Mod World Midterm
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:03 PM on 1/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
**1. How was imperial power restored after the collapse of the Han dynasty?**
Yang Jain founded the Sui Dynasty (in 589 CE) by uniting the three kingdoms of China.
2
New cards
Accomplishments and failures of Sui, Tang and Song
See chart
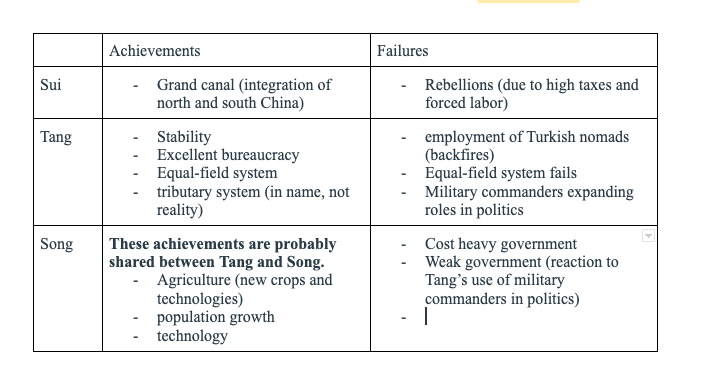
3
New cards
**3. What agricultural innovations occurred during this period and how did these affect China?**
* fast ripening rice (from Vietnam): 2-3x rice production
* Heavy iron plow
* Oxen and water buffalo
* fertilization
* irrigation systems
* terrace farmings
Led to a population explosion
* Heavy iron plow
* Oxen and water buffalo
* fertilization
* irrigation systems
* terrace farmings
Led to a population explosion
4
New cards
**4. What technological advancements took place during this period and how did these impact China?**
* porcelain (trading product)
* Metallurgy
* Printing and movable type (spread of knowledge)
* Gunpowder weapons
* Naval: magnetic compass, ship design (ocean going vessels), maps
* “flying cash” (credit): more economic activity
Improved trade and tools/weapons for productivity/defense
* Metallurgy
* Printing and movable type (spread of knowledge)
* Gunpowder weapons
* Naval: magnetic compass, ship design (ocean going vessels), maps
* “flying cash” (credit): more economic activity
Improved trade and tools/weapons for productivity/defense
5
New cards
**5. What factors contributed to the intensification of patriarchy?**
* ancestry worship (led by eldest male)
* foot binding
* foot binding
6
New cards
**6. What cultural and religious changes took place?**
* introduction of foreign religions
* Buddhism in particular
* Neo-Confucianism (combination of Buddhism and Confucianism)
* Buddhism in particular
* Neo-Confucianism (combination of Buddhism and Confucianism)
7
New cards
**7. How did China influence Vietnam, Korea and Japan?**
Vietnam: Confucian influences (became independent after Tang) + Tributary state (Retained indigenous religious traditions and, unlike China, women had a prominent role)
\n Korea: Tributary state (but didn’t develop a bureaucracy; aristocracy instead)
Japan: Nara Japan (Imperial state modeled on Tang) (capital modeled Tang capital; also had equal-field system); Heian Japan also had Chinese influence
\n Korea: Tributary state (but didn’t develop a bureaucracy; aristocracy instead)
Japan: Nara Japan (Imperial state modeled on Tang) (capital modeled Tang capital; also had equal-field system); Heian Japan also had Chinese influence
8
New cards
**8. Describe Japan during the time of the Tang and Song.**
Nara Japan (710-794): imperial state modeled on Tang
Heian Japan (794-1185): new capital, role of emperor, rise of Shogun, medieval Japan
Heian Japan (794-1185): new capital, role of emperor, rise of Shogun, medieval Japan
9
New cards
**9. Compare the Umayyad and Abbasid dynasties.**
see chart
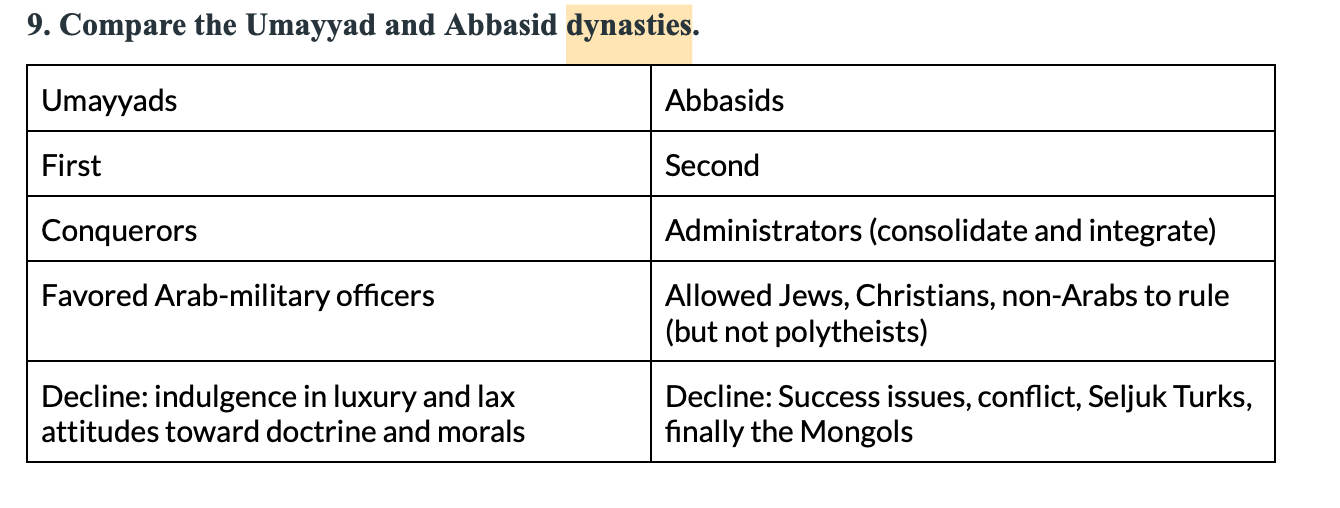
10
New cards
**10. How did sharia contribute to the consolidation and integration of Dar al-slam?**
It created a common basis of law that helped stabalize trade partnerships and other interactions.
11
New cards
**11. Specifically, how did agricultural innovations contribute to the growth of the economy of Dar al-Islam?**
* new food crops (better diet, more production, can grow year round) -> population growth and trade products
12
New cards
**12. How did the hajj facilitate integration and the spread of innovations throughout Dar al-Islam?**
“Forced”/created a mechanism where people from all over the empire interacted and, of course, shared ideas during their travels
13
New cards
**13. Why was the importance of the development of the dhow, the invention of the lateen sail and the introduction of the camel and camel saddle important to trade across Dar al-Islam?**
Dhow + lateen sail: didn’t have to rely on monsoon system
Camel + camel saddle: could carry more goods on land over difficult terrain (sand)
Camel + camel saddle: could carry more goods on land over difficult terrain (sand)
14
New cards
**14. Why was the introduction of paper from China into Dar al-Islam significant?**
* spread of knowledge through (argiculture) pamphlets
* more government records
* libraries and increase in education
* more government records
* libraries and increase in education
15
New cards
**15. What developments and innovations increased trade and prosperity in Dar al-Islam?**
* revival of silk roads
* network of roades
* technologies (particularly maritime)
* network of roades
* technologies (particularly maritime)
16
New cards
**16. Why were the Sufis important to the spread of Islam?**
* They attracted many converts because they were tolerant of indigenous traditions and more focused on emotion and devoltion than theology
* Influential in places like Africa
* Influential in places like Africa
17
New cards
**17. What factors enabled cultural integration in Dar al-Islam?**
* Common religion: Islam
* Common law: sharia
* Common language: Arabic
* hajj: the pilgrimage contributed to many interactions between cultures and sharing of idea
* Common law: sharia
* Common language: Arabic
* hajj: the pilgrimage contributed to many interactions between cultures and sharing of idea
18
New cards
18\.**What other cultures influenced Islam and Islamic culture?**
* Persia
* Government
* Administrative techniques
* Methods of imperial rule
* Idea of a wise, benevolent king
* Literature
* Art (didn’t have the orthodox Islam prohibition of painting)
* India
* Mathematics
* Hindi numerals (w/ 0), Algebra, Trig, Geometry
* Accounting and bookkeeping
* Greek
* Philosopies (especially Aristotle)
* Averroes and Scholasticism
* Use of reason to understand the world (but lost popularity due to reliance of reason and fear of Greek polytheism)
* Math
* Science
* Medicine
* Government
* Administrative techniques
* Methods of imperial rule
* Idea of a wise, benevolent king
* Literature
* Art (didn’t have the orthodox Islam prohibition of painting)
* India
* Mathematics
* Hindi numerals (w/ 0), Algebra, Trig, Geometry
* Accounting and bookkeeping
* Greek
* Philosopies (especially Aristotle)
* Averroes and Scholasticism
* Use of reason to understand the world (but lost popularity due to reliance of reason and fear of Greek polytheism)
* Math
* Science
* Medicine
19
New cards
19\. **Trace the origins of the Mexica.**
* Mexica origins are shrouded in myth
* They claim that they came from the island of Astlan
* The left in search of a promised land at the orders of their patron god, Huitzilopochtli
* They scoured the land, settling for a while and then moving later.
* They made some enemies during this time due to their bloodthirsty nature
* After escaping to an island in the middle of lake Texcoco, they realized that this was their promised land, which they then called Tenochtitlan
* They built the island into a magnificent city which would later become the capital of the Aztec empire.
* They claim that they came from the island of Astlan
* The left in search of a promised land at the orders of their patron god, Huitzilopochtli
* They scoured the land, settling for a while and then moving later.
* They made some enemies during this time due to their bloodthirsty nature
* After escaping to an island in the middle of lake Texcoco, they realized that this was their promised land, which they then called Tenochtitlan
* They built the island into a magnificent city which would later become the capital of the Aztec empire.
20
New cards
**20. Describe the structure of the Mexica empire.**
* Tributary empire (Mexica/Aztecs threatened them if they didn’t cooperate)
* joined with others to create Aztec Empire
* no bureaucracy
* joined with others to create Aztec Empire
* no bureaucracy
21
New cards
**21.Outline the social hierarchy of the Mexica.**
* Warriors (highest)
* Priests
* Cultivators (basically peasants)
* Slaves
* patriarchal (women’s role was largely child-bearing)
* Priests
* Cultivators (basically peasants)
* Slaves
* patriarchal (women’s role was largely child-bearing)
22
New cards
**22.. What were the privileges of the warrior class?**
* They were given land grants and money
* They were given special social price pages such as wearing finer clothing and jewelry than their middle And lower class compatriots
* They were given special social price pages such as wearing finer clothing and jewelry than their middle And lower class compatriots
23
New cards
**23.What were the duties/ responsibilities of the warrior class?**
The warriors were to defend Aztec land and expand it when possible, but more experienced warriors were also to teach other people the art of war and advise the emperor in his decision making.
24
New cards
**24.What were the duties/responsibilities of:**
**a. women**
* To give birth to great warriors, or die trying
**b. priests**
* To foresee upcoming events
* To perform sacrifice to appease the gods
**c. peasants**
* To farm the land for the state
* To join the military when they are needed
* To give birth to great warriors, or die trying
**b. priests**
* To foresee upcoming events
* To perform sacrifice to appease the gods
**c. peasants**
* To farm the land for the state
* To join the military when they are needed
25
New cards
**25. What was the importance of the chinampas and capulli to Mexica agriculture?**
The chinampas allowed for crops to be harvested like 7 times a year, which allowed for more food to be produced. The calpulli were the basic blocs of Aztec society, and they were to farm the land.
26
New cards
**26. Describe Mexica religious beliefs and practices.**
* It ended up being a sort of amalgamation of a bunch of other beliefs of the area.
* They believed in multiple gods, each pertaining to one aspect of the world, such as fire, water, war, etc.
* These gods needed sacrifice, otherwise the world would end.
* They saw that the greatest thing that they could sacrifice was human life and blood.
* The patron god of the Mexica was Huitzilopotcthli, the god of war.
* They believed in multiple gods, each pertaining to one aspect of the world, such as fire, water, war, etc.
* These gods needed sacrifice, otherwise the world would end.
* They saw that the greatest thing that they could sacrifice was human life and blood.
* The patron god of the Mexica was Huitzilopotcthli, the god of war.
27
New cards
**27. What was the role of bloodletting in Mesoamerican societies?**
* Blood was seen as sacred to these societies, and the sacrifice of it was seen as necessary to keep the world from ending.
28
New cards
**28. Compare the societies of North America and Central/South America.**
North: smaller (we didn’t really talk about the Missiippians)
Central/South: more organized; larger empires
Central/South: more organized; larger empires
29
New cards
**29.. How did the Inca consolidate, govern and integrate their empire?**
* Mit’a: “tax” of human labor
* Colonization (and hostage, likely of rules) to absorb new peoples
* Regional storehouses (quallqa)
* (standing-I think!) army (unlike Aztecs)
* Colonization (and hostage, likely of rules) to absorb new peoples
* Regional storehouses (quallqa)
* (standing-I think!) army (unlike Aztecs)
30
New cards
**30. What was the significance of the Inca systems of roads?**
Rapid movement of troops and communication
31
New cards
**31. Describe Inca society and religious beliefs.**
* Sin -> disruption of divine order
* Sun god
* Creator god
* Temples -> pilgrimage sites
* Animals and produce (not humans) for peasant sacrifices
* Sun god
* Creator god
* Temples -> pilgrimage sites
* Animals and produce (not humans) for peasant sacrifices
32
New cards
**32. Describe rise and fall the three kingdoms/empires of West Africa: Ghana, Mali and Songhai. What factors contributed to the rise of these states?**
see chart
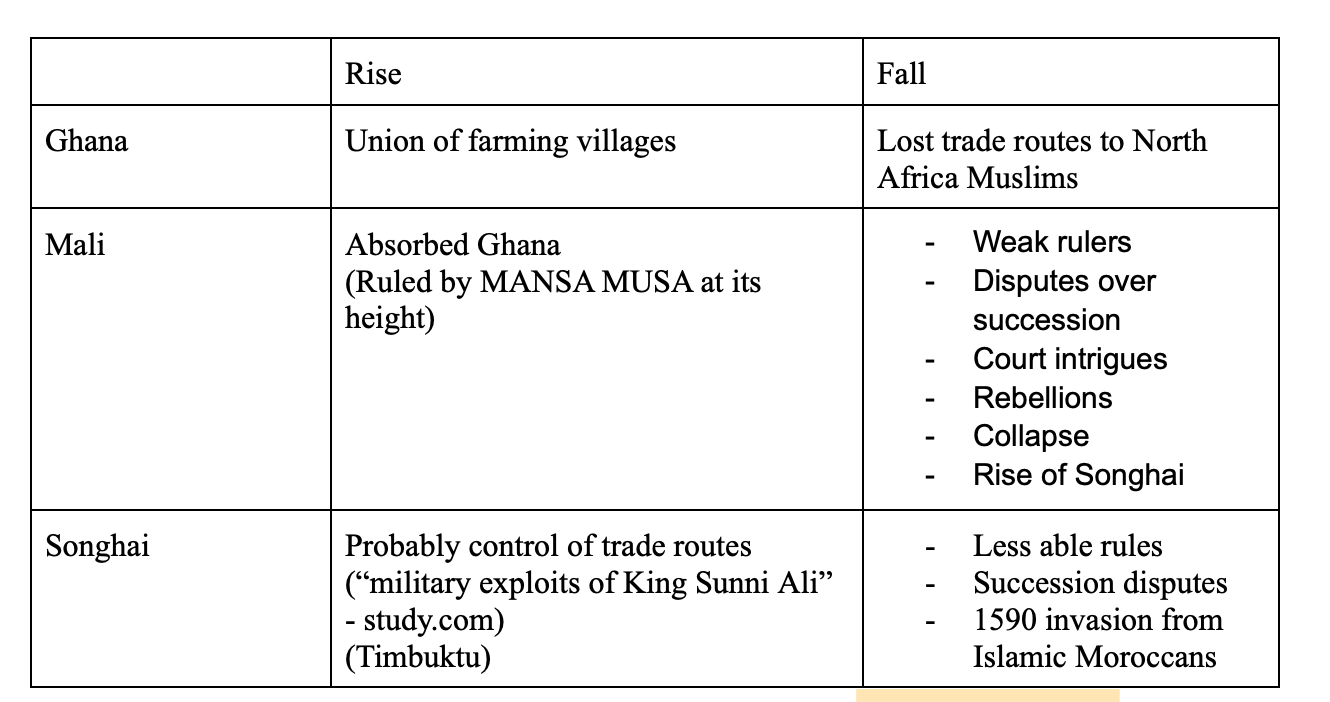
33
New cards
**33.. What the influence of Islam and Islamic culture on the "Grassland Empires" ?**
* Ghana: Islamic business practices
* Mali: based law code on Quran
* Mansa Musa’s hajj
* Timbuktu: major center of Islamic learning
* Songhai
* Islamic
* Timbuktu (\[again!\] community of Islamic scholars)
* Aided in trade relationships (I think)
* Mali: based law code on Quran
* Mansa Musa’s hajj
* Timbuktu: major center of Islamic learning
* Songhai
* Islamic
* Timbuktu (\[again!\] community of Islamic scholars)
* Aided in trade relationships (I think)
34
New cards
**34.What was the importance of Axum/Ethiopia?**
* Only Christian state
* A major trading power in the Mediterranean & IOB (w/ port city Adulis)
* A major trading power in the Mediterranean & IOB (w/ port city Adulis)
35
New cards
**35.What are the origins and characteristics of Swahili culture?**
* Swahili = coast dwellers; coasters
* Language: Arabic + native Bantu languages (several dialects)
* Hybrid of Islam and African cultures
* Origins: (I think) unique combination of Islam and native African traditions/languages/etc that resulted from IOB trade relationships
* Language: Arabic + native Bantu languages (several dialects)
* Hybrid of Islam and African cultures
* Origins: (I think) unique combination of Islam and native African traditions/languages/etc that resulted from IOB trade relationships
36
New cards
**36.What was the relationship of the Swahili states to each other and to the Indian Ocean basin?**
* relied on IOB trade
* Competitors for trade between each other (often fought)
* Competitors for trade between each other (often fought)
37
New cards
**37.What factors contributed to the decline and collapse of the Swahili states?**
* Portuguese takeover (“gunboat diplomacy”)
38
New cards
**38. Compare the states of West Africa and those of East Africa.**
West: Several large empires with warring small states later
East: City-states!
East: City-states!
39
New cards
**39. Analyze African slavery.**
* not permanent/hereditary
* slaves = wealth (in Africa)
* often prisoners of war, criminals, or debtors
* important East African export (by extention an important part of IOB trade)
* slaves = wealth (in Africa)
* often prisoners of war, criminals, or debtors
* important East African export (by extention an important part of IOB trade)
40
New cards
**40. How did trade, production and the accumulation of wealth affect the caste system?**
* challenged caste system
* Islam promised equality
* Urbanization gave people other economic means, made caste less applicable
* Islam promised equality
* Urbanization gave people other economic means, made caste less applicable
41
New cards
**41.Describe northern India BEFORE and AFTER Harsha’s reign.**
* DISUNIFIED BEFORE AND AFTER, cult of personality
42
New cards
**42.How did each of the following contribute to the introduction and spread of Islam in India?**
**Islamic conquests- incorporated the Sind into the rest of Dar-al Islam, installed Abbasid caliphs, still ruled over mainly Buddhists, Hindus, and Parsees**
\
**Arab Islamic merchants- Dominated trade networks, formed small communities in the major cities of coastal India, played a prominent role in Indian business and commercial life, and married Indian women**
\
**Islamic Turkic invasions and migrations-** Turks entered India bc they acquiannted themselves with the Abbasids (they also converted to Islam), some were mercenaries, others migrated into the Abbasid empire- including the Byzantine Anatola and Afghanistan (where they established Islamic empire)
\
**Arab Islamic merchants- Dominated trade networks, formed small communities in the major cities of coastal India, played a prominent role in Indian business and commercial life, and married Indian women**
\
**Islamic Turkic invasions and migrations-** Turks entered India bc they acquiannted themselves with the Abbasids (they also converted to Islam), some were mercenaries, others migrated into the Abbasid empire- including the Byzantine Anatola and Afghanistan (where they established Islamic empire)
43
New cards
42. **Describe the Sultanate of Delhi and its impact on northern India.**
Mahmud of Ghazni’s successors created a new type of campaign to conquer Northern India and place it under Islamic rule. They conquered most North Indian Hindu kingdoms and established a state called the Sultanate of Delhi. They ruled from 1206-1526. Despite this long reign, they had a weak administrative structure, and of the 35 sultans that ruled, 19 were assassinated. Gave some unity to Northern India.
44
New cards
42. **Compare the political situation in northern and southern India.**
* North was more unstable bc of constant threat of invasion
* Chola kingdom built a more flexible, less centralized state
* While Harsha also built a loose form of government, his system of government ended when he died- it was a cult of personality
* Chola in the south and Vijayanagar in the north
* Chola kingdom built a more flexible, less centralized state
* While Harsha also built a loose form of government, his system of government ended when he died- it was a cult of personality
* Chola in the south and Vijayanagar in the north
45
New cards
42. **How did the monsoon system affect Indian agriculture? Long distance trade?**
Agriculture-
made water infrastructure necessary for prosperity because of risk of droughts
Long distance trade-
enabled long distance trade because winds were very predictable making travel more consistant
made water infrastructure necessary for prosperity because of risk of droughts
Long distance trade-
enabled long distance trade because winds were very predictable making travel more consistant
46
New cards
42. **Other than religious activities, what were the various functions and roles of Hindu temples?**
* orginized irrigation and other agricultural activities
* banking
* education
* banking
* education
47
New cards
42. **What were emporia? How did these affect Indian life?**
* shops with many types of good
* increased the importance of India in IOB trade because they were a central point where many different types of goods could be found
* increased the importance of India in IOB trade because they were a central point where many different types of goods could be found
48
New cards
42. **How did the following affect the caste system?**
1. **Migrations**
Messed up the organization of the caste system
\n
1. **Spread of Islam**
Islam promises equality among believers, so this was a challenge to the caste system
\n
1. **Urbanization**
Challenged the caste system because people could be more unanimous in cities -> people couldn’t keep track of everyone else’s caste
\n \n
1. **Jati system**
unions of subcastes (they had a fair amount of power particularly merchants and skilled labor jati)
\n
1. **Expansion of the caste system.**
caste system become more common in Southern India after originating in the North
49
New cards
42. **Analyze the impact of Islam on India.**
\-Islam as a religion just didn’t last, but it did still influence India while it was still there.
\-Territories such as the Sultanate of Delhi held political influence in India and were Islamic.
\-Territories such as the Sultanate of Delhi held political influence in India and were Islamic.
50
New cards
42. **What was the role of the Sufis in the spread of Islam in India?**
* They were the main force in spreading Islam in India, as their relaxed nature towards non-emotional devotion to Allah allowed for more people to join
* They also aided in the Bhakti movement, as they were already accustomed to adopting traits of outside religions.
* They also aided in the Bhakti movement, as they were already accustomed to adopting traits of outside religions.
51
New cards
42. **What was the Bhakti movement/ Why did it fail?**
* it was a movement that tried to essentially combine elements of Hinduism and Islam into one religion
* It failed due to a variety of reasons
* It never managed to properly combine the two religions, thus failing in its primary goal
* The movement didn’t make much of any long term impact in India, as they had no set structure and since their ranks mostly consisted of the lower class, they could not make many governmental changes if they wanted to
* It failed due to a variety of reasons
* It never managed to properly combine the two religions, thus failing in its primary goal
* The movement didn’t make much of any long term impact in India, as they had no set structure and since their ranks mostly consisted of the lower class, they could not make many governmental changes if they wanted to
52
New cards
42. **How did India influence Southeast Asia?**
* India brought ideas such as Islam and Buddhism to Southeast Asia through trade and its traders (think southernization)
* The form of Islam that came to Southeast Asia was the Sufi version, which influenced Islam in the entire region.
* The form of Islam that came to Southeast Asia was the Sufi version, which influenced Islam in the entire region.
53
New cards
42. **What was the importance of Hunan, Srivijaya, Majaphit and Melaka?**
1. **Funan**
The first Hindu kingdom in Southeast Asia
\n
1. **Srivijaya**
They strengthened trade between India and China due to their fixation with their sea route that is located in the northern part of modern day Indonesia
\n
1. **Majapahit**
They took the advantages of previous empires in the area and ran with them, getting rich and powerful within the sphere of Southeast Asia
\n
1. **Melaka**
Was the most important trading port in Southeast Asia by the 16th century