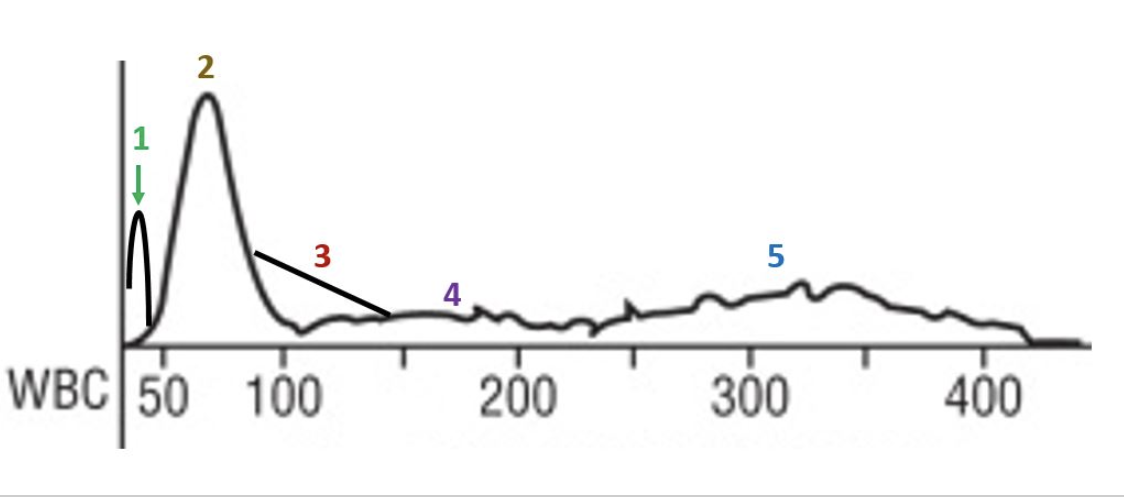
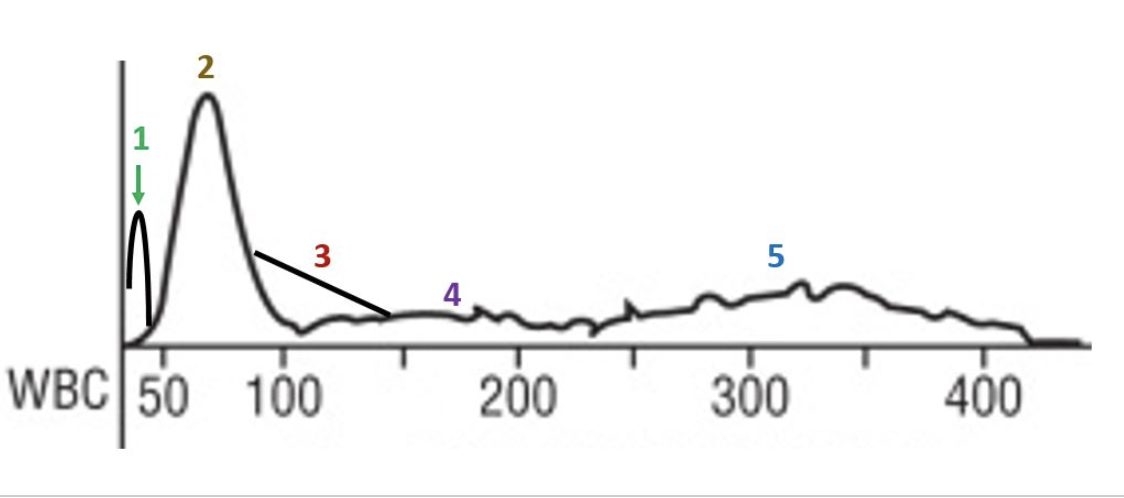
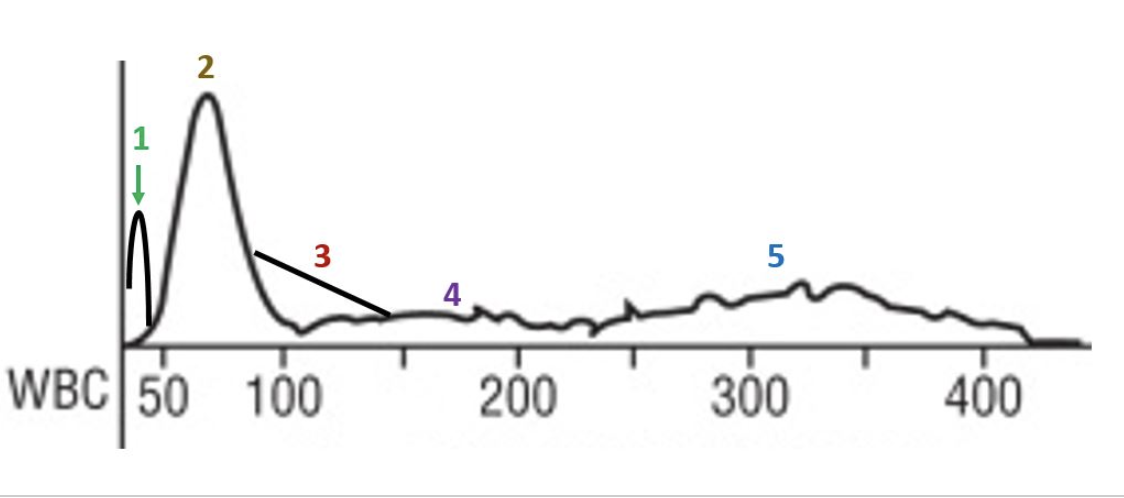
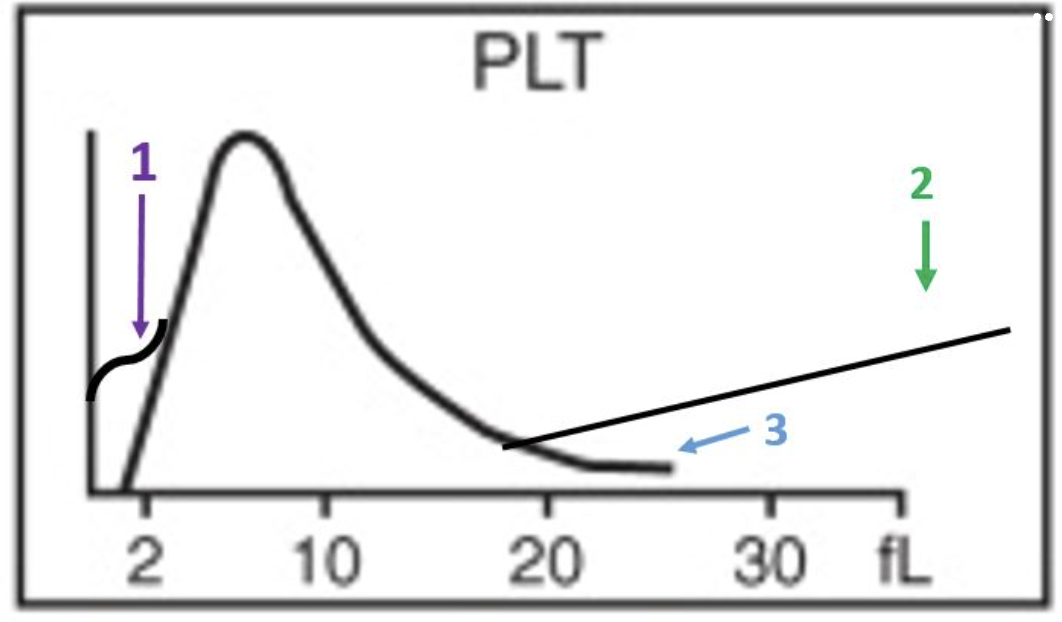
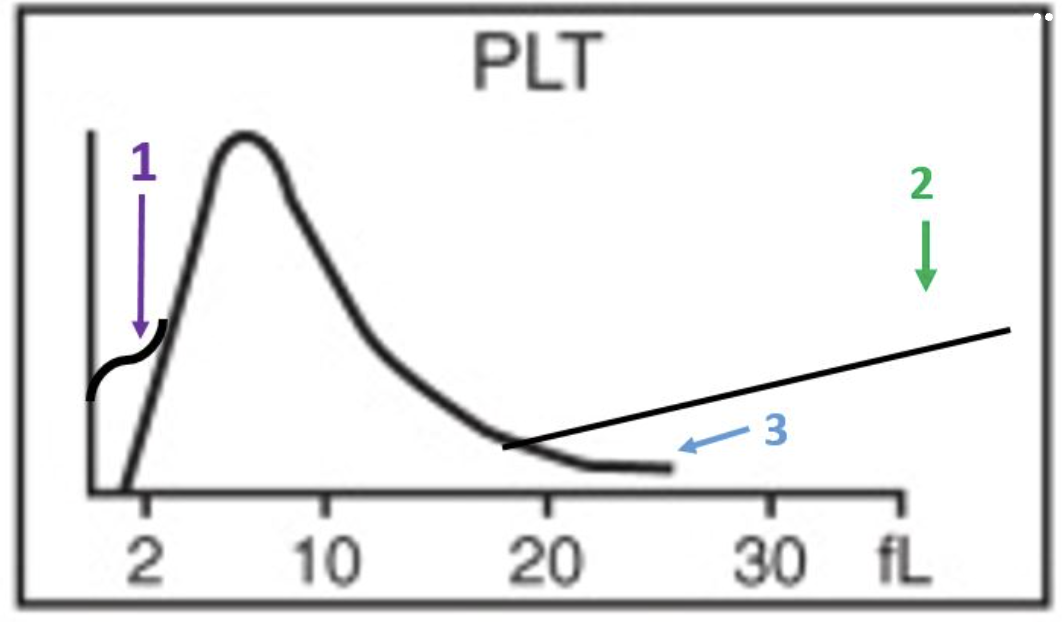
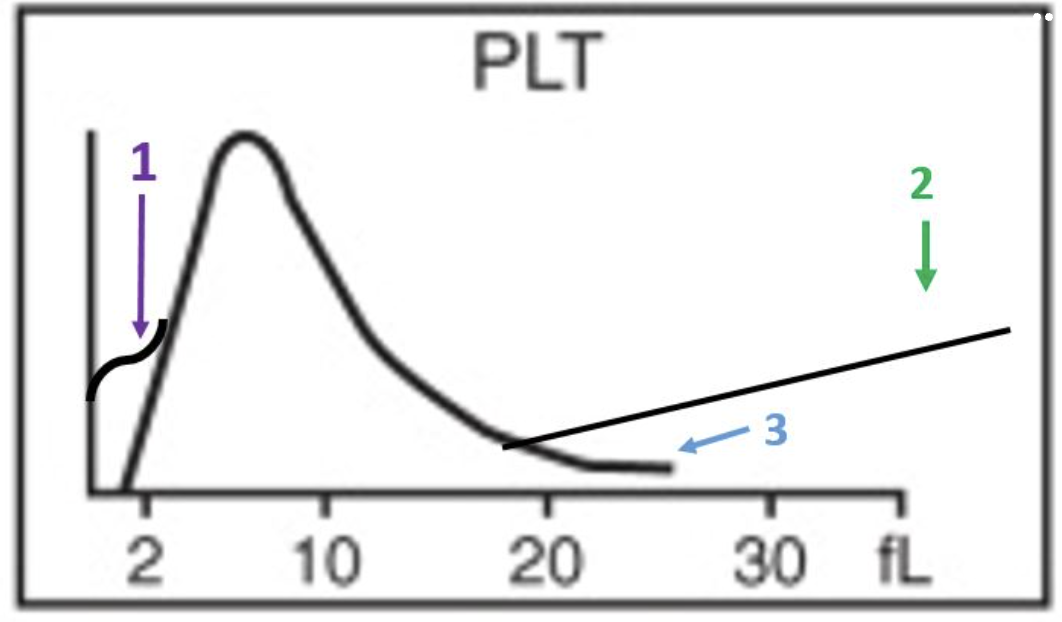
red cell morphology would be normochromic and macrocytic
the lymphocyte peak starts early and ends early
this patient likely has a folate or B12 deficiency
the smear would show marked anisocytosis
there is a decrease in the number of granulocytes
there is a decrease in the total number of red cells
this patient has a macrocytic anemia
the R1 flag can mean platelet clumps, giant platelets, sickle cells, nRBCs, or intracellular parasites
platelets are basically normal
this slide would likely have some hypersegmented neutrophils
which statements apply to this histogram?